Introduction
Mesenteric lymphadenitis (ML) is a benign
inflammation of the lymphatic system that is specifically found in
the lower quadrant of the abdomen. It presents a distinct
inclination for the paediatric and adolescent population,
demonstrating a notably greater prevalence among male than female
patients (1). Remarkably, this
condition shares similarities in terms of abdominal pain
presentations with various pathological conditions, including acute
appendicitis, intestinal intussusception and constipation (2). Furthermore, analogous to numerous
cases of acute abdominal pain, ML often displays mild to moderate
elevations in peripheral leukocyte count and C-reactive protein
levels.
The diagnosis of ML in young children is challenging
due to the absence of distinct clinical manifestations and specific
laboratory findings, often leading to the mimicking of other
diseases (3). Additionally, it is
frequently misreported as the primary cause of pseudoappendicitis
(4). Distinguishing ML from other
conditions associated with abdominal pain remains a formidable task
for paediatric practitioners. This diagnostic ambiguity or
inadequate management has the potential to hinder timely
identification and intervention, substantially impacting early
diagnosis and treatment in affected infants. Hence, there exists a
pressing need to actively explore more precise and effective
diagnostic approaches to enhance both diagnostic accuracy and
therapeutic outcomes in paediatric patients with ML.
Shear-wave elastography (SWE) is an innovative
technology commonly used to assess tissue stiffness qualitatively
and quantitatively in a variety of tissues and organs, with the
liver, breast, and thyroid being the most frequently examined
(5-7).
Previously, flow through certain organs was assessed using a 2D
system to examine changes in blood vessels, determining the flow
rate and volume in systole and diastole (8). Changes in blood flow affect tissue
stiffness. Elastography techniques, such as Virtual Touch Tissue
Imaging and Quantification (VTIQ), can detect alterations in tissue
stiffness caused by changes in blood flow. VTIQ provides a 2D image
that measures tissue stiffness in a specified region of interest.
It offers a precise measurement of shear velocity as it propagates
in a direction perpendicular to the detection pulse. By contrast,
earlier external pressure elastography methods relied solely on
semiquantitative approaches, which depended greatly on the skills
of the investigator. Additionally, VTIQ addresses the drawbacks of
traditional elastography by providing quantitative data on the
structures being examined, such as wave propagation speed values
measured in m/sec, presenting them visually on a two-dimensional
color-coded map. The substantial diagnostic challenges, such as the
condition's resemblance to other abdominal issues, frequently
result in misinterpretation, impeding the prompt identification and
intervention, highlighting the need for more accurate and effective
diagnostic approaches in paediatric patients with ML. Therefore, in
the present study, it was aimed to explore the value of
conventional ultrasound (US) and VTIQ in the assessment of ML in a
paediatric population. The objectives of the present study were to
perform non-invasive quantification of MLN stiffness in patients in
the ML and control groups; and to investigate the correlation
between the diagnostic performance, conventional US and VTIQ
characteristics, and laboratory findings.
Materials and methods
Patient enrolment and group
allocation
The present retrospective study involved patients
who underwent abdominal ultrasound in Pudong New Area People's
Hospital affiliated to Shanghai University of Medicine and Health
Sciences (Shanghai, China) between November 2022 and March 2023.
The inclusion criteria for the ML group required a clinical
diagnosis of ML and the provision of complete imaging data. ML was
defined as a clinical diagnosis according to the discharge summary
found in patients with right lower quadrant pain or tenderness, as
well as based on sonographic findings of enlarged MLNs. Enlarged
abdominal lymph nodes were specifically identified as those with
the shortest diameter of 5 mm (1).
Laboratory data, including eosinophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, white
blood cell (WBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, were
collected for subsequent analysis. For a comparison, a control
group of 60 symptom-free healthy patients was recruited; the
aforementioned patients had normal cortical lymph node size, shape
and echogenicity along with normal laboratory data. The laboratory
data were acquired through a blood test.
The present study was approved (approval no.
2022-K-42; 12 July 2022) by the Shanghai Pudong New Area People's
Hospital Ethics Committee (Shanghai, China), and informed consent
was waived given the retrospective nature of the study.
Imaging technique and evaluation
All MLNs in both the ML and control groups underwent
grayscale US and VTIQ examinations. The US assessments in both
groups began with an initial abdominal examination using a Toshiba
Aplio 500 (Canon Medical Systems Corporation), which was equipped
with a 14 MHz line array transducer. This examination included
transverse and longitudinal scans of the lower abdominal area for
each patient. Conventional US characteristics such as dimensions
and shapes were recorded. Dimensions included the longest diameter
(cm) and the relative proportions of the longest and shortest
diameter, represented by the longest diameter/shortest diameter
ratio.
Afterwards, VTIQ examinations were performed using a
Siemens Oxana2 machine (Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc.)
equipped with a 9 MHz frequency 9L4 linear transducer. To ensure
consistency, the same operator conducted all US and VTIQ
examinations, and patients were requested to maintain the same
position throughout both tests. Shear-wave velocity (SWV) values
were quantified using a strategically placed 2x2 mm region of
interest (ROI). Notably, SWV measurements were rigorously obtained
on eight occasions for each MLN under scrutiny. When the MLNs
exhibited a uniform stiffness distribution, eight ROI boxes were
randomly placed by the operator. In cases where the MLN displayed
varying degrees of stiffness distribution, a meticulous approach
was taken. Based on the color scale of the velocity map, the ROIs
were positioned from the area with the highest SWV to the one with
the lowest SWV, encompassing the stiffest and softest regions, each
represented by one area. The study derived three distinct SWV
values: SWVMean, SWVMax and
SWVMin.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were analysed through
independent unpaired t-tests or Mann-Whitney U tests, while
categorical variables were compared using the Chi-squared
(X2) test or Fisher's exact test. SWV values were
compared between those with ML and healthy individuals using the
Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Pearson or Spearman bivariate correlation
analyses was performed to examine the associations between clinical
parameters and the stiffness of the largest MLN. Multivariate
logistic regression analysis was utilized to determine the impact
of various clinical factors on MLN stiffness. Receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the
diagnostic performance of US alone and US + VTIQ, with clinical
confirmation (including clinical symptoms, laboratory results and
imaging information) by a paediatrician serving as the gold
standard. Statistically significant difference was considered when
the P<0.05. The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS
24.0 software (IBM Corp.) and Stata 15.0 software (StataCorp
LP).
Results
Baseline characteristics
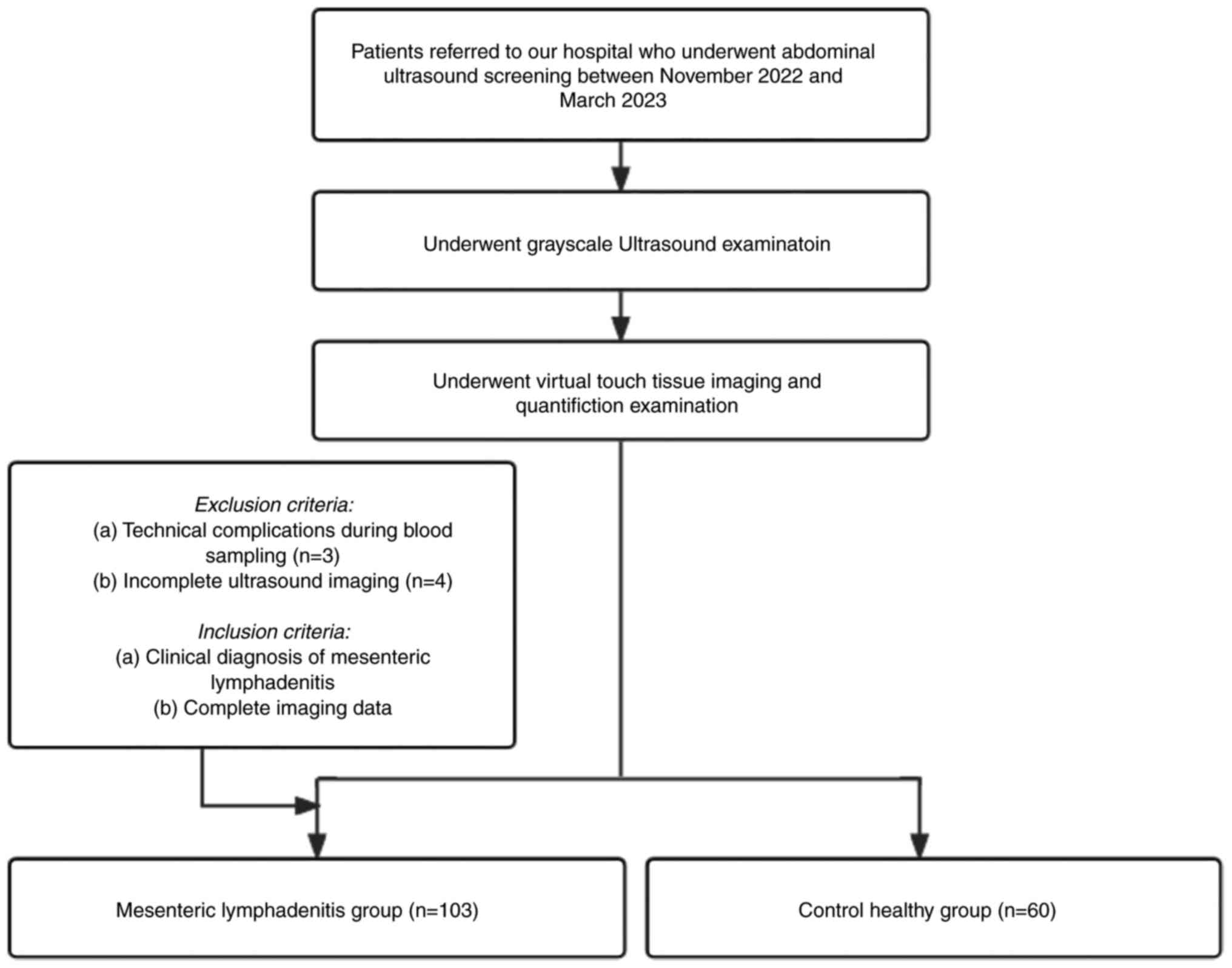
In the present study, 103 patients who were
diagnosed with ML and 60 healthy individuals were included
(Fig. 1). Notably, there were no
significant differences in age or sex distribution between the two
groups (both P>0.05) (Table I).
The median age of the individuals in the control cohort was
6.02±1.52 years (range, 3-9 years) and that of the individuals in
the reference cohort was 6.24±1.40 years (range, 4-9 years). In
children afflicted with ML, common clinical manifestations included
a body temperature of 37.90±0.80˚C, nausea (77.67%) and anorexia
(50.49%).
 | Table IDemographic and clinical parameters of
children with mesenteric lymphadenitis and children in the control
group. |
Table I
Demographic and clinical parameters of
children with mesenteric lymphadenitis and children in the control
group.
| Parameters | ML group (n=103) | Control group
(n=60) | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years | 6.24±1.40 | 6.02±1.52 | 0.338 |
| Sex, n | | | 0.949 |
|
Female | 63 | 37 | |
|
Male | 40 | 23 | |
| Number of MLNs | 292 | 167 | 0.762 |
| Temperature,˚C | 37.90±0.80 | 36.70±0.20 | <0.001 |
| Duration of abdominal
pain, days | 2.38±1.26 | N/A | N/A |
| Nausea, n (%) | 80 (77.67) | N/A | N/A |
| Vomiting, n (%) | 46 (44.67) | N/A | N/A |
| Anorexia, n (%) | 52 (50.49) | N/A | N/A |
| Constipation, n
(%) | 6 (5.83) | N/A | N/A |
| WBCs,
109/l | 11.09±3.41 | 8.83±1.56 | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dl | 8.22±1.85 | 5.40±1.50 | <0.001 |
| Eosinophils, % | 2.07±1.16 | 0.21±0.07 | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 24.46±10.51 | 6.01±1.56 | <0.001 |
| Monocytes, % | 7.90±3.03 | 0.50±0.08 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dl | 13.00±0.78 | 12.46±1.47 | 0.003 |
In children with ML, a total of 292 MLNs were
identified, with a median patient count of 2.83±1.00. Conversely,
in the cohort of healthy controls, 167 MLNs were detected, with a
median count of 2.78±1.12 (Table
I). It is noteworthy, however, that no significant disparity in
the observed number of MLNs was detected between the two cohorts
(P=0.762). Within the ML group, 71.92% (210/292) of the MLNs were
enlarged (Table II). Conversely,
in the control cohort, 66.47% (111/167) of the MLNs exhibited
enlargement. The 210 enlarged MLNs in children with ML were located
in the right lower quadrant. In the left lower quadrant, 8 healthy
children displayed 19 out of 111 enlarged MLNs. The dimensions of
MLNs in children with ML outstripped those in the control cohort.
In children with ML, the longest diameter (1.29±0.31 cm vs.
1.08±0.21 cm) of the MLNs was significantly greater than that in
the healthy cohort (P<0.001).
 | Table IISize and shape of enlarged mesenteric
lymph nodes. |
Table II
Size and shape of enlarged mesenteric
lymph nodes.
| Group | Longest diameter,
cm | L/S, cm |
|---|
| ML group
(n=210) | 1.29±0.31 | 2.32±0.85 |
| Control group
(n=111) | 1.08±0.21 | 2.26±0.54 |
| P-value | <0.001 | 0.589 |
Laboratory findings
Compared with those in the control cohort (all
P<0.001), the WBC (11.09±3.41x109/l vs.
8.83±1.56x109/l), CRP level (8.22±1.85 mg/dl vs.
5.40±1.50 mg/dl), eosinophil (2.07±1.16% vs. 0.21±0.07), lymphocyte
(24.46±10.51% vs. 6.01±1.56) and monocyte (7.90±3.03% vs.
0.50±0.08) counts in children with ML were significantly increased
(Table I).
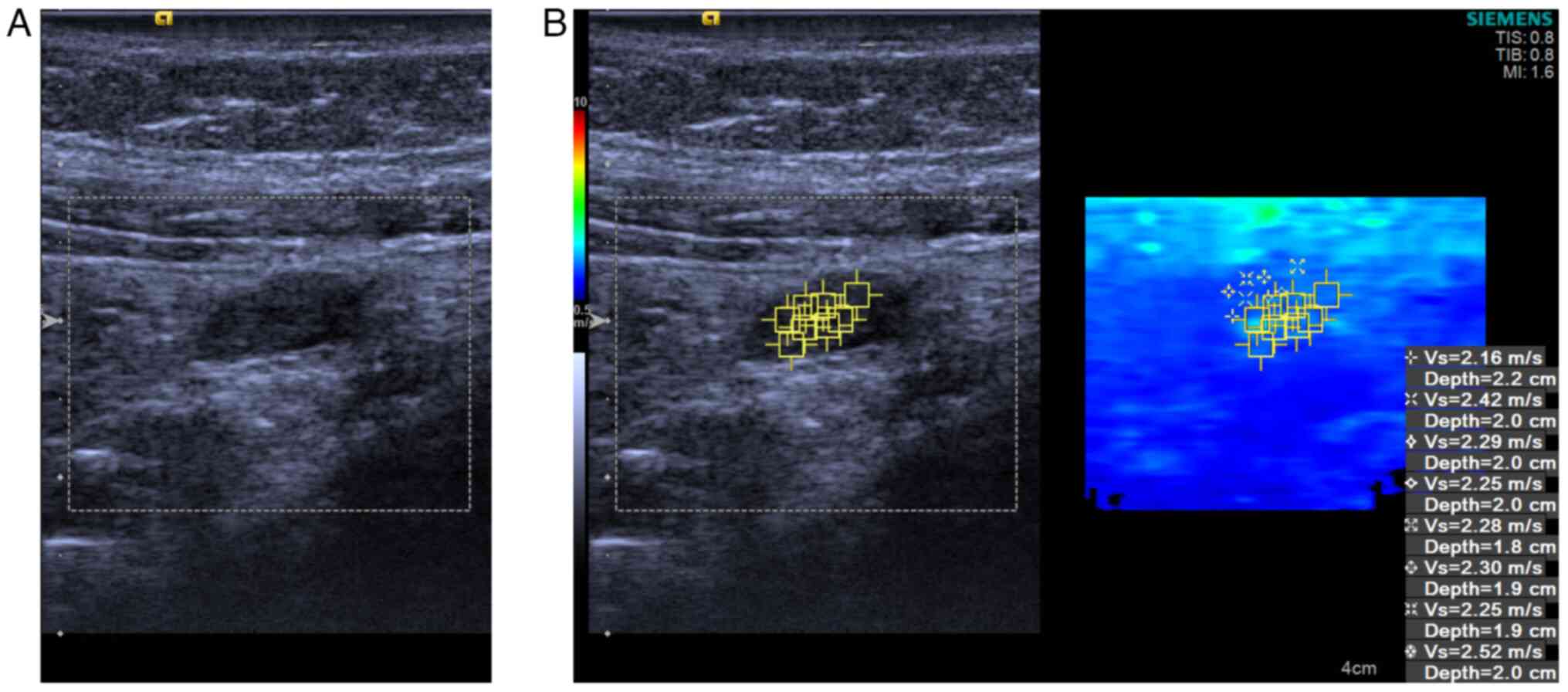
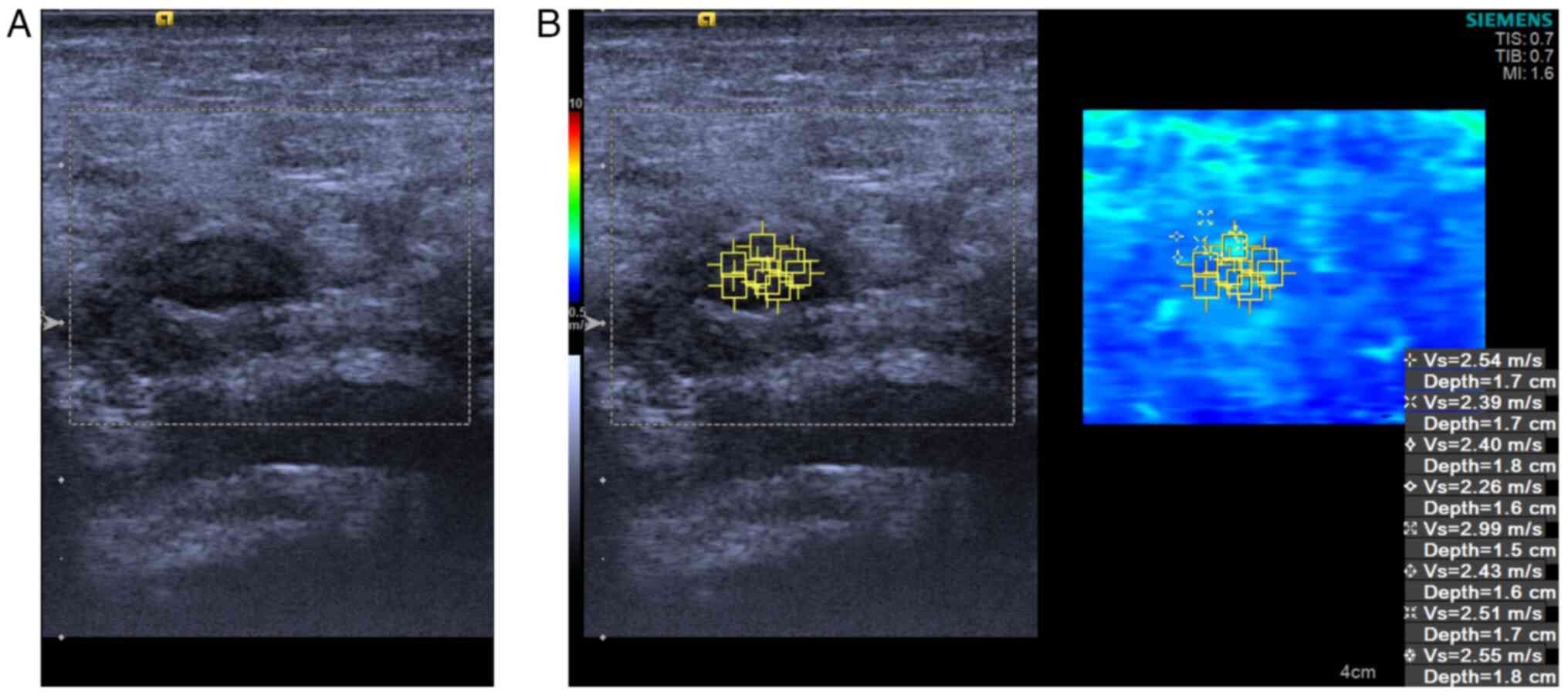
Stiffness observations
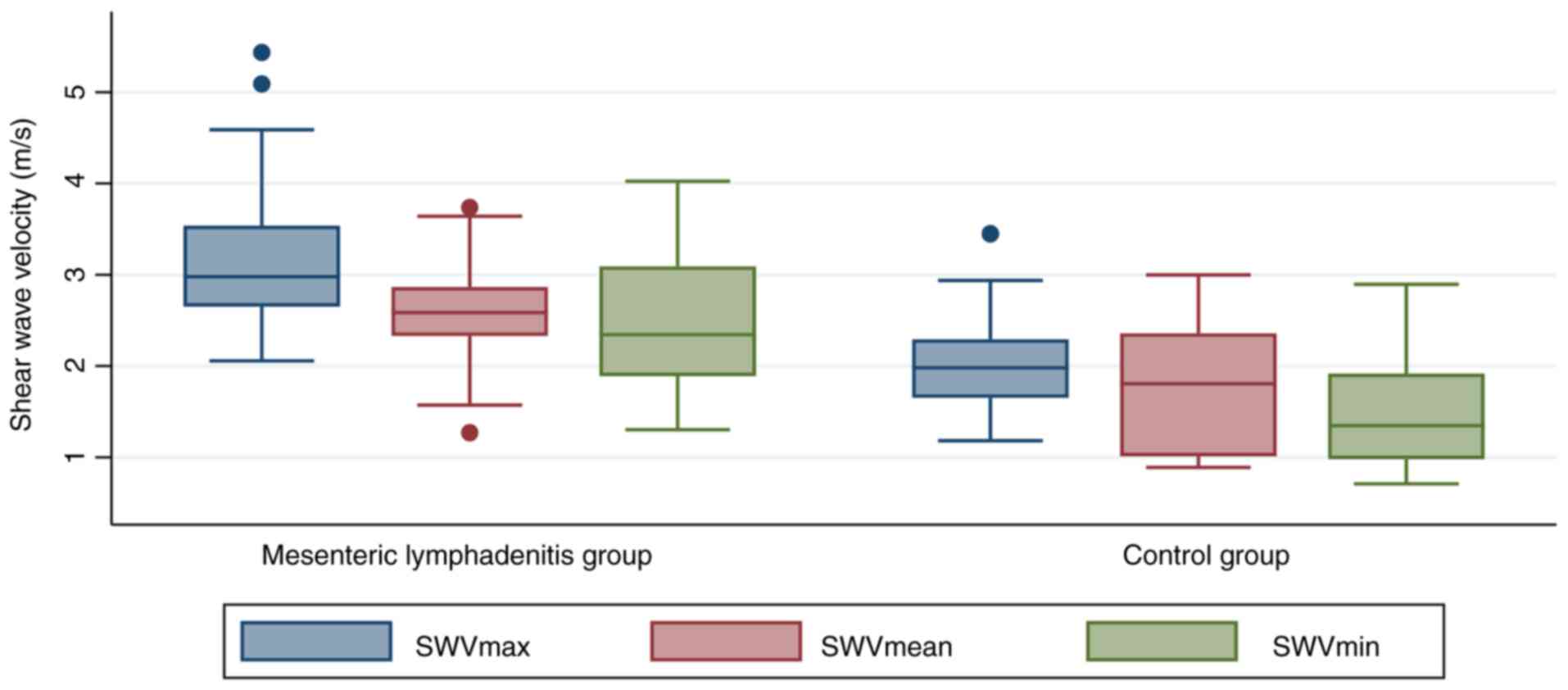
All the quantitative VTIQ parameters (including the
SWVMean, SWVMax and SWVMin) were
significantly greater for MLNs in the control group than for MLNs
in the ML group (Fig. 2) (all
P<0.001). The SWV in the control group was nearly 2-fold greater
than that in the ML group (Table
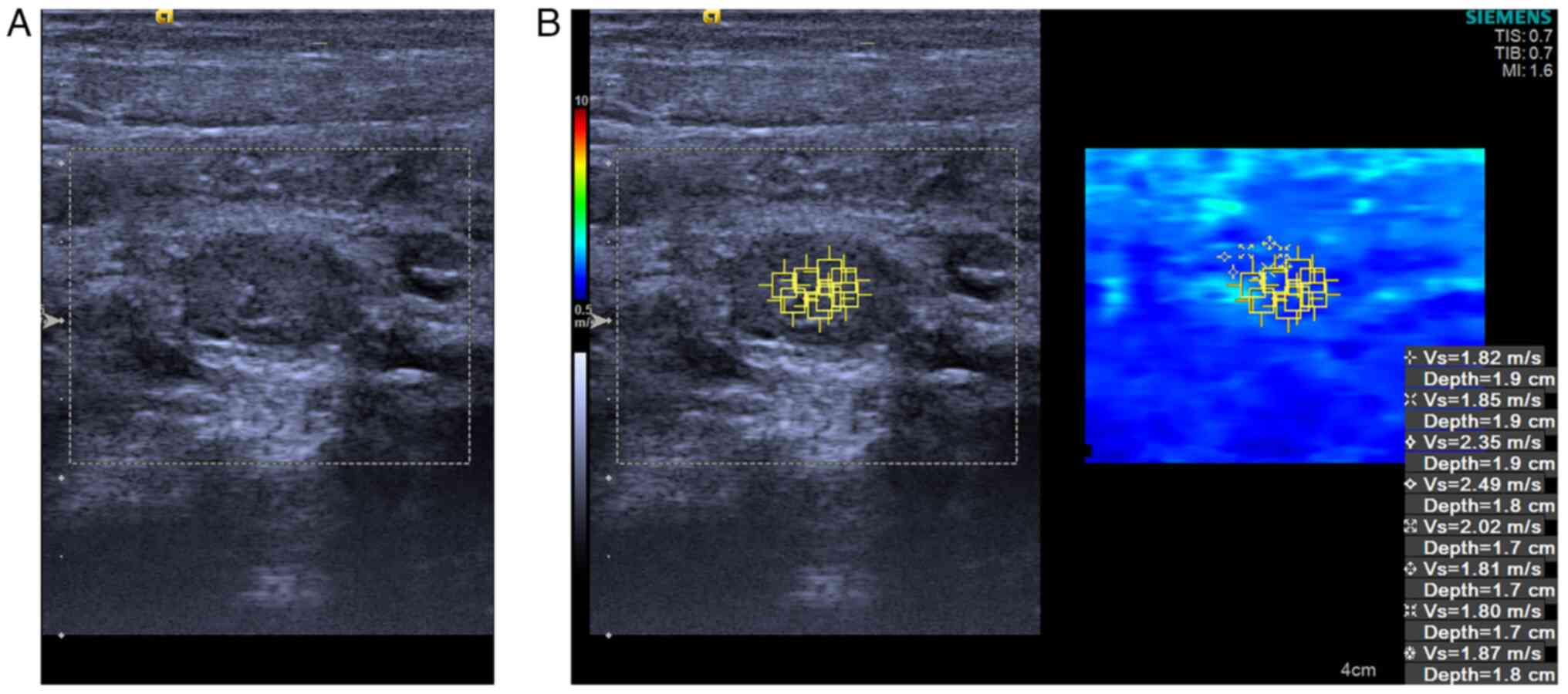
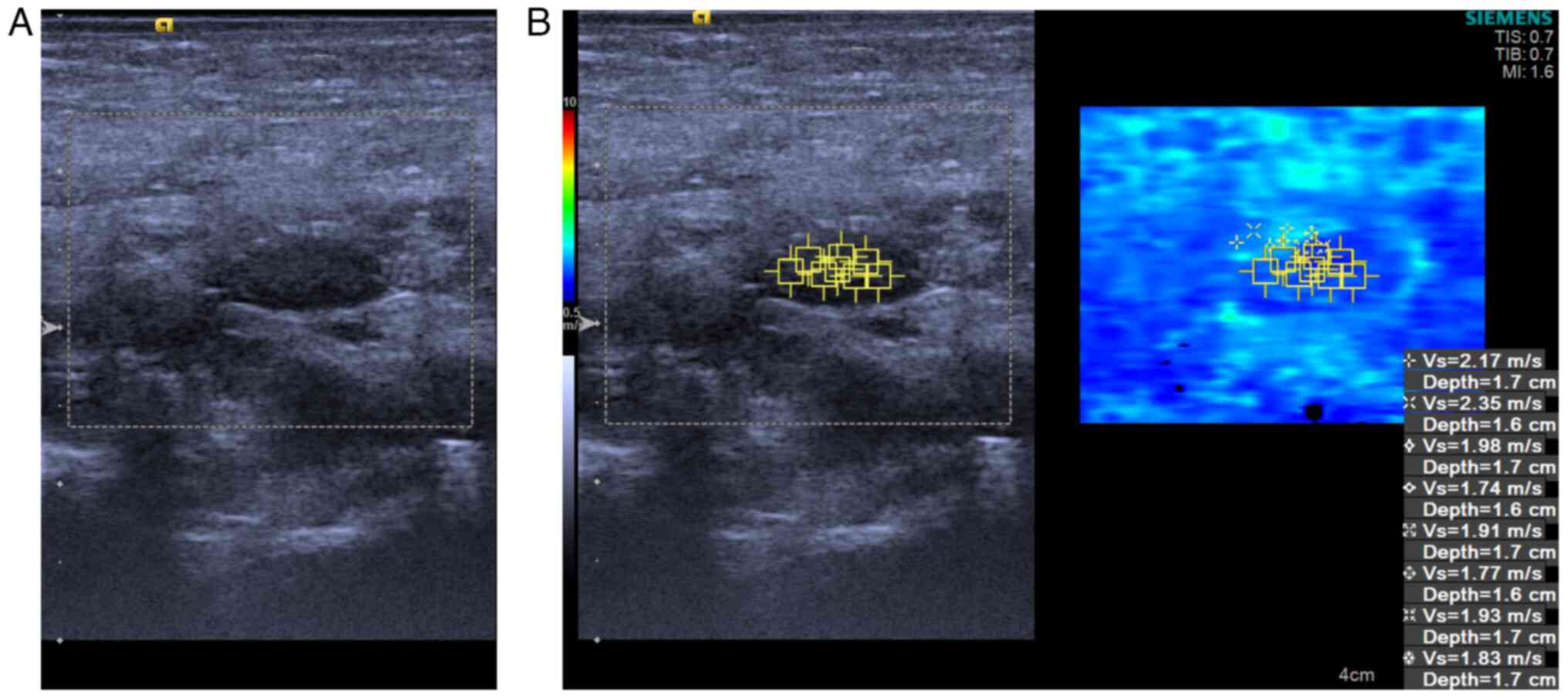
III). Consequently, patients afflicted in ML (Figs. 3 and 4) demonstrated stiffer MLNs in comparison
with those in the healthy group (Figs.
5 and 6).
 | Table IIIMesenteric lymph node stiffness of
the study cohorts. |
Table III
Mesenteric lymph node stiffness of
the study cohorts.
| | Q50 (Q25-Q75) |
|---|
| Group | SWVMin,
m/sec | SWVMean,
m/sec | SWVMax,
m/sec |
|---|
| ML group
(n=103) | 1.35
(0.98-1.92) | 1.81
(1.01-2.36) | 1.98
(1.65-2.29) |
| Control group
(n=60) | 2.34
(1.89-3.10) | 2.59
(2.33-2.88) | 2.98
(2.65-3.55) |
| z | -7.302 | -6.793 | -9.263 |
| P-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Univariate and multivariate logistic
analyses
The results of univariate logistic regression
analysis are summarized in Table
IV. Binary logistic regression analysis revealed that monocytes
≥7.90% [odds ratio (OR)=63.078; P=0.038], longest diameter ≥1.29 cm
(OR=18.123, P<0.001), and CRP≥8.22 mg/dl (OR=2.501; P<0.001)
were independent factors related to ML. In addition, the VTIQ
parameter (SWVMean ≥1.81 m/s; OR=0.106; P<0.001) was
also significantly correlated with ML. According to the
multivariate logistic regression analysis, the longest diameter
(OR=6.042; P=0.046) was revealed to be the strongest independent
predictor for ML, followed by the CRP level (OR=2.310; P<0.001)
and the SWVMean (OR=0.108; P<0.001) (Table IV).
 | Table IVUnivariate logistic regression and
multivariate logistic regression. |
Table IV
Univariate logistic regression and
multivariate logistic regression.
| Logistic Regression
Item | Odds ratio | P-value |
|---|
| Univariate
analysis | | |
|
CRP (mg/dl)
≥8.22 | 2.501 | <0.001 |
|
Longest
diameter (cm) ≥1.29 | 18.123 | <0.001 |
|
Monocytes
(%) ≥7.90 | 63.078 | 0.038 |
|
SWVMean
(m/sec) ≥1.81 | 0.106 | <0.001 |
| Multivariate
analysis | | |
|
Longest
diameter (cm) ≥1.29 | 6.042 | 0.046 |
|
CRP (mg/dl)
≥8.22 | 2.310 | <0.001 |
|
SWVMean
(m/sec) ≥1.81 | 0.108 | <0.001 |
Diagnostic performance of conventional
US and US elastography
According to the ROC analyses, the associated AUC
for US alone was 0.798 (95% CI: 0.724-0.872), with a sensitivity of
79.61% and a specificity of 80.00% (Table V). The AUC for US combined with
VTIQ was 0.890 (95% CI: 0.831-0.949), with a high sensitivity of
91.26% and a high specificity of 86.67%. Both methods were assessed
by taking laboratory findings into consideration.
 | Table VDiagnostic performance of two
modalities. |
Table V
Diagnostic performance of two
modalities.
| Modality | AUC | 95% CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy |
|---|
| US alone | 0.798 | 0.724-0.872 | 79.61%
(82/103) | 80.00% (48/60) | 79.75%
(130/163) |
| US + VTIQ | 0.890 | 0.831-0.949 | 91.26%
(94/103) | 86.67% (52/60) | 89.57%
(146/163) |
Discussion
VTIQ, a two-dimensional quantitative SWV imaging
technique based on ARFI technology, employs a pulse sequence
encompassing reference, excitation and tracking sonic pulses.
Compared with conventional point SWV measurements, the 2D SWV
imaging provided by VTIQ offers more precise information regarding
tissue stiffness (7). Quantitative
reflection of nodular hardness is achieved by VTIQ through multiple
measurements conducted in a clear quality mode with minimal
interference. Different color levels indicate quality, with a
transition to the speed mode indicating favorable quality. This
quantitative representation of tissue hardness enhances the
reliability of the measurements. In recent years, VTIQ has gained
traction in diverse clinical applications across organs, including
the thyroid (9), breast (10) and cervical lymph nodes (11). However, the assessment of MLN
stiffness, a potential indicator of ML, has scarcely been explored.
In a research study involving 263 paediatric MLNs, Bayramoglu et
al (12) reported that the
median elasticity and velocity values obtained through SWE were
markedly greater in patients with lymphoma than in those with
lymphadenitis and normal MLNs. However, the present study yielded
contrasting results; it represents a pioneering effort to
quantitatively and non-invasively evaluate MLN stiffness in
patients with ML compared with a healthy group. Remarkably,
compared with those in the reference group, the ML group exhibited
a significant increase in the mean, maximum and minimum SWV. ML is
a condition characterized by inflammation of the lymph nodes in the
mesentery. Cells involved in inflammation, and found in lymph
nodes, and the mediators and cytokines produced by these cells play
important roles in defense against infection (13,14).
Tissue stiffness is a characteristic that may reflect the nature of
lymph nodes (15). It is
conceivable that a majority of MLNs in the ML group may be in an
acute inflammatory edema phase, rendering them appear soft and
relatively less dense in structure, thereby resulting in lower SWV
values than those of normal MLN tissue. Similar findings were
observed in head and neck lymph nodes, with a greater emphasis on
distinguishing between benign and malignant lymph nodes (16-18).
VTIQ, when combined with conventional US, exhibited
enhanced sensitivity in the identification of ML, with a
sensitivity of 91.26% for the mean SWV and heightened specificity
of 86.67%, compared with the use of conventional US alone. The AUC
for US combined with VTIQ was greater (AUC: 0.890; 95% CI:
0.831-0.949) than that for the standalone US method (AUC: 0.798;
95% CI: 0.724-0.872), supporting the conclusion that combining US
with VTIQ enhances the diagnostic accuracy and effectiveness of
detecting ML. ML often mimics the clinical presentations of acute
appendicitis, intussusception, ovarian torsion and other acute
abdominal conditions (19,20). The accurate identification of ML is
of utmost importance. With the help of VTIQ, the false-negative
rate decreased from 20.39% (21/103) to 8.74% (9/103), while the
accuracy rate significantly improved from 79.75% (130/163) to
89.57% (146/163) when considering both US and VTIQ
characteristics.
Neither US nor VTIQ parameters in isolation could
substantially contribute to ML identification. Binary logistic
regression analysis revealed that a monocyte count ≥7.90%
(OR=63.078; P=0.038), longest diameter ≥1.29 cm (OR=18.123;
P<0.001), and CRP level ≥8.22 mg/dl (OR=2.501; P<0.001) were
independent factors associated with ML. Among the 103 ML patients,
47 exhibited an elevated monocyte percentage (≥7.90%), while
patients in the reference group maintained a normal monocyte
percentage. Furthermore, 58 out of 103 ML patients demonstrated
elevated CRP levels (≥8.22 mg/dl), whereas only 6 out of 60 healthy
patients had elevated CRP levels. These findings aligned with those
of Gross et al (21), where
ML patients exhibited a median CRP level of 0.475 (range, 0-19.3
mg%) and a monocyte percentage of 7.64±3.41.
Traditionally, the diagnosis of lymph node
abnormalities relies on size criteria (2). However, these size criteria vary
among different scholars, with some considering MLNs with the
longest diameters exceeding 10 mm to be pathologically enlarged
(22), while others defined
enlarged lymph nodes as those with the shortest diameter of 4 mm or
greater (23). In the present
study, the longest diameter of the enlarged MLNs in the ML group
was 1.29±0.31 cm, whereas in the reference group, it was 1.08±0.21
cm. However, in clinical practice, size measurements alone are not
sufficient for assessing whether an MLN is pathological. According
to the present multivariate analysis, the longest diameter of the
enlarged MLN significantly contributed to the identification of ML,
followed by the CRP and the VTIQ parameters (SWVMean
≥1.81 m/s, OR=0.106, P<0.001). In terms of diagnostic
performance, the integration of VTIQ with US substantially enhanced
the sensitivity (91.26% vs. 79.61%), specificity (86.67% vs.
80.00%), and accuracy (89.57% vs. 79.75%) in contrast to the use of
US in isolation. The false-negative rate decreased significantly
from 20.39% (21/103) to 8.74% (9/103).
Given the retrospective design and the relatively
modest sample size inherent to this single-centre investigation, it
is imperative to interpret the current findings as preliminary,
necessitating validation through expansive multicentre studies.
Furthermore, the VTIQ examinations in the present study were
conducted by only one operator. This implies that for future
research, it is essential to engage multiple operators to assess
inter- and intra-observer reliability.
In conclusion, the use of VTIQ to assess mesenteric
lymph node (MLN) stiffness offers a non-invasive, convenient,
reliable and reproducible approach for identifying mesenteric
lymphadenopathy. A significant positive correlation between
increased VTIQ parameters and ML was observed. Although this
approach shows promise for the evaluation of MLN stiffness in
patients with ML, its full potential and clinical utility
necessitate further comprehensive investigation.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the General Project
Grant from the Pudong Health Commission of Shanghai (grant no.
PW2022A-05) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China
(grant no. 82302231).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
YCZ designed the study. LZ and JS collected and
analysed the patients' data regarding tissue stiffness. DMZ
collected and analysed the patients' laboratory and clinical
diagnosis data. YZ, QJ, XRS and SHD interpreted the data. LZ and JS
were major contributors to the writing of the manuscript. YCZ and
QJ confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors have
read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved (approval no.
2022-K-42; 12 July 2022) by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Pudong
New Area People's Hospital (Shanghai, China). Informed consent was
waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Devine M and Coffey JC: Mesenteric
Adenopathy and Adenitis. Prog Inflammation Res. 90:127–148.
2023.
|
|
2
|
Simanovsky N and Hiller N: Importance of
sonographic detection of enlarged abdominal lymph nodes in
children. J Ultrasound Med. 26:581–584. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Toorenvliet B, Vellekoop A, Bakker R,
Wiersma F, Mertens B, Merkus J, Breslau P and Hamming J: Clinical
differentiation between acute appendicitis and acute mesenteric
lymphadenitis in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 21:120–123.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ozdamar MY and Karavas E: Acute mesenteric
lymphadenitis in children: Findings related to differential
diagnosis and hospitalization. Arch Med Sci. 16:313–320.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K, McLean D,
Brauer K, Purdie C, Baker L, Jordan L, Rauchhaus P and Thompson A:
Invasive breast cancer: Relationship between shear-wave
elastographic findings and histologic prognostic factors.
Radiology. 263:673–677. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wong VW, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Foucher J,
Chan HL, Le Bail B, Choi PC, Kowo M, Chan AW, Merrouche W, et al:
Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness
measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
51:454–462. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun CY, Lei KR, Liu BJ, Bo XW, Li XL, He
YP, Wang D, Ren WW, Zhao CK and Xu HX: Virtual touch tissue imaging
and quantification (VTIQ) in the evaluation of thyroid nodules: The
associated factors leading to misdiagnosis. Sci Rep.
7(41958)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Glišić TM, Perišić MD, Dimitrijevic S and
Jurišić V: Doppler assessment of splanchnic arterial flow in
patients with liver cirrhosis: Correlation with ammonia plasma
levels and MELD score. J Clin Ultrasound. 42:264–269.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhou H, Zhou XL, Xu HX, Li DD, Liu BJ,
Zhang YF, Xu JM, Bo XW, Li XL, Guo LH and Qu S: Virtual touch
tissue imaging and quantification in the evaluation of thyroid
nodules. J Ultrasound Med. 36:251–260. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kong WT, Zhou WJ, Wang Y, Zhuang XM and Wu
M: The value of virtual touch tissue imaging quantification in the
differential diagnosis between benign and malignant breast lesions.
J Med Ultrason (2001). 46:459–466. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ruger H, Psychogios G, Jering M and Zenk
J: Multimodal ultrasound including virtual touch imaging
quantification for differentiating cervical lymph nodes. Ultrasound
Med Biol. 46:2677–2682. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bayramoglu Z, Caliskan E, Karakas Z,
Karaman S, Tugcu D, Somer A, Acar M, Akıcı F and Adaletli I:
Diagnostic performances of superb microvascular imaging, shear wave
elastography and shape index in pediatric lymph nodes
categorization: A comparative study. Br J Radiol.
91(20180129)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jurisic V, Terzic T, Colic S and Jurisic
M: The concentration of TNF-alpha correlate with number of
inflammatory cells and degree of vascularization in radicular
cysts. Oral Dis. 14:600–605. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dzopalić T, Božić-Nedeljković B and
Jurišić V: Function of innate lymphoid cells in the immune-related
disorders. Hum Cell. 32:231–239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Handorf AM, Zhou Y, Halanski MA and Li WJ:
Tissue stiffness dictates development, homeostasis, and disease
progression. Organogenesis. 11:1–15. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Desmots F, Fakhry N, Mancini J, Reyre A,
Vidal V, Jacquier A, Santini L, Moulin G and Varoquaux A: Shear
wave elastography in head and neck lymph node assessment: Image
quality and diagnostic impact compared with B-Mode and doppler
ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med Biol. 42:387–398. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang JR, Song Y, Jia YL and Ruan LT:
Application of multimodal ultrasonography for differentiating
benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy. Jpn J Radiol.
39:938–945. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dudea SM, Botar-Jid C, Dumitriu D,
Vasilescu D, Manole S and Lenghel ML: Differentiating benign from
malignant superficial lymph nodes with sonoelastography. Med
Ultrason. 15:132–139. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grossman M and Shiramizu B: Evaluation of
lymphadenopathy in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 6:68–76.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lau WY, Fan ST, Yiu TF, Chu KW and Wong
SH: Negative findings at appendectomy. Am J Surg. 148:375–378.
1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gross I, Siedner-Weintraub Y, Stibbe S,
Rekhtman D, Weiss D, Simanovsky N, Arbell D and Hashavya S:
Characteristics of mesenteric lymphadenitis in comparison with
those of acute appendicitis in children. Eur J Pediatr.
176:199–205. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Schulte B, Beyer D, Kaiser C, Horsch S and
Wiater A: Ultrasonography in suspected acute appendicitis in
childhood-report of 1285 cases. Eur J Ultrasound. 8:177–182.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sivit CJ, Newman KD and Chandra RS:
Visualization of enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes at US examination.
Clinical significance. Pediatr Radiol. 23:471–475. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|