1. Introduction
The spinal vertebrae (spinal column) consist of a
sequence of vertebrae, each separated and united by an
intervertebral disc. The intervertebral disc is elastic and acts as
a cushion between vertebrae. This multilayer structure supports the
body trunk and provides movement for the trunk, such as bending
forward, backward and to the side, and rotation (1). Furthermore, the spinal cord and
central nervous system are protected from physical impact because
they travel through the vertebral foramen (spinal canal). The spine
consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, 5 lumbar
vertebrae, and 5 sacral vertebrae that are fused together to form
the sacrum, and several caudal vertebrae that are fused together to
form the coccyx (2).
The spinal vertebrae are originally vertical on the
coronal (frontal) plane. However, on the sagittal plane, the
cervical and lumbar spines have lordosis and the thoracic and
sacral spines have kyphosis. Furthermore, the pelvis was tilted
forward by approximately 30 degrees. These physiological curvatures
arose during the evolution of humans to two-legged locomotion
(bipedalism). This physiological curvature results in a 10-fold
increase in the resistance to pressure applied in the vertical
direction relative to a straight spinal column (3).
On the other hand, scoliosis is a condition in which
the spinal vertebrae are curved laterally in the frontal plane
(4). Scoliosis can be divided into
functional scoliosis and structural scoliosis. Functional scoliosis
(not featured in this review) includes painful scoliosis, which
occurs reflexively and defensively in response to pain, and
compensatory scoliosis, which is caused by lateral inclination due
to a difference in the length of the left and right legs.
Functional scoliosis is characterized by a mild degree of spinal
curvature that disappears when the cause is removed.
There are 3 main types of structural scoliosis:
congenital, idiopathic, and symptomatic secondary to another
condition (e.g., cerebral palsy, acute poliomyelitis, or spinal
muscular atrophy) (5). Idiopathic
scoliosis accounts for 65% of all scoliosis cases (6). Depending on the age of onset,
scoliosis can be divided into infantile, juvenile, and adolescent
scoliosis. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) occurs in
adolescents over 11 years of age and affects the majority of
patients. Most cases occur in young females. On the other hand,
congenital scoliosis is not a rare disease; rather, it is a common
condition that occurs in 0.5 to 1 in 1,000 births worldwide
(7,8). Congenital scoliosis is difficult to
detect in its early stages because the curvature is almost
painless. Currently, surgery is the only treatment option available
for scoliosis. If the pathogenic mechanism is analyzed in detail
and a genetic diagnosis enables the early detection of the disease,
it may prevent the disease from progressing, reduce the pain and
burden on the patient, and enable surgery to be avoided.
In this review, we summarize the current state of
kyphoscoliosis research and discuss the results of a comprehensive
analysis of genes that may be associated with spinal malformations
using a rat model of congenital kyphoscoliosis. Four-legged
locomotion, such as in laboratory rodents, requires less rotation
of the spine, whereas two-legged locomotion places a greater load
of gravity and motion on the spine. Therefore, the incidence of
scoliosis was higher in 2 locomotion than in 4-legged locomotion.
Considering the anatomical structure and the load placed on the
spine, human samples are desirable but extremely difficult to
obtain for research, so research is being conducted using animals
with similar spinal structures (9). This review adds new findings and
insights to the mini-review article on kyphosis that was previously
published (10).
2. Current situation of kyphoscoliosis
research
In recent years, the analysis of genes associated
with AIS has progressed. Genetic testing for AIS was initiated in
2009 and is ongoing (11).
Neurotrophin 3 (NT3) (12),
transforming growth factor β1(13), and basonuclein 2(14) have been reported as candidate genes
for AIS. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs 11190870, which
is strongly correlated with AIS, was discovered in ladybird
homeobox 1 (LBX1) by a genome-wide association study (GWAS)
(15). The LBX1 gene is located in
the vicinity of rs 11190870. The genomic region containing
rs11190870 interacts with the promoter region of the human LBX1
gene and causes the overexpression of LBX1, which has been shown to
be involved in the pathogenesis of AIS (16). Moreover, a GWAS identified SNPs
(rs6570507) in the genes encoding G protein-coupled receptor 126
(GPR126), which is reported to be associated with AIS (17). The knockdown of gpr126 in zebrafish
(Danio rerio) caused delayed ossification (calcification of
soft tissue into bonelike tissue) of the developing spinal
vertebrae. Thus, significant progress has been made in the analysis
of genes associated with the pathogenesis of AIS. However, the
exact pathogenesis of AIS remains unknown and no clear genetic
factors directly related to AIS have been identified. It has only
been reported that 9 genes have been implicated in the pathogenesis
of AIS and that the incidence of the disease is higher in families
in which at least one other first-degree relative is affected
(18). Genetic studies on AIS
provide direction for the diagnosis and treatment of this disease
and for future research. However, currently, the only curative
treatment is surgery. One limitation is the lack of strategies to
approach the causative gene itself, such as genome editing.
Recently, an interesting study on genes associated
with the development of congenital scoliosis was reported in China
and Japan. Polymorphisms (19) and
heterozygous null mutations (20)
of the T-box transcription factor 6 (TBX6) gene have been
identified in Han Chinese patients with congenital scoliosis.
Takeda et al (21) examined
94 Japanese patients with congenital scoliosis for genetic
abnormalities in TBX6 and found deletions in 5 cases and severe
mutations in 3 cases. Otomo et al (22) screened the mutations in the TBX6
gene in 196 Japanese patients with congenital scoliosis. An in
vitro functional analysis of novel and known missense mutations
revealed that most of the mutations cause abnormal subcellular
localization of TBX6 protein. Congenital scoliosis associated with
TBX6 in these Japanese cohorts accounted for approximately 10% of
the total incidence of the disease, which is comparable to the
aforementioned Chinese report. The Tbx6 gene encodes a T-box
transcription factor that is expressed in cells that pass through
the striae (primitive streak, a ridge seen on the midline of the
caudal end of the blastoderm and gives a head-tail and a left-right
axis to the developing embryo) and induces the differentiation of
chondrocytes, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle from the mesoderm
(23,24). In Tbx6-deficient mouse embryos, the
neural tube is ectopically formed caudally from the neck in the
region that normally differentiates into the somitic mesoderm that
differentiates into bone and muscle (25,26).
The decreased expression of this gene due to mutations or deletions
may inhibit differentiation into chondrocytes and consequently
prevent the formation of normal vertebrae.
Spondylostal dysostosis is a congenital disorder
that causes severe deformities of the axial skeleton and is
diagnosed based on radiographic features such as a combination of
multiple segmental defects of the vertebrae and abnormalities of
the ribs. In addition, most patients present with mild to severe
scoliosis. The disease is caused by pathogenic mutations in
delta-like protein 3, mesoderm posterior protein 2,
O-fucosylpeptide 3-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
(LFNG), Hes family BHLH transcription factor 7, and Ripply
Transcriptional Repressor 2. These mutations are inherited in an
autosomal recessive fashion. Abnormalities in these genes have been
reported to be strongly involved in the development of congenital
scoliosis (27,28). In fact, a missense mutation in LFNG
was identified in a patient with congenital scoliosis. LFNG
encodes an N-acetylglucosamine-transferase, and this mutant was
shown to have lost its enzymatic function (27). Takeda et al (27) experimentally demonstrated-for the
first time-that LFNG is one of the leading candidate
causative genes of congenital scoliosis. Since all of these genes,
including LFNG, are involved in the signal transduction of
Notch1, their analysis may shed light on the pathogenesis of this
disease (28). However, as Takeda
et al (27) stated, ‘the
current list of known disease genes could explain only a small
fraction of genetic cause’ and it is still difficult to understand
the full picture.
Thus, there are only a few interesting reports on
the analysis of the causative genes of congenital kyphoscoliosis.
However, this research has not progressed quickly and its expansion
has been limited. Studies using animal models are needed to advance
research quickly and widely. Oda et al (29) performed spinal fusion surgery on
sheep as a model animal of spinal kyphosis. While this may be
useful for analyzing the effects of kyphotic deformities on
adjacent motor segments. However, it is not appropriate for studies
to determine the pathogenesis of kyphosis. To accelerate this
research, we analyzed rats with spontaneous lumbar kyphoscoliosis
as an animal model of congenital kyphoscoliosis.
3. Ishibashi rats, an animal model of
kyphoscoliosis
There is no need to mention that studies using
animal models are useful for the rapid and efficient progression of
human disease research. Recently, transgenic or-deficient mice
showing the development of kyphosis have been reported. Chae et
al (30) reported that mice
deficient in the mitochondrial enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase 2
gene exhibit spinal kyphosis. More recently, the transgenic
LmnaG609G progeric mouse has been developed as an animal model for
studying human Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, which is
caused by mutations in the LMNA (lamin A/C) gene, showing severe
kyphosis (31). Furthermore,
thoracic kyphosis also appears in mice homozygous for a humpback
mutation in Notch3 (32).
Ishibashi (IS) rats were used in the present study.
This rat strain was maintained at The National Bio Resource Project
(NBRP) for the Rat in Japan (strain No. 0008). IS rats were
provided by the Institute of Laboratory Animals, Graduate School of
Medicine, Kyoto University (Kyoto, Japan), and all researchers can
use this rat (http://www.anim.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/NBR/strains/Strains_d.aspx?StrainID=5&s_Strainname=is).
IS rats have an agouti coat color. We believe that
this rat has good reproductive performance, but a somewhat rough
temperament. This rat is characterized by malformation of the
lumbar spine, leading to kyphoscoliosis with restricted spinal
canals and spinal cord. IS rats were established by Ishibashi
(Azabu University School of Veterinary Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan)
in 1968 as an inbred strain from a male wild-type and female Wistar
rat (33). Wistar rats are
medium-sized albinos that originated from the Wistar Institute in
Philadelphia (PA, USA). Spinal abnormalities are spontaneous and
are not caused by artificial genetic modifications. As reported by
Seki et al (34), IS rats
exhibit typical and pronounced kyphoscoliosis of the lumbar
vertebrae. In addition to kyphoscoliosis, homeotic transformation
was observed only in the lumbosacral transitional areas of adult IS
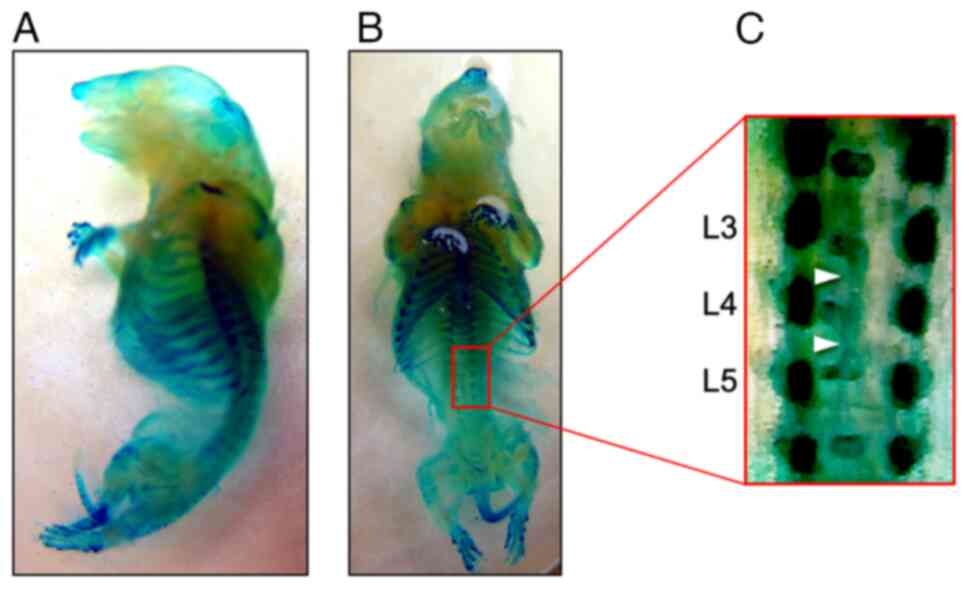
rats. In the fetus, unilateral unions of ventral primary
ossification centers were observed in the lumbar vertebrae
(Fig. 1). Almost all homozygous
individuals crossed between male and female IS rats have vertebral
anomalies (34). IS rats are
generally regarded as an animal model of human spinal malformation
in which bone deformities are restricted to the spinal vertebrae.
Furthermore, the number of clinical cases of human scoliosis is
relatively small, making it difficult to compare scoliosis sites
with the normal areas of the spine in the same individual.
Therefore, we considered that an analysis of IS in rats might lead
to a new understanding of human scoliosis.
In contrast, a mouse with kyphoscoliosis was
identified in the offspring of mice treated with a chemical mutagen
(N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea) (35). The
mice showed an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance and were
named hereditary vertebral fusion (HVF) mice. The phenotype of HVF
mice was similar to that of IS rats. They mainly have lumbar
segmental defects, narrowing of the intervertebral space,
irregularity of the adjacent ends of the vertebral bodies, and
kyphosis with wedging and complete spinal fusion of the adjacent
vertebral bodies. However, no specific genetic mutations or
expression abnormalities have been reported in the HVF mice.
Thus far, with the exception of our studies, only 6
studies have investigated malformations of the spinal vertebrae in
IS rats. The main findings of these studies are as follows: ⅰ) The
administration of the sex hormones estrogen and testosterone
inhibited the progression of kyphosis in male IS rats (36,37);
ⅱ) Plasma alkaline phosphatase activity is low in IS rats, but this
is not related to the malformation of the spinal vertebrae
(38); ⅲ) The phenotypic spinal
abnormality in IS rats is not due to a single gene, but may be due
to multiple genes (39); ⅳ)
IS-Tlk/Kyo, a rat mutant strain derived from the IS strain,
exhibits abnormalities of the sacral and tail vertebrae, in
addition to a congenital malformation of the lumbar spine, which is
a significant phenotype of IS rats (40,41).
These studies were interesting but sporadic and did not focus on
the pathogenesis of kyphoscoliosis.
4. Comprehensive analysis of the gene
expression in the flexed lumbar spine using IS rats
When we first analyzed congenital kyphoscoliosis in
IS rats, we thought that because congenital scoliosis is a skeletal
abnormality, the cause of the disease could be determined by
analyzing the abnormalities in homeotic genes that determine the
composition of the skeleton. For example, in HoxA10 knockout
mice, the first lumbar vertebra is altered to look like the 13th
thoracic vertebra just anterior to it (on the head side), resulting
in ribs that do not arise normally (42,43).
In addition, for HoxA11 and HoxD11, no significant
changes were observed with the knockout of each gene alone
(HoxA11-/-/HoxD11+/+ or
HoxA11+/+/HoxD11-/-); however,
in the double knockout
(HoxA11-/-/HoxD11-/-), a
pronounced trait change appeared in the form of bone loss in the
forearm (44).
Based on these reports, the third to fifth lumbar
spine segments (L3-L5), the segments that are the most common area
of deformity in IS rats (36),
were analyzed to determine the Hox gene expression levels
(34). The expression of
Hox a10 and c11 in the vertebrae of IS and heterozygotes was
not significantly different from that of Wistar (control) rats.
However, the expression levels of Hox 10 and 11 paralogs
(c10, d10, a11, and d11) in the vertebrae of both IS rats and
heterozygotes were significantly lower than those in Wistar rats
(Table I). In knockout and
transgenic mice with Hox 10 and 11, malformations of the vertebrae
and homeotic transformation in the lumbosacral vertebrae were
observed (45). As mentioned in
the previous section. In addition to kyphoscoliosis, homeotic
transformation in adult IS rats was only observed in the
lumbosacral transitional areas (34). Taken together, the partial
reduction of the Hox 10 and 11 expression may cause spinal
deformities and homeotic transformation of the 1st sacral vertebra
into the 7th lumbar vertebra.
 | Table IList of genes/proteins with abnormal
expression in the lumbar spine of Ishibashi. |
Table I
List of genes/proteins with abnormal
expression in the lumbar spine of Ishibashi.
| Classification by
function | Symbol | Description | Array | mRNA | Protein | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Vertebral
formation | Hox a11 | Homeobox a11 | - | ↓ 0.09 | - | (34) |
| | Hox c10 | Homeobox c10 | ↓ 0.86 | ↓ 0.10 | - | (34) |
| | Hox d10 | Homeobox d10 | - | ↓ 0.38 | - | (34) |
| | Hox d11 | Homeobox d11 | - | ↓ 0.19 | - | (34) |
| NGF receptor | Ntrk1 | trkA; High affinity
nerve growth factor receptor | ↓ 0.10 | ↓ 0.45 | ↓ 0.34 | (46) |
| | Ntrk2 | trkB; BDNF/NT-3
growth factors receptor | ↓ 0.11 | ↓ 0.32 | ↓ 0.53 | (46) |
| | Ntrk3 | trkC; NT-3 growth
factor receptor | ↓ 0.09 | ↓ 0.54 | ↓ 0.27 | (46) |
| Retinol
metabolism | Adh1 | Alcohol
dehydrogenase 1 | ↓ 0.37 | ↓ 0.55 | ↓ 0.58 | (47) |
| | Aldh1a2 | Aldehyde
dehydrogenase family 1 member A2 | ↓ 0.31 | ↓ 0.33 | ↓ 0.40 | (47) |
| | Rara | Retinoic acid
receptor α | ↓ 0.83 | ↓ 0.69 | ↓ 0.58 | (47) |
| | Stra6 | Stimulated by
retinoic acid 6 | ↓ 0.33 | - | - | (47) |
| Osteogenesis | BMP-2 | Bone morphogenetic
protein 2 | ↓ 0.83 | ↓ 0.71 | ↓ 0.35 | (47) |
| | Col1A1 | Collagen α-1 | ↓ 0.45 | - | ↓ 0.44 | (48) |
| RNA
interference |
miR-224-5p |
rat-miRNA-224-5p | 2.82 | 3.46 | - | (48) |
| Bone loss | Pai-1 | Plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 | ↓ 0.58 | 2.20 | 2.48 | (48) |
| | Serbp1 | Pai-1 RNA binding
protein 1 | 1.43 | - | - | (48) |
| Ca2+
signaling | CaSR | Calcium-sensing
receptor | ↓ 0.14 | - | ↓ 0.27 | (75) |
| | Trpv1 | Transient receptor
potential vanilloid 1 | ↓ 0.10 | - | ↓ 0.14 | (75) |
| | Nell-1 | Neural EGFL-like
1 | ↓ 0.17 | ↓ 0.56 | - | (75) |
| | Jnk1 | c-Jun N-terminal
kinase 1 | ↓ 0.31 | ↓ 0.62 | - | (75) |
Thus, it is worth examining each scoliosis-related
gene that may be associated with the development of scoliosis. In
contrast, spinal abnormalities, such as spinal curvature, homeotic
transformation, and fusion/division of primary ossification, in IS
rats are extremely diverse. We therefore changed our strategy from
analyzing individual genes that might be involved in the
development of kyphoscoliosis to conducting a comprehensive genetic
analysis. For this purpose, we performed a DNA microarray (DNA
chip) analysis. We are the first to apply this method in a
comprehensive analysis of the gene expression in congenital
kyphoscoliosis (46-48).
A DNA microarray, also known as a DNA chip, is an analytical tool
in which a large number of DNA fragments are densely arranged on a
substrate, such as resin or glass, to analyze changes in the gene
expression levels of specimens (49,50).
This method enables a comprehensive analysis of the gene expression
in various organisms with a small number of specimens in a
relatively short time. It is currently used in various research
fields. Protein arrays that use antibodies and peptides instead of
nucleic acids have also been developed (51).
For the DNA microarray analysis, total RNA was
extracted from L3-L5 of male rats on postnatal day 4 (when
ossification is less advanced). RNA samples from IS and wild-type
(Wistar, Wt) rats were labeled with Cyanine3 (Cy3) and Cyanine5
(Cy5) fluorescent dyes, respectively. The rat gene expression was
analyzed using the 3D-Gene Rat Oligo chip 20k (approximately 20,000
distinct genes; Toray Industries, Tokyo, Japan). In the lumbar
spine, 194 genes showed altered expression levels in IS rats in
comparison to WT rats. Among these, 90 genes were upregulated
(Cy3/Cy5 ratio ≥8.0-fold) and 104 genes were downregulated (Cy3/Cy5
ratio ≤0.125) in IS rats in comparison to WT rats (46). The experiments and results
presented in the five original papers that have been published to
date analyzed specimens of similar severity (i.e., the degree of
lumbar spine curvature) in the pathogenesis of kyphoscoliosis.
Therefore, the same conclusion was reached regardless of who
interpreted it, and the reproducibility of the experiment is
assured. According to the results of a gene clustering analysis for
genome-wide expression data, the genes significantly downregulated
in IS rats were classified into several functional groups.
i) Neurotrophin receptor family signaling. We
first focused on the receptors for nerve growth factors, since
there have been no previous reports of their relevance to the
pathogenesis of scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis. Significant decreases
in the expression levels of neurotrophin receptors (a tropomyosin
receptor kinases (Trks): TrkA, TrkB and TrkC) were observed in the
spines of IS rats (Table I)
(46). In all Trks, a significant
decrease was confirmed in the mRNA and protein expression as well
as in the DNA microarray results. Furthermore, an
immunohistochemical analysis showed that Trk-immunopositive cells
were reduced by 50-70% in IS rats relative to WT rats. TrkA is the
receptor for nerve growth factor (NGF), TrkB is the receptor for
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin (NT)
-4/5, and TrkC is the receptor for NT 3(52). It has recently been reported that
neuronal factors and their receptors play critical roles in bone
formation. For example, in the developing mouse skeleton,
TrkA-expressing sensory neurons innervate the cartilage of the
developing femur. NGF serves as a skeletal neurotrophin and
NGF-TrkA signal is required for the differentiation and
mineralization of bone progenitor cells at sites of NGF production
(53). During recovery from ulnar
stress fracture in mice, the injection of TrkA catalytic inhibitor
(1 NMPP1) reduced the numbers of sensory fibers, and then delayed
ossification of the fracture callus (54). Recently, Rivera et al
(55) reported that the endogenous
expression of NGF and TrkA during tibial fracture repair peak
during the cartilaginous phase, and that NGF injections to the
fracture site at that time can increase the bone formation by
decreasing cartilage tissue. On the other hand, TrkB mRNA is
expressed in the developing spine of rats on embryonic day
17.5(56). TrkB is also widely
expressed in bone tissues, such as chondrocytes and osteoblasts
(57). Hutchison reported that
BDNF-TrkB signals promote growth plate chondrocytes differentiation
(58) and mice lacking TrkB showed
dwarfism and delayed hypertrophic differentiation (59). Genetic testing for AIS reported
that NT-3, the ligand for TrkC, is a candidate causative gene
(12). Our previous analysis of
congenital kyphoscoliosis also found that TrkC, a receptor for NT3,
is a pivotal gene/molecule in this disease (46). NT3-TrkC signaling appears to be
deeply involved in the pathogenesis of scoliosis. On the other
hand, during the repair of rib fracture in mice, NT-3 and TrkC is
observed in osteoblast-like cells and hypertrophic chondrocytes
(60). Moreover, NT-3-TrkC signal
promotes the repair of injured growth plate cartilage and bone in
the tibia of rats through bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and
vascular endothelial growth factor activation (61). Thus, evidence is accumulating to
support that Trks are essential for normal bone formation. The gene
transfer of Trks in early embryos to IS rats, in which the gene
expression of all Trks is severely reduced, may help prevent the
development of congenital kyphoscoliosis.
ii) Retinol-retinoic acid metabolic pathway.
Next, we analyzed the retinol-retinoic acid metabolic pathway
because retinol (vitamin A1) and its metabolite,
all-trans-retinoic acid (atRA), are morphogens involved in
various developmental phenomena. In particular, this pathway plays
an important role in osteogenesis, anterior-posterior patterning,
and left-right asymmetry of axis formation (62). Excess or insufficient retinol/atRA
causes congenital anomalies and bone malformation. Vitamin
A-deficient rats show hypoplasia of the skull, ectopic bone at the
dorsal root of the C1 spinal nerve, and malformation of the sternum
and pelvic region (63).
Furthermore, congenital spinal deformity is caused in the fetuses
of pregnant rats given a vitamin A-deficient diet (64). In our DNA microarray analysis, we
showed that the expression levels of the 2 rate-limiting enzymes of
retinol metabolism, alcohol dehydrogenase I and aldehyde
dehydrogenase 1 family member A2, and retinoic acid receptor α
(Rarα) are significantly decreased in the lumbar spine of IS rats
(Table I) (47). Furthermore, the mRNA level of
stimulated by retinoic acid 6 (Stra6), which encodes the
transmembrane receptor that mediates the cellular uptake of blood
retinol (65), was also low
(Table I) (47). Interestingly, however, the serum
retinol levels in IS rats were higher than those of WT rats
(47). These findings seem to
reflect impaired retinol utilization and metabolism through the
downregulation of the retinol metabolic pathway in IS rats
(Fig. 2). Regarding the
involvement of retinol/atRA in spinal malformation in IS rats,
there are two possibilities based on the previous reports described
above and our results. First, metabolic abnormalities in RA in IS
rats may induce spinal deformities. Retinoic acid regulates the
expression of the Hox gene that define the pattern of the body plan
along the head-tail axis of an embryo (66,67),
especially Hox 10 and 11 regulate the formation of the lumbar and
sacral vertebrae (68). In a
previous study, we also found that the expression levels of Hox10
and 11 paralogs were extremely low in the lumbosacral transition of
IS rats in comparison to WT rats (34). These findings suggest that
kyphoscoliosis in IS rats may be caused, at least in part, by the
reduced expression of the Hox genes due to impaired retinol
utilization and metabolism. Second, the low expression of Rarα may
induce abnormal spine formation in IS rats by reducing the
expression of TrkC via BMP-2 (Fig.
2). In vitro experiments have shown that Rarα-specific
agonists and atRAs induce the expression of BMP-2 via Rarα
(69) and that BMP-2 induces the
expression of TrkC (70). Asaumi
et al (60) reported that
NT-3 and its receptor TrkC promote osteogenesis in rat bone marrow
stromal cells and enhance the expression of BMP-2 as an osteogenic
factor located upstream of BMP-2. In our previous study, the mRNA
and protein expression levels of TrkC in IS rats were 54 and 27%
lower, respectively, in comparison to WT rats (46). Similarly, the expression levels of
BMP-2 mRNA and protein were 71 and 35%, respectively, in comparison
to WT rats (47). Taken together,
it is strongly suggested that the breakdown of BMP-2-mediated
crosstalk between RA-Rarα and NT3-TrkC signals causes
kyphoscoliosis (Fig. 2). Thus,
this is an extremely attractive scenario. However, for this to be
convincing, further studies are needed to examine in detail the
interrelationship between the retinol-retinoic acid metabolic
pathway involved in osteogenesis and BMP-2 and TrkC.
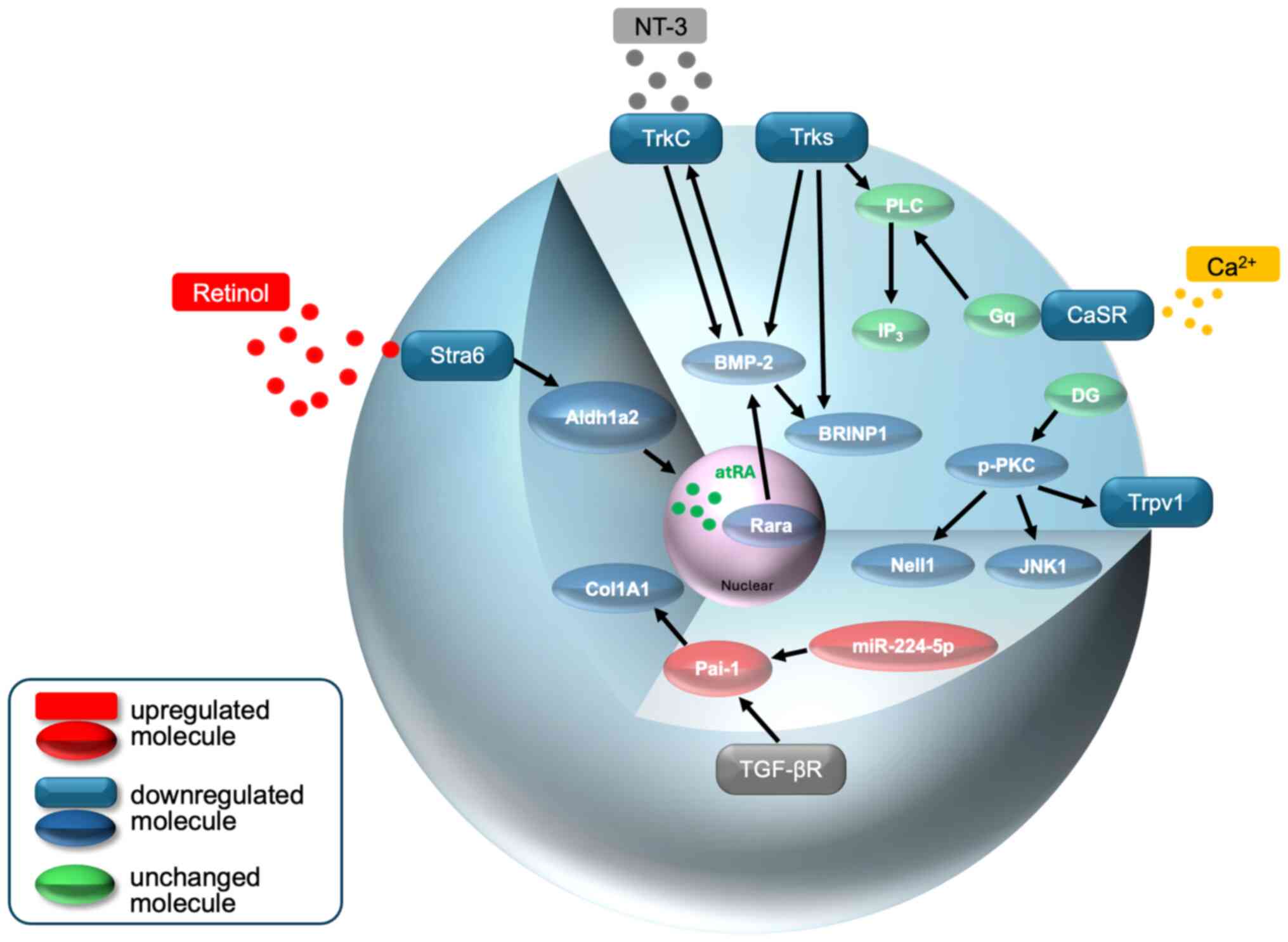 | Figure 2A schematic model of Trks, retinol,
Ca2+ and Pai-1 (via miR-224-5p) signaling in osteocytes
of the curved lumbar spine of IS rats. Details of the intensity of
the expression of each molecule and its role in the development of
kyphoscoliosis are described in the text. These combined disorders
may be at least partly responsible for kyphoscoliosis. Stra6,
stimulated by retinoic acid 6; Aldh1a2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 1
family member A2; atRA, all-trans-retinoic acid; Rarα, retinoic
acid receptor α; BMP-2, bone morphogenetic protein-2; TrkC,
tropomyosin receptor kinase 3; NT3, neurotrophin-3; BRINP1,
BMP/retinoic acid inducible neural specific 1; TGF-βr, transforming
growth factor-beta receptor; Pai-1, plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1; Col1A1, type 1 collagen α1; N, nucleus, |
iii) Ca2+
sensing/signaling. Bone contains 99% of the calcium in the
body and buffers fluctuations in blood calcium. While maintaining
calcium homeostasis, the bone also functions to maintain itself
through a process called bone remodeling. When blood calcium is
low, the mobilization of calcium from the bone to the blood, that
is, bone resorption, is accelerated (71). Maintaining calcium homeostasis
in vivo is crucial for normal bone formation and metabolism.
Calcium homeostasis involves a balance between calcium deposition
and bone absorption, the uptake of calcium by the gastrointestinal
tract, and calcium excretion by the kidneys. The maintenance of
this homeostasis is controlled by3 calcium-regulating hormones
(parathyroid hormone; PTH, calcitonin, and activated vitamin
D3) (72). On the other
hand, a Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaSR) was identified on
the cell surface of chief cells in the parathyroid glands that
sense the Ca2+ concentration in the blood (73). This receptor is activated by
elevated blood Ca2+ levels and inhibits the secretion of
PTH. Conversely, a decrease in blood Ca2+ levels
promotes PTH secretion. Functional CaSR is also expressed in
osteoblasts and osteoclasts, so that these cells are able to sense
changes in the extracellular Ca2+ and as a result
control intracellular Ca2+ signaling (74). A DNA microarray analysis revealed
that the expression of CaSR was very low in the deformed lumbar
spines of IS rats (Cy3/Cy5 ratio: 0.14) (Table I) (75). The protein expression is also
significantly lower than that of WT rats (0.27). Accordingly, the
expression of PTH (Cy3/Cy5 ratio: 2.99) and its receptor (PTHR)
(Cy3/Cy5 ratio: 2.48) was markedly upregulated.
The Trpv1 channel, also known as a capsaicin
receptor, is a member of the Ca2+-permeable cation
channel subfamily (76). The
channel is widely expressed in tissues/cells, including osteoblasts
and osteoclasts (77).
Interestingly, Ca2+ transport through Trpv channels is
required for bone remodeling (77,78).
Idris et al (79) reported
that the antagonist (capsazepine) of Trpv1 inhibits alkaline
phosphatase activity and bone nodule formation in osteoblasts.
Furthermore, TRPV1 deficient mice had reduced intracellular
Ca2+ concentrations and decreased calcium deposition in
osteoclast precursor cells during fracture healing (80). Therefore, the appropriate signaling
of Ca2+ in osteoblasts and osteoclasts by Trpv1 is
required for normal osteogenesis. Our previous studies have shown
that the Trpv1 gene expression, as well as the number of
Trpv1-expressing cells, is lower in the lumbar spine of IS rats
than in WT rats. In fact, the calcium content in the lumbar spine
of IS rats was 73.1% of that in WT rats. Therefore, we believe that
the cause of kyphoscoliosis in IS rats involves, at least in part,
the impairment of calcium sensing and uptake due to the decreased
expression of CaSR and Trpv1.
Based on these findings, we performed a pathway
analysis and found that the 2 critical molecules that regulate
normal bone formation downstream of protein kinase C were
decreased. One is neural EGFL-like 1 (Nell-1), and the other is
c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1). Nell-1 accelerates osteogenic
differentiation in vitro and the bone formation of the top
part of the skull (calvaria) in vivo (81). Moreover, a study using
Nell-1-deficient mice revealed that Nell-1 serves an indispensable
function in the development and growth of normal craniofacial and
skeletal structures (82). On the
other hand, Xu et al (83)
reported that JNK1-deficient mice are severely osteopenic due to
impaired phosphorylation of molecules downstream of JNK1 signaling
in osteoblasts. They concluded that JNK1 is a critical mediator of
the osteoblast function. Furthermore, the inhibition of JNK1 in
osteoclasts increases apoptosis. This indicates that JNK1 is
involved in an autophagic mechanism underlying the regulation of
osteoclastogenesis (84). Thus,
Nell-1 and JNK1-mediated signaling initiated by CaSR and/or Trpv1
in osteocytes may provide a novel pathway for osteogenesis.
In contrast, Slc39a13/ZIP13, an intracellular
Zn2+ transporter localized in the Golgi apparatus, is
responsible for zinc transport from the Golgi apparatus to the
cytoplasm. Mice deficient in this gene exhibit growth failure of
bone tissue and kyphosis (85). In
addition to intracellular Ca2+ signaling, the
development of scoliosis due to impaired Zn2+ signaling
should also be considered.
iv) Impairment of osteoblast differentiation by
the upregulation of Pai-1 via miR-224-5p. We attempted to
comprehensively analyze gene expression in the kyphoscoliotic
region in the spines of IS rats using a microRNA (miRNA) array in
addition to the DNA microarray. miRNAs are short (~22 nucleotides)
and functional RNA molecules that bind complementarily to the 3'
untranslated region of specific mRNA and regulate gene expression
(86). Recent accumulating
evidence indicates that miRNA-based regulation of the
differentiation and proliferation of bone and chondrocytes is
essential for the normal function of the bone (87). For example, miR-21(88) and miR-2861(89) play a protective role against
osteoporosis by suppressing the expression of programmed cell death
4 and histone deacetylase 5, respectively. More than 10 miRNAs are
able to suppress osteocyte differentiation using runt-related
transcription factor 2 as a target gene (90). In addition, miR-224-5p suppresses
osteoblast differentiation (91).
We reported that the expression of miR-224-5p is significantly
increased in the lumbar spines of IS rats in comparison to WT rats
(Table I) (48). A pathway analysis revealed that
miR-224-5p is linked to the expression of plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1 (Pai-1). Two reports support the involvement of Pai-1
in the formation of osteoblasts through collagen synthesis. First,
the lack of Pai-1 is associated with the upregulation of collagen
synthesis by Smad and non-Smad (ERK1/2 MAPK) signaling (92). Second, Pai-1 deficiency increased
the level of type I collagen (Col I) mRNA in the femoral bone of
female mice (93). This means that
Pai-1 regulates normal bone formation through the expression of Col
I, which is a marker of osteoblast differentiation. Indeed, we
confirmed that the protein expression of Col I is reduced in the
lumbar spine of IS rats (Table I)
(48). These findings suggest that
congenital kyphoscoliosis may be caused by impaired osteoblast
differentiation due to the miR-224-5p-mediated overexpression of
Pai-1 (Fig. 2).
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is an inherited
disorder characterized by systemic connective tissue fragility,
including fragility of the skin, joints, and blood vessels. EDS
also includes symptoms of bone formation abnormalities, such as
kyphoscoliosis and spondylodysplasia (94). Alpha-1 Col I, (COL1A1), which
encodes the major component of ColI, is one of the genes
responsible for EDS (95). Whether
or not miR-224-5p or Pai-1 is involved in the aberrant expression
of COL1A1 in EDS is expected to be the focus of future studies.
5. Conclusions and future perspectives
A comprehensive analysis of the RNA/miRNA expression
in IS rats has identified several genes that are likely to be
responsible for the development of kyphoscoliosis. In the future,
the analysis of these pathways in the lumbar spine of IS rats will
provide new insights into the causes of congenital kyphoscoliosis.
However, the results of genetic analysis of rat lumbar spine may
not be directly applicable to the causative genes of human
congenital kyphoscoliosis. Furthermore, our series of studies did
not consider the influence of epigenetics, a mechanism of gene
expression regulation that does not involve changes in the DNA base
sequences. Therefore, further studies are warranted. Moreover,
there are considerable limitations to faithfully reproducing human
diseases in animal models. In the future, we need to shift our
focus to studies using human-derived tissues and cells, including
specimens from patients with kyphoscoliosis.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
TS and NS conceptualized the study. TS, IT, YW and
NS made a substantial contribution to data interpretation and
analysis. TS and NS wrote and prepared the draft of the manuscript.
DY provided critical revisions. All authors contributed to
manuscript revision, and have read and approved the final version
of the manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Authors' information
Professor Noriaki Shimokawa, ORCID:
0000-0003-2129-1313.
References
|
1
|
Frost BA, Camarero-Espinosa S and Foster
EJ: Materials for the Spine: Anatomy, problems, and solutions.
Materials (Basel). 12(253)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Galbusera F: The spine: Its evolution,
function, and shape. In: Biomechanics of the Spine Basic Concepts,
Spinal Disorders and Treatments. Galbusera F and Wilke HJ (eds).
Academic Press, New York, NY, pp3-9, 2018.
|
|
3
|
Izzoa R, Guarnieria G, Guglielmib G and
Muto M: Biomechanics of the spine. Part I: Spinal stability. Eur J
Radiol. 82:118–126. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Goldberg CJ, Moore DP, Fogarty EE and
Dowling FE: Scoliosis: A review. Pediatr Surg Int. 24:129–144.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goldstein LA and Waugh TR: Classification
and terminology of scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 93:10–22.
1973.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Agabegi ED and Agabegi SS: Step-Up to
Medicine (Step-Up Series). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.,
Philadelphia PH, pp90, 2008.
|
|
7
|
Giampietro PF: Genetic aspects of
congenital and idiopathic scoliosis. Scientifica (Cairo).
2012(152365)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Giampietro PF, Raggio CL, Blank RD,
McCarty C, Broeckel U and Pickart MA: Clinical, genetic and
environmental factors associated with congenital vertebral
malformations. Mol Syndromol. 4:94–105. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Janssen MM, de Wilde RF, Kouwenhoven JW
and Castelein RM: Experimental animal models in scoliosis research:
A review of the literature. Spine J. 11:347–358. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shimokawa N, Takahashi I and Iizuka H:
Spinal malformation-A biochemical analysis using congenital
kyphosis rats. J Cell Biochem. 123:501–505. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Terhune EA, Heyn PC, Piper CR and
Hadley-Miller N: Genetic variants associated with the occurrence
and progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic
review protocol. Syst Rev. 11(118)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qiu Y, Mao SH, Qian BP, Jiang J, Qui XS,
Zhao Q and Liu Z: A promoter polymorphism of neurotrophin 3 gene is
associated with curve severity and bracing effectiveness in
adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:127–133.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ryzhkov II, Borzilov EE, Churnosov MI,
Ataman AV, Dedkov AA and Polonikov AV: Transforming growth factor
beta 1 is a novel susceptibility gene for adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:E699–E704. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ogura Y, Kou I, Miura S, Takahashi A, Xu
L, Takeda K, Takahashi Y, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, et al: A
functional SNP in BNC2 is associated with adolescent idiopathic
scoliosis. Am J Hum Genet. 97:337–342. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Takahashi Y, Kou I, Takahashi A, Johnson
TA, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, Ito M, Minami S, Yanagida H, et al:
A genome-wide association study identifies common variants near
LBX1 associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Genet.
43:1237–1240. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guo L, Yamashita H, Kou I, Takimoto A,
Mrguro-Horie M, Horike S, Sakuma T, Miura S, Adachi T, Tamamoto T,
et al: Functional investigation of a non-coding variant associated
with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in zebrafish: Elevated
expression of the ladybird homeobox gene causes body axis
deformation. PLoS Genet. 12(e1005802)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kou I, Takahashi Y, Johnson TA, Tkahashi
A, Guo L, Dai J, Qiu X, Sharma S, Takimoto A, Ogura Y, et al:
Genetic variants in GPR126 are associated with adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Genet. 45:676–679. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
De Salvatore S, Ruzzini L, Longo UG,
Marino M, Greco A, Piergentili I, Costici PF and Denaro V:
Exploring the association between specific genes and the onset of
idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review. BMC Med Genomics.
15(115)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fei Q, Wu Z, Wang H, Zhou X, Wang N, Ding
Y, Wang Y and Qiu G: The association analysis of TBX6 polymorphism
with susceptibility to congenital scoliosis in a Chinese Han
population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:983–988. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu N, Ming X, Xiao J, Wu Z, Chen X,
Shinawi M, Shen Y, Yu G, Liu J, Xie H, et al: TBX6 null variants
and a common hypomorphic allele in congenital scoliosis. N Engl J
Med. 372:341–350. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Takeda K, Kou I, Kawakami N, Iida A,
Nakajima M, Ogura Y, Imagawa E, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, Yasuhiko Y,
et al: Compound heterozygosity for null mutations and a common
hypomorphic risk haplotype in TBX6 causes congenital scoliosis. Hum
Mutat. 38:317–323. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Otomo N, Takeda K, Kawai S, Kou I, Guo L,
Osawa M, Alev C, Kawakami N, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, et al:
Bi-allelic loss of function variants of TBX6 causes a spectrum of
malformation of spine and rib including congenital scoliosis and
spondylocostal dysostosis. J Med Genet. 56:622–628. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chapman DL, Agulnik I, Hancock S, Silver
LM and Papaioannou VE: Tbx6, a mouse T-Box gene implicated in
paraxial mesoderm formation at gastrulation. Dev Biol. 180:534–542.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sadahiro T, Isomi M, Muraoka N, Kojima H,
Haginiwa S, Kurotsu S, Tamura F, Tani H, Tohyama S, Fujita J, et
al: Tbx6 induces nascent mesoderm from pluripotent stem cells and
temporally controls cardiac versus somite lineage diversification.
Cell Stem Cell. 23:382–395.e5. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chapman DL and Papaioannou VE: Three
neural tubes in mouse embryos with mutations in the T-box gene
Tbx6. Nature. 391:695–697. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Takemoto T, Uchikawa M, Yoshida M, Bell
DM, Lovell-Badge R, Papaioannou VE and Kondoh H: Tbx6-dependent
Sox2 regulation determines neural or mesodermal fate in axial stem
cells. Nature. 470:394–398. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Takeda K, Kou I, Mizumoto S, Yamada S,
Kawakami N, Nakajima M, Otomo N, Ogura Y, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, et
al: Screening of known disease genes in congenital scoliosis. Mol
Genet Genomic Med. 6:966–974. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Turnpenny PD, Sloman M, Dunwoodie S, Adam
MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Gripp KW,
et al: Spondylocostal Dysostosis, Autosomal Recessive. 2009 Aug 25
(Updated 2023 Aug 17). Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA,
Wallace SE, Bean LJ, Gripp KW and Amemiya A (eds). GeneReviews,
Seattle, WA, 1993.
|
|
29
|
Oda I, Cunningham BW, Buckley RA, Goebel
MJ, Haggerty CJ, Orbegoso CM and McAfee PC: Does spinal kyphotic
deformity influence the biomechanical characteristics of the
adjacent motion segments? An in vivo animal model. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 24:2139–2146. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chae U, Park NR, Kim ES, Choi JY, Yim M,
Lee HS, Lee SR, Lee S, Paerk JW and Lee DS: IDH2-deficient mice
develop spinal deformities with aging. Physiol Res. 67:487–494.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zaghini A, Sarli G, Barboni C, Sanapo M,
Pellegrino V, Diana A, Linta N, Rambaldi J, D'Apice MR, Murdocca M,
et al: Long term breeding of the Lmna G609G progeric mouse:
Characterization of homozygous and heterozygous models. Exp
Gerontol. 130(110784)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Torres HM, Rodezno-Antunes T, VanCleave A,
Cao Y, Callahan DL, Westendorf JJ and Tao J: Precise detection of a
murine germline mutation of the Notch3 gene associated with
kyphosis and developmental disorders. J Adv Vet Anim Res. 8:7–13.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ishibashi M: Congenital vertebral
malformation (Ishibashi rats). In: Handbook on Animal Models of
Human Diseases. Kawamata J and Matushita H (eds). Ishiyaku Shuppan,
Tokyo, pp430-434, 1979.
|
|
34
|
Seki T, Shimokawa N, Iizuka H, Takagishi K
and Koibuchi N: Abnormalities of vertebral formation and Hox
expression in congenital kyphoscoliotic rat. Mol Cell Biochem.
312:193–199. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Esapa CT, Piret SE, Nesbit MA, Thomas GP,
Coulton LA, Gallagher OM, Simon MM, Kumar S, Mallon AM, Bellantuono
I, et al: An N-Ethyl-N-Nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenized mouse model
for autosomal dominant nonsyndromic kyphoscoliosis due to vertebral
fusion. JBMR Plus. 2:154–163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Moritake S, Yamamuro T, Yamada J and
Watanabe H: Progression of congenital kyphosis in Ishibashi rats.
Acta Orthop Scand. 53:841–846. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Moritake S, Yamamuro T and Yamada J:
Effects of sex hormones on congenital kyphosis in Ishibashi rats.
Acta Orthop Scand. 57:62–66. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Maekawa R, Yamada J and Nikaido H:
Genetical studies of low plasma alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
in the IS strain of rats. Jikken Dobutsu. 31:13–19. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yamada J, Nikaido H, Moritake S and
Maekawa R: Genetic analyses of the vertebral anomalies of the IS
strain of rat and the development of a BN congenic line with the
anomalies. Lab Anim. 16:40–47. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Takano M, Katsumata Y, Ogawa J, Ebata T,
Urasoko Y, Asano Y, Serikawa T and Kuramoto T: Morphological
features of mutant rat, IS-Tlk/Kyo, fetuses with caudal vertebral
anomalies. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 52:42–47. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Takano M, Ogawa E, Saitou T, Yamaguchi Y,
Asano Y, Serikawa T and Kuramoto T: Morphological features of adult
rats of IS/Kyo and IS-Tlk/Kyo strains with lumbar and caudal
vertebral anomalies. Exp Anim. 63:269–275. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Satokata I, Benson G and Maas R: Sexually
dimorphic sterility phenotypes in Hoxa10-deficient mice. Nature.
374:460–463. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Favier B, Rijli FM, Fromental-Ramain C,
Fraulob V, Chambon P and Dollé P: Functional cooperation between
the non-paralogous genes Hoxa-10 and Hoxd-11 in the developing
forelimb and axial skeleton. Development. 122:449–460.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Davis AP, Witte DP, Hsieh-Li HM, Potter SS
and Capecchi MR: Absence of radius and ulna in mice lacking hoxa-11
and hoxd-11. Nature. 375:791–795. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Boulet AM and Capecchi MR: Duplication of
the Hoxd11 gene causes alterations in the axial and appendicular
skeleton of the mouse. Dev Biol. 249:96–107. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tsunoda D, Iizuka H, Ichinose T, Iizuka Y,
Mieda T, Shimokawa N, Takagishi K and Koibuchi N: The Trk family of
neurotrophin receptors is downregulated in the lumbar spines of
rats with congenital kyphoscoliosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 412:11–18.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sonoda H, Iizuka H, Ishiwata S, Tsunoda D,
Abe M, Takagishi K, Chikuda H, Koibuchi N and Shimokawa N: The
retinol-retinoic acid metabolic pathway is impaired in the lumbar
spine of a rat model of congenital kyphoscoliosis. J Cell Biochem.
120:15007–15017. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ishiwata S, Iizuka H, Sonoda H, Tsunoda D,
Tajika Y, Chikuda H, Koibuchi N and Shimokawa N: Upregulated
miR-224-5p suppresses osteoblast differentiation by increasing the
expression of Pai-1 in the lumbar spine of a rat model of
congenital kyphoscoliosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 475:53–62.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Maskos U and Southern EM: A novel method
for the analysis of multiple sequence variants by hybridisation to
oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2267–2268. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW and Brown PO:
Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a
complementary DNA microarray. Science. 270:467–470. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Emili AQ and Cagney G: Large-scale
functional analysis using peptide or protein arrays. Nat
Biotechnol. 18:393–397. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Uren RT and Turnley AM: Regulation of
neurotrophin receptor (Trk) signaling: Suppressor of cytokines
signaling 2 (SOCS2) is a new player. Front Mol Neurosci.
7(39)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tomlinson RE, Li Z, Zhang Q, Goh BC, Li Z,
Thorek DLJ, Rajbhandari L, Brushart TM, Minichiello L, Zhou F, et
al: NGF-TrkA signaling by sensory nerves coordinates the
vascularization and ossification of developing endochondral bone.
Cell Rep. 16:2723–2735. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li Z, Meyers CA, Chang L, Lee S, Li Z,
Tomlinson R, Hoke A, Clemens TL and James AW: Fracture repair
requires TrkA signaling by skeletal sensory nerves. J Clin Invest.
129:5137–5150. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Rivera KO, Russo F, Boileau RM, Tomlinson
RE, Miclau T, Marcucio RS, Desai TA and Bahney CS: Local injections
of beta-NGF accelerates endochondral fracture repair by promoting
cartilage to bone conversion. Sci Rep. 10(22241)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wheeler EF, Gong H, Grimes R, Benoit D and
Vazquez L: p75NTR and Trk receptors are expressed in reciprocal
patterns in a wide variety of non-neural tissues during rat
embryonic development, indicating independent receptor functions. J
Comp Neurol. 391:407–428. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yamashiro T, Fukunaga T, Yamashita K,
Kobashi N and Takano-Yamamoto T: Gene and protein expression of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB in bone and cartilage.
Bone. 28:404–409. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hutchison MR: BDNF alters ERK/p38 MAPK
activity ratios to promote differentiation in growth plate
chondrocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 26:1406–1416. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hutchison MR: Mice with a conditional
deletion of the neurotrophin receptor TrkB are dwarfed, and are
similar to mice with a MAPK14 deletion. PLoS One.
8(e66206)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Asaumi K, Nakanishi T, Asahara H, Inoue H
and Takigawa M: Expression of neurotrophins and their receptors
(TRK) during fracture healing. Bone. 26:625–633. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Su YW, Chung R, Ruan CS, Chim SM, Kuek V,
Dwivedi PP, Hassanshahi M, Chen KM, Xie Y, Chen L, et al:
Neurotrophin-3 induces BMP-2 and VEGF activities and promotes the
bony repair of injured growth plate cartilage and bone in rats. J
Bone Miner Res. 31:1258–1274. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Blomhoff R and Blomhoff HK: Overview of
retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol. 66:606–630.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
See AW, Kaiser ME, White JC and
Clagett-Dame M: A nutritional model of late embryonic vitamin A
deficiency produces defects in organogenesis at a high penetrance
and reveals new roles for the vitamin in skeletal development. Dev
Biol. 316:171–190. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Wang X, Liang J, Qiu
G and Liu J: Vitamin A deficiency induces congenital spinal
deformities in rats. PLoS One. 7(e46565)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Amengual J, Zhang N, Kemerer M, Maeda T,
Palczewski K and Von Lintig J: STRA6 is critical for cellular
vitamin A uptake and homeostasis. Hum Mol Genet. 23:5402–5417.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Boncinelli E, Simeone A, Acampora D and
Mavilio F: HOX gene activation by retinoic acid. Trends Genet.
7:329–334. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Marshall H, Morrison A, Studer M, Pöpperl
H and Krumlauf R: Retinoids and Hox genes. FASEB J. 10:969–978.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wellik DM and Capecchi MR: Hox10 and Hox11
genes are required to globally pattern the mammalian skeleton.
Science. 301:363–367. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Rogers MB: Receptor-selective retinoids
implicate retinoic acid receptor alpha and gamma in the regulation
of bmp-2 and bmp-4 in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell Growth
Differ. 7:115–122. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kobayashi M, Fujii M, Kurihara K and
Matsuoka I: Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and retinoic acid induce
neurotrophin-3 responsiveness in developing rat sympathetic
neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 53:206–217. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Nordin BE: Calcium and osteoporosis.
Nutrition. 13:664–686. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Matikainen N, Pekkarinen T, Ryhänen EM and
Schalin-Jäntti C: Physiology of calcium homeostasis: An overview.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 50:575–590. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M,
Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J and Hebert SC:
Cloning and characterization of an extracellular
Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature.
366:575–580. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cianferotti L, Gomes AR, Fabbri S, Tanini
A and Brandi ML: The calcium-sensing receptor in bone metabolism:
From bench to bedside and back. Osteoporos Int. 26:2055–2071.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Takahashi I, Watanabe Y, Sonoda H, Tsunoda
D, Amano I, Koibuchi N, Iizuka H and Shimokawa N: Calcium sensing
and signaling are impaired in the lumbar spine of a rat model of
congenital kyphosis. Eur Spine J. 32:3403–3412. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M,
Rosen TA, Levine JD and Julius D: The capsaicin receptor: A
heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature.
389:816–824. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Lieben L and Carmeliet G: The involvement
of TRP channels in bone homeostasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
3(99)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Liu N, Lu W, Dai X, Qu X and Zhu C: The
role of TRPV channels in osteoporosis. Mol Biol Rep. 49:577–585.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Idris AI, Landao-Bassonga E and Ralston
SH: The TRPV1 ion channel antagonist capsazepine inhibits
osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation in vitro and ovariectomy
induced bone loss in vivo. Bone. 46:1089–1099. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
He LH, Liu M, He Y, Xiao E, Zhao L, Zhang
T, Yang HQ and Zhang Y: TRPV1 deletion impaired fracture healing
and inhibited osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation. Sci Rep.
7(42385)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Lu SS, Zhang X, Soo C, Hsu T, Napoli A,
Aghaloo T, Wu BM, Tsou P, Ting K and Wang JC: The osteoinductive
properties of Nell-1 in a rat spinal fusion model. Spine J.
7:50–60. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Li C, Zhang X, Zheng Z, Nguyen A, Ting K
and Soo C: Nell-1 is a key functional modulator in
osteochondrogenesis and beyond. J Dent Res. 98:1458–1468.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Xu R, Zhang C, Shin DY, Kim JM, Lalani S,
Li N, Yang YS, Liu Y, Eiseman M, Davis RJ, et al: c-Jun N-terminal
kinases (JNKs) are critical mediators of osteoblast activity in
vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 32:1811–1815. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Ke D, Ji L, Wang Y, Fu X, Chen J, Wang F,
Zhao D, Xue Y, Lan X and Hou J: JNK1 regulates RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis via activation of a novel
Bcl-2-Beclin1-autophagy pathway. FASEB J. 33:11082–11095.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Fukada T, Civic N, Furuichi T, Shimoda S,
Mishima K, Higashiyama H, Idaira Y, Asada Y, Kitamura H, Yamasaki
S, et al: The zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 is required for
connective tissue development; its involvement in BMP/TGF-beta
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 3(e3642)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Moore BT and Xiao P: MiRNAs in bone
diseases. Microrna. 2:20–31. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Yang N, Wang G, Hu C, Shi Y, Liao L, Shi
S, Cai Y, Cheng S, Wang X, Liu Y, et al: Tumor necrosis factor
alpha suppresses the mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis promoter
miR-21 in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis. J Bone Miner
Res. 28:559–573. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Li H, Xie H, Liu W, Hu R, Huang H, Tan YF,
Xu K, Sheng ZF, Zhou HD, Wu XP and Luo XH: A novel microRNA
targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and
contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest.
119:3666–3677. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian
JB, Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: A program of microRNAs controls
osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor
Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9863–9868. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Luo Y, Cao X, Chen J, Gu J, Zhao J and Sun
J: MicroRNA-224 suppresses osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting
SMAD4. J Cell Physiol. 233:6929–6937. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ghosh AK, Bradham WS, Gleaves LA, De Taeye
B, Murphy SB, Covington JW and Vaughan DE: Genetic deficiency of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes cardiac fibrosis in aged
mice: Involvement of constitutive transforming growth factor-beta
signaling and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Circulation.
122:1200–1209. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Mao L, Kawao N, Tamura Y, Okumoto K, Okada
K, Yano M, Matsuo O and Kaji H: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
is involved in impaired bone repair associated with diabetes in
female mice. PLoS One. 9(e92686)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Ghali N, Sobey G and Burrows N:
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. BMJ. 366(l4966)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Nuytinck L, Freund M, Lagae L, Pierard GE,
Hermanns-Le T and De Paepe A: Classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
caused by a mutation in type I collagen. Am J Hum Genet.
66:1398–1402. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|