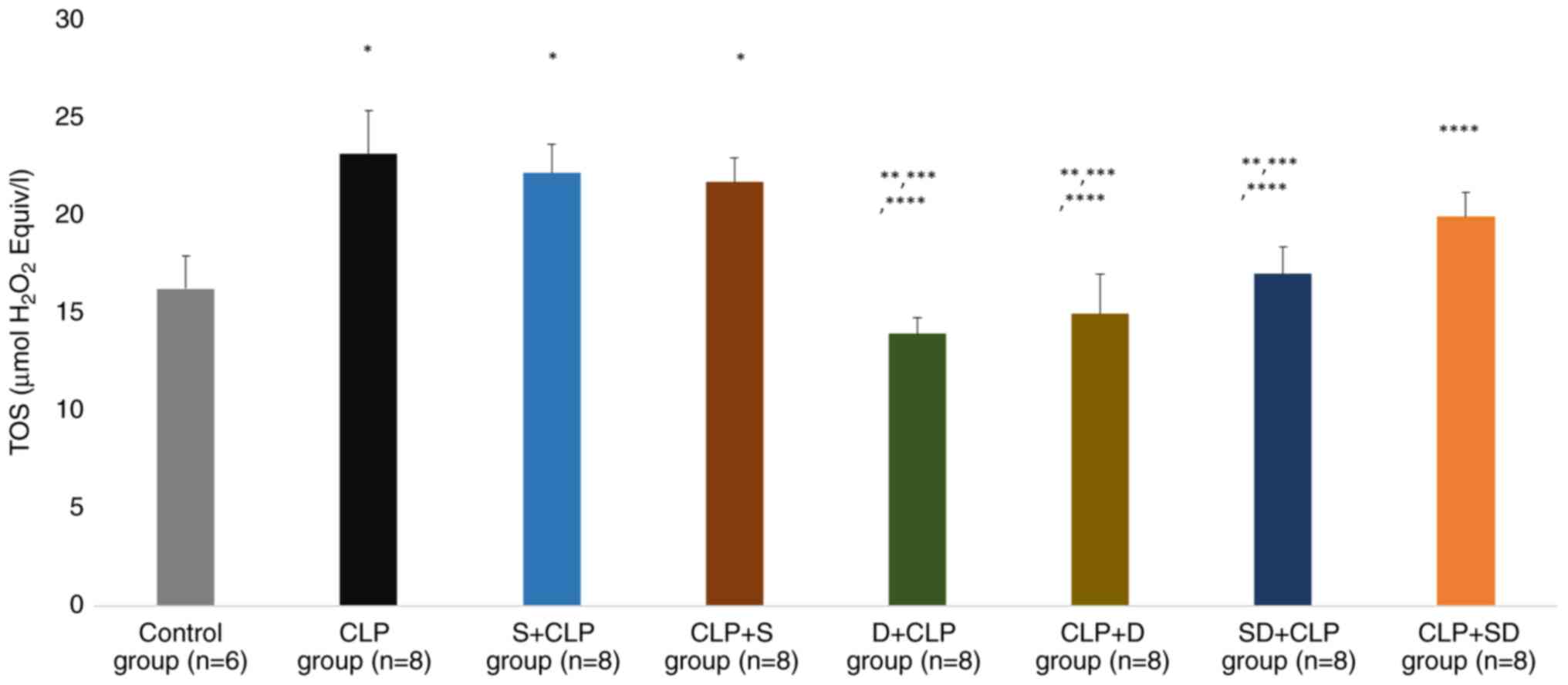
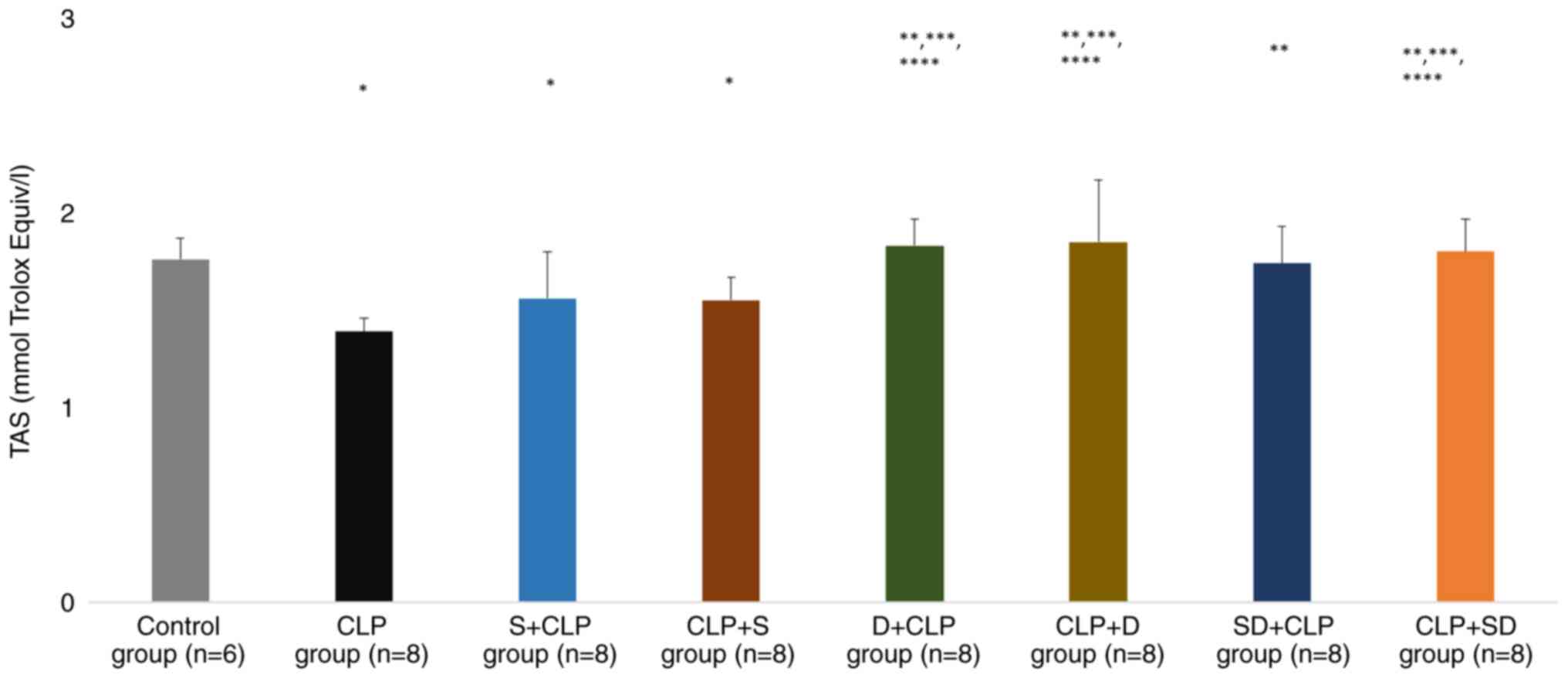
|
1
|
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli
M, Coopersmith CM, French C, Machado FR, Mcintyre L, Ostermann M,
Prescott HC, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International
guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021.
Intensive Care Med. 47:1181–1247. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Beisel WR: Metabolic response to
infection. Annu Rev Med. 26:9–20. 1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dyck B, Unterberg M, Adamzik M and Koos B:
The impact of pathogens on sepsis prevalence and outcome.
Pathogens. 13(89)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Aziz M, Jacob A, Yang WL, Matsuda A and
Wang P: Current trends in inflammatory and immunomodulatory
mediators in sepsis. J Leukoc Biol. 93:329–342. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen XH, Yin YJ and Zhang JX: Sepsis and
immune response. World J Emerg Med. 2:88–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arina P and Singer M: Pathophysiology of
sepsis. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 34:77–84. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fleischmann-Struzek C, Mellhammar L, Rose
N, Cassini A, Rudd KE, Schlattmann P, Allegranzi B and Reinhart K:
Incidence and mortality of hospital- and ICU-treated sepsis:
Results from an updated and expanded systematic review and
meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 46:1552–1562. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Engel C, Brunkhorst FM, Bone HG,
Brunkhorst R, Gerlach H, Grond S, Gruendling M, Huhle G, Jaschinski
U, John S, et al: Epidemiology of sepsis in Germany: Results from a
national prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med.
33:606–618. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Karlsson S, Varpula M, Ruokonen E, Pettilä
V, Parviainen I, Ala-Kokko TI, Kolho E and Rintala EM: Incidence,
treatment, and outcome of severe sepsis in ICU-treated adults in
Finland: The Finnsepsis study. Intensive Care Med. 33:435–443.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Blanco J, Muriel-Bombín A, Sagredo V,
Taboada F, Gandía F, Tamayo L, Collado J, García-Labattut A,
Carriedo D, Valledor M, et al: Incidence, organ dysfunction and
mortality in severe sepsis: A Spanish multicentre study. Crit Care.
12(R158)2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sakr Y, Elia C, Mascia L, Barberis B,
Cardellino S, Livigni S, Fiore G, Filippini C and Ranieri VM:
Epidemiology and outcome of sepsis syndromes in Italian ICUs: A
muticentre, observational cohort study in the region of Piedmont.
Minerva Anestesiol. 79:993–1002. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weng L, Xu Y, Yin P, Wang Y, Chen Y, Liu
W, Li S, Peng JM, Dong R, Hu XY, et al: National incidence and
mortality of hospitalized sepsis in China. Crit Care.
27(84)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rhee C, Dantes R, Epstein L, Murphy DJ,
Seymour CW, Iwashyna TJ, Kadri SS, Angus DC, Danner RL, Fiore AE,
et al: Incidence and trends of sepsis in US hospitals using
clinical vs claims data, 2009-2014. JAMA. 318:1241–1249.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lamontagne F, Rochwerg B, Lytvyn L, Guyatt
GH, Møller MH, Annane D, Kho ME, Adhikari NKJ, Machado F, Vandvik
PO, et al: Corticosteroid therapy for sepsis: A clinical practice
guideline. BMJ. 362(k3284)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rochwerg B, Oczkowski SJ, Siemieniuk RAC,
Agoritsas T, Belley-Cote E, D'Aragon F, Duan E, English S,
Gossack-Keenan K, Alghuroba M, et al: Corticosteroids in sepsis: An
updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med.
46:1411–1420. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vignon P, Laterre PF, Daix T and François
B: New agents in development for sepsis: Any reason for hope?
Drugs. 80:1751–1761. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Üstündağ H, Doğanay S, Kalındemirtaş FD,
Demir Ö, Huyut MT, Kurt N, Özgeriş FB and Akbaba Ö: A new treatment
approach: Melatonin and ascorbic acid synergy shields against
sepsis-induced heart and kidney damage in male rats. Life Sci.
329(121875)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Usmani J, Khan T, Ahmad R and Sharma M:
Potential role of herbal medicines as a novel approach in sepsis
treatment. Biomed Pharmacother. 144(112337)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang W, Jiang H, Wu G, Huang P, Wang H,
An H, Liu S and Zhang W: The pathogenesis and potential therapeutic
targets in sepsis. MedComm (2020). 4(e418)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Holubar M, Meng L, Alegria W and
Deresinski S: Bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant
staphylococcus aureus: An update on new therapeutic approaches.
Infect Dis Clin North Am. 34:849–861. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hadi A, Pourmasoumi M, Mohammadi H,
Symonds M and Miraghajani M: The effects of silymarin
supplementation on metabolic status and oxidative stress in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of clinical trials. Complement Ther Med. 41:311–319.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Koltai T and Fliegel L: Role of silymarin
in cancer treatment: Facts, hypotheses, and questions. J Evid Based
Integr Med. 27(2515690X211068826)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Soleimani V, Delghandi PS, Moallem SA and
Karimi G: Safety and toxicity of silymarin, the major constituent
of milk thistle extract: An updated review. Phytother Res.
33:1627–1638. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abenavoli L, Izzo AA, Milić N, Cicala C,
Santini A and Capasso R: Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A
concise overview on its chemistry, pharmacological, and
nutraceutical uses in liver diseases. Phytother Res. 32:2202–2213.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Camini FC and Costa DC: Silymarin: Not
just another antioxidant. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.
31(20190206)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tighe SP, Akhtar D, Iqbal U and Ahmed A:
Chronic liver disease and silymarin: A biochemical and clinical
review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 8:454–458. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aghazadeh S, Amini R, Yazdanparast R and
Ghaffari SH: Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of
Silybum marianum in treatment of experimental
steatohepatitis. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 63:569–574. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Saller R, Melzer J, Reichling J, Brignoli
R and Meier R: An updated systematic review of the pharmacology of
silymarin. Forsch Komplementmed. 14:70–80. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Surai A and Surai PF: Chapter 10 Silymarin
and inflammation: From understanding molecular mechanisms to
practical applications. In: Silymarin Puzzle. Wageningen Academic,
pp287-317, 2023.
|
|
31
|
Sharma S, Kumar P, Ashawat MS, Pandit V,
Verma CS and Sharma DK: Silymarin: A Phytoconstituent with
Significant Therapeutic Potential-A Narrative Review. Curr Drug
Ther. 18:89–97. 2023.
|
|
32
|
Kang JS, Jeon YJ, Park SK, Yang KH and Kim
HM: Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis and
inhibition of interleukin-1beta and prostaglandin E2 synthesis by
silymarin. Biochem Pharmacol. 67:175–181. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schrieber SJ, Hawke RL, Wen Z, Smith PC,
Reddy KR, Wahed AS, Belle SH, Afdhal NH, Navarro VJ, Meyers CM, et
al: Differences in the disposition of silymarin between patients
with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic hepatitis C. Drug
Metab Dispos. 39:2182–2190. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shahbazi F, Sadighi S, Dashti-Khavidaki S,
Shahi F, Mirzania M, Abdollahi A and Ghahremani MH: Effect of
silymarin administration on cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Report from a
pilot, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Phytother Res. 29:1046–1053. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fried MW, Navarro VJ, Afdhal N, Belle SH,
Wahed AS, Hawke RL, Doo E, Meyers CM and Reddy KR: Silymarin in
NASH and C Hepatitis (SyNCH) Study Group. Effect of silymarin (milk
thistle) on liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C
unsuccessfully treated with interferon therapy: A randomized
controlled trial. JAMA. 308:274–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Marmouzi I, Bouyahya A, Ezzat SM, El Jemli
M and Kharbach M: The food plant Silybum marianum (L.)
Gaertn.: Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacology and clinical evidence. J
Ethnopharmacol. 265(113303)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nguyen V, Tiemann D, Park E adz and Salehi
A: Alpha-2 agonists. Anesthesiol Clin. 35:233–245. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Giovannitti JA Jr, Thoms SM and Crawford
JJ: Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: A review of current
clinical applications. Anesth Prog. 62:31–39. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cioccari L, Luethi N, Bailey M, Shehabi Y,
Howe B, Messmer AS, Proimos HK, Peck L, Young H, Eastwood GM, et
al: The effect of dexmedetomidine on vasopressor requirements in
patients with septic shock: A subgroup analysis of the Sedation
Practice in Intensive care evaluation [SPICE III] trial. Crit Care.
24(441)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ferreira J: The Theory is out there: The
use of ALPHA-2 agonists in treatment of septic shock. Shock.
49:358–363. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Morelli A, Sanfilippo F, Arnemann P,
Hessler M, Kampmeier TG, D'Egidio A, Orecchioni A, Santonocito C,
Frati G, Greco E, et al: The effect of propofol and dexmedetomidine
sedation on norepinephrine requirements in septic shock patients: A
crossover trial. Crit Care Med. 47:e89–e95. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Suzuki T, Suzuki Y, Okuda J, Kurazumi T,
Suhara T, Ueda T, Nagata H and Morisaki H: Sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction and β-adrenergic blockade therapy for sepsis. J
Intensive Care. 5(22)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ferreira JA and Bissell BD: Misdirected
sympathy: The role of sympatholysis in sepsis and septic shock. J
Intensive Care Med. 33:74–86. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pichot C, Géloën A, Ghignone M and Quintin
L: Alpha-2 agonists to reduce vasopressor requirements in septic
shock? Med Hypotheses. 75:652–656. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Geloen A, Chapelier K, Cividjian A,
Dantony E, Rabilloud M, May CN and Quintin L: Clonidine and
dexmedetomidine increase the pressor response to norepinephrine in
experimental sepsis: A pilot study. Crit Care Med. 41:e431–e438.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Møller MH, Alhazzani W, Lewis K,
Belley-Cote E, Granholm A, Centofanti J, McIntyre WB, Spence J, Al
Duhailib Z, Needham DM, et al: Use of dexmedetomidine for sedation
in mechanically ventilated adult ICU patients: A rapid practice
guideline. Intensive Care Med. 48:801–810. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wiegand A, Behal M, Robbins B, Bissell B,
Pandya K and Mefford B: Niche roles for dexmedetomidine in the
intensive care unit. Ann Pharmacother. 57:1207–1220.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Page V and McKenzie C: Sedation in the
intensive care unit. Curr Anesthesiol Rep. 11:92–100.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zi SF, Li JH, Liu L, Deng C, Ao X, Chen DD
and Wu SZ: Dexmedetomidine-mediated protection against septic liver
injury depends on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling downregulation partly
via cholinergic anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Int Immunopharmacol.
76(105898)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Chang Y, Huang X, Liu Z, Han G, Huang L,
Xiong YC and Wang Z: Dexmedetomidine inhibits the secretion of high
mobility group box 1 from lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages
in vitro. J Surg Res. 181:308–314. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang T, Mei Q, Dai S, Liu Y and Zhu H:
Use of dexmedetomidine in patients with sepsis: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Ann Intensive
Care. 12(81)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhang XY, Liu ZM, Wen SH, Li YS, Li Y, Yao
X, Huang WQ and Liu KX: Dexmedetomidine administration before, but
not after, ischemia attenuates intestinal injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Anesthesiology.
116:1035–1046. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kuyrukluyildiz U, Delen LA, Onk D, Yazici
GN, Gulaboglu M and Suleyman H: The effect of dexmedetomidine on
gastric ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Biochemical and
histopathological evaluation. Acta Cir Bras.
36(e360104)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kotanoğlu MS, Kadioğlu E, Emerce E, Kaymak
C, Özcan A and Başar H: Antioxidant effects of dexmedetomidine
against hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in vitro by alkaline
Comet assay. Turk J Med Sci. 50:1393–1398. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li W, Chen M, Gong Y, Lin F and Sun C:
Effects of dexmedetomidine on oxidative stress, programmed cell
death, liver function, and expression of peripheral immune cells in
patients with primary liver cancer undergoing hepatectomy. Front
Physiol. 14(1159746)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Poli-de-Figueiredo LF, Garrido AG,
Nakagawa N and Sannomiya P: Experimental models of sepsis and their
clinical relevance. Shock. 30 (Suppl 1):S53–S59. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sjaastad FV, Jensen IJ, Berton RR,
Badovinac VP and Griffith TS: Inducing experimental polymicrobial
sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Curr Protoc Immunol.
131(e110)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Alverdy JC, Keskey R and Thewissen R: Can
the cecal ligation and puncture model be repurposed to better
inform therapy in human sepsis? Infect Immun. 88:e00942–19.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Drechsler S and Osuchowski M: Cecal
ligation and puncture. In: Sepsis: Methods and Protocols; Walker WE
(ed). Springer: New York, NY, USA, pp1-8, 2021.
|
|
60
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 40:1769–1777.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Care IoLARCo, Animals UoL: Guide for the
care and use of laboratory animals: US Department of Health and
Human Services, Public Health Service, National Academies Press
(US), 2011.
|
|
62
|
Al-Kadi A, Ahmed AS, El-Tahawy NFG,
Khalifa MMA and El-Daly M: Silymarin protects against
sepsis-induced acute liver and kidney injury via anti-inflammatory
and antioxidant mechanisms in the rat. J Adv Biomed Pharm Sci.
3:190–197. 2020.
|
|
63
|
Canikli Adıgüzel Ş, Pirat A, Türkoğlu S,
Bayraktar N, Özen Ö and Kaya M: A rat model of acute respiratory
distress silymarin's antiinflamatory and antioxidant effect. J Turk
Soc Intens Care. 14:18–27. 2016.
|
|
64
|
Schick MA, Isbary TJ, Schlegel N, Brugger
J, Waschke J, Muellenbach R, Roewer N and Wunder C: The impact of
crystalloid and colloid infusion on the kidney in rodent sepsis.
Intensive Care Med. 36:541–548. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Li XH, Gong X, Zhang L, Jiang R, Li HZ, Wu
MJ and Wan JY: Protective effects of polydatin on septic lung
injury in mice via upregulation of HO-1. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(354087)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Abraha I, Cozzolino F, Orso M, Marchesi M,
Germani A, Lombardo G, Eusebi P, De Florio R, Luchetta ML, Iorio A
and Montedori A: A systematic review found that deviations from
intention-to-treat are common in randomized trials and systematic
reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 84:37–46. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gupta SK: Intention-to-treat concept: A
review. Perspect Clin Res. 2:109–112. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tripepi G, Chesnaye NC, Dekker FW, Zoccali
C and Jager KJ: Intention to treat and per protocol analysis in
clinical trials. Nephrology (Carlton). 25:513–517. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Dardalas I, Stamoula E, Rigopoulos P,
Malliou F, Tsaousi G, Aidoni Z, Grosomanidis V, Milonas A,
Papazisis G, Kouvelas D and Pourzitaki C: Dexmedetomidine effects
in different experimental sepsis in vivo models. Eur J Pharmacol.
856(172401)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ni J, He J, Kang L, Zhong Z, Wang L and
Yin S: Effects of dexmedetomidine pretreatment on rats with
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury and miR-146a expression. Cell
Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 66:93–98. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ustyol L, Demiroren K, Kandemir I, Erten
R, Bulan K, Kaba S, Demir N and Basunlu MT: Comparative
nephroprotective effects of silymarin, N-acetylcysteine, and
thymoquinone against carbon tetrachloride-induced nephrotoxicity in
rats. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 19(e37746)2017.
|
|
72
|
Guzel S, Sahinogullari ZU, Canacankatan N,
Antmen SE, Kibar D and Coskun Yilmaz B: Potential renoprotective
effects of silymarin against vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in
rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 43:630–636. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ozdemir A, Topçu A, Mercantepe T, Arpa M,
Karakaş SM, Ozdemir A, Tümkaya L and Mercantepe F: The effects of
dexmedetomidine on early acute kidney injury in severely burned
rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 27:1311–1321. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Gonullu E, Ozkardesler S, Kume T, Duru LS,
Akan M, Guneli ME, Ergur BU, Meseri R and Dora O: Comparison of the
effects of dexmedetomidine administered at two different times on
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Braz J Anesthesiol.
64:152–158. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Cakir M, Polat A, Tekin S, Vardi N,
Taslidere E, Rumeysa Duran Z and Tanbek K: The effect of
dexmedetomidine against oxidative and tubular damage induced by
renal ischemia reperfusion in rats. Ren Fail. 37:704–708.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Qiu R, Yao W, Ji H, Yuan D, Gao X, Sha W,
Wang F, Huang P and Hei Z: Dexmedetomidine restores septic renal
function via promoting inflammation resolution in a rat sepsis
model. Life Sci. 204:1–8. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Tanaka S, Genève C, Zappella N, Yong-Sang
J, Planesse C, Louedec L, Viranaïcken W, Bringart M, Montravers P,
Denamur E, et al: Reconstituted high-density lipoprotein therapy
improves survival in mouse models of sepsis. Anesthesiology.
132:825–838. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Bedet A, Voiriot G, Ternacle J, Marcos E,
Adnot S, Derumeaux G and Mekontso Dessap A: Heart rate control
during experimental sepsis in mice: Comparison of ivabradine and
β-blockers. Anesthesiology. 132:321–329. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Zhong M, Wu W, Wang Y, Mao H, Song J, Chen
S and Zhu D: Inhibition of sphingosine kinase 1 attenuates
sepsis-induced microvascular leakage via inhibiting macrophage
NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mice. Anesthesiology.
132:1503–1515. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Park D, Ro M, Lee A-J, Kwak DW, Chung Y
and Kim JH: Contributory role of BLT2 in the production of
proinflammatory cytokines in cecal ligation and puncture-induced
sepsis. Mol Cells. 44:893–899. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Abdelnaser M, Alaaeldin R, Attya ME and
Fathy M: Hepatoprotective potential of gabapentin in cecal ligation
and puncture-induced sepsis; targeting oxidative stress, apoptosis,
and NF-kB/MAPK signaling pathways. Life Sci.
320(121562)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Kim GO, Kim N, Song GY and Bae JS:
Inhibitory activities of rare ginsenoside Rg4 on cecal ligation and
puncture-induced sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. 23(10836)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Li J, Li M, Li L, Ma J, Yao C and Yao S:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates ferroptosis and stimulates autophagy by
blocking mTOR signaling in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Mol
Immunol. 141:318–327. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Tripathi AS, Awasthi S, Maurya RK, Yasir
M, Mohapatra L and Srivastav V: Protective effect of vanillin on
the management of cecal ligation and puncture induced sepsis rat
model. Microb Pathog. 165(105493)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Daenen K, Andries A, Mekahli D, Van
Schepdael A, Jouret F and Bammens B: Oxidative stress in chronic
kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 34:975–991. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Krzemińska J, Wronka M, Młynarska E,
Franczyk B and Rysz J: Arterial hypertension-oxidative stress and
inflammation. Antioxidants (Basel). 11(172)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Zhao X, Wang H, Yang Y, Gou Y, Wang Z,
Yang D and Li C: Protective effects of silymarin against
D-Gal/LPS-induced organ damage and inflammation in mice. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 15:1903–1914. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Alikiaii B, Bagherniya M, Askari G,
Johnston TP and Sahebkar A: The role of phytochemicals in sepsis: A
mechanistic and therapeutic perspective. Biofactors. 47:19–40.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Mei B, Li J and Zuo Z: Dexmedetomidine
attenuates sepsis-associated inflammation and encephalopathy via
central α2A adrenoceptor. Brain Behav Immun. 91:296–314.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Hu H, An S, Sha T, Wu F, Jin Y, Li L, Zeng
Z, Wu J and Chen Z: Association between dexmedetomidine
administration and outcomes in critically ill patients with
sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. J Clin Anesth.
83(110960)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Esposito S, De Simone G, Boccia G, De Caro
F and Pagliano P: Sepsis and septic shock: New definitions, new
diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. J Glob Antimicrob Resist.
10:204–212. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Fujishima S: Organ dysfunction as a new
standard for defining sepsis. Inflamm Regen. 36(24)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Sun S, Chen R, Dou X, Dai M, Long J, Wu Y
and Lin Y: Immunoregulatory mechanism of acute kidney injury in
sepsis: A narrative review. Biomed Pharmacother.
159(114202)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Toklu HZ, Akbay TT, Velioglu-Ogunc A,
Ercan F, Gedik N, Keyer-Uysal M and Sener G: Silymarin, the
antioxidant component of Silybum marianum, prevents
sepsis-induced acute lung and brain injury. J Surg Res.
145:214–222. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Turgut F, Bayrak O, Catal F, Bayrak R,
Atmaca AF, Koc A, Akbas A, Akcay A and Unal D: Antioxidant and
protective effects of silymarin on ischemia and reperfusion injury
in the kidney tissues of rats. Int Urol Nephrol. 40:453–460.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Malekinejad H, Rahmani F, Valivande-Azar
S, Taheri-Broujerdi M and Bazargani-Gilani B: Long-term
administration of Silymarin augments proinflammatory mediators in
the hippocampus of rats: Evidence for antioxidant and pro-oxidant
effects. Hum Exp Toxicol. 31:921–930. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Sajedianfard J, Nazifi S, Izadi A,
Chahardahcherik M and Honarmand M: Effect of various doses of
silymarin on the oxidative stress induced by busulfan
administration in the different organs of rats. Turk J Pharm Sci.
13:233–240. 2016.
|
|
98
|
Yardımcı M, Göz M, Aydın MS, Kankılıç N
and Temiz E: Antioxidant actions of thymoquinone, silymarin, and
curcumin on experimental aortic ischemia-reperfusion model in
wistar albino rats. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 37:807–813.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Azizoğlu M, Arslan S, Gökalp Özkorkmaz E,
Aşır F, Basuguy E, Okur MH, Aydoğdu B, Alagöz Karabel M and Kaplan
I: Protective effects of Silymarin on testicular torsion/detorsion
in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 27:10446–10453. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Surai PF: Silymarin as a natural
antioxidant: An overview of the current evidence and perspectives.
Antioxidants (Basel). 4:204–247. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Taleb A, Ahmad KA, Ihsan AU, Qu J, Lin N,
Hezam K, Koju N, Hui L and Qilong D: Antioxidant effects and
mechanism of silymarin in oxidative stress induced cardiovascular
diseases. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:689–698. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Kim MJ, Kim DU, Choi JW, Kim DG, Song HJ,
Bae GS and Park SJ: Silymarin attenuates the severity of
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 49:89–95.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Cormack JR, Orme RM and Costello TG: The
role of alpha2-agonists in neurosurgery. J Clin Neurosci.
12:375–378. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Carollo DS, Nossaman BD and Ramadhyani U:
Dexmedetomidine: A review of clinical applications. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 21:457–461. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Aidoni Z, Pourzitaki C, Stamoula E,
Kotzampassi K, Tsaousi G, Kazakos G, Foroulis CN, Skourtis C,
Vasilakos DG and Grosomanidis V: Circulatory effects of
dexmedetomidine in early sepsis: A randomised controlled
experimental study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 393:89–97.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Wang C, Yuan W, Hu A, Lin J, Xia Z, Yang
CF, Li Y and Zhang Z: Dexmedetomidine alleviated sepsis-induced
myocardial ferroptosis and septic heart injury. Mol Med Rep.
22:175–184. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Koca U, Olguner ÇG, Ergür BU, Altekin E,
Taşdöğen A, Duru S, Girgin P, Gündüz K, Cilaker Mıcılı S, Güzeldağ
S and Akkuş M: The effects of dexmedetomidine on secondary acute
lung and kidney injuries in the rat model of intra-abdominal
sepsis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013(292687)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Li Y, Wu B, Hu C, Hu J, Lian Q, Li J and
Ma D: The role of the vagus nerve on dexmedetomidine promoting
survival and lung protection in a sepsis model in rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 914(174668)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Wu Y, Liu Y, Huang H, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Lu F
and Zhou C, Huang L, Li X and Zhou C: Dexmedetomidine inhibits
inflammatory reaction in lung tissues of septic rats by suppressing
TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2013(562154)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Şengel N, Köksal Z, Dursun AD, Kurtipek Ö,
Sezen ŞC, Arslan M and Kavutçu M: Effects of dexmedetomidine
administered through different routes on kidney tissue in rats with
spinal cord ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Drug Des Devel Ther.
16:2229–2239. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Hernández G, Tapia P, Alegría L, Soto D,
Luengo C, Gomez J, Jarufe N, Achurra P, Rebolledo R, Bruhn A, et
al: Effects of dexmedetomidine and esmolol on systemic hemodynamics
and exogenous lactate clearance in early experimental septic shock.
Crit Care. 20(234)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Zhao W, Jia L, Yang HJ, Xue X, Xu WX, Cai
JQ, Guo RJ and Cao CC: Taurine enhances the protective effect of
dexmedetomidine on sepsis-induced acute lung injury via balancing
the immunological system. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1362–1368.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Yang CL, Chen CH, Tsai PS, Wang TY and
Huang CJ: Protective effects of dexmedetomidine-ketamine
combination against ventilator-induced lung injury in endotoxemia
rats. J Surg Res. 167:e273–e281. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Özkan F, Yüksek A, Demirel A and Kantekin
Ç: Effects of dexmetatomidine and midazolam on immunity in
sepsis-induced rats. Med J Bakirkoy. 19:180–185. 2023.
|
|
115
|
Choi MW, Ko DR, Kong T, Choa MH, You JS
and Chung SP: Comparison of silymarin, penicillin, N-acetylcysteine
in patient with amatoxin poisoning: A systematic review. J Korean
Soc Clin Toxicol. 16:33–41. 2018.
|
|
116
|
Abdel Salam OM, Sleem AA, Omara EA and
Hassan NS: Effect of ribavirin alone or combined with silymarin on
carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic damage in rats. Drug Target
Insights. 2:19–27. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|