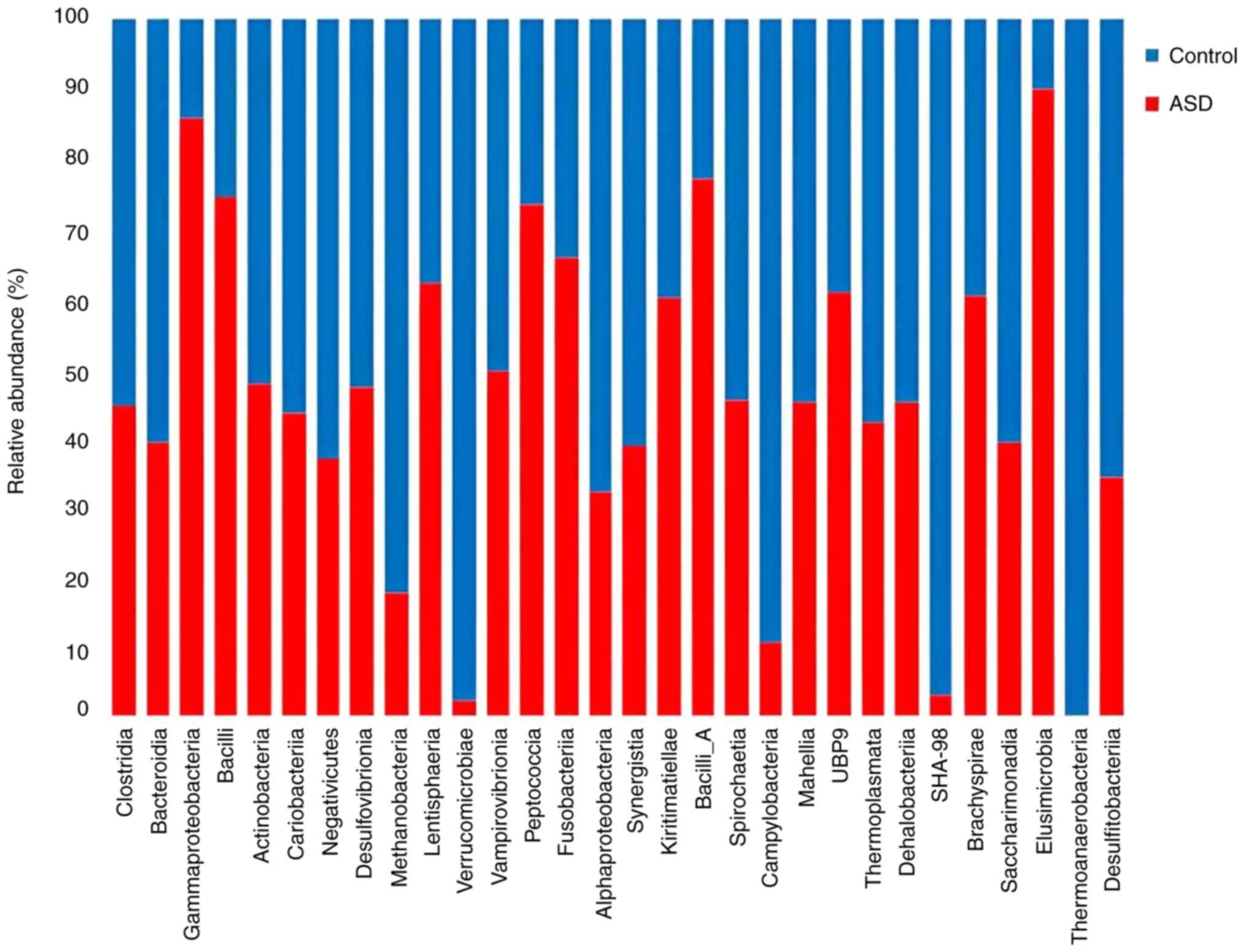
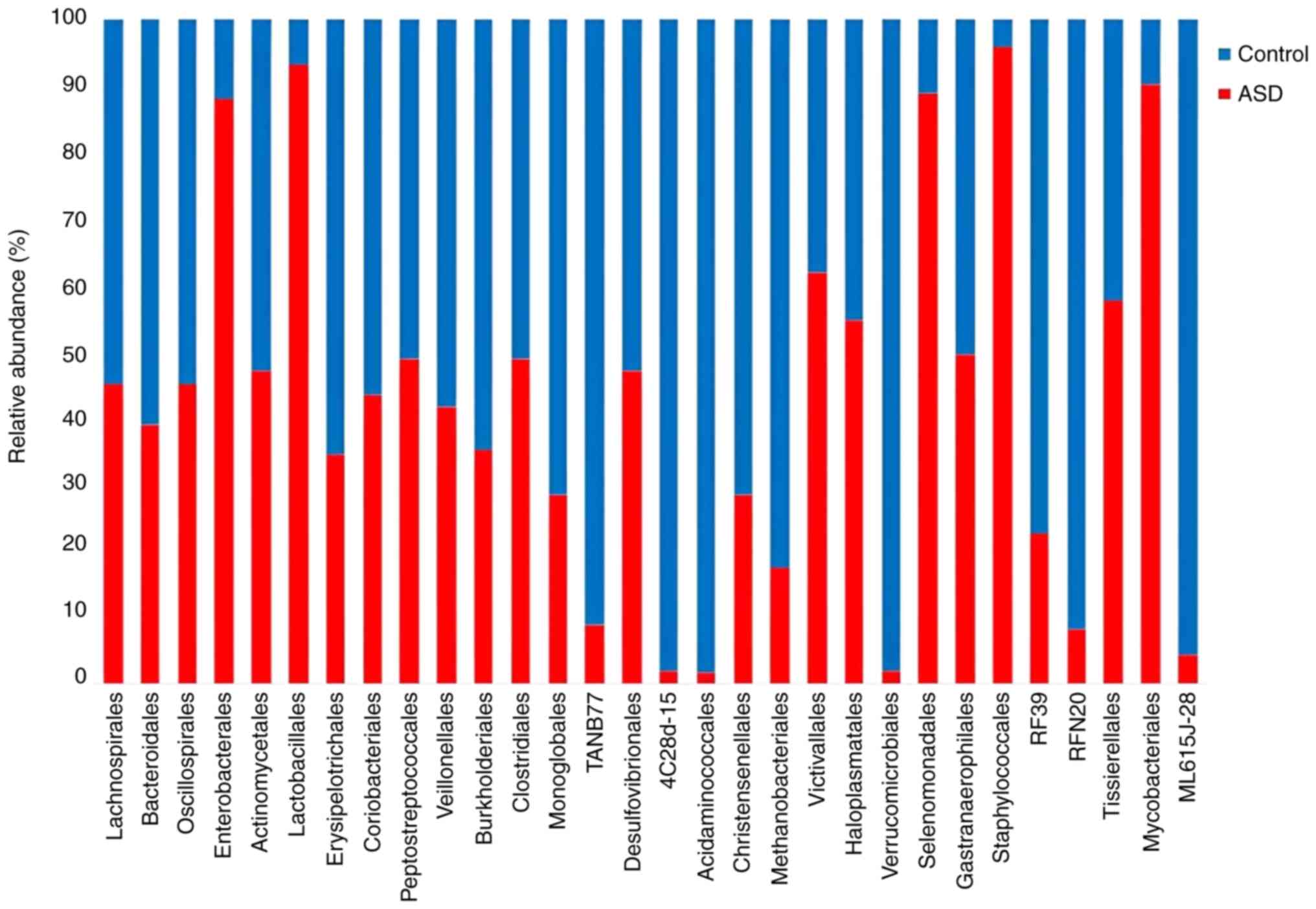
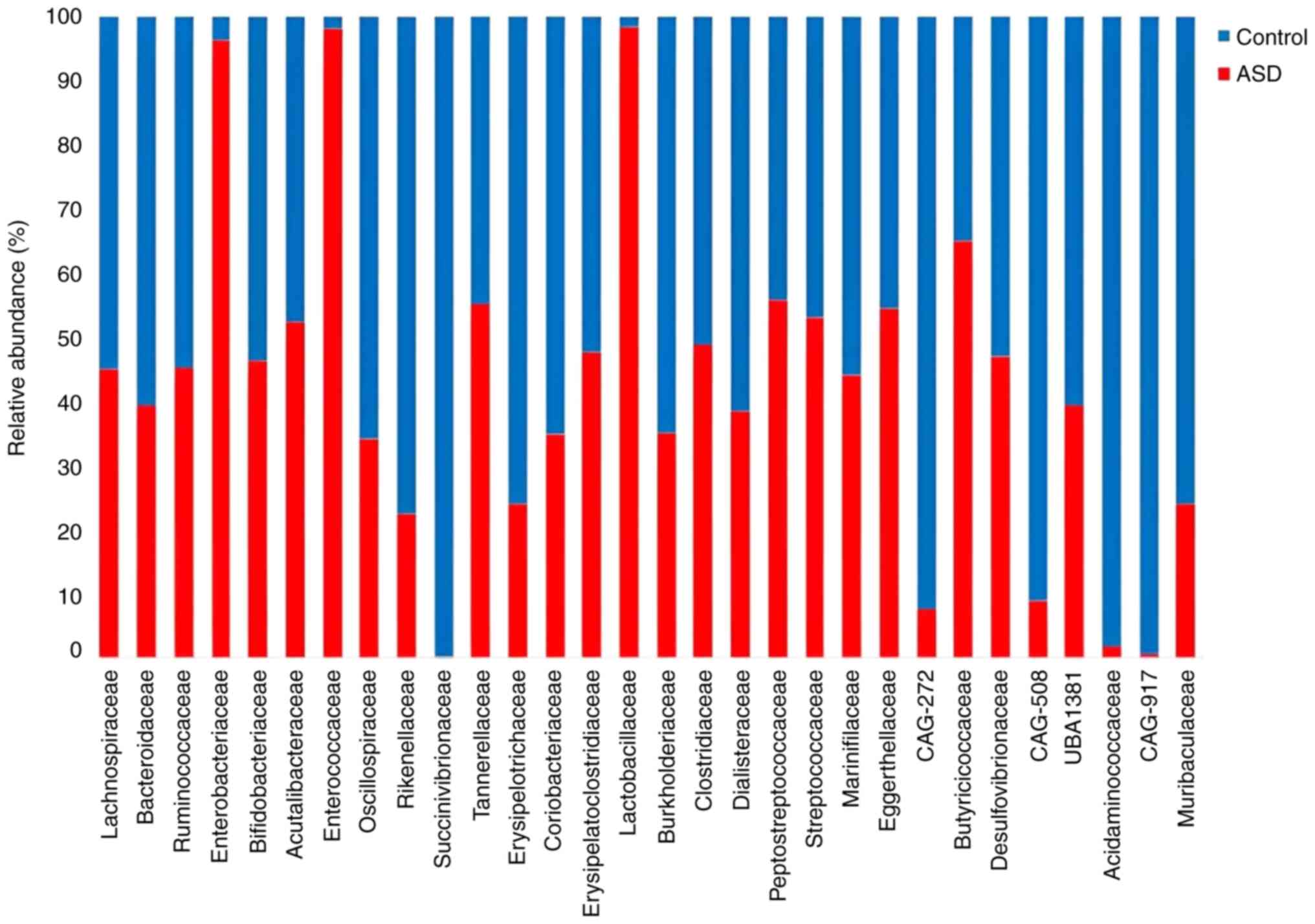
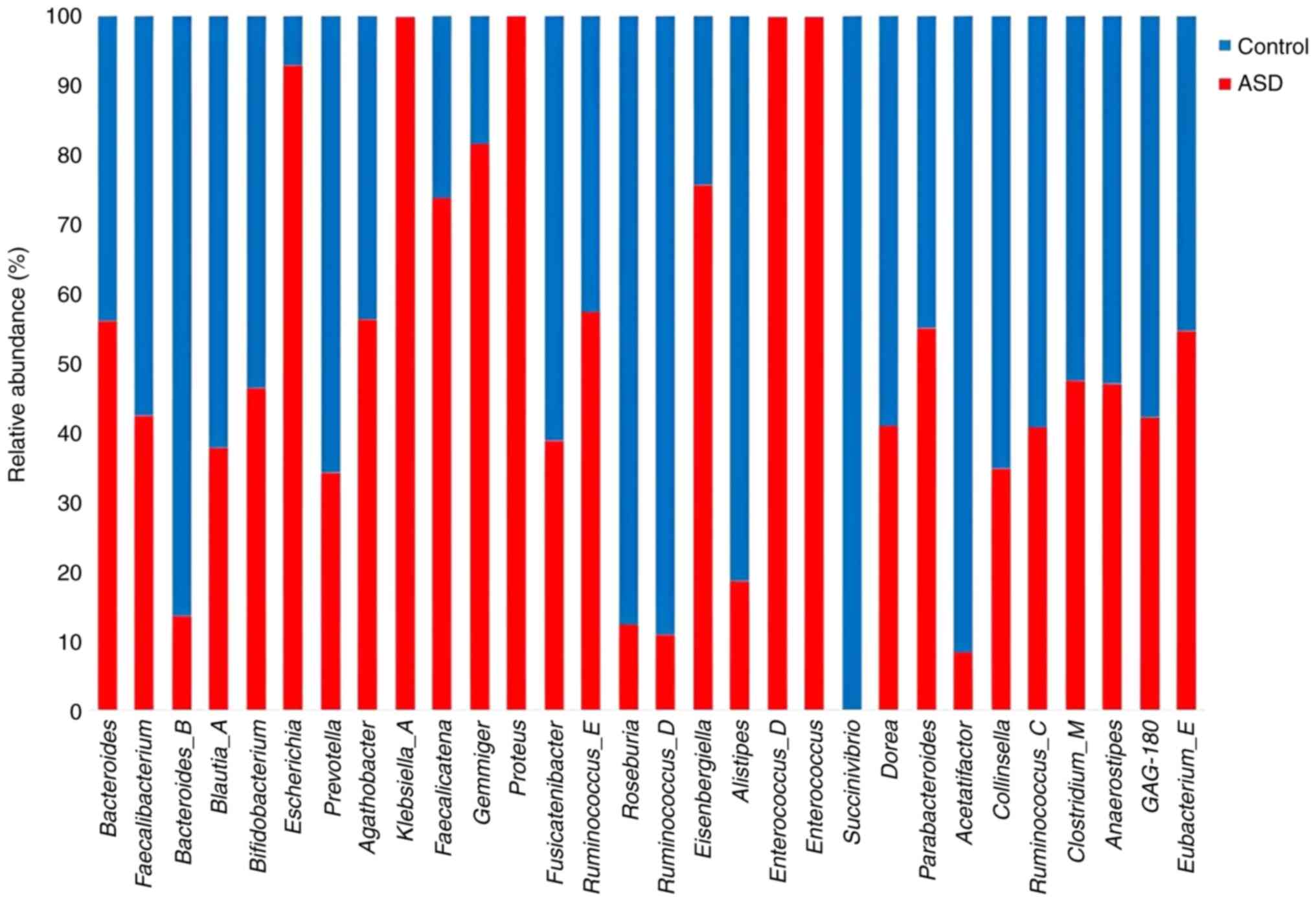
|
1
|
Bölte S, Girdler S and Marschik PB: The
contribution of environmental exposure to the etiology of autism
spectrum disorder. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:1275–1297. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kral TVE, Eriksen WT, Souders MC and
Pinto-Martin JA: Eating behaviors, diet quality, and
gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism spectrum
disorders: a brief review. J Pediatr Nurs. 28:548–556.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mukherjee SB: Autism spectrum
disorders-diagnosis and management. Indian J Pediatr. 84:307–314.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Heintz-Buschart A and Wilmes P: Human gut
microbiome: Function matters. Trends Microbiol. 26:563–574.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schären OP and Hapfelmeier S: Robust
microbe immune recognition in the intestinal mucosa. Genes Immun.
22:268–275. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ellis JL, Karl JP, Oliverio AM, Fu X,
Soares JW, Wolfe BE, Hernandez CJ, Mason JB and Booth SL: Dietary
vitamin K is remodeled by gut microbiota and influences community
composition. Gut Microbes. 13:1–16. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bosco N and Noti M: The aging gut
microbiome and its impact on host immunity. Genes Immun.
22:289–303. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu J, Wang K, Wang X, Pang Y and Jiang C:
The role of the gut microbiome and its metabolites in metabolic
diseases. Protein Cell. 12:360–373. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Davoli-Ferreira M, Thomson CA and McCoy
KD: Microbiota and microglia interactions in ASD. Front Immunol.
12(676255)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Han VX, Patel S, Jones HF and Dale RC:
Maternal immune activation and neuroinflammation in human
neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 17:564–579.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kushak RI, Sengupta A and Winter HS:
Interactions between the intestinal microbiota and epigenome in
individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol.
64:296–304. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Morais LH, Schreiber HL and Mazmanian SK:
The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat
Rev Microbiol. 19:241–255. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zengeler KE and Lukens JR: Innate immunity
at the crossroads of healthy brain maturation and
neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat Rev Immunol. 21:454–468.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shreiner AB, Kao JY and Young VB: The gut
microbiome in health and in disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
31:69–75. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mirzaei MK and Maurice CF: Ménage à trois
in the human gut: Interactions between host, bacteria and phages.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 15:397–408. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Saurman V, Margolis KG and Luna RA: Autism
spectrum disorder as a brain-gut-microbiome axis disorder. Dig Dis
Sci. 65:818–828. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lefter R, Ciobica A, Timofte D, Stanciu C
and Trifan A: A descriptive review on the prevalence of
gastrointestinal disturbances and their multiple associations in
autism spectrum disorder. Medicina (Kaunas). 56(11)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Penzol MJ, Salazar de Pablo G, Llorente C,
Moreno C, Hernández P, Dorado ML and Parellada M: Functional
gastrointestinal disease in autism spectrum disorder: A
retrospective descriptive study in a clinical sample. Front
Psychiatry. 10(179)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kang V, Wagner GC and Ming X:
Gastrointestinal dysfunction in children with autism spectrum
disorders. Autism Res. 7:501–506. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bresciani G, Da Lozzo P, Lega S, Bramuzzo
M, Di Leo G, Dissegna A, Colonna V, Barbi E, Carrozzi M and
Devescovi R: Gastrointestinal disorders and food selectivity:
Relationship with sleep and challenging behavior in children with
autism spectrum disorder. Children (Basel). 10(253)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lasheras I, Real-López M and Santabárbara
J: Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in autism spectrum
disorder: A meta-analysis. An Pediatr (Engl Ed). 99:102–110.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li Q, Han Y, Dy ABC and Hagerman RJ: The
gut microbiota and autism spectrum disorders. Front Cell Neurosci.
11(120)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Breitwieser FP, Lu J and Salzberg SL: A
review of methods and databases for metagenomic classification and
assembly. Brief Bioinform. 20:1125–1136. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mehra A, Arora G, Kaur M, Singh H, Singh B
and Kaur S: Gut microbiota and autism spectrum disorder: From
pathogenesis to potential therapeutic perspectives. J Tradit
Complement Med. 13:135–149. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mead J and Ashwood P: Evidence supporting
an altered immune response in ASD. Immunol Lett. 163:49–55.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen YC, Lin HY, Chien Y, Tung YH, Ni YH
and Gau SSF: Altered gut microbiota correlates with behavioral
problems but not gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with
autism. Brain Behav Immun. 106:161–178. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Meng F, Chen X, Chang T,
Huang H, He F and Zheng Y: Altered gut microbiota as potential
biomarker biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder in early
childhood. Neuroscience. 523:118–131. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Korteniemi J, Karlsson L and Aatsinki A:
Systematic review: Autism spectrum disorder and the gut microbiota.
Acta Psychiatr Scand. 148:242–254. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhong JG, Lan WT, Feng YQ, Li YH, Shen YY,
Gong JH, Zou Z and Hou X: Associations between dysbiosis gut
microbiota and changes of neurotransmitters and short-chain fatty
acids in valproic acid model rats. Front Physiol.
14(1077821)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kennedy MS and Chang EB: The microbiome:
Composition and locations. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 176:1–42.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Feng P, Zhao S, Zhang Y and Li E: A review
of probiotics in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders:
Perspectives from the gut-brain axis. Front Microbiol.
14(1123462)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Davies C, Mishra D, Eshraghi RS, Mittal J,
Sinha R, Bulut E, Mittal R and Eshraghi AA: Altering the gut
microbiome to potentially modulate behavioral manifestations in
autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav
Rev. 128:549–557. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Naveed M, Zhou QG, Xu C, Taleb A, Meng F,
Ahmed B, Zhang Y, Fukunaga K and Han F: Gut-brain axis: A matter of
concern in neuropsychiatric disorders…! Prog Neuropsychopharmacol
Biol. Psychiatry. 104(110051)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Maiuolo J, Gliozzi M, Musolino V, Carresi
C, Scarano F, Nucera S, Scicchitano M, Oppedisano F, Bosco F, Ruga
S, et al: The contribution of gut microbiota-brain axis in the
development of brain disorders. Front Neurosci.
15(616883)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Muller PA, Matheis F, Schneeberger M,
Kerner Z, Jové V and Mucida D: Microbiota-modulated
CART+ enteric neurons autonomously regulate blood
glucose. Science. 370:314–321. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shi Y, Zhang L, Do KA, Peterson CB and
Jenq RR: aPCoA: Covariate adjusted principal coordinates analysis.
Bioinformatics. 36:4099–4101. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Finegold SM, Dowd SE, Gontcharova V, Liu
C, Henley KE, Wolcott RD, Youn E, Summanen PH, Granpeesheh D, Dixon
D, et al: Pyrosequencing study of fecal microflora of autistic and
control children. Anaerobe. 16:444–453. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L,
Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni
ME, Gobbetti M and Francavilla R: Fecal microbiota and metabolome
of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not
otherwise specified. PLoS One. 8(e76993)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shin NR, Whon TW and Bae JW:
Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut
microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 33:496–503. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhu Y, Carvey PM and Ling Z: Altered
glutathione homeostasis in animals prenatally exposed to
lipopolysaccharide. Neurochem Int. 50:671–680. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chauhan A and Chauhan V: Oxidative stress
in autism. Pathophysiology. 13:171–181. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Tomova A, Husarova V, Lakatosova S, Bakos
J, Vlkova B, Babinska K and Ostatnikova D: Gastrointestinal
microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol Behav.
138:179–187. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li QM, Zhou YL, Wei ZF and Wang Y:
Phylogenomic insights into distribution and adaptation of
Bdellovibrionota in marine waters. Microorganisms.
9(757)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Varon M: Selection of predation-resistant
bacteria in continuous culture. Nature. 277:386–388. 1979.
|
|
45
|
Zou R, Xu F, Wang Y, Duan M, Guo M, Zhang
Q, Zhao H and Zheng H: Changes in the gut microbiota of children
with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res. 13:1614–1625.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Espín JC, González-Sarrías A and
Tomás-Barberán FA: The gut microbiota: A key factor in the
therapeutic effects of (poly)phenols. Biochem Pharmacol. 139:82–93.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Settanni CR, Bibbò S, Ianiro G, Rinninella
E, Cintoni M, Mele MC, Cammarota G and Gasbarrini A:
Gastrointestinal involvement of autism spectrum disorder: Focus on
gut microbiota. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:599–622.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gyawali S and Patra BN: Trends in concept
and nosology of autism spectrum disorder: A review. Asian J
Psychiatr. 40:92–99. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Pulikkan J, Mazumder A and Grace T: Role
of the gut microbiome in autism spectrum disorders. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1118:253–269. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lowe SE, Jain MK and Zeikus JG: Biology,
ecology, and biotechnological applications of anaerobic bacteria
adapted to environmental stresses in temperature, pH, salinity, or
substrates. Microbiol Rev. 57:451–509. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Van Zyl WH and
Pretorius IS: Microbial cellulose utilization: Fundamentals and
biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 66:506–577. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wiegel J, Mothershed CP and Puls J:
Differences in xylan degradation by various noncellulolytic
thermophilic anaerobes and Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 49:656–659. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shukla SK, Khan A and Rao TS: Microbial
fouling in water treatment plants. In: Microbial and Natural
Macromolecules. Elsevier, pp589-622, 2021.
|
|
54
|
Pozuelo M, Panda S, Santiago A, Mendez S,
Accarino A, Santos J, Guarner F, Azpiroz F and Manichanh C:
Reduction of butyrate- and methane-producing microorganisms in
patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Sci Rep.
5(12693)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Anderson JR, Carroll I, Azcarate-Peril MA,
Rochette AD, Heinberg LJ, Peat C, Steffen K, Manderino LM, Mitchell
J and Gunstad J: A preliminary examination of gut microbiota,
sleep, and cognitive flexibility in healthy older adults. Sleep
Med. 38:104–107. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Plaza-Díaz J, Gómez-Fernández A, Chueca N,
Torre-Aguilar MJ, Gil Á, Perez-Navero JL, Flores-Rojas K,
Martín-Borreguero P, Solis-Urra P, Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, et al: Autism
spectrum disorder (ASD) with and without mental regression is
associated with changes in the fecal microbiota. Nutrients.
11(337)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Chandarana KA, Gohil K, Dwivedi MK and
Amaresan N: Culture-independent and culture-dependent approaches in
symbiont analysis. In: Microbial Symbionts. Elsevier, pp723-742,
2023.
|
|
58
|
Turnbull PC, Kramer J and Melling J:
Bacillus: Chapter 15. Medical microbiology, pp1-7, 1996.
|
|
59
|
Bujňáková D, Puvača N and Ćirković I:
Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance of
Enterobacterales. Microorganisms. 10(1588)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Bhakdi S and Tranum-Jensen J: Alpha-toxin
of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 55:733–751.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gupta RS, Lo B and Son J: Phylogenomics
and comparative genomic studies robustly support division of the
genus Mycobacterium into an emended genus Mycobacterium and four
novel genera. Front Microbiol. 9(67)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Manjeese W, Mvubu NE, Steyn AJ and Mpofana
T: Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced maternal immune
activation promotes autism-like phenotype in infected mice
offspring. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18(4513)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Baldelli V, Scaldaferri F, Putignani L and
Del Chierico F: The role of Enterobacteriaceae in gut
microbiota dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Microorganisms. 9(697)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Pulikkan J, Maji A, Dhakan DB, Saxena R,
Mohan B, Anto MM, Agarwal N, Grace T and Sharma VK: Gut microbial
dysbiosis in Indian children with autism spectrum disorders. Microb
Ecol. 76:1102–1114. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Derrien M and van Hylckama Vlieg JE: Fate,
activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut
microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 23:354–366. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Martín R, Miquel S, Benevides L,
Bridonneau C, Robert V, Hudault S, Chain F, Berteau O, Azevedo V,
Chatel JM, et al: Functional characterization of novel
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains isolated from healthy
volunteers: A step forward in the use of F. prausnitzii as a
next-generation probiotic. Front Microbiol. 8(1226)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Milani C, Ticinesi A, Gerritsen J,
Nouvenne A, Lugli GA, Mancabelli L, Turroni F, Duranti S,
Mangifesta M, Viappiani A, et al: Gut microbiota composition and
Clostridium difficile infection in hospitalized elderly
individuals: A metagenomic study. Sci Rep. 6(25945)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Labus JS, Hollister EB, Jacobs J, Kirbach
K, Oezguen N, Gupta A, Acosta J, Luna RA, Aagaard K, Versalovic J,
et al: Differences in gut microbial composition correlate with
regional brain volumes in irritable bowel syndrome. Microbiome.
5(49)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Bryant MP and Small N: Characteristics of
two new genera of anaerobic curved rods isolated from the rumen of
cattle. J Bacteriol. 72:22–26. 1956.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Wang L, Cen S, Wang G, Lee YK, Zhao J,
Zhang H and Chen W: Acetic acid and butyric acid released in large
intestine play different roles in the alleviation of constipation.
J Funct Foods. 69(103953)2020.
|
|
71
|
Ma B, Liang J, Dai M, Wang J, Luo J, Zhang
Z and Jing J: Altered gut microbiota in Chinese children with
autism spectrum disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
9(40)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Cui Y, Zhang L, Wang X, Yi Y, Shan Y, Liu
B, Zhou Y and Lü X: Roles of intestinal Parabacteroides in
human health and diseases. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
369(fnac072)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ho LKH, Tong VJW, Syn N, Nagarajan N, Tham
EH, Tay SK, Shorey S, Tambyah PA and Law ECN: Gut microbiota
changes in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic
review. Gut Pathog. 12(6)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
MacFabe DF, Cain DP, Rodriguez-Capote K,
Franklin AE, Hoffman JE, Boon F, Taylor AR, Kavaliers M and
Ossenkopp KP: Neurobiological effects of intraventricular propionic
acid in rats: Possible role of short chain fatty acids on the
pathogenesis and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders.
Behav Brain Res. 176:149–169. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Hamilton AL, Kamm MA, Ng SC and Morrison
M: Proteus spp. as putative gastrointestinal pathogens. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 31:e00085–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Iglesias-Vázquez L, Van Ginkel Riba G,
Arija V and Canals J: Composition of gut microbiota in children
with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Nutrients. 12(792)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Srikantha P and Mohajeri MH: The possible
role of the microbiota-gut-brain-axis in autism spectrum disorder.
Int J Mol Sci. 20(2115)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Shen J: Modeling the glutamate-glutamine
neurotransmitter cycle. Front Neuroenergetics. 5(1)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Horder J, Petrinovic MM, Mendez MA, Bruns
A, Takumi T, Spooren W, Barker GJ, Künnecke B and Murphy DG:
Glutamate and GABA in autism spectrum disorder-a translational
magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in man and rodent models.
Transl Psychiatry. 8(106)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Wierońska JM, Stachowicz K, Nowak G and
Pilc A: The loss of glutamate-GABA harmony in anxiety disorders.
Anxiety disord. 24:135–156. 2011.
|
|
81
|
Kang DW, Park JG, Ilhan ZE, Wallstrom G,
Labaer J, Adams JB and Krajmalnik-Brown R: Reduced incidence of
Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of
autistic children. PLoS One. 8(e68322)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
McNabney SM and Henagan TM: Short chain
fatty acids in the colon and peripheral tissues: A focus on
butyrate, colon cancer, obesity and insulin resistance. Nutrients.
9(1348)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Scott KP, Martin JC, Campbell G, Mayer CD
and Flint HJ: Whole-genome transcription profiling reveals genes
up-regulated by growth on fucose in the human gut bacterium
‘Roseburia inulinivorans’. J Bacteriol. 188:4340–4349.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Barratt MJ, Nuzhat S, Ahsan K, Frese SA,
Arzamasov AA, Sarker SA, Islam MM, Palit P, Islam MR, Hibberd MC,
et al: Bifidobacterium infantis treatment promotes weight
gain in Bangladeshi infants with severe acute malnutrition. Sci
Transl Med. 14(eabk1107)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Högenauer C, Langner C, Beubler E, Lippe
IT, Schicho R, Gorkiewicz G, Krause R, Gerstgrasser N, Krejs GJ and
Hinterleitner TA: Klebsiella oxytoca as a causative organism
of antibiotic-associated hemorrhagic colitis. N Engl J Med.
355:2418–2426. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Herzog KA, Schneditz G, Leitner E, Feierl
G, Hoffmann KM, Zollner-Schwetz I, Krause R, Gorkiewicz G, Zechner
EL and Högenauer C: Genotypes of Klebsiella oxytoca isolates
from patients with nosocomial pneumonia are distinct from those of
isolates from patients with antibiotic-associated hemorrhagic
colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 52:1607–1616. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Sievert DM, Ricks P, Edwards JR, Schneider
A, Patel J, Srinivasan A, Kallen A, Limbago B and Fridkin S:
National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Team and Participating
NHSN Facilities. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with
healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the
National healthcare safety network at the centers for disease
control and prevention, 2009-2010. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol.
34:1–14. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Molton JS, Tambyah PA, Ang BSP, Ling ML
and Fisher DA: The global spread of healthcare-associated
multidrug-resistant bacteria: A perspective from Asia. Clin Infect
Dis. 56:1310–1318. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Hawari I, Eskandar MB and Alzeer S: The
role of lead, manganese, and zinc in autism spectrum disorders
(ASDS) and attention-deficient hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A
case-control study on Syrian children affected by the Syrian
crisis. Biol Trace Elem Res. 197:107–114. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Faber S, Zinn GM, Kern JC II and Kingston
HM: The plasma zinc/serum copper ratio as a biomarker in children
with autism spectrum disorders. Biomarkers. 14:171–180.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Ji X, Grandner MA and Liu J: The
relationship between micronutrient status and sleep patterns: A
systematic review. Public Health Nutr. 20:687–701. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Liu J, Zhou G, Wang Y, Ai Y, Pinto-Martin
J and Liu X: Sleep problems, fatigue, and cognitive performance in
Chinese kindergarten children. J Pediatr. 161:520–525.e2.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Kawamura T, Ogawa Y, Nakamura Y, Nakamizo
S, Ohta Y, Nakano H, Kabashima K, Katayama I, Koizumi S, Kodama T,
et al: Severe dermatitis with loss of epidermal Langerhans cells in
human and mouse zinc deficiency. J Clin Invest. 122:722–732.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Prasad KM, Watson AMM, Dickerson FB,
Yolken RH and Nimgaonkar VL: Exposure to herpes simplex virus type
1 and cognitive impairments in individuals with schizophrenia.
Schizophr Bull. 38:1137–1148. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Hagmeyer S, Haderspeck JC and Grabrucker
AM: Behavioral impairments in animal models for zinc deficiency.
Front Behav Neurosci. 8(443)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Cezar LC, Kirsten TB, da Fonseca CCN, de
Lima APN, Bernardi MM and Felicio LF: Zinc as a therapy in a rat
model of autism prenatally induced by valproic acid. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 84:173–180. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Lakshmi Priya MD and Geetha A: Level of
trace elements (copper, zinc, magnesium and selenium) and toxic
elements (lead and mercury) in the hair and nail of children with
autism. Biol Trace Elem Res. 142:148–158. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Samal L and Mishra C: Significance of
nickel in livestock health and production. Int J Agro Vet Med Sci.
5:349–361. 2011.
|
|
99
|
Denkhaus E and Salnikow K: Nickel
essentiality, toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 42:35–56. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Costa-Pinto FA and Basso AS: Neural and
behavioral correlates of food allergy. Chem Immunol Allergy.
98:222–239. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Fiore M, Barone R, Copat C, Grasso A,
Cristaldi A, Rizzo R and Ferrante M: Metal and essential element
levels in hair and association with autism severity. J Trace Elem
Med Biol. 57(126409)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Das KK, Das SN and Dhundasi SA: Nickel,
its adverse health effects & oxidative stress. Indian J Med
Res. 128:412–425. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wang M, Hossain F, Sulaiman R and Ren X:
Exposure to inorganic arsenic and lead and autism spectrum disorder
in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chem Res
Toxicol. 32:1904–1919. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Saghazadeh A, Ahangari N, Hendi K, Saleh F
and Rezaei N: Status of essential elements in autism spectrum
disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Neurosci.
28:783–809. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Zhang C, Ge J, Lv M, Zhang Q, Talukder M
and Li JL: Selenium prevent cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity through
modulation of endoplasmic reticulum-resident selenoproteins and
attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Environ Pollut.
260(113873)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|