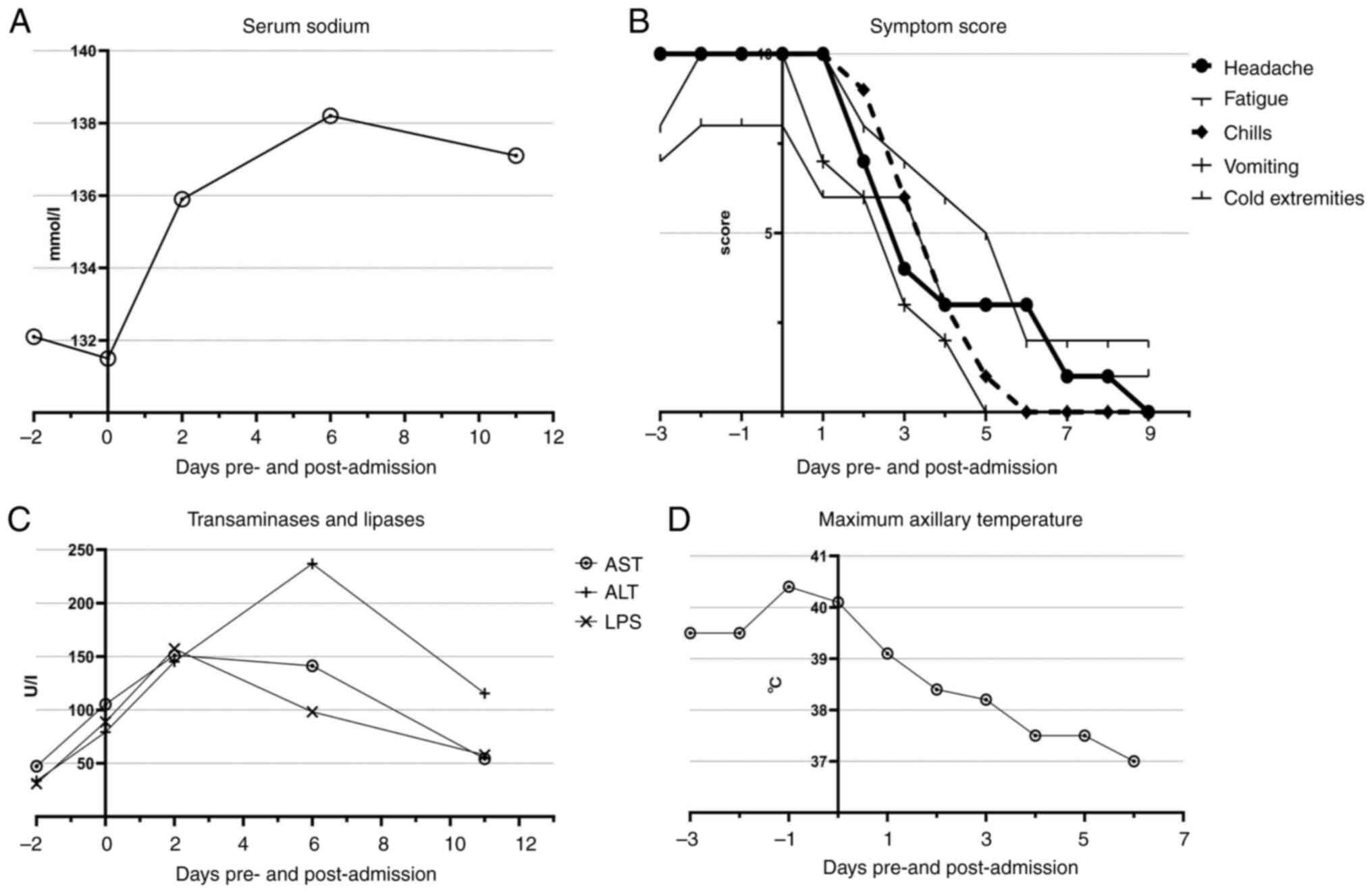
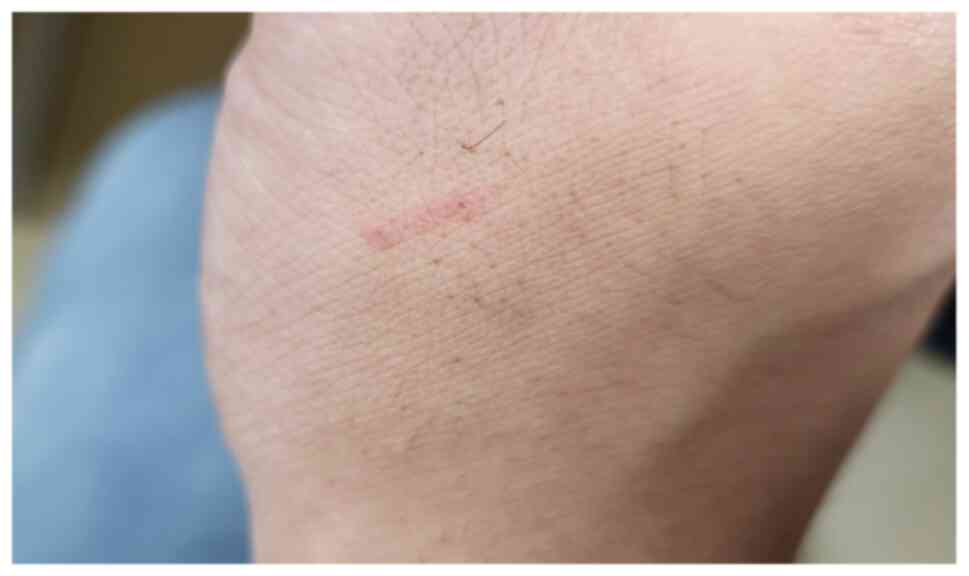
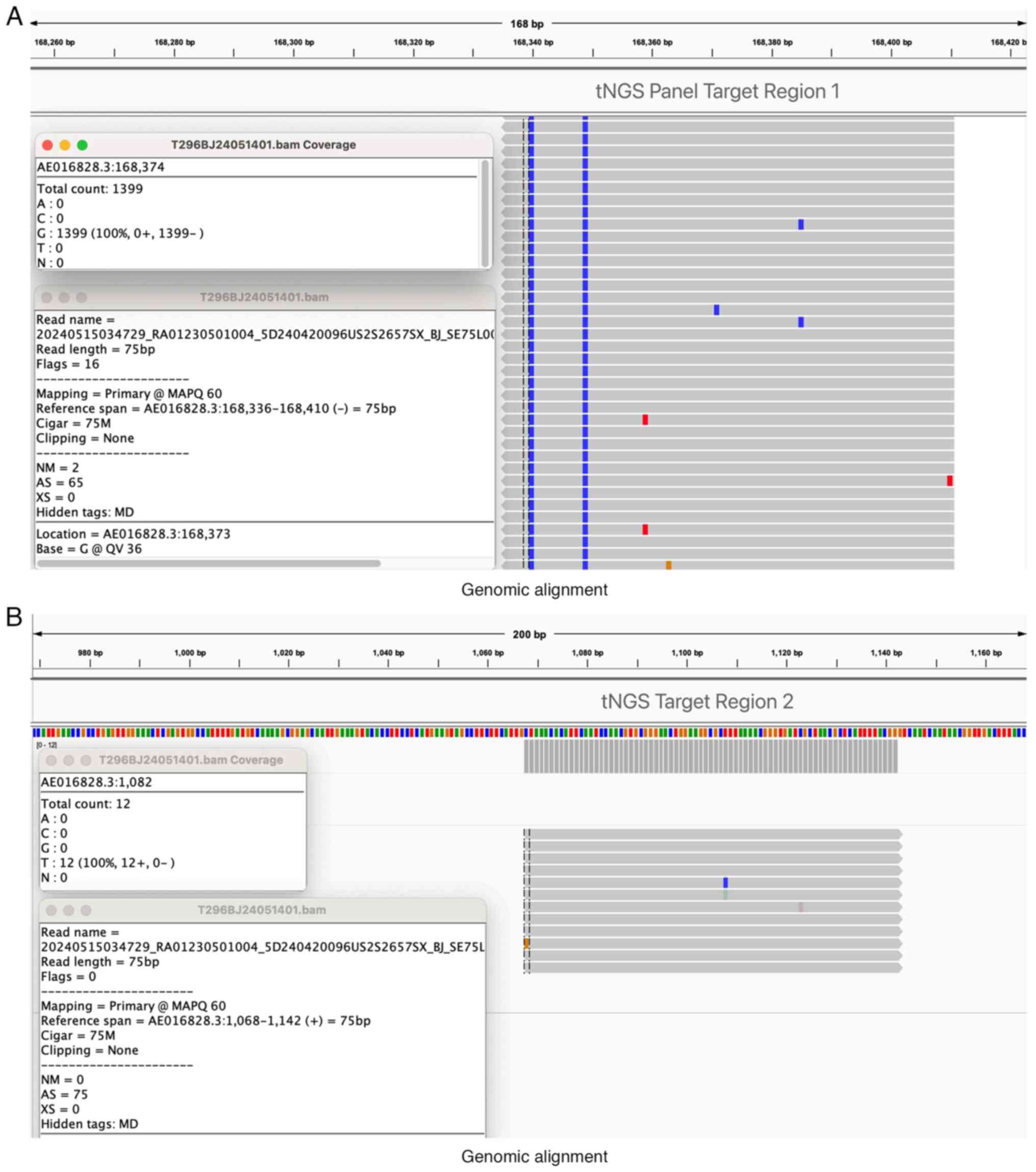
|
1
|
Duron O, Sidi-Boumedine K, Rousset E,
Moutailler S and Jourdain E: The importance of ticks in Q fever
transmission: What has (and has not) been demonstrated? Trends
Parasitol. 31:536–552. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pacheco RC, Echaide IE, Alves RN, Beletti
ME, Nava S and Labruna MB: Coxiella burnetii in ticks
Argentina. Emerg Infect Dis. 19:344–346. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Borawski K, Dunaj J, Czupryna P, Pancewicz
S, Świerzbińska R, Żebrowska A and Moniuszko-Malinowska A:
Assessment of Coxiella burnetii presence after tick bite in
north-eastern Poland. Infection. 48:85–90. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dehhaghi M, Kazemi Shariat Panahi H,
Holmes EC, Hudson BJ, Schloeffel R and Guillemin GJ: Human
tick-borne diseases in Australia. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
9(3)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Celina SS and Cerný J: Coxiella
burnetii in ticks livestock pets and wildlife: A mini-review.
Front Vet Sci. 9(1068129)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sopena N, Force L, Pedro-Botet ML,
Barrufet P, Sauca G, García-Núñez M, Tolchinsky G, Capdevila JA and
Sabrià M: Sporadic and epidemic community legionellosis: Two faces
of the same illness. Eur Respir J. 29:138–142. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cunha BA: The clinical diagnosis of
Legionnaires' disease: The diagnostic value of combining
non-specific laboratory tests. J Infect. 56:395–398.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Carratalà J and Garcia-Vidal C: An update
on Legionella. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 23:152–157.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Zheng J, Wang W, Wei W and Li K:
Diurnal questing activity of Haemaphysalis longicornis
(Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs in Xiaowutai mountain area. Chin J
Zoonoses. 35:779–784. 2019.
|
|
10
|
Zhu B, Lang S, Bian Y, et al: Epidemic
risk and response measures of novel tick-borne infectious diseases
in China. Chin Front Health Quarantine. 47:431–435. 2024.
|
|
11
|
Souche E, Beltran S, Brosens E, Belmont
JW, Fossum M, Riess O, Gilissen C, Ardeshirdavani A, Houge G, van
Gijn M, et al: Recommendations for whole genome sequencing in
diagnostics for rare diseases. Eur J Hum Genet. 30:1017–1021.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Manno G, Dalmastri C, Tabacchioni S,
Vandamme P, Lorini R, Minicucci L, Romano L, Giannattasio A,
Chiarini L and Bevivino A: Epidemiology and clinical course of
Burkholderia cepacia complex infections, particularly those
caused by different Burkholderia cenocepacia strains, among
patients attending an Italian cystic fibrosis center. J Clin
Microbiol. 42:1491–1497. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : El-Mahallawy HS, Lu
G, Kelly P, Xu D, Li Y, Fan W and Wang C: Q fever in China: A
systematic review, 1989-2013. Epidemiol Infect 143: 673-681,
2015.
|
|
13
|
Woldehiwet Z: Q fever (coxiellosis):
Epidemiology and pathogenesis. Res Vet Sci. 77:93–100.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lai CH, Huang CK, Chin C, Chung HC, Huang
WS, Lin CW, Hsu CY and Lin HH: Acute Q fever: An emerging and
endemic disease in southern Taiwan. Scand J Infect Dis. 40:105–110.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Todkill D, Fowler T and Hawker JI:
Estimating the incubation period of acute Q fever, a systematic
review. Epidemiol Infect. 146:665–672. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jaltotage B, Ali U, Dorai-Raj A, Rankin J,
Sanfilippo F and Dwivedi G: Q fever endocarditis: A review of local
and all reported cases in the literature. Heart Lung Circ.
30:1509–1515. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Chen H, Han D and Wu W: Clinical
usefulness of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for Rickettsia
and Coxiella burnetii diagnosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect
Dis. 42:681–689. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Antipov EA and Pokryshevskaya EB: The
effects of adverse drug reactions on patients' satisfaction:
Evidence from publicly available data on Tamiflu (oseltamivir). Int
J Med Inform. 125:30–36. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Greig SL and Garnock-Jones KP: Loxoprofen:
A review in pain and inflammation. Clin Drug Investig. 36:771–781.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shankar AH and Prasad AS: Zinc and immune
function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection.
Am J Clin Nutr. 68 Suppl):447S–463S. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ranganath N, Khodadadi RB and Abu Saleh
OM: Karius with a Q: Role for microbial cell-free DNA
next-generation sequencing in diagnosis of acute Q fever. Open
Forum Infect Dis. 10(ofac666)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang C, Ding H, Lin Y, Zhang Z, Fang X,
Chen Y, Chen Y, Zhang C, Li W, Zhang W and Huang Z: Diagnosis of
Coxiella burnetii prosthetic joint infection using mNGS and
ptNGS: A case report and literature review. Orthop Surg.
15:371–376. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li S, Tong J, Li H, Mao C, Shen W, Lei Y
and Hu P: L. pneumophila infection diagnosed by tNGS in a
lady with lymphadenopathy. Infect Drug Resist. 16:4435–4442.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li J, Zhang L, Yang X, Wang P, Feng L, Guo
E and Chen Y: Diagnostic significance of targeted next-generation
sequencing in central nervous system infections in neurosurgery of
pediatrics. Infect Drug Resist. 16:2227–2236. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ye J, Huang K, Xu Y, Chen N, Tu Y, Huang
J, Shao L, Kong W, Zhao D and Xie Y: Clinical application of
nanopore-targeted sequencing technology in bronchoalveolar lavage
fluid from patients with pulmonary infections. Microbiol Spectr.
12(e0002624)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shaikh A and Rodrigues C: What's new in
the molecular diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis? J Pediat Infect
Dis J. 42:e377–e379. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nafea AM, Wang Y, Wang D, Salama AM, Aziz
MA, Xu S and Tong Y: Application of next-generation sequencing to
identify different pathogens. Front Microbiol.
14(1329330)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ding L, Zhao Y, Li X, Wang R, Li Y, Tang
X, Sun B and He H: Early diagnosis and appropriate respiratory
support for Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia associated acute
respiratory distress syndrome in young and adult patients: A case
series from two centers. BMC Infect Dis. 20(367)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shi Y, Chen J, Shi X, Hu J, Li H, Li X,
Wang Y and Wu B: A case of chlamydia psittaci caused severe
pneumonia and meningitis diagnosed by metagenome next-generation
sequencing and clinical analysis: A case report and literature
review. BMC Infect Dis. 21(621)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huang T, Chen Y, Zhang J, He R, Qu D, Ye Q
and Chen X: Rapid and accurate diagnosis of brain abscess caused by
Nocardia asiatica with a combination of Ziehl-Neelsen staining and
metagenomics next-generation sequencing. Eur J Neurol. 28:355–357.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yue R, Wu X, Li T, Chang L, Huang X and
Pan L: Early detection of Legionella pneumophila and
Aspergillus by mNGS in a critically ill patient with
Legionella pneumonia after extracorporeal membrane
oxygenation treatment: Case report and literature review. Front Med
(Lausanne). 8(686512)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jin X, Li J, Shao M, Lv X, Ji N, Zhu Y,
Huang M, Yu F, Zhang C, Xie L, et al: Improving suspected pulmonary
infection diagnosis by bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomic
next-generation sequencing: A multicenter retrospective study.
Microbiol Spectr. 10(e0247321)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mitchell SL and Simner PJ: Next-generation
sequencing in clinical microbiology: Are we there yet? Clin Lab
Med. 39:405–418. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gaston DC, Miller HB, Fissel JA, Jacobs E,
Gough E, Wu J, Klein EY, Carroll KC and Simner PJ: Evaluation of
metagenomic and targeted next-generation sequencing workflows for
detection of respiratory pathogens from bronchoalveolar lavage
fluid specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 60(e0052622)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hong HL, Flurin L, Thoendel MJ, Wolf MJ,
Abdel MP, Greenwood-Quaintance KE and Patel R: Targeted versus
shotgun metagenomic sequencing-based detection of microorganisms in
sonicate fluid for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Clin
Infect Dis. 76:e1456–e1462. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bianconi I, Aschbacher R and Pagani E:
Current uses and future perspectives of genomic technologies in
clinical microbiology. Antibiotics (Basel). 12(1580)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Guatteo R, Seegers H, Taurel AF, Joly A
and Beaudeau F: Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii infection in
domestic ruminants: A critical review. Vet Microbiol. 149:1–16.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Körner S, Makert GR, Ulbert S, Pfeffer M
and Mertens-Scholz K: The prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in
hard ticks in Europe and their role in Q fever transmission
revisited-A systematic review. Front Vet Sci.
8(655715)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ghanem-Zoubi N, Mustafa-Hellou M, Zahran
M, Gazit L, Shalaginov R, Dabaja-Younis H and Szwarcwort M: The
integration of Coxiella burnetii PCR testing in serum into
the diagnostic algorithm of suspected acute Q fever in an endemic
setting. J Clin Microbiol. 62(e0170323)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Navaei H: Q fever: Etiology diagnosis and
treatment. J Zoonotic Dis. 7:260–274. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ullah Q, Jamil T, Saqib M, Iqbal M and
Neubauer H: Q fever-a neglected zoonosis. Microorganisms.
10(1530)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Diseko LJ, Tsotetsi-Khambule AM, Onyiche
TE, Ramatla T, Thekisoe O and Gcebe N: Coxiella burnetii
infections from animals and ticks in South Africa: A systematic
review. Vet Res Commun. 48:19–28. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Peng JM, Du B, Qin HY, Wang Q and Shi Y:
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of
suspected pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. J Infect.
82:22–27. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, Pan J, Zhang Y, Jin
W, Yao Y, Su Y, Huang Y, Wang M, et al: Microbiological diagnostic
performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied
to clinical practice. Clin Infect Dis. 67 (Suppl 2):S231–S240.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Duan H, Li X, Mei A, Li P, Liu Y, Li X, Li
W, Wang C and Xie S: The diagnostic value of metagenomic
next-generation sequencing in infectious diseases. BMC Infect Dis.
21(62)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Massung RF, Cutler SJ and Frangoulidis D:
Molecular typing of Coxiella burnetii (Q fever). In: Toman
R, Heinzen R, Samuel J and Mege JL (eds). Coxiella burnetii: Recent
Advances and New Perspectives in Research of the Q Fever Bacterium.
Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 984. Springer,
Dordrecht, pp381-396, 2012.
|
|
47
|
Kondo M, Dalai SC, Venkatasubrahmanyam S,
Eisenberg N, Robinson BD, Westblade LF and Marks KM: Diagnosis and
genotyping of Coxiella burnetii endocarditis in a patient
with prosthetic pulmonary valve replacement using next-generation
sequencing of plasma microbial cell-free DNA. Open Forum Infect
Dis. 6(ofz242)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Huang J, Wang R, Gao C, Lü Y, Cao Z, Deng
S and Yue C: A case of tick-transmitted Q fever in Lishui, China
diagnosed by next-generation sequencing. J Int Med Res.
49(3000605211025398)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Xing F, Ye H, Deng C, Sun L, Yuan Y, Lu Q,
Yang J, Lo SKF, Zhang R, Chen JHK, et al: Diverse and atypical
manifestations of Q fever in a metropolitan city hospital: Emerging
role of next-generation sequencing for laboratory diagnosis of
Coxiella burnetii. PLoS Negl Trop Dis.
16(e0010364)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Gao Y, Che L, Wang Z, Niu J, Wei W, Song M
and Liu Q: A case report of autochthonous Q fever with pneumonia
and hepatitis in northeastern China. Biosaf Health. 3:179–182.
2021.
|
|
51
|
Li D, Liu H, Liu M, Chang C, Zhao X, Yu H,
Yan L, Han H and Yu XJ: Delayed diagnosis of acute Q fever, China.
Emerg Infect Dis. 28:2580–2582. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang D, Zhang L, Cai Z and Liu Y:
Diagnosis of acute Q fever in a patient by using metagenomic
next-generation sequencing: A case report. Infect Drug Resist.
16:1923–1930. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Parker NR, Barralet JH and Bell AM: Q
fever. Lancet. 367:679–688. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Eldin C, Mélenotte C, Mediannikov O, Ghigo
E, Million M, Edouard S, Mege JL, Maurin M and Raoult D: From Q
fever to Coxiella burnetii infection: A paradigm change.
Clin Microbiol Rev. 30:115–190. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wu XB, Na RH, Wei SS, Zhu JS and Peng HJ:
Distribution of tick-borne diseases in China. Parasit Vectors.
6(119)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yu Z, Wang H, Wang T, Sun W, Yang X and
Liu J: Tick-borne pathogens and the vector potential of ticks in
China. Parasit Vectors. 8(24)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Li H, Zheng YC, Ma L, Jia N, Jiang BG,
Jiang RR, Huo QB, Wang YW, Liu HB, Chu YL, et al: Human infection
with a novel tick-borne Anaplasma species in China: A surveillance
study. Lancet Infect Dis. 15:663–670. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang ZD, Wang B, Wei F, Han SZ, Zhang L,
Yang ZT, Yan Y, Lv XL, Li L, Wang SC, et al: A new segmented virus
associated with human febrile illness in China. N Engl J Med.
380:2116–2125. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jiang BG, Jia N, Jiang JF, Zheng YC, Chu
YL, Jiang RR, Wang YW, Liu HB, Wei R, Zhang WH, et al: Borrelia
miyamotoi infections in humans and ticks Northeastern China. Emerg
Infect Dis. 24:236–241. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hysom DA, Naraghi-Arani P, Elsheikh M,
Carrillo AC, Williams PL and Gardner SN: Skip the alignment:
Degenerate, multiplex primer and probe design using K-mer matching
instead of alignments. PLoS One. 7(e34560)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Hugerth LW, Wefer HA, Lundin S, Jakobsson
HE, Lindberg M, Rodin S, Engstrand L and Andersson AF: DegePrime, a
program for degenerate primer design for broad-taxonomic-range PCR
in microbial ecology studies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 80:5116–5123.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhang XA, Ma YD, Zhang YF, Hu ZY, Zhang
JT, Han S, Wang G, Li S, Wang X, Tang F, et al: A new
orthonairovirus associated with human febrile illness. N Engl J
Med. 391:821–831. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Xia H, Zhang Z, Luo C, Wei K, Li X, Mu X,
Duan M, Zhu C, Jin L, He X, et al: MultiPrime: A reliable and
efficient tool for targeted next-generation sequencing. Imeta.
2(e143)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Caron F, Meurice JC, Ingrand P, Bourgoin
A, Masson P, Roblot P and Patte F: Acute Q fever pneumonia: A
review of 80 hospitalized patients. Chest. 114:808–813.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Schuetz P, Haubitz S, Christ-Crain M,
Albrich WC, Zimmerli W and Mueller B: ProHOSP Study Group.
Hyponatremia and anti-diuretic hormone in Legionnaires' disease.
BMC Infect Dis. 13(585)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Bellew S, Grijalva CG, Williams DJ,
Anderson EJ, Wunderink RG, Zhu Y, Waterer GW, Bramley AM, Jain S,
Edwards KM and Self WH: Pneumococcal and Legionella urinary
antigen tests in community-acquired pneumonia: Prospective
evaluation of indications for testing. Clin Infect Dis.
68:2026–2033. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|