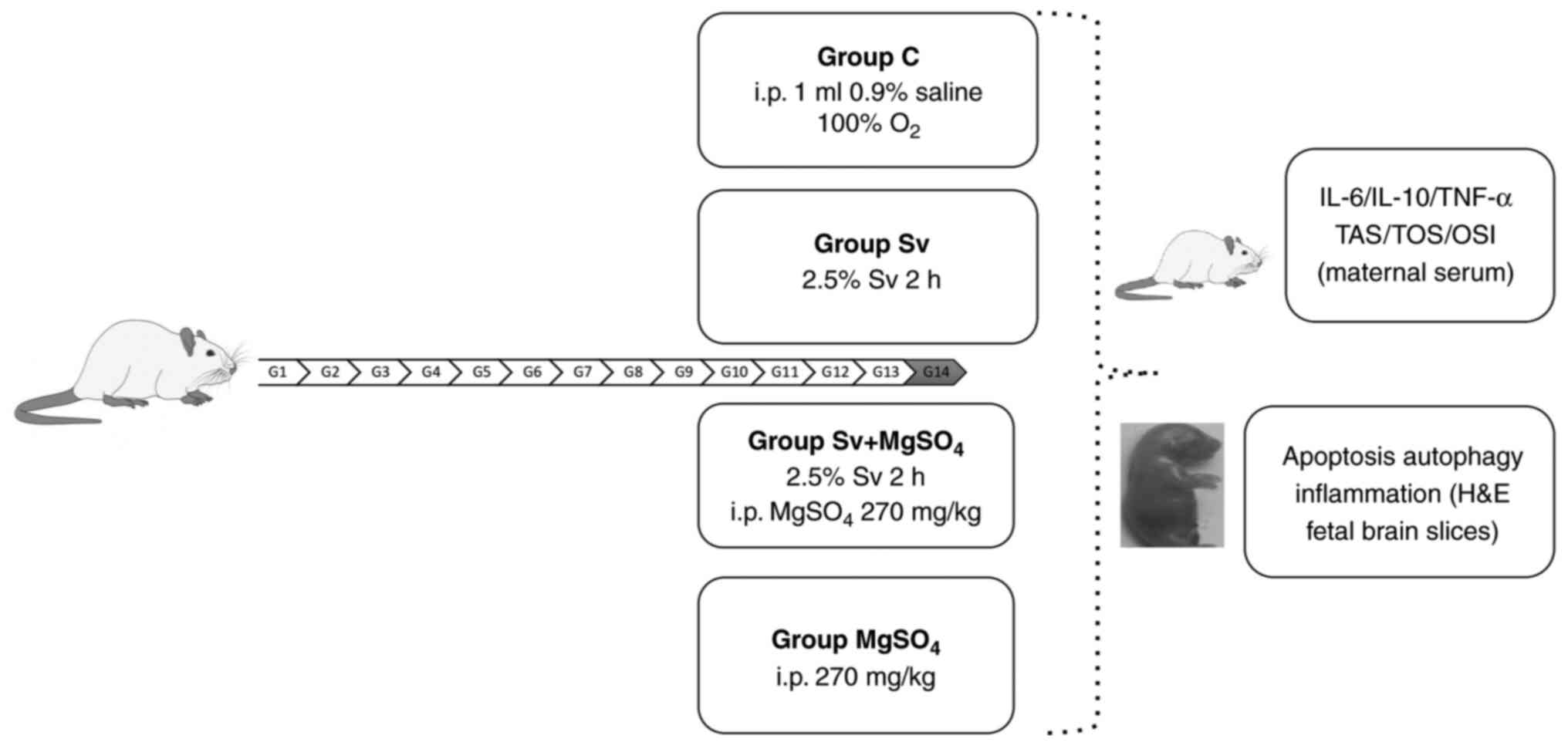
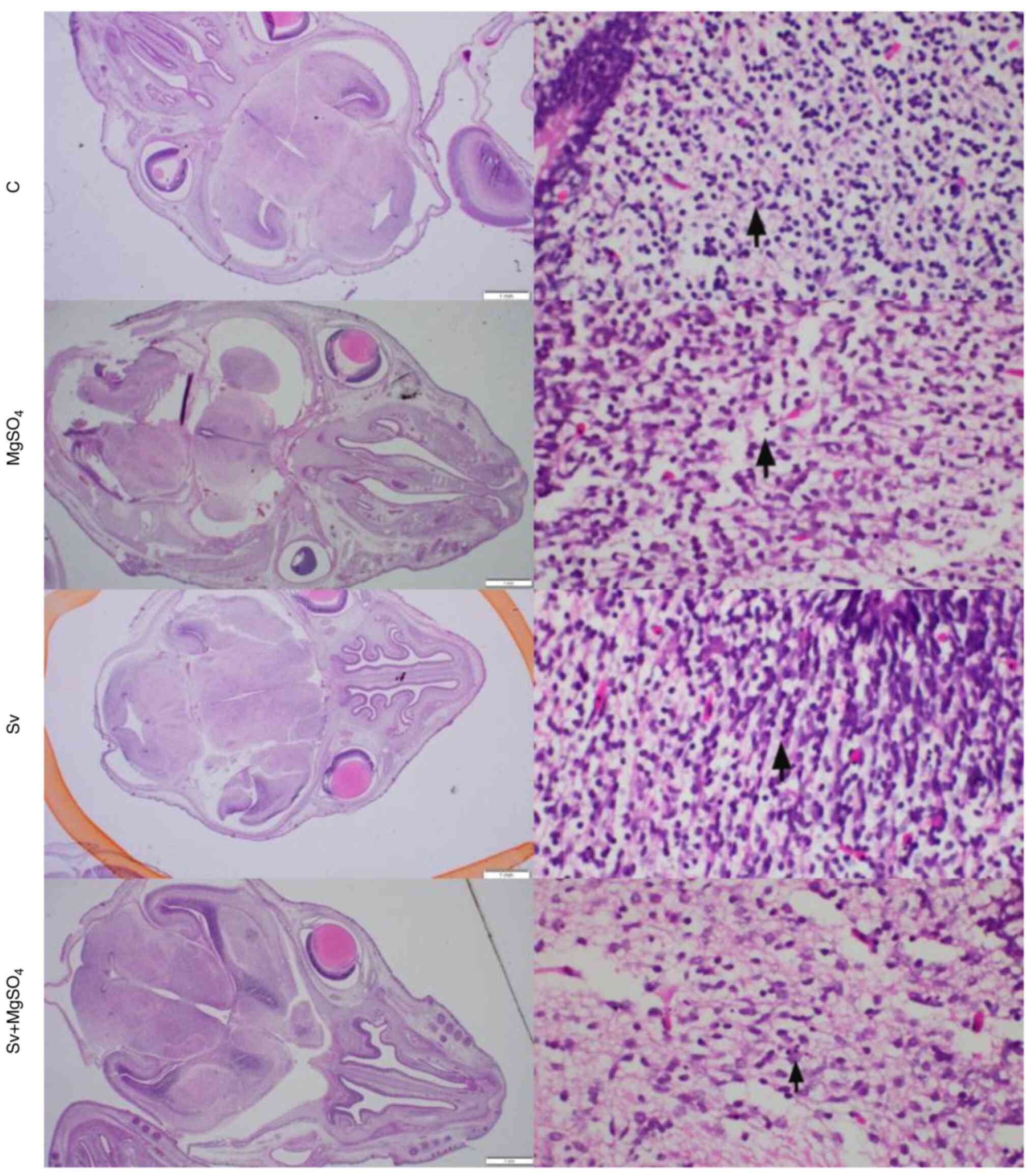
|
1
|
Ní Mhuireachtaigh R and O'Gorman DA:
Anesthesia in pregnant patients for nonobstetric surgery. J Clin
Anesth. 18:60–66. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Osterman MJ and Martin JA: Primary
cesarean delivery rates, by state: Results from the revised birth
certificate, 2006-2012. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 63:1–11.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
United States Food and Drug
Administration. FDA drug safety communication: FDA review results
in new warnings about using general anesthetics and sedation drugs
in young children and pregnant women. Updated 2016. Accessed
Februry 10, 2017.
|
|
4
|
Krasowski MD and Harrison NL: The actions
of ether, alcohol and alkane general anaesthetics on GABAA and
glycine receptors and the effects of TM2 and TM3 mutations. Br J
Pharmacol. 129:731–743. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Eger EI, Liao M, Laster MJ, Won A,
Popovich J, Raines DE, Solt K, Dutton RC, Cobos FV and Sonner JM:
Contrasting roles of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in the
production of immobilization by conventional and aromatic
anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 102:1397–1406. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lerner RA: A hypothesis about the
endogenous analogue of general anesthesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:13375–13377. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhou ZB, Yang XY, Tang Y, Zhou X, Zhou LH
and Feng X: Subclinical concentrations of sevoflurane reduce
oxidative stress but do not prevent hippocampal apoptosis. Mol Med
Rep. 14:721–727. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shen X, Dong Y, Xu Z, Wang H, Miao C and
Soriano SG: Selective anesthesia-induced neuroinflammation in
developing mouse brain and cognitive impairment. Anesthesiology.
118:502–515. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cui FH, Li J, Li KZ, Xie YG and Zhao XL:
Effects of sevoflurane exposure during different stages of
pregnancy on the brain development of rat offspring. J Anesth.
35:654–662. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zheng H, Dong Y, Xu Z, Crosby G, Culley
DJ, Zhang Y and Xie Z: Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant mice
induces neurotoxicity in fetal and offspring mice. Anesthesiology.
118:516–526. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bilotta F, Gelb AW, Stazi E, Titi L,
Paoloni FP and Rosa G: Pharmacological perioperative brain
neuroprotection: A qualitative review of randomized clinical
trials. Br J Anaesth. 110: (Suppl 1):S113–S120. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hudetz JA, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Patterson
KM, Byrne AJ, Hudetz AG, Pagel PS and Warltier DC: Ketamine
attenuates post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac
surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 53:864–872. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Roach GW, Newman MF, Murkin JM, Martzke J,
Ruskin A, Li J, Guo A, Wisniewski A and Mangano DT: Multicenter
Study of Perioperative Ischemia (MsSPI). Ineffectiveness of burst
suppression therapy in mitigating perioperative cerebrovascular
dysfunction. Anesthesiology. 99:1255–1264. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Han F, Xu L, Huang Y, Chen T, Zhou T and
Yang L: Magnesium sulphate can alleviate oxidative stress and
reduce inflammatory cytokines in rat placenta of intrahepatic
cholestasis of pregnancy model. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 298:631–638.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Khatib N, Ginsberg Y, Shalom-Paz E, Dabaja
H, Gutzeit O, Zmora O, Millo Z, Ross MG and Beloosesky R: Fetal
neuroprotective mechanism of maternal magnesium sulfate for late
gestation inflammation: In a rodent model. J Matern Fetal Neonatal
Med. 33:3732–3739. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Temkin NR, Anderson GD, Winn HR,
Ellenbogen RG, Britz GW, Schuster J, Lucas T, Newell D, Nelson
Mansfield P, Machamer JE, et al: Magnesium sulfate for
neuroprotection after traumatic brain injury: A randomised
controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 6:29–38. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hallak M, Hotra JW and Kupsky WJ:
Magnesium sulfate protection of fetal rat brain from severe
maternal hypoxia. Obstet Gynecol. 96:124–128. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Dong Y, Xu Z and Xie Z: Propofol
and magnesium attenuate isoflurane-induced caspase-3 activation via
inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Med Gas Res.
2(20)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Beloosesky R, Khatib N, Ginsberg Y,
Anabosy S, Shalom-Paz E, Dahis M, Ross MG and Weiner Z: Maternal
magnesium sulfate fetal neuroprotective effects to the fetus:
inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and nuclear factor
kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells activation in a
rodent model. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 215:382.e1–e6. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Animal Experiments Center Ethics
Committee. Legislation. Available from: https://hadmek.tarimorman.gov.tr/Sayfa/Detay/644.
Accessed November 22, 2022.
|
|
21
|
Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S,
Avey MT, Baker M and Browne WJ: Reporting animal research:
Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS
Biol. 18(e3000410)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Song R, Ling X, Peng M, Xue Z, Cang J and
Fang F: Maternal Sevoflurane exposure causes abnormal development
of fetal prefrontal cortex and induces cognitive dysfunction in
offspring. Stem Cells Int. 2027(6158468)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sameshima H, Ota A and Ikenoue T:
Pretreatment with magnesium sulfate protects against
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury but postasphyxial treatment worsens
brain damage in seven-day-old rats. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
180:725–730. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cho GJ, Hong HR, Hong SC, Oh MJ and Kim
HJ: The neuroprotective effect of magnesium sulfate in preterm
fetal mice. J Perinatal Med. 45:537–543. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dong Y, Zhang G, Zhang B, Moir RD, Xia W,
Marcantonio ER, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Tanzi RE and Xie Z: The common
inhalational anesthetic sevoflurane induces apoptosis and increases
beta-amyloid protein levels. Arch Neurol. 66:620–631.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Erel O: A new automated colorimetric
method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem.
12:1103–1111. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Rubio CP and Cerón JJ: Spectrophotometric
assays for evaluation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in serum:
General concepts and applications in dogs and humans. BMC Vet Res.
17(226)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Blaylock M, Engelhardt T and Bissonnette
B: Fundamentals of neuronal apoptosis relevant to pediatric
anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 20:383–395. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ikonomidou C: Triggers of apoptosis in the
immature brain. Brain Dev. 31:488–492. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li X, Jiang X and Zhao P: Effects of
pregnancy anesthesia on fetal nervous system. Front Pharmacol.
11(523514)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee S, Chung W, Park H, Park H, Yoon S,
Park S, Park J, Heo JY, Ju X, Yoon SH, et al: Single and multiple
sevoflurane exposures during pregnancy and offspring behavior in
mice. Paediatr Anaesth. 27:742–751. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wu Z, Li X, Zhang Y, Tong D, Wang L and
Zhao P: Effects of Sevoflurane exposure during mid-pregnancy on
learning and memory in offspring rats: Beneficial effects of
maternal exercise. Front Cell Neurosci. 12(122)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Andropoulos DB and Greene MF: Anesthesia
and developing brains-implications of the FDA warning. N Engl J
Med. 376:905–907. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Palanisamy A: Maternal anesthesia and
fetal neurodevelopment. Int J Obstet Anesth. 21:152–162.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Workman AD, Charvet CJ, Clancy B,
Darlington RB and Finlay BL: Modeling transformations of
neurodevelopmental sequences across mammalian species. J Neurosci.
33:7368–7383. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Brioni JD, Varughese S, Ahmed R and Bein
B: A clinical review of inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane:
From early research to emerging topics. J Anesth. 5:764–778.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhou X, Li W, Chen X, Yang X, Zhou Z, Lu D
and Feng X: Dose-dependent effects of sevoflurane exposure during
early lifetime on apoptosis in hippocampus and neurocognitive
outcomes in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol
Pharmacol. 8:111–119. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang S, Peretich K, Zhao Y, Liang G, Meng
Q and Wei H: Anesthesia-induced neurodegeneration in fetal rat
brains. Pediatr Res. 66:435–440. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hirotsu A, Iwata Y, Tatsumi K, Miyai Y,
Matsuyama T and Tanaka T: Maternal exposure to volatile anesthetics
induces IL-6 in fetal brains and affects neuronal development. Eur
J Pharmacol. 863(172682)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Li M, Cui E, Zhang H, Zhu X, Zhou
J, Yan M and Sun J: Dexmedetomidine attenuates sevoflurane-induced
neurocognitive impairment through α2-adrenoceptors. Mol Med Rep.
23(38)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bergdolt L and Dunaevsky A: Brain changes
in a maternal immune activation model of neurodevelopmental brain
disorders. Prog Neurobiol. 175:1–19. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wan Y, Xu J, Ma D, Zeng Y, Cibelli M and
Maze M: Postoperative impairment of cognitive function in rats: A
possible role for cytokine-mediated inflammation in the
hippocampus. Anesthesiology. 106:436–443. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Fan CH, Peng B and Zhang FC: The
postoperative effect of sevoflurane inhalational anesthesia on
cognitive function and inflammatory response of pediatric patients.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:3971–3975. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ginsberg Y, Khatib N, Weiner Z and
Beloosesky R: Maternal inflammation, fetal brain implications and
suggested neuroprotection: A summary of 10 years of research in
animal models. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 8(e0028)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hennessy E, Gormley S, Lopez-Rodriguez AB,
Murray C, Murray C and Cunningham C: Systemic TNF-α produces acute
cognitive dysfunction and exaggerated sickness behavior when
superimposed upon progressive neurodegeneration. Brain Behav Immun.
59:233–244. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pickering M, Cumiskey D and O'Connor JJ:
Actions of TNF-alpha on glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the
central nervous system. Exp Physiol. 90:663–670. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A,
Webb CL, Willette RN, Lysko PG and Feuerstein GZ: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke.
28:1233–1244. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Mayne M, Ni W, Yan HJ, Xue M, Johnston JB,
Del Bigio MR, Peeling J and Power C: Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide
inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression is
neuroprotective after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 32:240–248.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nawashiro H, Martin D and Hallenbeck JM:
Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor and amelioration of brain
infarction in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 17:229–232.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Carpentier PA, Dingman AL and Palmer TD:
Placental TNF-α signaling in illness-induced complications of
pregnancy. Am J Pathol. 6:2802–2810. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhao X, Bausano B, Pike BR,
Newcomb-Fernandez JK, Wang KK, Shohami E, Ringger NC, DeFord SM,
Anderson DK and Hayes RL: TNF-alpha stimulates caspase-3 activation
and apoptotic cell death in primary septo-hippocampal cultures. J
Neurosci Res. 64:121–131. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hemmer K, Fransen L, Vanderstichele H,
Vanmechelen E and Heuschling P: An in vitro model for the study of
microglia-induced neurodegeneration: Involvement of nitric oxide
and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Neurochem Int. 38:557–565.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Robertson J, Beaulieu JM, Doroudchi MM,
Durham HD, Julien JP and Mushynski WE: Apoptotic death of neurons
exhibiting peripherin aggregates is mediated by the proinflammatory
cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Cell Biol. 155:217–226.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Haddad JJ: Redox regulation of
pro-inflammatory cytokines and IkappaB-alpha/NF-kappaB nuclear
translocation and activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
296:847–856. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hoek JB and Pastorino JG: Ethanol,
oxidative stress, and cytokineinduced liver cell injury. Alcohol.
27:63–68. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wu Y, Song J, Wang Y, Wang X, Culmsee C
and Zhu C: The potential role of ferroptosis in neonatal brain
injury. Front Neurosci. 13(115)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA,
Masood A, Sofi MA and Ganie SA: Oxidative stress, mitochondrial
dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; a mechanistic insight.
Biomed Pharmacother. 74:101–110. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Xu Z and Qian B: Sevoflurane
anesthesia-mediated oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in
hippocampal neurons of old rats can be ameliorated by expression of
brain derived neurotrophic factor. Neurosci Lett.
721(134785)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Allaouchiche B, Debon R, Goudable J,
Chassard D and Duflo F: Oxidative stress status during exposure to
propofol, sevoflurane and desflurane. Anesth Analg. 93:981–985.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Tsuchiya M, Asada A, Kasahara E, Sato EF,
Shindo M and Inoue M: Antioxidant protection of propofol and its
recycling in erythrocyte membranes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
165:54–60. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Sun Z, Satomoto M, Adachi YU, Kinoshita H
and Makita K: Inhibiting NADPH oxidase protects against long-term
memory impairment induced by neonatal sevoflurane exposure in mice.
Br J Anaesth. 117:80–86. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Liu B, Gu Y, Xiao H, Lei X, Liang W and
Zhang J: Altered metabolomic profiles may be associated with
sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in neonatal rats. Neurochem Res.
40:788–799. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Xu G, Lu H, Dong Y, Shapoval D, Soriano
SG, Liu X, Zhang Y and Xie Z: Coenzyme Q10 reduces
sevoflurane-induced cognitive deficiency in young mice. Br J
Anaesth. 119:481–449. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Oppenheim RW: Cell death during
development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 14:453–501.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wang Y, Li Y, Xing Q, Han XG, Dong X, Lu Y
and Zhou M: Sevoflurane anesthesia in pregnant rats negatively
affects nerve function in offspring potentially via inhibition of
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol Med Rep. 15:2753–2759.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Yu Z, Wang J, Wang H, Wang J, Cui J and
Junzhang P: Effects of sevoflurane exposure during late pregnancy
on brain development and beneficial effects of enriched environment
on offspring cognition. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 40:1339–1352.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Areias J, Sola C, Chastagnier Y, Pico J,
Bouquier N, Dadure C, Perroy J and Szabo V: Whole-brain
characterization of apoptosis after sevoflurane anesthesia reveals
neuronal cell death patterns in the mouse neonatal neocortex. Sci
Rep. 13(14763)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Satomoto M, Itoh H, Uchida A and Makita K:
Resveratrol did not prevent sevoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in
the neonatal mice brain. Masui. 62:1184–1187. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang Y, Yin S, Xue H, Yang Y, Zhang N and
Zhao P: Mid-gestational sevoflurane exposure inhibits fetal neural
stem cell proliferation and impairs postnatal learning and memory
function in a dose-dependent manner. Dev Biol. 435:185–197.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Bercker S, Bert B, Bittigau P,
Felderhoff-Müser U, Bührer C, Ikonomidou C, Weise M, Kaisers UX and
Kerner T: Neurodegeneration in newborn rats following propofol and
sevoflurane anesthesia. Neurotox Res. 16:140–147. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Jia M, Liu WX and Yang JJ, Xu N, Xie ZM,
Ju LS, Ji MH, Martynyuk AE and Yang JJ: Role of histone acetylation
in long-term neurobehavioral effects of neonatal Exposure to
sevoflurane in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 91:209–220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang SQ, Fang F, Xue ZG, Cang J and Zhang
XG: Neonatal sevoflurane anesthesia induces long-term memory
impairment and decreases hippocampal PSD-95 expression without
neuronal loss. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:941–950.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Costantine MM and Drever N: Antenatal
exposure to magnesium sulfate and neuroprotection in preterm
infants. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 38:351–366. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Lamhot VB, Khatib N, Ginsberg Y, Anunu R,
Richter-Levin G, Weiner Z, Ross MG, Divon MY, Hallak M and
Beloosesky R: Magnesium sulfate prevents maternal
inflammation-induced impairment of learning ability and memory in
rat offspring. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213:851.e1–e8. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zhu X, Yao Y, Guo M, Li J, Yang P, Xu H
and Lin D: Sevoflurane increases intracellular calcium to induce
mitochondrial injury and neuroapoptosis. Toxicol Lett. 336:11–20.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Gao F, Ding B, Zhou L, Gao X, Guo H and Xu
H: Magnesium sulfate provides neuroprotection in
lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia by inhibiting NF-κB
pathway. J Surg Res. 184:944–950. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Andretta A, Schieferdecker MEM, Petterle
RR, Dos Santos Paiva E and Boguszewski CL: Relations between serum
magnesium and calcium levels and body composition and metabolic
parameters in women with fibromyalgia. Adv Rheumatol Lond Engl.
60(18)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Pan K and Garaschuk O: The role of
intracellular calcium-store-mediated calcium signals in in vivo
sensor and effector functions of microglia. J Physiol.
601:4203–4215. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Woodburn SC, Bollinger JL and Wohleb ES:
The semantics of microglia activation: Neuroinflammation,
homeostasis, and stress. J Neuroinflamm. 18(258)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Khatib N, Ginsberg Y, Ben David C, Ross
MG, Vitner D, Zipori Y, Zamora O, Weiner Z and Beloosesky R:
Magnesium sulphate neuroprotection mechanism is placental mediated
by inhibition of inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative stress.
Placenta. 127:29–36. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Mohammadi H, Shamshirian A, Eslami S,
Shamshirian D and Ebrahimzadeh MA: Magnesium sulfate attenuates
lethality and oxidative damage induced by different models of
hypoxia in mice. Biomed Res Int. 2020(2624734)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Yang H, Liang G, Hawkins BJ, Madesh M,
Pierwola A and Wei H: Inhalational anesthetics induce cell damage
by disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis with different
potencies. Anesthesiology. 109:243–250. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Dribben WH, Creeley CE, Wang HH, Smith DJ,
Farber NB and Olney JW: High dose magnesium sulfate exposure
induces apoptotic cell death in the developing neonatal mouse
brain. Neonatology. 96:23–32. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Wang Y, Yin SW, Zhang N and Zhao P:
High-concentration sevoflurane exposure in mid-gestation induces
apoptosis of neural stem cells in rat offspring. Neural Regen Res.
9:1575–1584. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Li D, Liu L, Li L, Li X, Huang B, Zhou C,
Zhang Z, Wang C, Dong P, Zhang X, et al: Sevoflurane induces
exaggerated and persistent cognitive decline in a type II diabetic
rat model by aggregating hippocampal inflammation. Front Pharmacol.
8(886)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|