|
1
|
Zaoral M, Kolc J and Šorm F: Amino acids
and peptides. LXXI. Synthesis of
1-deamino-8-D-γ-aminobutyrine-vasopressin,
1-deamino-8-D-lysine-vasopressin, and
1-deamino-8-D-arginine-vasopressin. Collect Czech Chem Commun.
32:1250–1257. 1967.
|
|
2
|
Robinson AG: DDAVP in the treatment of
central diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 294:507–511.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Desmopressin | Drugs | BNF content
published by NICE. https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drugs/desmopressin/. Accessed
March 22, 2023.
|
|
4
|
Cash JD: DDAVP and factor VIII: A tale
from Edinburgh. J Thromb Haemost. 1:619–621. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mannucci PM, Ruggeri ZM, Pareti FI and
Capitanio A: 1-Deamino-8-d-arginine vasopressin: A new
pharmacological approach to the management of haemophilia and von
Willebrands' diseases. Lancet. 1:869–872. 1977.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mannucci PM: Use of desmopressin in the
treatment of hemophilia A: Towards a golden jubilee. Haematologica.
103:379–381. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Robson WLM, Leung AKC and Norgaard JP: The
comparative safety of oral versus intranasal desmopressin for the
treatment of children with nocturnal enuresis. J Urol. 178:24–30.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Juul KV, Malmberg A, van der Meulen E,
Walle JV and Nørgaard JP: Low-dose desmopressin combined with serum
sodium monitoring can prevent clinically significant hyponatraemia
in patients treated for Nocturia. BJU Int. 119:776–784.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
De Bruyne P, De Guchtenaere A, Van
Herzeele C, Raes A, Dehoorne J, Hoebeke P, Van Laecke E and Walle
JV: Pharmacokinetics of desmopressin administered as tablet and
oral lyophilisate formulation in children with monosymptomatic
nocturnal enuresis. Eur J Pediatr. 173:223–228. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dossche L, Michelet R, De Bruyne P, Van
Herzeele C, Gasthuys E, Rittig S, Vermeulen A and Walle JV:
Desmopressin oral lyophilisate in young children: New insights in
pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Arch Dis Child. 106:597–602.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
De Guchtenaere A, Van Herzeele C, Raes A,
Dehoorne J, Hoebeke P, Van Laecke E and Walle JV: Oral lyophylizate
formulation of desmopressin: Superior pharmacodynamics compared to
tablet due to low food interaction. J Urol. 185:2308–2313.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fjellestad-Paulsen A, Höglund P, Lundin S
and Paulsen O: Pharmacokinetics of 1-deamino-8-D-arginine
vasopressin after various routes of administration in healthy
volunteers. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 38:177–182. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rembratt A, Graugaard-Jensen C,
Senderovitz T, Norgaard JP and Djurhuus JC: Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of desmopressin administered orally versus
intravenously at daytime versus night-time in healthy men aged
55-70 years. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 60:397–402. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mohinani A, Patel S, Tan V, Kartika T,
Olson S, DeLoughery TG and Shatzel J: Desmopressin as a hemostatic
and blood sparing agent in bleeding disorders. Eur J Haematol.
110:470–479. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
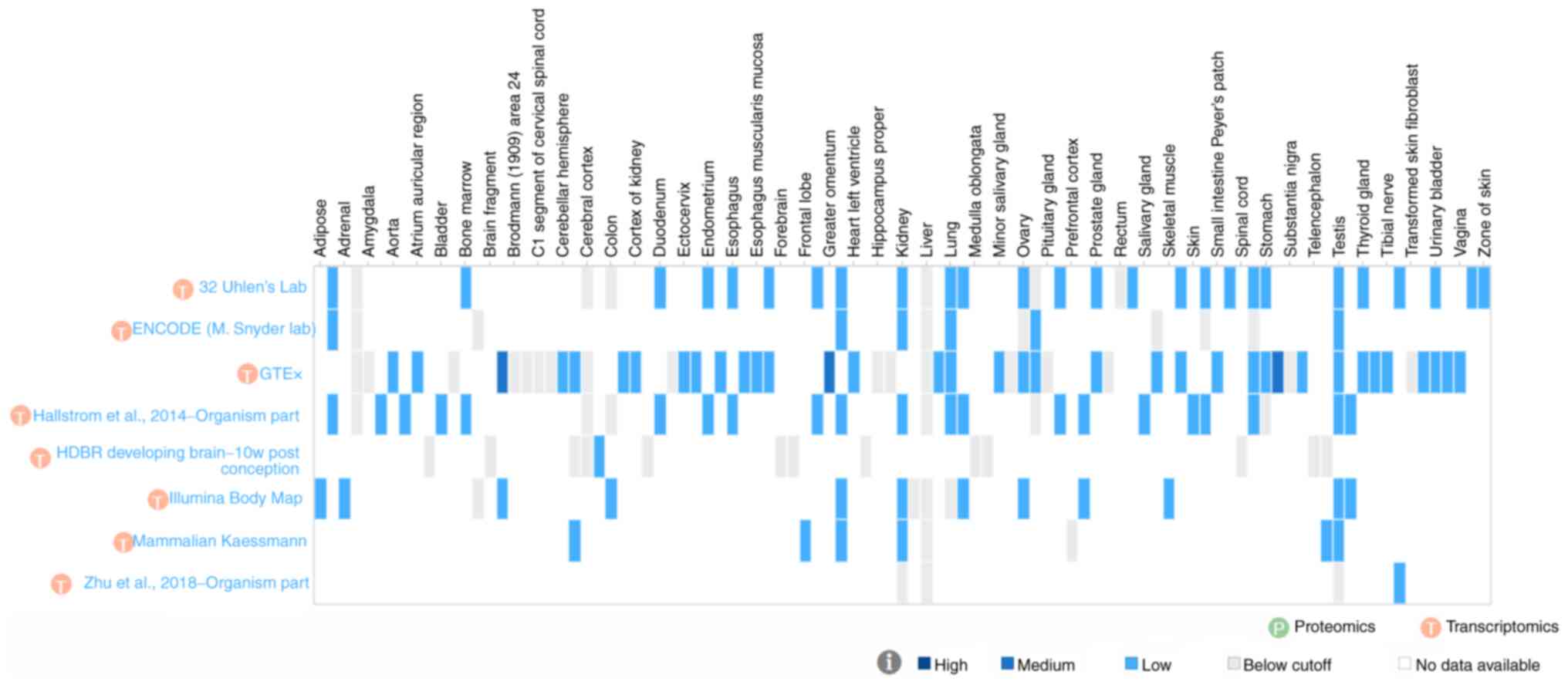
|
|
15
|
Mannucci PM: Desmopressin (DDAVP) in the
treatment of bleeding disorders, Revised edition, 2012.
|
|
16
|
Electronic Medicines Compendium:
DDAVP/Desmopressin Injection-Summary of Product Characteristics
(SmPC)-(emc). https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5447/smpc#gref.
Last accessed July 12, 2023.
|
|
17
|
Electronic medicines compendium: Octim
Nasal Spray-Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) - (emc).
https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/89/smpc#gref.
Last accessed 12 July, 2023.
|
|
18
|
Akin M: Response to low-dose desmopressin
by a subcutaneous route in children with type 1 von Willebrand
disease. Hematology. 18:115–118. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Furqan F, Sham R and Kouides P: Efficacy
and safety of half-dose desmopressin for bleeding prophylaxis in
bleeding disorder patients undergoing predominantly low to moderate
risk invasive procedures. Am J Hematol. 95:E285–E287.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Preijers T, Schütte LM, Kruip MJHA,
Cnossen MH, Leebeek FWG, van Hest RM and Mathôt RAA: Strategies for
individualized dosing of clotting factor concentrates and
desmopressin in hemophilia A and B. Ther Drug Monit. 41:192–212.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Preijers T, Schütte LM, Kruip MJHA,
Cnossen MH, Leebeek FWG, van Hest RM and Mathôt RAA: Population
pharmacokinetics of clotting factor concentrates and desmopressin
in hemophilia. Clin Pharmacokinet. 60:1–16. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Atiq F, Heijdra J, Snijders F, Boender J,
Kempers E, van Heerde WL, Maas DPMSM, Krouwel S, Schoormans SC, de
Meris J, et al: Desmopressin response depends on the presence and
type of genetic variants in patients with type 1 and type 2 von
Willebrand disease. Blood Adv. 6:5317–5326. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Trigg DE, Stergiotou I, Peitsidis P and
Kadir RA: A systematic review: The use of desmopressin for
treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding disorders in pregnancy.
Haemophilia. 18:25–33. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kouides PA, Byams VR, Philipp CS, Stein
SF, Heit JA, Lukes AS, Skerrette NI, Dowling NF, Evatt BL, Miller
CH, et al: Multisite management study of menorrhagia with abnormal
laboratory haemostasis: A prospective crossover study of intranasal
desmopressin and oral tranexamic acid. Br J Haematol. 145:212–220.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saccullo G and Makris M: Prophylaxis in
von Willebrand disease: Coming of age? Semin Thromb Hemost.
42:498–506. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Andersen LK, Hvas AM and Hvas CL: Effect
of desmopressin on platelet dysfunction during antiplatelet
therapy: A systematic review. Neurocrit Care. 34:1026–1046.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Benvenuto L, Qayum S, Kim H, Robbins H,
Shah L, Dimango A, Magda G, Grewal H, Lemaitre P, Stanifer BP, et
al: Lung transplantation for pulmonary fibrosis associated with
hermansky-pudlak syndrome. A single-center experience. Transplant
Direct. 8(e1303)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Merideth MA, Introne WJ, Wang JA, O'Brien
KJ, Huizing M and Gochuico BR: Genetic variants associated with
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Platelets. 31:544–547. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
MacDonald S, Wright A, Beuche F, Downes K,
Besser M, Symington E, Kelly A and Thomas W: Characterization of a
large cohort of patients with unclassified bleeding disorder
clinical features, management of haemostatic challenges and use of
global haemostatic assessment with proposed recommendations for
diagnosis and treatment. Int J Lab Hematol. 42:116–125.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Obaji S, Alikhan R, Rayment R, Carter P,
Macartney N and Collins P: Unclassified bleeding disorders: Outcome
of haemostatic challenges following tranexamic acid and/or
desmopressin. Haemophilia. 22:285–291. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Czer LS, Bateman TM, Gray RJ, Raymond M,
Stewart ME, Lee S, Goldfinger D, Chaux A and Matloff JM: Treatment
of severe platelet dysfunction and hemorrhage after cardiopulmonary
bypass: Reduction in blood product usage with desmopressin. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 9:1139–1147. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wademan BH and Galvin SD: Desmopressin for
reducing postoperative blood loss and transfusion requirements
following cardiac surgery in adults. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac
Surg. 18:360–370. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Radhakrishnan S, Chanchlani R, Connolly B
and Langlois V: Pre-procedure desmopressin acetate to reduce
bleeding in renal failure: Does it really work? Nephron Clin Pract.
128:45–48. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Athavale A, Kulkarni H, Arslan CD and Hart
P: Desmopressin and bleeding risk after percutaneous kidney biopsy.
BMC Nephrol. 20(413)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Akbarpour M, Jalali MM, Akbari M, Haddadi
S and Fani G: Effect of desmopressin on bleeding during endoscopic
sinus surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Laryngoscope Investig
Otolaryngol. 7:920–927. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Haddady-Abianeh S, Rajabpour AA,
Sanatkarfar M, Farahvash MR, Khorasani G and Molaei H: The
hemostatic effect of desmopressin on bleeding as a nasal spray in
open septorhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 43:1603–1606.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jahanshahi J, Tayebi E, Hashemian F,
Bakhshaei MH, Ahmadi MS and Rabiei MA: Effect of local desmopressin
administration on intraoperative blood loss and quality of the
surgical field during functional endoscopic sinus surgery in
patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A triple-blinded clinical
trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 276:1995–1999. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Safaeian R, Hassani V, Ghandi A and
Mohseni M: Desmopressin nasal spray reduces blood loss and improves
the quality of the surgical field during functional endoscopic
sinus surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 37:261–265.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shao H, Kuang LT, Hou WJ and Zhang T:
Effect of desmopressin administration on intraoperative blood loss
and quality of the surgical field during functional endoscopic
sinus surgery: A randomized, clinical trial. BMC Anesthesiol.
15(53)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Frontera JA, Lewin JJ III, Rabinstein AA,
Aisiku IP, Alexandrov AW, Cook AM, Del Zoppo GJ, Kumar M, Peerschke
EI, Stiefel MF, et al: Guideline for reversal of antithrombotics in
intracranial hemorrhage: Executive summary. A statement for
healthcare professionals from the neurocritical care society and
the society of critical care medicine. Crit Care Med. 44:2251–2257.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mengel A, Stefanou MI, Hadaschik KA, Wolf
M, Stadler V, Poli K, Lindig T, Ernemann U, Grimm F, Tatagiba M, et
al: Early administration of Desmopressin and platelet transfusion
for reducing hematoma expansion in patients with acute antiplatelet
therapy associated Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Crit Care Med.
48:1009–1017. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Loggini A, El Ammar F, Darzi AJ, Mansour
A, Kramer CL, Goldenberg FD and Lazaridis C: Effect of desmopressin
on hematoma expansion in antiplatelet-associated intracerebral
hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci.
86:116–121. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bultitude M and Rees J: Management of
renal colic. BMJ. 345(e5499)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Golzari SE, Soleimanpour H, Rahmani F,
Mehr NZ, Safari S, Heshmat Y and Bakhtavar HE: Therapeutic
approaches for renal colic in the emergency department: A review
article. Anesth Pain Med. 4(e16222)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kapila V, Kapila AK, Tailly T, Rappe B,
Juul KV and Everaert K: The analgesic action of desmopressin in
renal colic. Acta Clin Belg. 72:179–185. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Patti L and Leslie SW: Acute renal colic.
StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
|
|
47
|
Juul KV, Schroeder MK, Rittig S and
Nørgaard JP: Desmopressin as an adjuvant to opioids or NSAIDs in
treatment of renal colic: A nationwide register-based study.
Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 24:1155–1160. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Amer T, Osman B, Johnstone A, Mariappan M,
Gupta A, Brattis N, Jones G, Somani BK, Keeley FX Jr and
Aboumarzouk OM: Medical expulsive therapy for ureteric stones:
Analysing the evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analysis of
powered double-blinded randomised controlled trials. Arab J Urol.
15:83–93. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Campschroer T, Zhu X, Vernooij RW and Lock
MT: Alpha-blockers as medical expulsive therapy for ureteral
stones. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 5(CD08509)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lim I, Sellers DJ and Chess-Williams R:
Current and emerging pharmacological targets for medical expulsive
therapy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 130 (Suppl 1):S16–S22.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
European Association of Urology (EAU): EAU
Guidelines on Urolithiasis. EAU, Arnhem, 2024. https://d56bochluxqnz.cloudfront.net/documents/full-guideline/EAU-Guidelines-on-Urolithiasis-2024.pdf.
|
|
52
|
Jalili M, Shirani F, Entezari P,
Hedayatshodeh M, Baigi V and Mirfazaelian H:
Desmopressin/indomethacin combination efficacy and safety in renal
colic pain management: A randomized placebo controlled trial. Am J
Emerg Med. 37:1009–1012. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kimoto Y and Constantinou CE: Effects of
[1-desamino-8-D-arginine]vasopressin and papaverine on rabbit renal
pelvis. Eur J Pharmacol. 175:359–362. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
el-Sherif AE, Salem M, Yahia H,
al-Sharkawy WA and al-Sayrafi M: Treatment of renal colic by
desmopressin intranasal spray and diclofenac sodium. J Urol.
153:1395–1398. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hazhir S, Badr YAA and Darabi JN:
Comparison of intranasal desmopressin and intramuscular tramadol
versus pethidine in patients with renal colic. Urol J. 7:148–151.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kheirollahi AR, Tehrani M and Bashashati
M: A comparison of the effect of intranasal desmopressin and
intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide combination with
intramuscular hyoscine N-butyl bromide alone in acute renal colic.
J Res Med Sci. 15:214–218. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Roshani A, Falahatkar S, Khosropanah I,
Roshan ZA, Zarkami T, Palizkar M, Emadi SA, Akbarpour M and Khaki
N: Assessment of clinical efficacy of intranasal desmopressin spray
and diclofenac sodium suppository in treatment of renal colic
versus diclofenac sodium alone. Urology. 75:540–542.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Masoumi K, Darian AS, Forouzan A,
Barzegari H, Rahim F, Feli M, Sheidaii MF and Porozan S: The
efficacy of intranasal desmopressin as an adjuvant in the acute
renal colic pain management. Pain Res Treat.
2014(320327)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Shirvani MK, Mahboub MD, Ghazi M and
Delijani A: A comparison of the effects of morphine and sublingual
desmopressin combination therapy with morphine alone in treatment
of renal colic: A controlled clinical trial. Urol J. 12:2001–2004.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shirazi M, Salehipour M, Afrasiabi MA and
Aminsharifi A: Analgesic effects and safety of desmopressin,
tramadol and indomethacin in patients with acute renal colic; A
randomized clinical trial. Bull Emerg Trauma. 3:41–45.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dolatabadi AA, Memary E, Kariman H, Gigloo
KN and Baratloo A: Intranasal desmopressin compared with
intravenous ketorolac for pain management of patients with renal
colic referring to the emergency department: A randomized clinical
trial. Anesth Pain Med. 7(e43595)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ghafouri HB, Abazarian N, Yasinzadeh M and
Modirian E: Intravenous paracetamol vs intranasal desmopressin for
renal colic in the emergency department: A randomized clinical
trial. Pain Med. 21:3437–3442. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Pricop C, Branisteanu DD, Orsolya M, Puia
D, Matei A and Checherita IA: Sublingual desmopressin is efficient
and safe in the therapy of lithiasic renal colic. Int Urol Nephrol.
48:183–189. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kumar S, Behera NC, Sarkar D, Prasad S,
Mandal AK and Singh SK: A comparative assessment of the clinical
efficacy of intranasal desmopressin spray and diclofenac in the
treatment of renal colic. Urol Res. 39:397–400. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lopes T, Dias JS, Marcelino J, Varela J,
Ribeiro S and Dias J: An assessment of the clinical efficacy of
intranasal desmopressin spray in the treatment of renal colic. BJU
Int. 87:322–325. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Jalili M, Entezari P, Doosti-Irani A,
Masoomi R and Mirfazaelian H: Desmopressin effectiveness in renal
colic pain management: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J
Emerg Med. 34:1535–1541. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Seghatoleslami G, Jahromi MS, Farzaneh R,
Rahsepar S, Malekshoar M, Vatankhah M, Akhavan R, Abbasi B, Akhavan
H, Abiri S, et al: Alternative medical interventions versus
conventional treatment of renal colic: An updated systematic review
and network meta-analysis. Urol J. 19:412–419. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Kreek MJ, Zhou Y and Levran O: Functions
of arginine vasopressin and its receptors: Importance of human
molecular genetics studies in bidirectional translational research.
Biol Psychiatry. 70:502–503. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Albers HE: The regulation of social
recognition, social communication and aggression: Vasopressin in
the social behavior neural network. Horm Behav. 61:283–292.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Winter J and Jurek B: The interplay
between oxytocin and the CRF system: Regulation of the stress
response. Cell Tissue Res. 375:85–91. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Marsh N, Marsh AA, Lee MR and Hurlemann R:
Oxytocin and the neurobiology of prosocial behavior.
Neuroscientist. 27:604–619. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Müller D, Florkowski H, Chavez-Kattau K,
Carlsson G and Eggert P: The effect of desmopressin on short-term
memory in children with primary nocturnal enuresis. J Urol.
166:2432–2434. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Schulz-Juergensen S, Rieger M, Schaefer J,
Neusuess A and Eggert P: Effect of 1-desamino-8-D-arginine
vasopressin on prepulse inhibition of startle supports a central
etiology of primary monosymptomatic enuresis. J Pediatr.
151:571–574. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Laczi F, Valkusz Z, Lászlo FA, Wagner A,
Járdánházy T, Szász A, Szilárd J and Telegdy G: Effects of
lysine-vasopressin and 1-deamino-8-D-arginine-vasopressin on memory
in healthy individuals and diabetes insipidus patients.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 7:185–193. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
EMBL-EBI: Expression Atlas-gene expression
across species and biological conditions. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gxa/home. Last accessed 12
July, 2023.
|
|
76
|
Charles R, Sakurai T, Takahashi N, Elder
GA, Sosa MA, Young LJ and Buxbaum JD: Introduction of the human
AVPR1A gene substantially alters brain receptor expression patterns
and enhances aspects of social behavior in transgenic mice. Dis
Model Mech. 7:1013–1022. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ebstein RP, Knafo A, Mankuta D, Chew SH
and Lai PS: The contributions of oxytocin and vasopressin pathway
genes to human behavior. Horm Behav. 61:359–379. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
GTEX Consortium. Ardlie KG, Deluca DS,
Segrè AV, Sullivan TJ, Young T, Gelfand ET, Trowbridge C, Maller
JB, Tukiainen T, et al: The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) pilot
analysis: Multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science.
348:648–660. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Vargas KJ, Sarmiento JM, Ehrenfeld P,
Añazco CC, Villanueva CI, Carmona PL, Brenet M, Navarro J,
Müller-Esterl W and González CB: Postnatal expression of V2
vasopressin receptor splice variants in the rat cerebellum.
Differentiation. 77:377–385. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Kato Y, Igarashi N, Hirasawa A, Tsujimoto
G and Kobayashi M: Distribution and developmental changes in
vasopressin V2 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Differentiation.
59:163–169. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Schmahmann JD: Emotional disorders and the
cerebellum: Neurobiological substrates, neuropsychiatry, and
therapeutic implications. Handb Clin Neurol. 183:109–154.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Tomlinson SP, Davis NJ, Morgan HM and
Bracewell RM: Cerebellar contributions to verbal working memory.
Cerebellum. 13:354–361. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Sakai Y, Horiba N, Tozawa F, Sakai K,
Kuwayama A, Demura H and Suda T: Desmopressin stimulation test for
diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushing's syndrome. Endocr J.
44:687–695. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Vassiliadi DA and Tsagarakis S: Diagnosis
of Endocrine Disease: The role of the desmopressin test in the
diagnosis and follow-up of Cushing's syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol.
178:R201–R214. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Jonat S, Santer R, Schneppenheim R, Obser
T and Eggert P: Effect of DDAVP on nocturnal enuresis in a patient
with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Arch Dis Child. 81:57–59.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Robben JH, Sze M, Knoers NV, Eggert P,
Deen P and Müller D: Relief of nocturnal enuresis by desmopressin
is kidney and vasopressin type 2 receptor independent. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 18:1534–1539. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Stegner H, Artman HG, Leake RD and Fisher
DA: Does DDAVP (1-desamino-8-D-arginine-vasopressin) cross the
blood-CSF barrier? Neuroendocrinology. 37:262–265. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Sørensen PS, Vilhardt H, Gjerris F and
Warberg J: Impermeability of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
to 1-deamino-8-D-arginine-vasopressin (DDAVP) in patients with
acquired, communicating hydrocephalus. Eur J Clin Invest.
14:435–439. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Ferring Pharmaceuticals: DDAVP Tablets
0.2mg SmPC, 2012.
|
|
90
|
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Horvath A and Michals
EA: Carrier-mediated transport of vasopressin across the
blood-brain barrier of the mouse. J Neurosci Res. 18:326–332.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Su Y, Sun B, Gao X, Dong X, Fu L, Zhang Y,
Li Z, Wang Y, Jiang H and Han B: Intranasal delivery of targeted
nanoparticles loaded with miR-132 to brain for the treatment of
neurodegenerative diseases. Front Pharmacol.
11(1165)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Lochhead JJ, Kellohen KL, Ronaldson PT and
Davis TP: Distribution of insulin in trigeminal nerve and brain
after intranasal administration. Sci Rep. 9(2621)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Maeng J and Lee K: Systemic and brain
delivery of antidiabetic peptides through nasal administration
using cell-penetrating peptides. Front Pharmacol.
13(1068495)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Hallschmid M: Intranasal insulin for
Alzheimer's disease. CNS Drugs. 35:21–37. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Mutsuga N, Shahar T, Verbalis JG, Xiang
CC, Brownstein MJ and Gainer H: Regulation of gene expression in
magnocellular neurons in rat supraoptic nucleus during sustained
hypoosmolality. Endocrinology. 146:1254–1267. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Landgraf R, Hess J and Hartmann E: Effect
of oxytocin on regional 3H-orotic acid uptake in rat brain.
Endokrinologie. 70:45–52. 1977.PubMed/NCBI(In German).
|
|
97
|
Landgraf R, Hess J and Ermisch A: The
influence of vasopressin on the regional uptake of [3H] orotic acid
by rat brain. Acta Biol Med Ger. 37:655–658. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Burbach JP, Kovács GL, de Wied D, van
Nispen JW and Greven HM: A major metabolite of arginine vasopressin
in the brain is a highly potent neuropeptide. Science.
221:1310–1312. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Burbach JP, Bohus B, Kovács GL, Van Nispen
JW, Greven HM and De Wied D: Oxytocin is a precursor of potent
behaviourally active neuropeptides. Eur J Pharmacol. 94:125–131.
1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
van Bree JB, de Boer AG, Verhoef JC,
Danhof M and Breimer DD: Transport of vasopressin fragments across
the blood-brain barrier: In vitro studies using monolayer cultures
of bovine brain endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
249:901–905. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lee MR and Jayant RD: Penetration of the
blood-brain-barrier by peripheral neuropeptides: New approaches to
enhancing transport and endogenous expression. Cell Tissue Res.
375:287–293. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Lal S, Nair NP, Isaac I, Thavundayil J and
Guyda H: Effect of some peptides on dopaminergic function in man. J
Neural Transm Suppl. 29:173–181. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Brambilla F, Aguglia E, Massironi R,
Maggioni M, Grillo W, Castiglioni R, Catalano M and Drago F:
Neuropeptide therapies in chronic schizophrenia: TRH and
vasopressin administration. Neuropsychobiology. 15:114–121.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Brambilla F, Bondiolotti GP, Maggioni M,
Sciascia A, Grillo W, Sanna F, Latina A and Picotti GB: Vasopressin
(DDAVP) therapy in chronic schizophrenia: Effects on negative
symptoms and memory. Neuropsychobiology. 20:113–119.
1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Pifano M, Garona J, Capobianco CS,
Gonzalez N, Alonso DF and Ripoll GV: Peptide agonists of
vasopressin V2 receptor reduce expression of neuroendocrine markers
and tumor growth in human lung and prostate tumor cells. Front
Oncol. 7(11)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Keegan BP, Akerman BL, Péqueux C and North
WG: Provasopressin expression by breast cancer cells: Implications
for growth and novel treatment strategies. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
95:265–277. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Sobol NT, Solernó LM, Beltrán B, Vásquez
L, Ripoll GV, Garona J and Alonso DF: Anticancer activity of
repurposed hemostatic agent desmopressin on AVPR2-expressing human
osteosarcoma. Exp Ther Med. 21(566)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Bass R, Roberto D, Wang DZ, Cantu FP,
Mohamadi RM, Kelley SO, Klotz L and Venkateswaran V: Combining
desmopressin and docetaxel for the treatment of
castration-resistant prostate cancer in an orthotopic model.
Anticancer Res. 39:113–118. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Weinberg RS, Grecco MO, Ferro GS,
Seigelshifer DJ, Perroni NV, Terrier FJ, Sánchez-Luceros A, Maronna
E, Sánchez-Marull R, Frahm I, et al: A phase II dose-escalation
trial of perioperative desmopressin (1-desamino-8-d-arginine
vasopressin) in breast cancer patients. Springerplus.
4(428)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Iseas S, Roca EL, O'Connor JM, Eleta M,
Sanchez-Luceros A, Di Leo D, Tinelli M, Fara ML, Spitzer E, Demarco
IA, et al: Administration of the vasopressin analog desmopressin
for the management of bleeding in rectal cancer patients: Results
of a phase I/II trial. Invest New Drugs. 38:1580–1587.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Hermo GA, Torres P, Ripoll GV, Scursoni
AM, Gomez DE, Alonso DF and Gobello C: Perioperative desmopressin
prolongs survival in surgically treated bitches with mammary gland
tumours: A pilot study. Vet J. 178:103–108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Ikeda Y, Zabbarova I, de Rijk M, Kanai A,
Wolf-Johnston A, Weiss JP, Jackson E and Birder L: Effects of
vasopressin receptor agonists on detrusor smooth muscle tone in
young and aged bladders: Implications for nocturia treatment.
Continence (Amst). 2022(100032)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Papatheodorou I, Moreno P, Manning J,
Fuentes AM, George N, Fexova S, Fonseca NA, Füllgrabe A, Green M,
Huang N, et al: Expression atlas update: From tissues to single
cells. Nucl Acids Res. 48:D77–D83. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Oiso Y, Robertson GL, Nørgaard JP and Juul
KV: Clinical review: Treatment of neurohypophyseal diabetes
insipidus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:3958–3967. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Altun G, Hemşinli D, Pulathan Z and
Civelek A: Emergency coronary bypass surgery in patients under the
influence of dualantiplatelet therapy: Effects of tranexamic acid
and desmopressin acetate. Turk J Med Sci. 47:doi:
10.3906/sag-1612-140. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Bignami E, Cattaneo M, Crescenzi G,
Ranucci M, Guarracino F, Cariello C, Baldassarri R, Isgrò G,
Baryshnikova E, Fano G, et al: Desmopressin after cardiac surgery
in bleeding patients. A multicenter randomized trial. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 60:892–900. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Jahangirifard A, Razavi MR, Ahmadi ZH and
Forozeshfard M: Effect of desmopressin on the amount of bleeding
and transfusion requirements in patients undergoing heart
transplant surgery. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 121:175–180.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Jin L and Ji HW: Effect of desmopressin on
platelet aggregation and blood loss in patients undergoing valvular
heart surgery. Chin Med J. 128:644–647. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Mirmansoori A, Farzi F, Sedighinejad A,
Imantalab V, Mohammadzadeh A, Roushan ZA, Tehran SZ, Nemati M and
Dehghan A: The effect of desmopressin on the amount of bleeding in
patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery with a
cardiopulmonary bypass pump after taking anti-platelet medicine.
Anesth Pain Med. 6(e39226)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Cheong M, Lee TY, Lee J and Kim SB: No
effect of desmopressin administration before kidney biopsy on the
risk of major post-biopsy bleeding. Nefrologia (Engl Ed).
26:S0211–S6995. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
121
|
Leclerc S, Nadeau-Fredette AC, Elftouh N,
Lafrance JP, Pichette V and Laurin LP: Use of desmopressin prior to
kidney biopsy in patients with high bleeding risk. Kidney Int Rep.
5:1180–1187. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Wang LC, Hu YF, Chen L, Xing R, Lin XF and
Kou QY: Desmopressin acetate decreases blood loss in patients with
massive hemorrhage undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. Turk J
Gastroenterol. 31:474–481. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Anderson LT, David R, Bonnet K and Dancis
J: Passive avoidance learning in Lesch-Nyhan disease: Effect of
1-desamino-8-arginine-vasopressin. Life Sci. 24:905–910.
1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Beckwith BE, Petros T, Kanaan-Beckwith S,
Couk DI, Haug RJ and Ryan C: Vasopressin analog (DDAVP) facilitates
concept learning in human males. Peptides. 3:627–630.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Eisenberg J, Hamburger-Bar R and Belmaker
RH: The effect of vasopressin treatment on learning in Down's
syndrome. J Neural Transm. 60:143–147. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Beckwith BE, Petros TV, Bergloff PJ and
Staebler RJ: Vasopressin analogue (DDAVP) facilitates recall of
narrative prose. Behav Neurosci. 101:429–432. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Beckwith BE, Petros TV, Bergloff PJ,
Swenson RR and Paulson R: Failure of posttrial administration of
vasopressin analogue (DDAVP) to influence memory in healthy, young,
male volunteers. Peptides. 16:1327–1328. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Beckwith BE, Till RE, Reno CR and Poland
RE: Dose-dependent effects of DDAVP on memory in healthy young
adult males: A preliminary study. Peptides. 11:473–476.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Eisenhofer G, Lambie DG and Robinson BJ:
No improvement in ethanol-induced memory deficits after
administration of a vasopressin analog. Life Sci. 37:2499–2505.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Guard O, Marchal G, Graule A, Dumas R and
D'Athis P: Effects of vasopressin and desmopressin on memory. A
double-blind study in 40 healthy volunteers. Neuropsychobiology.
15:80–83. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Jenkins JS, Mather HM and Coughlan AK:
Effect of desmopressin on normal and impaired memory. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 45:830–831. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Millar K, Jeffcoate WJ and Walder CP:
Vasopressin and memory: Improvement in normal short-term recall and
reduction of alcohol-induced amnesia. Psychol Med. 17:335–341.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Nebes RD, Reynolds CF III and Horn LC: The
effect of vasopressin on memory in the healthy elderly. Psychiatry
Res. 11:49–59. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Till RE and Beckwith BE: Sentence memory
affected by vasopressin analog (DDAVP) in cross-over experiment.
Peptides. 6:397–402. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Weingartner H, Gold P, Ballenger JC,
Smallberg SA, Summers R, Rubinow DR, Post RM and Goodwin FK:
Effects of vasopressin on human memory functions. Science.
211:601–603. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Abdollahian E, Sargolzaee MR, Hajzade M,
Mohebbi MD and Javanbakht A: Effects of desmopressin (DDAVP) on
memory impairment following electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Acta
Neuropsychiatr. 16:130–137. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Lerer B, Zabow T, Egnal N and Belmaker RH:
Effect of vasopressin on memory following electroconvulsive
therapy. Biol Psychiatry. 18:821–824. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Beckwith BE, Couk DI and Till TS:
Vasopressin analog influences the performance of males on a
reaction time task. Peptides. 4:707–709. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Jennings JR, Nebes RD and Reynolds CF III:
Vasopressin peptide (DDAVP) may narrow the focus of attention in
normal elderly. Psychiatry Res. 17:31–39. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Tsikunov SG and Belokoskova SG:
Psychophysiological analysis of the influence of vasopressin on
speech in patients with post-stroke aphasias. Span J Psychol.
10:178–188. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Gold PW, Weingartner H, Ballenger JC,
Goodwin FK and Post RM: Effects of 1-desamo-8-D-arginine
vasopressin on behaviour and cognition in primary affective
disorder. Lancet. 2:992–994. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Hosseini SMR, Farokhnia M, Rezaei F,
Gougol A, Yekehtaz H, Iranpour N, Salehi B, Tabrizi M, Tajdini M,
Ghaleiha A and Akhondzadeh S: Intranasal desmopressin as an adjunct
to risperidone for negative symptoms of schizophrenia: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Eur
Neuropsychopharmacology. 24:846–855. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|