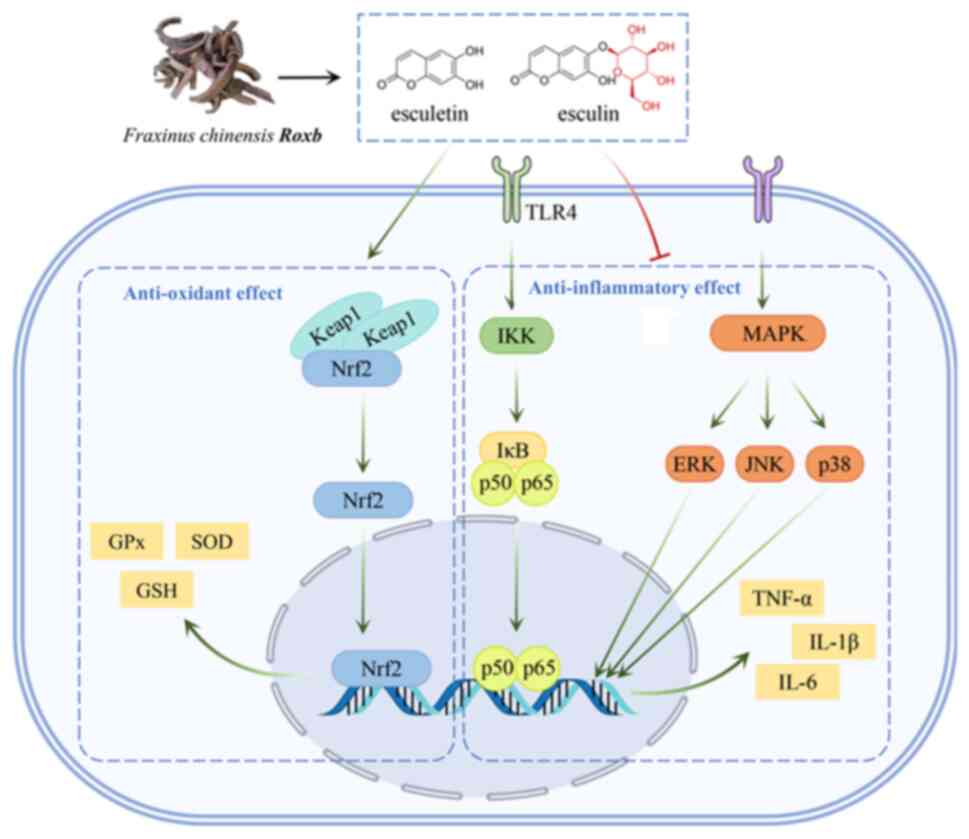
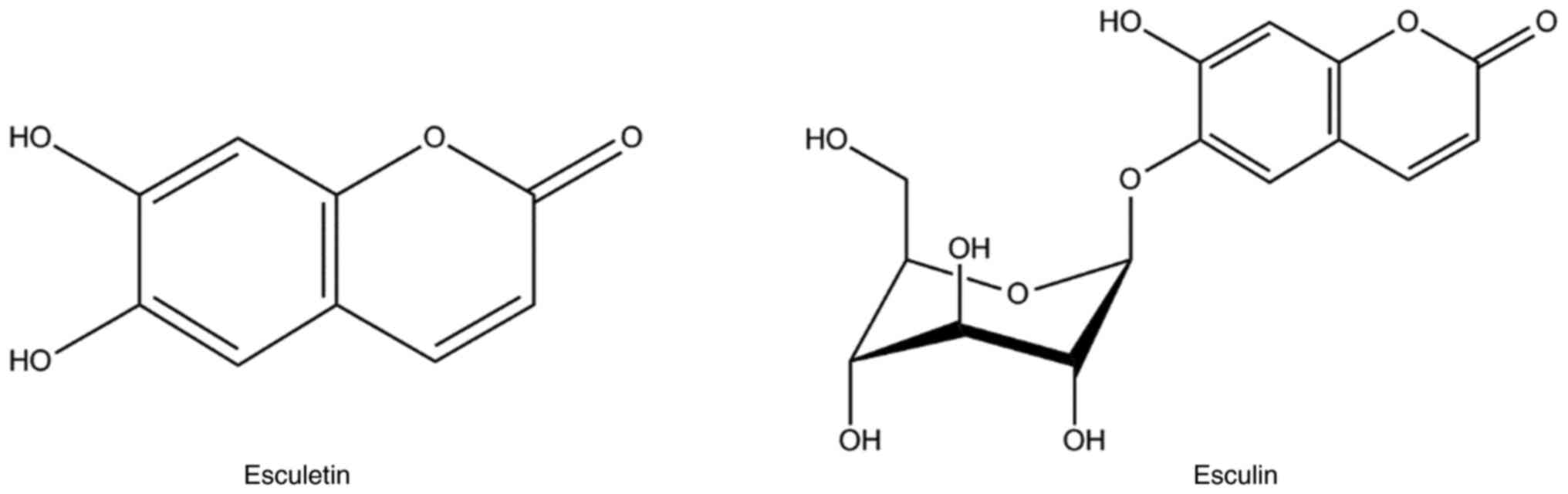
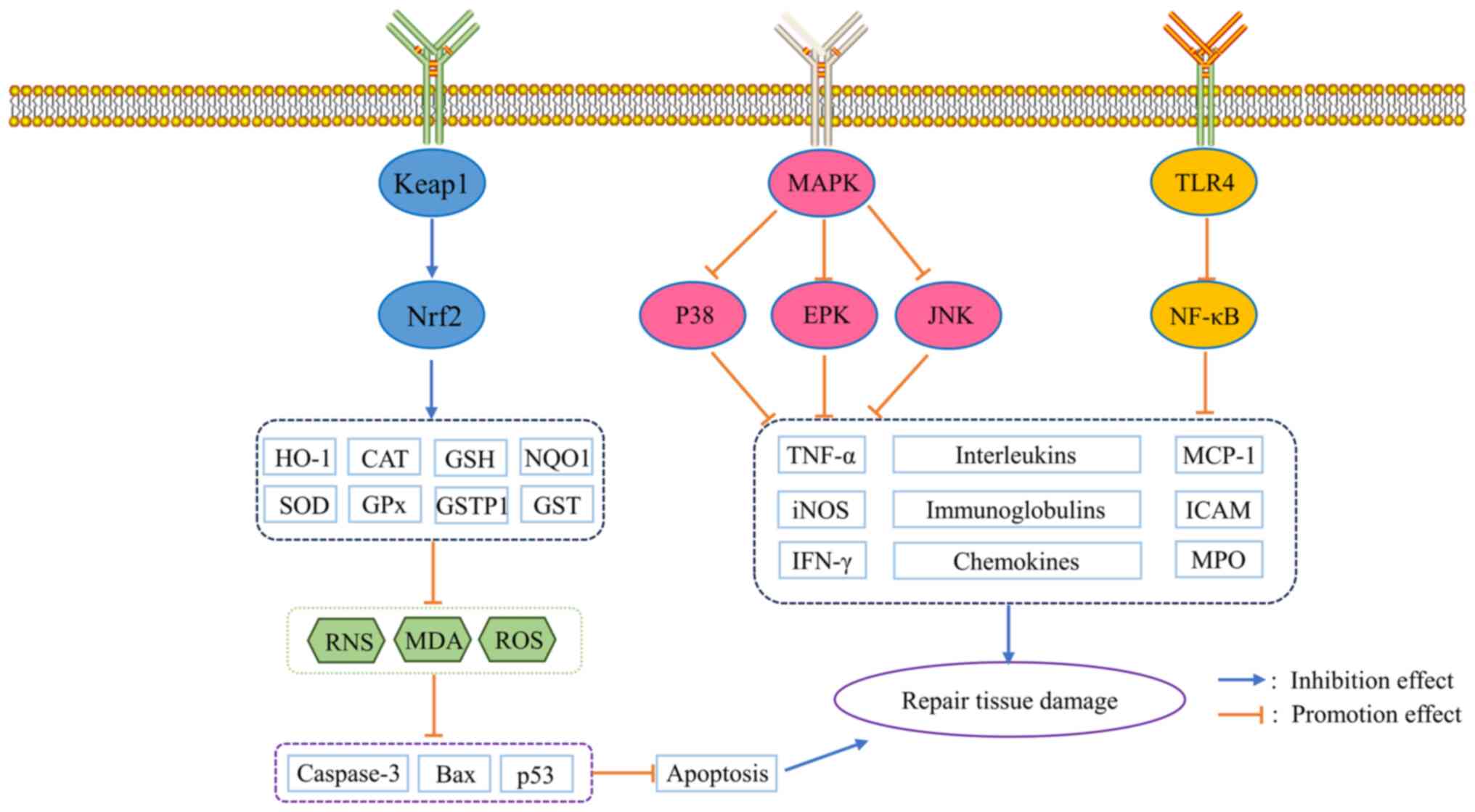
|
1
|
Chen Z and Zhong C: Oxidative stress in
Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Bull. 30:271–281. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Müller N, Myint AM and Schwarz MJ:
Inflammation in schizophrenia. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol.
88:49–68. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu J, Li Y, Sun C, Liu S, Yan Y, Pan H,
Fan M, Xue L, Nie C, Zhang H, et al: Geniposide reduces cholesterol
accumulation and increases its excretion by regulating the
FXR-mediated liver-gut crosstalk of bile acids. Pharmacol Res.
152(104631)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fernández-Sánchez A, Madrigal-Santillán E,
Bautista M, Esquivel-Soto J, Morales-González A, Esquivel-Chirino
C, Durante-Montiel I, Sánchez-Rivera G, Valadez-Vega C and
Morales-González JA: Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity.
Int J Mol Sci. 12:3117–3132. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang J, Xiang D, Xiang D, He W, Liu Y, Lan
L, Li G, Jiang C, Ren X, Liu D and Zhang C: Baicalin protects
against 17α-ethinylestradiol-induced cholestasis via the sirtuin
1/hepatic nuclear receptor-1α/farnesoid X receptor pathway. Front
Pharmacol. 10(1685)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Butler MS, Robertson AAB and Cooper MA:
Natural product and natural product derived drugs in clinical
trials. Nat Prod Rep. 31:1612–1661. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sarfraz I, Rasul A, Jabeen F, Younis T,
Zahoor MK, Arshad M and Ali M: Fraxinus: A plant with
versatile pharmacological and biological activities. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2017(4269868)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hong S and Kim MM: Aesculetin inhibits
cell invasion through inhibition of MMP-9 activity and antioxidant
activity. J Life Sci. 26:673–679. 2016.
|
|
9
|
Li CX, Li JC, Lai J and Liu Y: The
pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of esculin: A
comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 36:2434–2448. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Xie Q and Li X: Esculetin: A
review of its pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res.
36:279–298. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lin Q, Wang W, Li X, Lun J and Shao T:
Ameliorative effect of esculetin against streptozotocin-induced
experimental dementia via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 axis and
suppression of NF-κB. Lat Am J Pharm. 36:399–407. 2017.
|
|
12
|
Medina ME, Galano A and Alvarez-Idaboy JR:
Theoretical study on the peroxyl radicals scavenging activity of
esculetin and its regeneration in aqueous solution. Phys Chem Chem
Phys. 16:1197–1207. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhen AX, Piao MJ, Kang KA, Fernando PDSM,
Kang HK, Koh YS and Hyun JW: Esculetin prevents the induction of
matrix metalloproteinase-1 by hydrogen peroxide in skin
keratinocytes. J Cancer Prev. 24:123–128. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Grover J and Jachak SM: Coumarins as
privileged scaffold for anti-inflammatory drug development. RSC
Adv. 5:38892–38905. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Diniz BS, Mendes-Silva AP, Silva LB,
Bertola L, Vieira MC, Ferreira JD, Nicolau M, Bristot G, da Rosa
ED, Teixeira AL and Kapczinski F: Oxidative stress markers
imbalance in late-life depression. J Psychiatr Res. 102:29–33.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang K, Zhang Y, Ekunwe S, Yi X, Liu X,
Wang H and Pan YM: Antioxidant activity and inhibition effect on
the growth of human colon carcinoma (HT-29) cells of esculetin from
Cortex Fraxini. Med Chem Res. 20:968–974. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Jeong GS, Yoon KH, Kim HC, Oh SH, Kim M,
Kang DG, Lee HS and Kim YC: Cytoprotective constituents of the stem
barks of Fraxinus rhynchophylla on mouse hippocampal HT22 cells and
their antioxidative activity. Korean J Pharmacogn. 38:287–290.
2007.
|
|
18
|
Kim HC, An RB, Jeong GS and Kim YC:
1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging compounds of
Fraxini Cortex. Nat Prod Sci. 11:150–154. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Vianna DR, Bubols G, Meirelles G, Silva
BV, Da Rocha A, Lanznaster M, Monserrat JM, Garcia SC, Von Poser G
and Eifler-Lima VL: Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of
synthesized coumarins. Int J Mol Sci. 13:7260–7270. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee JM, Tseng TH and Lee YJ: An efficient
synthesis of neoflavonoid antioxidants based on Montmorillonite
K-10 catalysis. Synthesis. 2247–2254. 2001.
|
|
21
|
Hsia CW, Lin KC, Lee TY, Hsia CH, Chou DS,
Jayakumar T, Velusamy M, Chang CC and Sheu JR: Esculetin, a
coumarin derivative, prevents thrombosis: Inhibitory signaling on
PLCγ2-PKC-AKT activation in human platelets. Int J Mol Sci.
20(2731)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee BC, Lee SY, Lee HJ, Sim GS, Kim JH,
Kim JH, Cho YH, Lee DH, Pyo HB, Choe TB, et al: Anti-oxidative and
photo-protective effects of coumarins isolated from Fraxinus
chinensis. Arch Pharm Res. 30:1293–1301. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Potapovich MV, Metelitsa DI and Shadyro
OI: Antioxidant activity of hydroxy derivatives of coumarin. Prikl
Biokhim Mikrobiol. 48:282–288. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
24
|
Rubio V, García-Pérez AI, Herráez A,
Tejedor MC and Diez JC: Esculetin modulates cytotoxicity induced by
oxidants in NB4 human leukemia cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
69:700–712. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Rubio V, García-Pérez AI, Tejedor MC,
Herráez A and Diez JC: Esculetin neutralises cytotoxicity of t-BHP
but Not of H2O2 on human leukaemia NB4 cells.
Biomed Res Int. 2017(9491045)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee CR, Shin EJ, Kim HC, Choi YS, Shin T
and Wie MB: Esculetin inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotoxicity
via glutathione preservation in primary cortical cultures. Lab Anim
Res. 27:259–263. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
de Jesus Souza M, De Moraes JA, Da Silva
VN, Helal-Neto E, Uberti AF, Scopel-Guerra A, Olivera-Severo D,
Carlini CR and Barja-Fidalgo C: Helicobacter pylori urease
induces pro-inflammatory effects and differentiation of human
endothelial cells: Cellular and molecular mechanism. Helicobacter.
24(e12573)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Abdallah H, Farag M, Osman S, Kim DH, Kang
K, Pan CH and Abdel-Sattar E: Isolation of major phenolics from
Launaea spinosa and their protective effect on HepG2 cells damaged
with t-BHP. Pharm Biol. 54:536–541. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hong S, Heo H, Lee H, Lee M, Lee J and
Park JH: Protective effects of the methanol extract from calyx of
Diospyros kaki on alcohol-induced liver injury. J Korean Soc Food
Sci Nutr. 50:339–346. 2021.
|
|
30
|
Sen Z, Weida W, Jie M, Li S, Dongming Z
and Xiaoguang C: Coumarin glycosides from Hydrangea paniculata slow
down the progression of diabetic nephropathy by targeting Nrf2
anti-oxidation and smad2/3-mediated profibrosis. Phytomedicine.
57:385–395. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rubio V, García-Pérez AI, Herráez A and
Diez JC: Different roles of Nrf2 and NFKB in the antioxidant
imbalance produced by esculetin or quercetin on NB4 leukemia cells.
Chem Biol Interact. 294:158–166. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gao Y, Shi W, Yao H, Ai Y, Li R, Wang Z,
Liu T, Dai W, Xiao X, Zhao J, et al: An integrative pharmacology
based analysis of refined liuweiwuling against liver injury: A
novel component combination and hepaprotective mechanism. Front
Pharmacol. 12(747010)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim JH, Jeong MS, Kim DY, Her S and Wie
MB: Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis
and necrosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Int.
90:204–214. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gao JL and Gong XY: Esculetin attenuates
neurotoxicity induced by Aβ25-35 in SH-SY5Y cells via
inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Acta Pol Pharm. 75:1177–1185. 2018.
|
|
35
|
Pruccoli L, Morroni F, Sita G, Hrelia P
and Tarozzi A: Esculetin as a bifunctional antioxidant prevents and
counteracts the oxidative stress and neuronal death induced by
amyloid protein in SH-SY5Y cells. Antioxidants (Basel).
9(551)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
He Y, Li C, Ma Q and Chen S: Esculetin
inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes
following hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
501:139–144. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, An Y, He X, Zhang D and He W:
Esculetin protects human corneal epithelial cells from oxidative
stress through Nrf-2 signaling pathway. Exp Eye Res.
202(108360)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim Y and Lee J: Esculetin inhibits
adipogenesis and increases antioxidant activity during adipocyte
differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 22:118–123.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shi T, Li T, Jiang X, Jiang X, Zhang Q,
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang L, Qin X, Zhang W and Zheng Y: Baicalin
protects mice from infection with methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus via alleviating inflammatory response. J
Leukoc Biol. 108:1829–1839. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Subramaniam SR and Ellis EM:
Esculetin-induced protection of human hepatoma HepG2 cells against
hydrogen peroxide is associated with the Nrf2-dependent induction
of the NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 gene. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 250:130–136. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lee J, Yang J, Jeon J, Jeong HS, Lee J and
Sung J: Hepatoprotective effect of esculetin on ethanol-induced
liver injury in human HepG2 cells and C57BL/6J mice. J Funct Foods.
40:536–543. 2018.
|
|
42
|
Subramaniam SR and Ellis EM:
Neuroprotective effects of umbelliferone and esculetin in a mouse
model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res. 91:453–461.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Xu BR, Zhu LY, Chu J, Ma Z, Fu Q, Wei W,
Deng X and Ma S: Esculetin improves cognitive impairments induced
by transient cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion in mice via
regulation of mitochondrial fragmentation and mitophagy. Behav
Brain Res. 372(112007)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Martín-Aragón S, Villar Á and Benedí J:
Age-dependent effects of esculetin on mood-related behavior and
cognition from stressed mice are associated with restoring brain
antioxidant status. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
65:1–16. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Atmaca M, Bilgin HM, Obay BD, Diken H,
Kelle M and Kale E: The hepatoprotective effect of coumarin and
coumarin derivates on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic injury
by antioxidative activities in rats. J Physiol Biochem. 67:569–576.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Subramaniam SR and Ellis EM: Umbelliferone
and esculetin protect against N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced
hepatotoxicity in rats. Cell Biol Int. 40:761–769. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Prabakaran D and Ashokkumar N: Protective
effect of esculetin on hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative damage in
the hepatic and renal tissues of experimental diabetic rats.
Biochimie. 95:366–373. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Han MH, Park C, Lee DS, Hong SH, Choi IW,
Kim GY, Choi SH, Shim JH, Chae JI, Yoo YH and Choi YH:
Cytoprotective effects of esculetin against oxidative stress are
associated with the upregulation of Nrf2-mediated NQO1 expression
via the activation of the ERK pathway. Int J Mol Med. 39:380–386.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Arora R, Sawney S, Saini V, Steffi C,
Tiwari M and Saluja D: Esculetin induces antiproliferative and
apoptotic response in pancreatic cancer cells by directly binding
to KEAP1. Mol Cancer. 15(64)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Weiwei T, Ting Z, Chunhua M and Hongyan L:
Suppressing receptor-interacting protein 140: A new sight for
esculetin to treat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. RSC Adv.
6:112117–112128. 2016.
|
|
51
|
Türk E, Ozan Tekeli I, Özkan H, Uyar A,
Cellat M, Kuzu M, Yavas I, Alizadeh Yegani A, Yaman T and Güvenç M:
The protective effect of esculetin against aluminium
chloride-induced reproductive toxicity in rats. Andrologia.
53(e13930)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Owczarek A, Kolodziejczyk-Czepas J,
Woźniak-Serwata J, Magiera A, Kobiela N, Wąsowicz K and Olszewska
MA: Potential activity mechanisms of aesculus hippocastanum bark:
Antioxidant effects in chemical and biological in vitro models.
Antioxidants (Basel). 10(995)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Witaicenis A, Seito LN, da Silveira Chagas
A, de Almeida LD Jr, Luchini AC, Rodrigues-Orsi P, Cestari SH and
Di Stasi LC: Antioxidant and intestinal anti-inflammatory effects
of plant-derived coumarin derivatives. Phytomedicine. 21:240–246.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Raghunath A, Nagarajan R, Sundarraj K,
Palanisamy K and Perumal E: Identification of compounds that
inhibit the binding of Keap1a/Keap1b Kelch DGR domain with Nrf2
ETGE/DLG motifs in zebrafish. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
125:259–270. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hassanein EHM, Sayed AM, Hussein OE and
Mahmoud AM: Coumarins as modulators of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020(1675957)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Naaz F, Abdin MZ and Javed S: Protective
effect of esculin against prooxidant aflatoxin B1-induced
nephrotoxicity in mice. Mycotoxin Res. 30:25–32. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yao Y, Zhao X, Xin J, Wu Y and Li H:
Coumarins improved type 2 diabetes induced by high-fat diet and
streptozotocin in mice via antioxidation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
96:765–771. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zhao DL, Zou LB, Lin S, Shi JG and Zhu HB:
Anti-apoptotic effect of esculin on dopamine-induced cytotoxicity
in the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Neuropharmacology.
53:724–732. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wispriyono B, Jalaludin J, Kusnoputranto
H, Pakpahan S, Aryati GP, Pratama S, Librianty N, Rozaliyani A,
Taufik FF and Novirsa R: Glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase
(SOD) levels among junior high school students induced by indoor
particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) exposure.
J Public Health Res. 10(2372)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kaneko T, Baba N and Matsuo M: Protection
of coumarins against linoleic acid hydroperoxide-induced
cytotoxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 142:239–254. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Qi SP and Yu JC: Protective effect of
esculin in hyperoxic lung injury in neonatal rats. La Am J Pharm.
35:1177–1181. 2016.
|
|
62
|
Liu A, Shen Y, Du Y, Chen J, Pei F, Fu W
and Qiao J: Esculin prevents
Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-induced acute liver injury in
mice. Microb Pathog. 125:418–422. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Song Y, Wang X, Qin S, Zhou S, Li J and
Gao Y: Esculin ameliorates cognitive impairment in experimental
diabetic nephropathy and induces anti-oxidative stress and
anti-inflammatory effects via the MAPK pathway. Mol Med Rep.
17:7395–7402. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zheng L, Yang L, Wang Z, Chen C and Su Y:
Protective effect of Esculin in adjuvant-induced arthritic (AIA)
rats via attenuating pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative
stress. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 61:1–5. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee H, Lee JH, Koh SJ and Park H:
Bidirectional relationship between atopic dermatitis and
inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Am Acad Dermatol. 83:1385–1394. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Nakajima A, Yamamoto Y, Yoshinaka N, Namba
M, Matsuo H, Okuyama T, Yoshigai E, Okumura T, Nishizawa M and
Ikeya Y: A new flavanone and other flavonoids from green perilla
leaf extract inhibit nitric oxide production in interleukin
1β-treated hepatocytes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 79:138–146.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kim AR, Jin Q, Jin HG, Ko HJ and Woo ER:
Phenolic compounds with IL-6 inhibitory activity from Aster yomena.
Arch Pharm Res. 37:845–851. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Wang F, Jia QW, Yuan ZH, Lv LY, Li M,
Jiang ZB, Liang DL and Zhang DZ: An anti-inflammatory C-stiryl
iridoid from Camptosorus sibiricus Rupr. Fitoterapia. 134:378–381.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Hu J, Zhao L, Li N, Yang Y, Qu T, Ren H,
Cui X, Tao H, Chen Z and Peng Y: Investigation of the active
ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms of Porana sinensis
Hemsl. Against rheumatoid arthritis using network pharmacology and
experimental validation. PLoS One. 17(e0264786)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Lee MW, Kang SJ, Park M, Yoon JH, Han BH,
Choi SE and Lee MW: Anti-oxidative and nitric oxide production
inhibitory activities of phenoliccompounds from the fruits of
actinidia arguta. Nat Prod Sci. 12:221–225. 2006.
|
|
71
|
Kim Y, Park Y, Namkoong S and Lee J:
Esculetin inhibits the inflammatory response by inducing heme
oxygenase-1 in cocultured macrophages and adipocytes. Food Funct.
5:2371–2377. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Sun B, Wang B and Xu M: Esculetin inhibits
histamine-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and mucin in
nasal epithelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:821–827.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Hong SH, Jeong HK, Han MH, Park C and Choi
YH: Esculetin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
mediators and cytokines by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB
translocation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 10:3241–3246.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Lee SJ, Lee US, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Inhibitory effect of esculetin on migration, invasion and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression in TNF-α-induced vascular smooth
muscle cells. Mol Med Rep. 4:337–341. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Xie C, Li Y, Gao J and Wang Y: Esculetin
regulates the phenotype switching of airway smooth muscle cells.
Phytother Res. 33:3008–3015. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Song WJ, Yun JH, Jeong MS, Kim KN, Shin T,
Kim HC and Wie MB: Inhibitors of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2
attenuate trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity through regulating
oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines in human
neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Sci. 11(1116)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ozal SA, Turkekul K, Gurlu V, Guclu H and
Erdogan S: Esculetin protects human retinal pigment epithelial
cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and cell death.
Curr Eye Res. 43:1169–1176. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Torres R, Mascayano C, Núñez C, Modak B
and Faini F: Coumarins of haplopappus multifolius and derivative as
inhibitors of lox: Evaluation in-vitro and docking studies. J Chil
Chem Soc. 58:2027–2030. 2013.
|
|
79
|
Kwon OS, Choi JS, Islam MN, Kim YS and Kim
HP: Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase and skin inflammation by the
aerial parts of Artemisia capillaris and its constituents. Arch
Pharm Res. 34:1561–1569. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Lee HC, Liu FC, Tsai CN, Chou AH, Liao CC
and Yu HP: Esculetin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury in mice via modulation of the AKT/ERK/NF-κB and
RORγt/IL-17 pathways. Inflammation. 43:962–974. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Chen T, Guo Q, Wang H, Zhang H, Wang C,
Zhang P, Meng S, Li Y, Ji H and Yan T: Effects of esculetin on
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury via regulation
of RhoA/Rho Kinase/NF-кB pathways in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic
Res. 49:1459–1468. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Oh SY, Kim YH, Kang MK, Lee EJ, Kim DY, Oh
H, Kim SI, Na W and Kang YH: Aesculetin attenuates alveolar injury
and fibrosis induced by close contact of alveolar epithelial cells
with blood-derived macrophages via IL-8 signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
21(5518)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Hongyan L: Esculetin attenuates Th2 and
Th17 responses in an ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mouse model.
Inflammation. 39:735–743. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Oh SY, Kim YH, Kang MK, Lee EJ, Kim DY, Oh
H, Kim SI, Na W, Kang IJ and Kang YH: Aesculetin inhibits airway
thickening and mucus overproduction induced by urban particulate
matter through blocking inflammation and oxidative stress involving
TLR4 and EGFR. Antioxidants (Basel). 10(494)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Yum S, Jeong S, Lee S, Kim W, Nam J and
Jung Y: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase is a potential molecular target for
esculetin-mediated anti-colitic effects. Fitoterapia. 103:55–62.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Wang SK, Chen TX, Wang W, Xu LL, Zhang YQ,
Jin Z, Liu YB and Tang YZ: Aesculetin exhibited anti-inflammatory
activities through inhibiting NF-кB and MAPKs pathway in vitro and
in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 296(115489)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Witaicenis A, Luchini AC, Hiruma-Lima CA,
Felisbino SL, Justulin LA Jr, Garrido-Mesa N, Utrilla P, Gálvez J
and Di Stasi LC: Mechanism and effect of esculetin in an
experimental animal model of inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J
Inflamm. 11:433–446. 2013.
|
|
88
|
Xu J, Wang H, Wen H, Zhang J and Wu A:
Evaluation of antioxidant, antiulcer, and analgesic activities of
esculetin. La Am J Pharm. 40:1584–1591. 2021.
|
|
89
|
Choi RY, Ham JR and Lee MK: Esculetin
prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver in diabetic mice fed high-fat
diet. Chem Biol Interact. 260:13–21. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Song WJ, Kim J, Shin T, Jeong MS, Kim KN,
Yun JH and Wie MB: Esculetin and fucoidan attenuate autophagy and
apoptosis induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles through modulating
reactive astrocyte and proinflammatory cytokines in the rat brain.
Toxics. 10(194)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Zhu L, Nang C, Luo F, Pan H, Zhang K, Liu
J, Zhou R, Gao J, Chang X, He H, et al: Esculetin attenuates
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammatory processes and
depressive-like behavior in mice. Physiol Behav. 163:184–192.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Sulakhiya K, Keshavlal GP, Bezbaruah BB,
Dwivedi S, Gurjar SS, Munde N, Jangra A, Lahkar M and Gogoi R:
Lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety- and depressive-like behaviour
in mice are prevented by chronic pre-treatment of esculetin.
Neurosci Lett. 611:106–111. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Jeong NH, Yang EJ, Jin M, Lee JY, Choi YA,
Park PH, Lee SR, Kim SU, Shin TY, Kwon TK, et al: Esculetin from
Fraxinus rhynchophylla attenuates atopic skin inflammation by
inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines. Int
Immunopharmacol. 59:209–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Chen Y, Zhang Q, Liu H, Lu C, Liang CL,
Qiu F, Han L and Dai Z: Esculetin ameliorates psoriasis-like skin
disease in mice by inducing CD4+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells. Front Immunol. 9(2092)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Cheng YJ, Tian XL, Zeng YZ, Lan N, Guo LF,
Liu KF, Fang HL, Fan HY and Peng ZL: Esculetin protects against
early sepsis via attenuating inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and
STAT1/STAT3 signaling. Chin J Nat Med. 19:432–441. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Jiang D, Liu X and Hu J: Topical
administration of Esculetin as a potential therapy for experimental
dry eye syndrome. Eye (Lond). 31:1724–1732. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Pullaiah CP, Nelson VK, Rayapu S, G V NK
and Kedam T: Exploring cardioprotective potential of esculetin
against isoproterenol induced myocardial toxicity in rats: In vivo
and in vitro evidence. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 22(43)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Singh L, Kaur A, Garg S, Singh AP and
Bhatti R: Protective effect of esculetin, natural coumarin in mice
model of fibromyalgia: Targeting pro-inflammatory cytokines and
MAO-A. Neurochem Res. 45:2364–2374. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Yang XD, Chen Z, Ye L, Chen J and Yang YY:
Esculin protects against methionine choline-deficient diet-induced
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating the Sirt1/NF-κ B p65
pathway. Pharm Biol. 59:922–932. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Tian X, Peng Z, Luo S, Zhang S, Li B, Zhou
C and Fan H: Aesculin protects against DSS-induced colitis though
activating PPARγ and inhibiting NF-кB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
857(172453)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Choi HJ, Chung TW, Kim JE, Jeong HS, Joo
M, Cha J, Kim CH and Ha KT: Aesculin inhibits matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression via p38 mitogen activated protein
kinase and activator protein 1 in lipopolysachride-induced RAW264.7
cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:267–274. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Niu X, Wang Y, Li W, Zhang H, Wang X, Mu
Q, He Z and Yao H: Esculin exhibited anti-inflammatory activities
in vivo and regulated TNF-α and IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated
mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro through MAPK pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 29:779–786. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Tianzhu Z and Shumin W: Esculin inhibits
the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via
regulation of TLR/NF-κB pathways. Inflammation. 38:1529–1536.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Li W, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang H, He Z, Zhi
W, Liu F and Niu X: Gastroprotective effect of esculin on
ethanol-induced gastric lesion in mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
31:174–184. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Kim YR, Park BK, Seo CS, Kim NS and Lee
MY: Antidepressant and anxiolytic-like effects of the stem bark
extract of fraxinus rhynchophylla hance and its components in a
mouse model of depressive-like disorder induced by reserpine
administration. Front Behav Neurosci. 15(650833)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Chen T, Zheng M, Li Y, Liu S and He L: The
role of CCR5 in the protective effect of Esculin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive symptom in mice. J Affect
Disord. 277:755–764. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Cheng X, Yang Y, Li W, Liu M, Zhang S,
Wang Y and Du G: Esculin alleviates acute kidney injury and
inflammation induced by LPS in mice and its possible mechanism. J
Chin Pharm Sci. 29:322–332. 2020.
|
|
108
|
Wang YH, Liu YH, He GR, Lv Y and Du GH:
Esculin improves dyslipidemia, inflammation and renal damage in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med.
15(402)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Li W, Wang Y, Wang X, He Z, Liu F, Zhi W,
Zhang H and Niu X: Esculin attenuates endotoxin shock induced by
lipopolysaccharide in mouse and NO production in vitro through
inhibition of NF-κB activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:726–734.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Cai T and Cai B: Pharmacological
activities of esculin and esculetin: A review. Medicine
(Baltimore). 102(e35306)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|