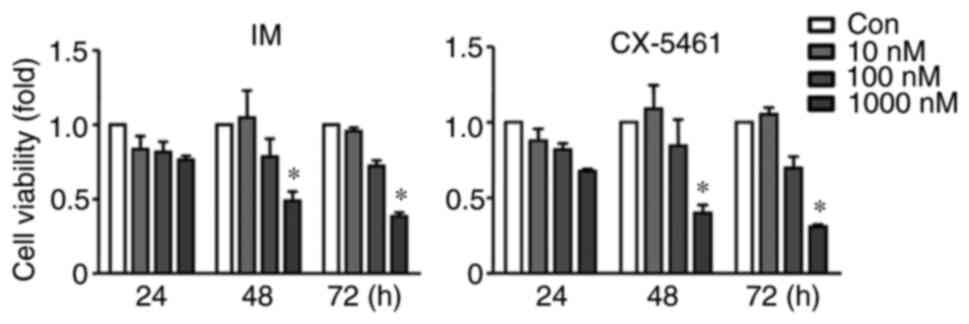
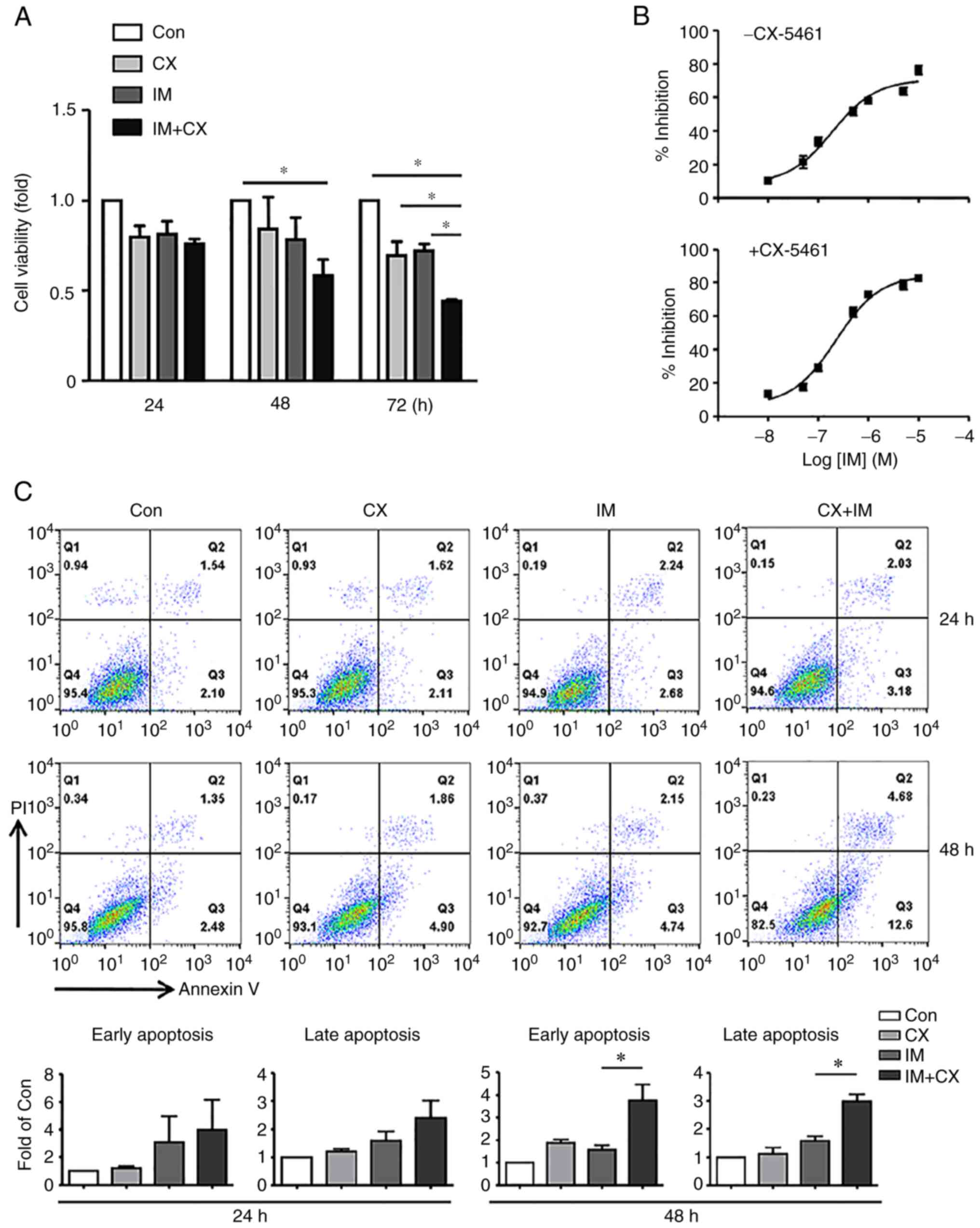
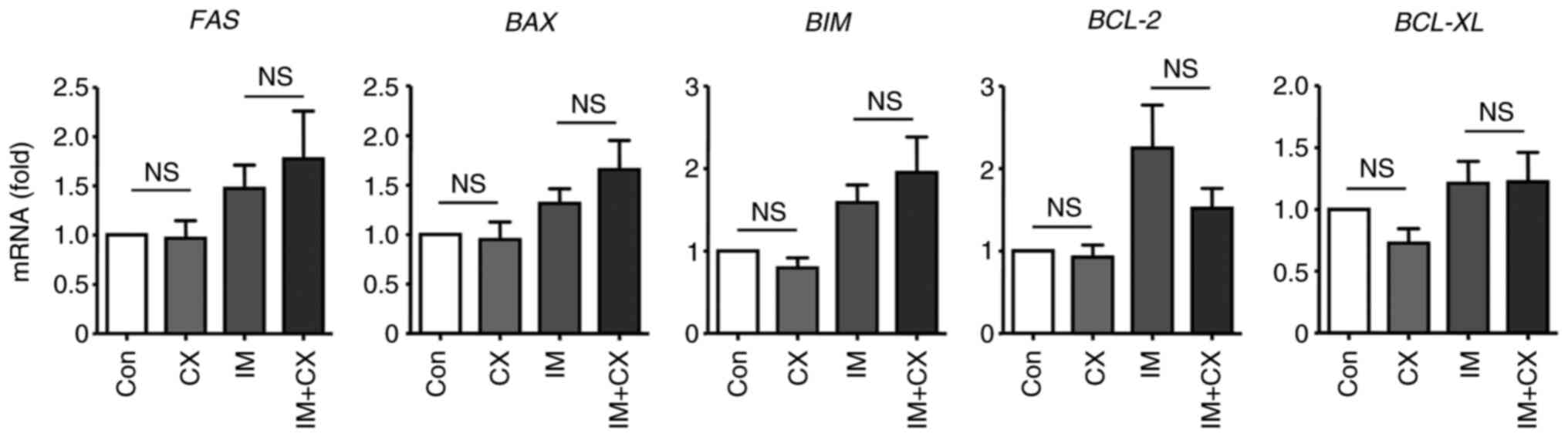
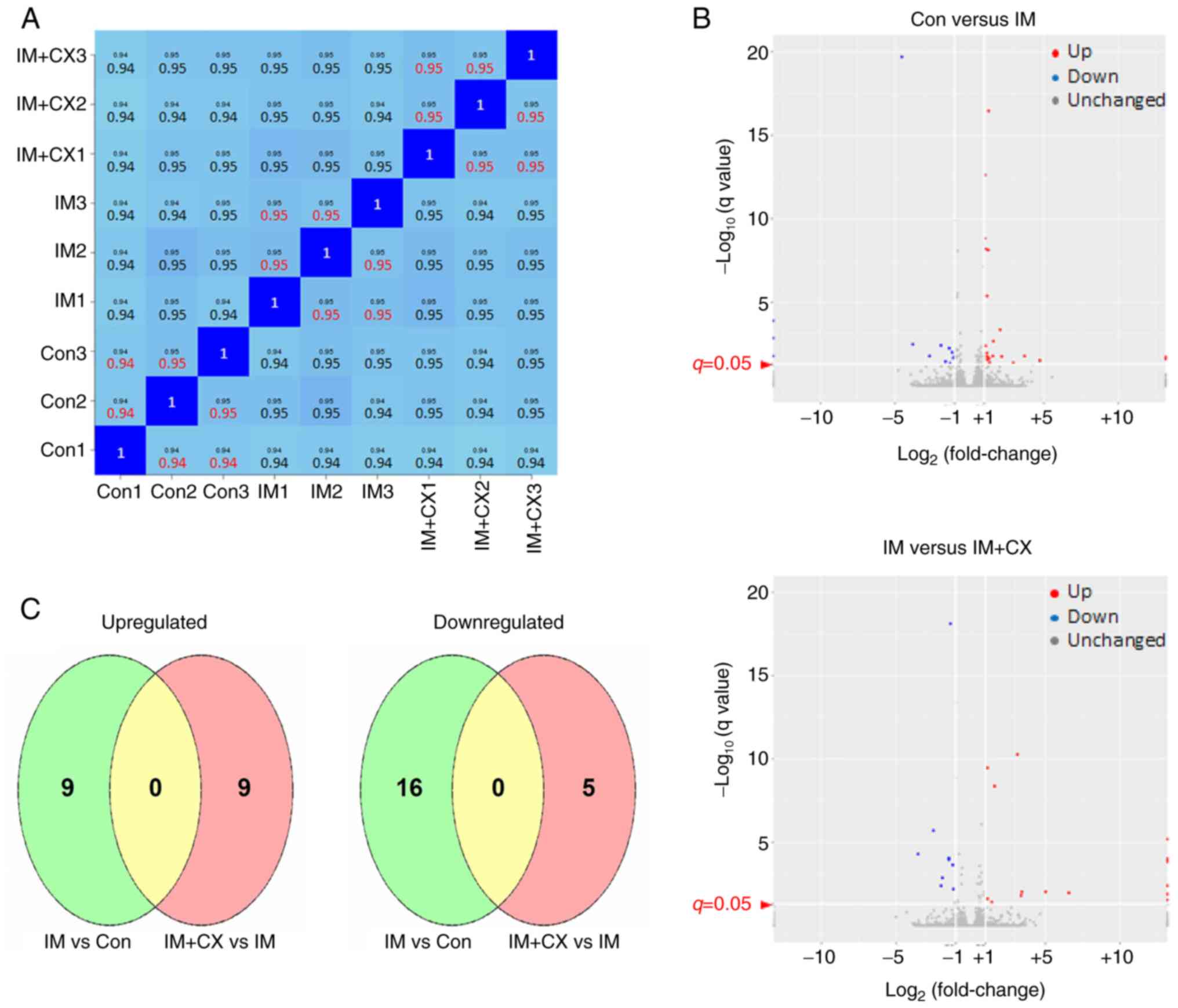
|
1
|
Butturini A, Arlinghaus RB and Gale RP:
BCR/ABL and leukemia. Leuk Res. 20:523–529. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, Druker BJ and
Talpaz M: Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias: From basic
mechanisms to molecular therapeutics. Ann Intern Med. 138:819–830.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Maru Y: Molecular biology of chronic
myeloid leukemia. Cancer Sci. 103:1601–1610. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Patel AB, O'Hare T and Deininger MW:
Mechanisms of resistance to ABL kinase inhibition in chronic
myeloid leukemia and the development of next generation ABL kinase
inhibitors. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 31:589–612.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS,
Milojkovic D, Reid AG, Bua M, Szydlo R, Olavarria E, Kaeda J,
Goldman JM and Marin D: Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with
chronic myeloid leukemia: Incidence of sustained responses in an
intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 26:3358–3363.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Burchert A, Wang Y, Cai D, von Bubnoff N,
Paschka P, Müller-Brüsselbach S, Ottmann OG, Duyster J, Hochhaus A
and Neubauer A: Compensatory PI3-kinase/Akt/mTor activation
regulates imatinib resistance development. Leukemia. 19:1774–1782.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wendel HG, de Stanchina E, Cepero E, Ray
S, Emig M, Fridman JS, Veach DR, Bornmann WG, Clarkson B, McCombie
WR, et al: Loss of p53 impedes the antileukemic response to BCR-ABL
inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7444–7449. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li L, Wang L, Wang Z, Ho Y, McDonald T,
Holyoake TL, Chen W and Bhatia R: Activation of p53 by SIRT1
inhibition enhances elimination of CML leukemia stem cells in
combination with imatinib. Cancer Cell. 21:266–281. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Peterson LF, Lo MC, Liu Y, Giannola D,
Mitrikeska E, Donato NJ, Johnson CN, Wang S, Mercer J and Talpaz M:
Induction of p53 suppresses chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 58:1–14. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Abraham SA, Hopcroft LE, Carrick E, Drotar
ME, Dunn K, Williamson AJ, Korfi K, Baquero P, Park LE, Scott MT,
et al: Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates
leukaemic stem cells. Nature. 534:341–346. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Guinn BA, Smith M, Padua RA, Burnett A and
Mills K: Changing p53 mutations with the evolution of chronic
myeloid leukaemia from the chronic phase to blast crisis. Leuk Res.
19:519–525. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Marasca R, Longo G, Luppi M, Barozzi P and
Torelli G: Double P53 point mutation in extramedullary blast crisis
of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 16:171–175.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Stuppia L, Calabrese G, Peila R,
Guanciali-Franchi P, Morizio E, Spadano A and Palka G: p53 loss and
point mutations are associated with suppression of apoptosis and
progression of CML into myeloid blastic crisis. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 98:28–35. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mitelman F: The cytogenetic scenario of
chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 11 (Suppl 1):S11–S15.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Luo J, Solimini NL and Elledge SJ:
Principles of cancer therapy: Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction.
Cell. 136:823–837. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Janczar S, Nautiyal J, Xiao Y, Curry E,
Sun M, Zanini E, Paige AJ and Gabra H: WWOX sensitises ovarian
cancer cells to paclitaxel via modulation of the ER stress
response. Cell Death Dis. 8(e2955)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nguyen HG, Conn CS, Kye Y, Xue L, Forester
CM, Cowan JE, Hsieh AC, Cunningham JT, Truillet C, Tameire F, et
al: Development of a stress response therapy targeting aggressive
prostate cancer. Sci Transl Med. 10(eaar2036)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Boulon S, Westman BJ, Hutten S, Boisvert
FM and Lamond AI: The nucleolus under stress. Mol Cell. 40:216–227.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
James A, Wang Y, Raje H, Rosby R and
DiMario P: Nucleolar stress with and without p53. Nucleus.
5:402–426. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Drygin D, Lin A, Bliesath J, Ho CB,
O'Brien SE, Proffitt C, Omori M, Haddach M, Schwaebe MK,
Siddiqui-Jain A, et al: Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral
small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis and solid
tumor growth. Cancer Res. 71:1418–1430. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hein N, Cameron DP, Hannan KM, Nguyen NN,
Fong CY, Sornkom J, Wall M, Pavy M, Cullinane C, Diesch J, et al:
Inhibition of Pol I transcription treats murine and human AML by
targeting the leukemia-initiating cell population. Blood.
129:2882–2895. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bywater MJ, Poortinga G, Sanij E, Hein N,
Peck A, Cullinane C, Wall M, Cluse L, Drygin D, Anderes K, et al:
Inhibition of RNA polymerase I as a therapeutic strategy to promote
cancer-specific activation of p53. Cancer Cell. 22:51–65.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Law JC, Ritke MK, Yalowich JC, Leder GH
and Ferrell RE: Mutational inactivation of the p53 gene in the
human erythroid leukemic K562 cell line. Leuk Res. 17:1045–1050.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Di Bacco AM and Cotter TG: p53 expression
in K562 cells is associated with caspase-mediated cleavage of c-ABL
and BCR-ABL protein kinases. Br J Haematol. 117:588–597.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bi S, Hughes T, Bungey J, Chase A, de
Fabritiis P and Goldman JM: p53 in chronic myeloid leukemia cell
lines. Leukemia. 6:839–842. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chylicki K, Ehinger M, Svedberg H, Bergh
G, Olsson I and Gullberg U: p53-mediated differentiation of the
erythroleukemia cell line K562. Cell Growth Differ. 11:315–324.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
ENCODE Guidelines and Best Practices for
RNA-Seq. https://www.encodeproject.org/about/experiment-guidelines.
|
|
28
|
Real-time PCR handbook. https://www.thermofisher.com/content/dam/LifeTech/global/Forms/PDF/real-time-pcr-handbook.pdf.
|
|
29
|
Foucquier J and Guedj M: Analysis of drug
combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol Res
Perspect. 3(e00149)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Picard S, Titier K, Etienne G, Teilhet E,
Ducint D, Bernard MA, Lassalle R, Marit G, Reiffers J, Begaud B, et
al: Trough imatinib plasma levels are associated with both
cytogenetic and molecular responses to standard-dose imatinib in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 109:3496–3499. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Arya AD, Wilson DI, Baralle D and Raponi
M: RBFOX2 protein domains and cellular activities. Biochem Soc
Trans. 42:1180–1183. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Braeutigam C, Rago L, Rolke A, Waldmeier
L, Christofori G and Winter J: The RNA-binding protein Rbfox2: An
essential regulator of EMT-driven alternative splicing and a
mediator of cellular invasion. Oncogene. 33:1082–1092.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Quentmeier H, Pommerenke C, Bernhart SH,
Dirks WG, Hauer V, Hoffmann S, Nagel S, Siebert R, Uphoff CC,
Zaborski M, et al: RBFOX2 and alternative splicing in B-cell
lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 8(77)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Munirajan AK, Ando K, Mukai A, Takahashi
M, Suenaga Y, Ohira M, Koda T, Hirota T, Ozaki T and Nakagawara A:
KIF1Bbeta functions as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene
mapped to chromosome 1p36.2 by inducing apoptotic cell death. J
Biol Chem. 283:24426–24434. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Schlisio S, Kenchappa RS, Vredeveld LC,
George RE, Stewart R, Greulich H, Shahriari K, Nguyen NV, Pigny P,
Dahia PL, et al: The kinesin KIF1Bbeta acts downstream from EglN3
to induce apoptosis and is a potential 1p36 tumor suppressor. Genes
Dev. 22:884–893. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Choo Z, Koh RY, Wallis K, Koh TJ, Kuick
CH, Sobrado V, Kenchappa RS, Loh AH, Soh SY, Schlisio S, et al:
XAF1 promotes neuroblastoma tumor suppression and is required for
KIF1Bβ-mediated apoptosis. Oncotarget. 7:34229–34239.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li S, Fell SM, Surova O, Smedler E, Wallis
K, Chen ZX, Hellman U, Johnsen JI, Martinsson T, Kenchappa RS, et
al: The 1p36 tumor suppressor KIF 1Bβ is required for calcineurin
activation, controlling mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. Dev
Cell. 36:164–178. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ando K, Yokochi T, Mukai A, Wei G, Li Y,
Kramer S, Ozaki T, Maehara Y and Nakagawara A: Tumor suppressor
KIF1Bβ regulates mitochondrial apoptosis in collaboration with
YME1L1. Mol Carcinog. 58:1134–1144. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen ZX, Wallis K, Fell SM, Sobrado VR,
Hemmer MC, Ramsköld D, Hellman U, Sandberg R, Kenchappa RS,
Martinson T, et al: RNA helicase A is a downstream mediator of
KIF1Bβ tumor-suppressor function in neuroblastoma. Cancer Discov.
4:434–451. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gordon MA, Babbs B, Cochrane DR, Bitler BG
and Richer JK: The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes ovarian
cancer progression by regulating RBFOX2-mediated alternative
splicing. Mol Carcinog. 58:196–205. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wolf D, Tilg H, Rumpold H, Gastl G and
Wolf AM: The kinase inhibitor imatinib-an immunosuppressive drug?
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 7:251–258. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ferreira R, Schneekloth JS Jr, Panov KI,
Hannan KM and Hannan RD: Targeting the RNA polymerase I
transcription for cancer therapy comes of age. Cells.
9(266)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Quin J, Chan KT, Devlin JR, Cameron DP,
Diesch J, Cullinane C, Ahern J, Khot A, Hein N, George AJ, et al:
Inhibition of RNA polymerase I transcription initiation by CX-5461
activates non-canonical ATM/ATR signaling. Oncotarget.
7:49800–49818. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Mars JC, Tremblay MG, Valere M, Sibai DS,
Sabourin-Felix M, Lessard F and Moss T: The chemotherapeutic agent
CX-5461 irreversibly blocks RNA polymerase I initiation and
promoter release to cause nucleolar disruption, DNA damage and cell
inviability. NAR Cancer. 2(zcaa032)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu H, Di Antonio M, McKinney S, Mathew V,
Ho B, O'Neil NJ, Santos ND, Silvester J, Wei V, Garcia J, et al:
CX-5461 is a DNA G-quadruplex stabilizer with selective lethality
in BRCA1/2 deficient tumours. Nat Commun. 8(14432)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bruno PM, Lu M, Dennis KA, Inam H, Moore
CJ, Sheehe J, Elledge SJ, Hemann MT and Pritchard JR: The primary
mechanism of cytotoxicity of the chemotherapeutic agent CX-5461 is
topoisomerase II poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:4053–4060.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lipton JH, Brümmendorf TH,
Gambacorti-Passerini C, Garcia-Gutiérrez V, Deininger MW and Cortes
JE: Long-term safety review of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
chronic myeloid leukemia-What to look for when treatment-free
remission is not an option. Blood Rev. 56(100968)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Honda H, Ushijima T, Wakazono K, Oda H,
Tanaka Y, Aizawa Si, Ishikawa T, Yazaki Y and Hirai H: Acquired
loss of p53 induces blastic transformation in
p210(bcr/abl)-expressing hematopoietic cells: A transgenic study
for blast crisis of human CML. Blood. 95:1144–1150. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yan S, Xuan J, Brajanovski N, Tancock MRC,
Madhamshettiwar PB, Simpson KJ, Ellis S, Kang J, Cullinane C,
Sheppard KE, et al: The RNA polymerase I transcription inhibitor
CX-5461 cooperates with topoisomerase 1 inhibition by enhancing the
DNA damage response in homologous recombination-proficient
high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 124:616–627.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shi S, Luo H, Wang L, Li H, Liang Y, Xia
J, Wang Z, Cheng B, Huang L, Liao G and Xu B: Combined inhibition
of RNA polymerase I and mTORC1/2 synergize to combat oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 133(110906)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Devlin JR, Hannan KM, Hein N, Cullinane C,
Kusnadi E, Ng PY, George AJ, Shortt J, Bywater MJ, Poortinga G, et
al: Combination therapy targeting ribosome biogenesis and mRNA
translation synergistically extends survival in MYC-driven
lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 6:59–70. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lawrence MG, Porter LH, Choo N, Pook D,
Grummet JP, Pezaro CJ, Sandhu S, Ramm S, Luu J, Bakshi A, et al:
CX-5461 sensitizes DNA damage repair-proficient castrate-resistant
prostate cancer to PARP inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 20:2140–2150.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Rebello RJ, Kusnadi E, Cameron DP, Pearson
HB, Lesmana A, Devlin JR, Drygin D, Clark AK, Porter L, Pedersen J,
et al: The dual inhibition of RNA Pol I transcription and PIM
kinase as a new therapeutic approach to treat advanced prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5539–5552. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lehman SL, Schwartz KR, Maheshwari S,
Camphausen K and Tofilon PJ: CX-5461 induces radiosensitization
through modification of the DNA damage response and not inhibition
of RNA polymerase I. Sci Rep. 12(4059)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Khot A, Brajanovski N, Cameron DP, Hein N,
Maclachlan KH, Sanij E, Lim J, Soong J, Link E, Blombery P, et al:
First-in-Human RNA polymerase I transcription inhibitor CX-5461 in
patients with advanced hematologic cancers: Results of a phase I
dose-escalation study. Cancer Discov. 9:1036–1049. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lindqvist CM, Nordlund J, Ekman D,
Johansson A, Moghadam BT, Raine A, Övernäs E, Dahlberg J, Wahlberg
P, Henriksson N, et al: The mutational landscape in pediatric acute
lymphoblastic leukemia deciphered by whole genome sequencing. Hum
Mutat. 36:118–128. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ochiai H, Takenobu H, Nakagawa A,
Yamaguchi Y, Kimura M, Ohira M, Okimoto Y, Fujimura Y, Koseki H,
Kohno Y, et al: Bmi1 is a MYCN target gene that regulates
tumorigenesis through repression of KIF1Bbeta and TSLC1 in
neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 29:2681–2690. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Astolfi A, Vendemini F, Urbini M,
Melchionda F, Masetti R, Franzoni M, Libri V, Serravalle S, Togni
M, Paone G, et al: MYCN is a novel oncogenic target in pediatric
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. 5:120–130.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Taylor JS, Zeki J, Ornell K, Coburn J,
Shimada H, Ikegaki N and Chiu B: Down-regulation of MYCN protein by
CX-5461 leads to neuroblastoma tumor growth suppression. J Pediatr
Surg. 54:1192–1197. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wetzel R, Goss VL, Norris B, Popova L,
Melnick M and Smith BL: Evaluation of CML model cell lines and
imatinib mesylate response: Determinants of signaling profiles. J
Immunol Methods. 305:59–66. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|