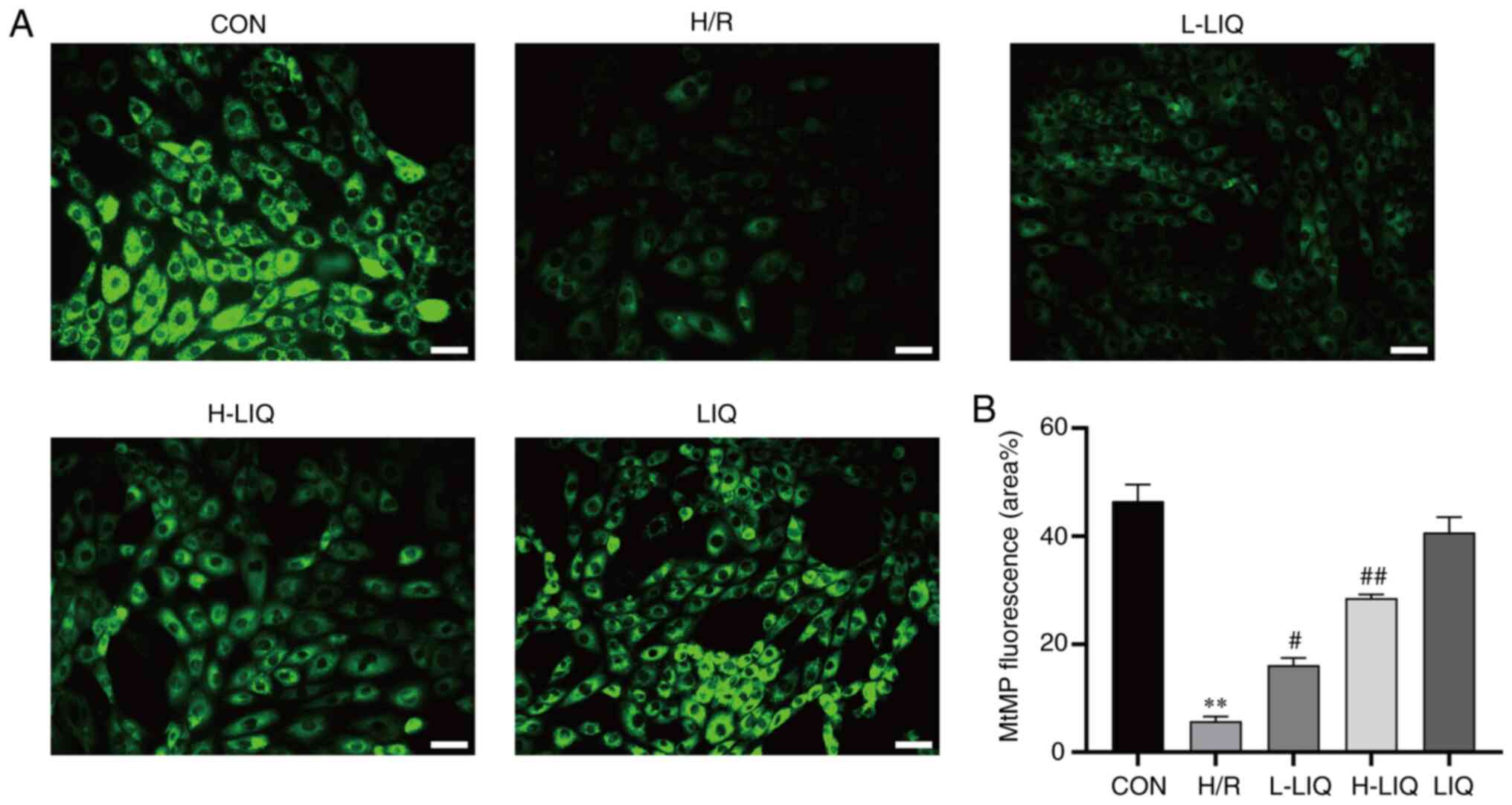
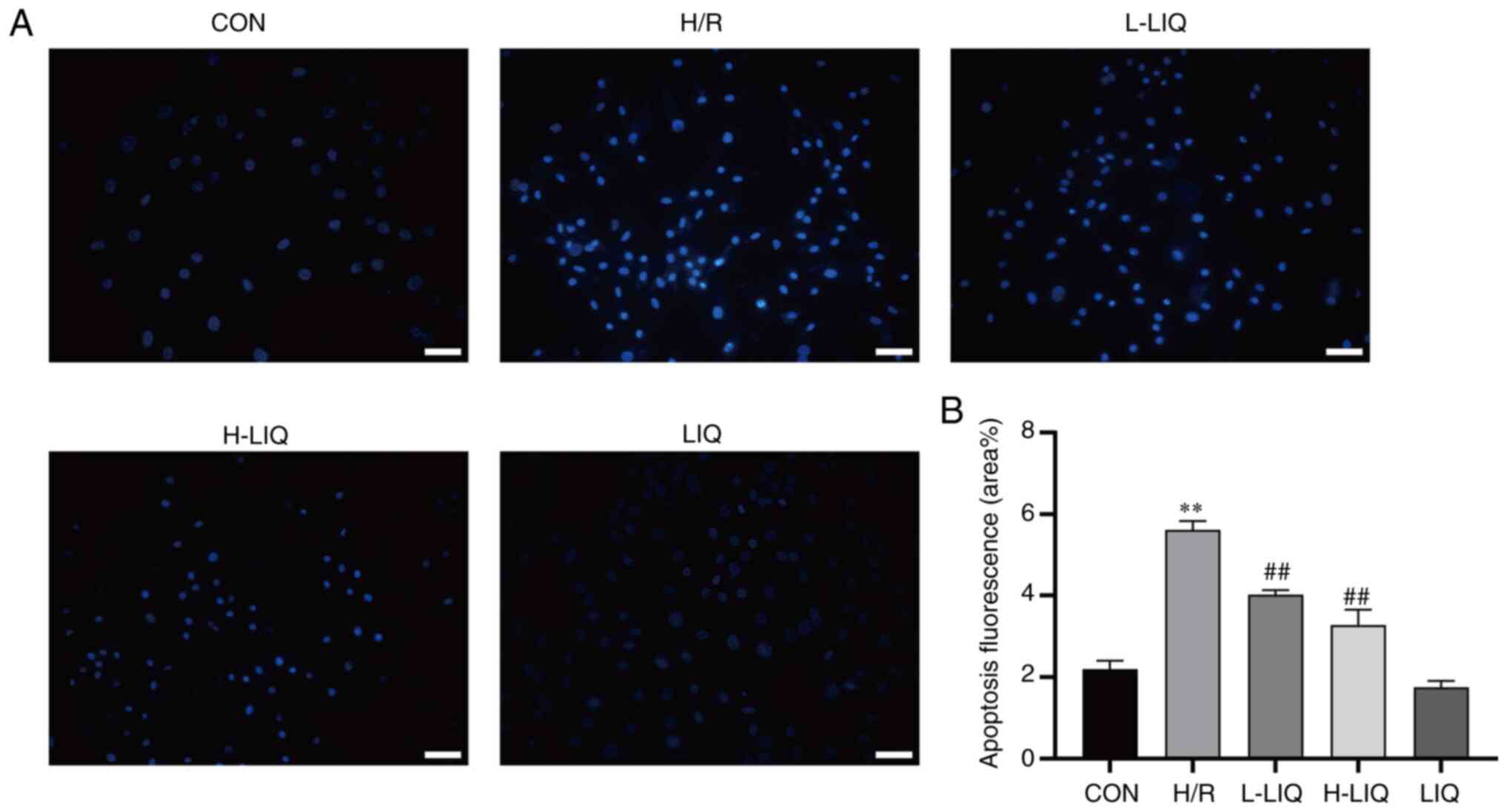
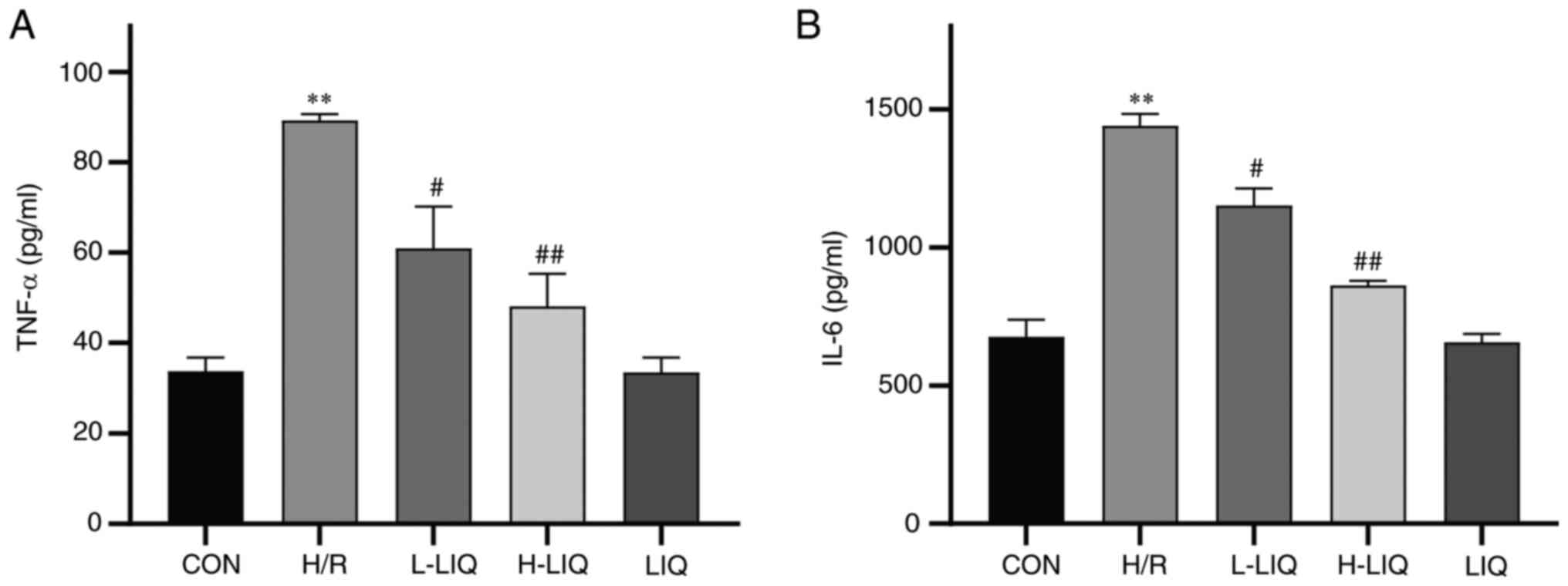
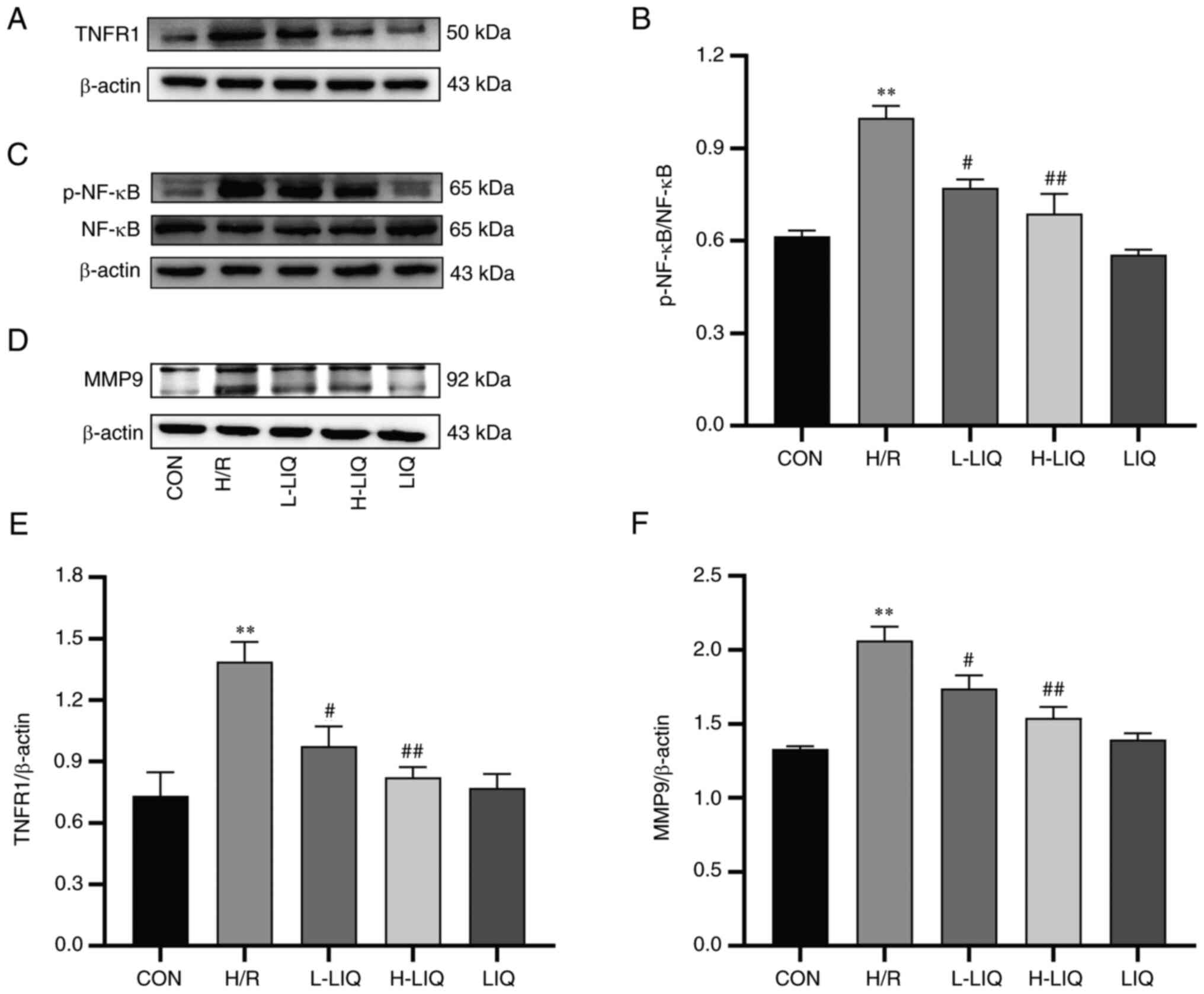
|
1
|
Pollard TJ: The acute myocardial
infarction. Prim Care. 27:631–649. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Eltzschig HK, Bonney SK and Eckle T:
Attenuating myocardial ischemia by targeting A2B adenosine
receptors. Trends Mol Med. 19:345–354. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang H, Wang C, Zhang L, Lv J and Ni H:
Rutin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in myocardial
cells by up-regulating SIRT1 expression. Chem Biol Interact.
297:44–49. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Cui M, Jin L, Wang Y, Lv
F, Liu Y, Zheng W, Shang H, Zhang J, et al: CaMKII is a RIP3
substrate mediating ischemia- and oxidative stress-induced
myocardial necroptosis. Nat Med. 22:175–182. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Murphy E and Steenbergen C: Mechanisms
underlying acute protection from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Physiol Rev. 88:581–609. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Du L, Shen T, Liu B, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Jia
N, Wang Q and He Q: Shock Wave Therapy Promotes Cardiomyocyte
Autophagy and Survival during Hypoxia. Cell Physiol Biochem.
42:673–684. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gao X, Zhang H, Zhuang W, Yuan G, Sun T,
Jiang X, Zhou Z, Yuan H, Zhang Z and Dong H: PEDF and PEDF-derived
peptide 44mer protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced
apoptosis and necroptosis via anti-oxidative effect. Sci Rep.
4(5637)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yao H, Xie Q, He Q, Zeng L, Long J, Gong
Y, Li X, Li X, Liu W, Xu Z, et al: Pretreatment with panaxatriol
saponin attenuates mitochondrial apoptosis and oxidative stress to
facilitate treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via
the regulation of Keap1/Nrf2 activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(9626703)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pastorino G, Cornara L, Soares S,
Rodrigues F and Oliveira M: Liquorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra): A
phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother Res.
32:2323–2339. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fan S, Gu K, Wu Y, Luo H, Wang Y, Zhang T,
Wang X, Zhang Y and Li Y: Liquiritinapioside-A
mineralocorticoid-like substance from liquorice. Food Chem.
289:419–425. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hou Y and Jiang JG: Origin and concept of
medicine food homology and its application in modern functional
foods. Food Funct. 4:1727–1741. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Xu JJ, Sun LL
and Li SZ: The protective role of liquiritin in high
fructose-induced myocardial fibrosis via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1337–1349.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mou SQ, Zhou ZY, Feng H, Zhang N, Lin Z,
Aiyasiding X, Li WJ, Ding W, Liao HH, Bian ZY and Tang QZ:
Liquiritin attenuates lipopolysaccharides-induced cardiomyocyte
injury via an AMP-Activated protein kinase-dependent signaling
pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12(648688)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Thu VT, Yen NTH and Ly NTH: Liquiritin
from radix glycyrrhizae protects cardiac mitochondria from
Hypoxia/Reoxygenation damage. J Anal Methods Chem.
2021(1857464)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Han X, Yang Y, Zhang M, Li L, Xue Y, Jia
Q, Wang X and Guan S: Liquiritin Protects against cardiac fibrosis
after myocardial infarction by inhibiting CCL5 expression and the
NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:4111–4125.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Boezio B, Audouze K, Ducrot P and
Taboureau O: Network-based approaches in pharmacology. Mol Inform:
36, 2017 doi: 10.1002/minf.201700048.
|
|
17
|
Otasek D, Morris JH, Bouças J, Pico AR and
Demchak B: Cytoscape Automation: Empowering workflow-based network
analysis. Genome biology. 20(185)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hu X, Jiao R, Li H, Wang X, Lyu H, Gao X,
Xu F, Li Z, Hua H and Li D: Antiproliferative hydrogen sulfide
releasing evodiamine derivatives and their apoptosis inducing
properties. Eur J Med Chem. 151:376–388. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fang Z, Luo W and Luo Y: Protective effect
of α-mangostin against CoCl2-induced apoptosis by
suppressing oxidative stress in H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts. Mol Med
Rep. 17:6697–6704. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Munoz-Sanchez J and Chanez-Cardenas ME:
The use of cobalt chloride as a chemical hypoxia model. J Appl
Toxicol. 39:556–570. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Amani M, Jeddi S, Ahmadiasl N, Usefzade N
and Zaman J: Effect of HEMADO on level of CK-MB and LDH enzymes
after ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart.
Bioimpacts. 3:101–104. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Raedschelders K, Ansley DM and Chen DD:
The cellular and molecular origin of reactive oxygen species
generation during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Pharmacol
Ther. 133:230–255. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Farias JG, Molina VM, Carrasco RA, Zepeda
AB, Figueroa E, Letelier P and Castillo RL: Antioxidant therapeutic
strategies for cardiovascular conditions associated with oxidative
stress. Nutrients. 9(996)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rodrigo R: Prevention of postoperative
atrial fibrillation: Novel and safe strategy based on the
modulation of the antioxidant system. Front Physiol.
3(93)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xiang M, Lu Y, Xin L, Gao J, Shang C,
Jiang Z, Lin H, Fang X, Qu Y, Wang Y, et al: Role of oxidative
stress in reperfusion following myocardial ischemia and its
treatments. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021(6614009)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Marin W, Marin D, Ao X and Liu Y:
Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury (Review). Int J Mol Med. 47:485–499.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Carreira RS, Lee P and Gottlieb RA:
Mitochondrial therapeutics for cardioprotection. Curr Pharm Des.
17:2017–2035. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Su X, Zhou M, Li Y, An N, Yang F, Zhang G,
Xu L, Chen H, Wu H and Xing Y: Mitochondrial damage in myocardial
Ischemia/Reperfusion injury and application of natural plant
products. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022(8726564)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lesnefsky EJ, Chen Q, Tandler B and Hoppel
CL: Mitochondrial dysfunction and myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion:
Implications for novel therapies. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
57:535–565. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Anzell AR, Maizy R, Przyklenk K and
Sanderson TH: Mitochondrial quality control and disease: Insights
into Ischemia-Reperfusion injury. Mol Neurobiol. 55:2547–2564.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chazotte B: Labeling mitochondria with
rhodamine 123. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2011:892–894.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou H, Ma Q, Zhu P, Ren J, Reiter RJ and
Chen Y: Protective role of melatonin in cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury: From pathogenesis to targeted therapy.
J Pineal Res: 64, 2018 doi: 10.1111/jpi.12471.
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Guo X, Yang J, Ding JW, Li S, Yang
R, Fan ZX and Yang CJ: RP105 Protects against apoptosis in
Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced myocardial damage in rats by
suppressing TLR4-Mediated signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:2137–2148. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li X, Hu X, Wang J, Xu W, Yi C, Ma R and
Jiang H: Short-Term hesperidin pretreatment attenuates rat
myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion injury by inhibiting high mobility
group box 1 protein expression via the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:1850–1862. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang BF, Jiang H, Chen J, Guo X, Li Y, Hu
Q and Yang S: Nobiletin ameliorates myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated apoptosis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT
signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 73:98–107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang Y, Lv J, Jiang S, Ma Z, Wang D, Hu W,
Deng C, Fan C, Di S, Sun Y and Yi W: The emerging role of Toll-like
receptor 4 in myocardial inflammation. Cell Death Dis.
7(e2234)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Naidu BV, Farivar AS, Woolley SM, Grainger
D, Verrier ED and Mulligan MS: Novel broad-spectrum chemokine
inhibitor protects against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Heart Lung Transplant. 23:128–134. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen L, Liu P, Feng X and Ma C:
Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:3178–3189. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ting AT and Bertrand MJM: More to Life
than NF-κB in TNFR1 Signaling. Trends Immunol. 37:535–545.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pasparakis M and Vandenabeele P:
Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 517:311–320.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Van der Heiden K, Cuhlmann S, Luong le A,
Zakkar M and Evans PC: Role of nuclear factor kappaB in
cardiovascular health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 118:593–605.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Newby AC: Dual role of matrix
metalloproteinases (matrixins) in intimal thickening and
atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Physiol Rev. 85:1–31.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Spinale FG, Coker ML, Heung LJ, Bond BR,
Gunasinghe HR, Etoh T, Goldberg AT, Zellner JL and Crumbley AJ: A
matrix metalloproteinase induction/activation system exists in the
human left ventricular myocardium and is upregulated in heart
failure. Circulation. 102:1944–1949. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Spinale FG: Matrix metalloproteinase gene
polymorphisms in heart failure: New pieces to the myocardial matrix
puzzle. Eur Heart J. 25:631–633. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Luo X, Wu J and Wu G: PPARγ activation
suppresses the expression of MMP9 by downregulating NF-κB post
intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosci Lett. 752(135770)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kleinbongard P, Heusch G and Schulz R:
TNFalpha in atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and
heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. 127:295–314. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Regulation of NF-κB
by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol. 26:253–266. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB, the first
quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions.
Genes Dev. 26:203–234. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Blackwell K, Zhang L, Thomas GS, Sun S,
Nakano H and Habelhah H: TRAF2 phosphorylation modulates tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced gene expression and cell resistance
to apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 29:303–314. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Devin A, Cook A, Lin Y, Rodriguez Y,
Kelliher M and Liu Z: The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK
activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP
mediates IKK activation. Immunity. 12:419–429. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wei Q, Tu Y, Zuo L, Zhao J, Chang Z, Zou Y
and Qiu J: MiR-345-3p attenuates apoptosis and inflammation caused
by oxidized low-density lipoprotein by targeting TRAF6 via
TAK1/p38/NF-kB signaling in endothelial cells. Life Sci.
241(117142)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Howell JA and Bidwell GL III: Targeting
the NF-κB pathway for therapy of ischemic stroke. Ther Deliv.
11:113–123. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gum R, Lengyel E, Juarez J, Chen JH, Sato
H, Seiki M and Boyd D: Stimulation of 92-kDa gelatinase B promoter
activity by ras is mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
1-independent and requires multiple transcription factor binding
sites including closely spaced PEA3/ets and AP-1 sequences. J Biol
Chem. 271:10672–10680. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wu HT, Sie SS, Kuan TC and Lin CS:
Identifying the regulative role of NF-κB binding sites within
promoter region of human matrix metalloproteinase 9 (mmp-9) by
TNF-α induction. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 169:438–449.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Neri M, Riezzo I, Pascale N, Pomara C and
Turillazzi E: Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury following Acute
Myocardial Infarction: A critical issue for clinicians and forensic
pathologists. Mediators Inflamm. 2017(7018393)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Hescheler J, Meyer R, Plant S, Krautwurst
D, Rosenthal W and Schultz G: Morphological, biochemical, and
electrophysiological characterization of a clonal cell (H9c2) line
from rat heart. Circ Res. 69:1476–1486. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhu A, Wei X, Zhang Y, You T, Yao S, Yuan
S, Xu H, Li F and Mao W: Propofol provides cardiac protection by
suppressing the proteasome degradation of caveolin-3 in
ischemic/reperfused rat hearts. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 69:170–177.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|