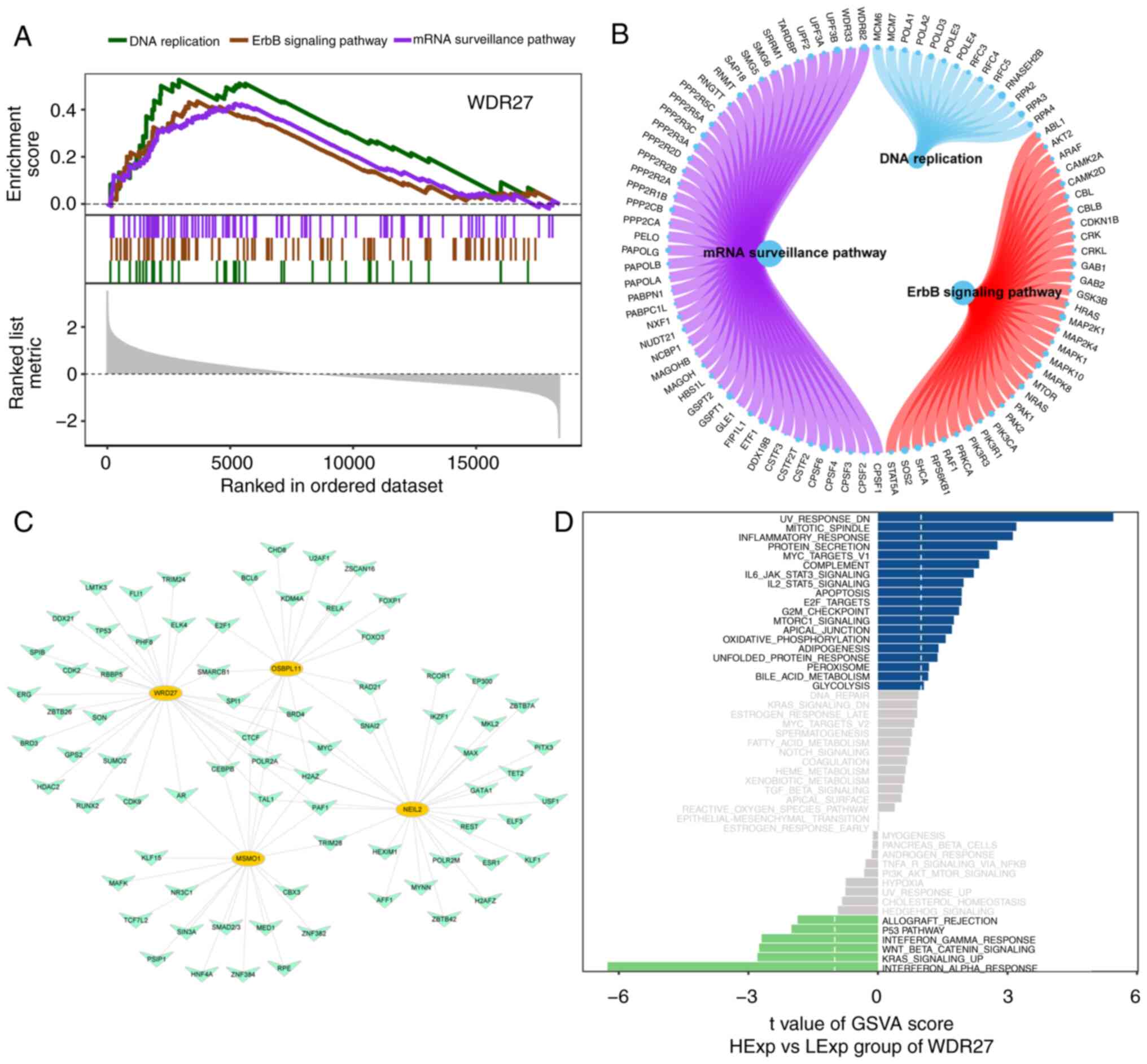
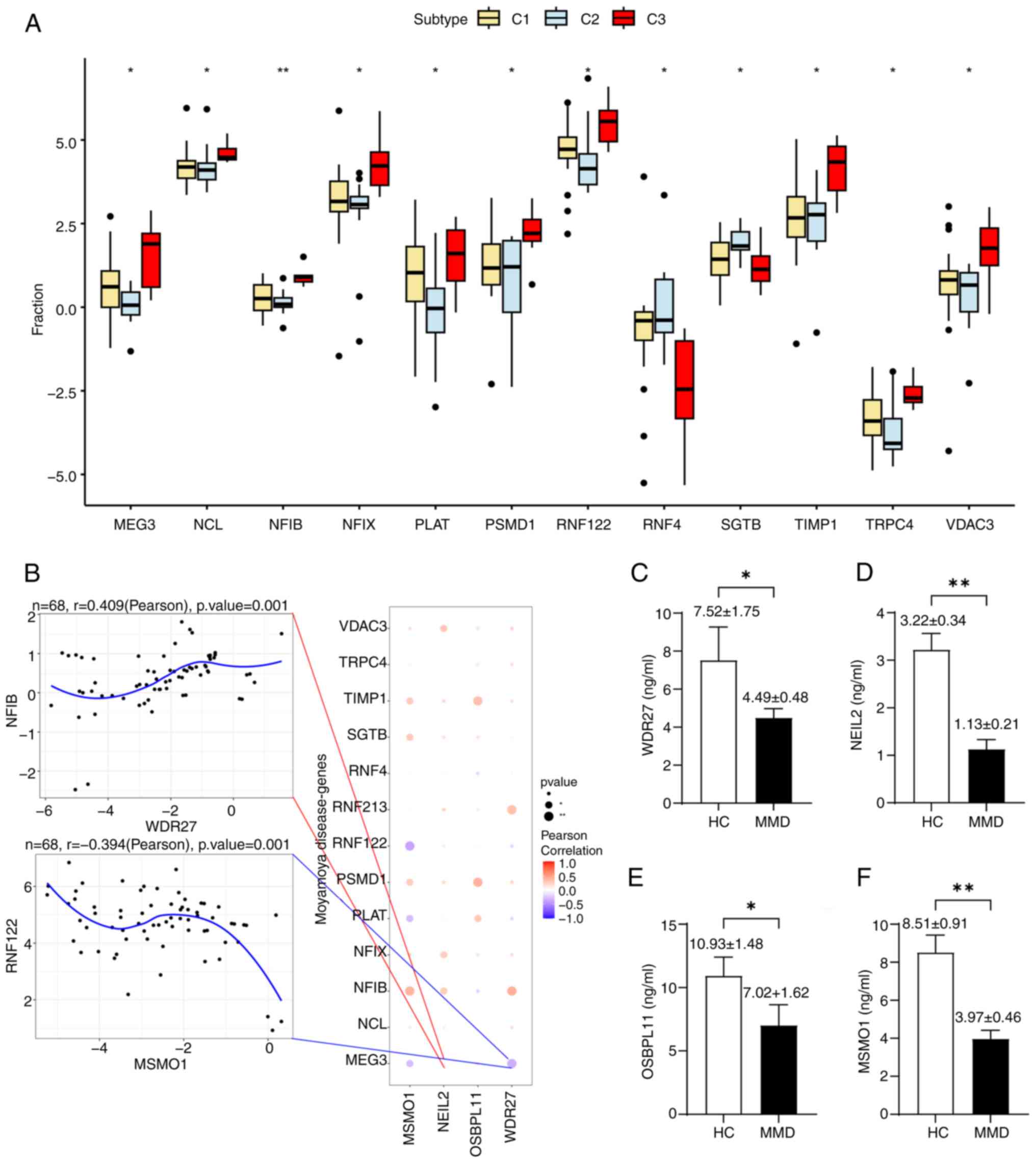
|
1
|
Suzuki J and Takaku A: Cerebrovascular
‘moyamoya’ disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in
base of brain. Arch Neurol. 20:288–299. 1969.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ihara M, Yamamoto Y, Hattori Y, Liu W,
Kobayashi H, Ishiyama H, Yoshimoto T, Miyawaki S, Clausen T, Bang
OY, et al: Moyamoya disease: Diagnosis and interventions. Lancet
Neurol. 21:747–758. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mertens R, Graupera M, Gerhardt H, Bersano
A, Tournier-Lasserve E, Mensah MA, Mundlos S and Vajkoczy P: The
genetic basis of moyamoya disease. Transl Stroke Res. 13:25–45.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fujimura M, Fujimura T, Kakizaki A,
Sato-Maeda M, Niizuma K, Tomata Y, Aiba S and Tominaga T: Increased
serum production of soluble CD163 and CXCL5 in patients with
moyamoya disease: Involvement of intrinsic immune reaction in its
pathogenesis. Brain Res. 1679:39–44. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sun H, Li W, Xia C, Ren Y, Ma L, Xiao A,
You C, Liu Y and Tian R: Angiographic and hemodynamic features in
asymptomatic hemispheres of patients with moyamoya disease. Stroke.
53:210–217. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Takekawa Y, Umezawa T, Ueno Y, Sawada T
and Kobayashi M: Pathological and immunohistochemical findings of
an autopsy case of adult moyamoya disease. Neuropathology.
24:236–242. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
He S, Zhang J, Liu Z, Wang Y, Hao X, Wang
X, Zhou Z, Ye X, Zhao Y, Zhao Y and Wang R: Upregulated
cytoskeletal proteins promote pathological angiogenesis in moyamoya
disease. Stroke. 54:3153–3164. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Nie L, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Wang C,
Colic M, Olszewski K, Horbath A, Chen X, Lei G, et al: Actin
cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates
disulfidptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 25:404–414. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Koppula P, Zhuang L and Gan B: Cystine
transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient
dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 12:599–620.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Rashad S, Zhou Y, Niizuma K and
Tominaga T: RNF213 loss of function reshapes vascular transcriptome
and spliceosome leading to disrupted angiogenesis and aggravated
vascular inflammatory responses. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
42:2107–2122. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang M, Zhang B, Jin F, Li G, Cui C and
Feng S: Exosomal MicroRNAs: Biomarkers of moyamoya disease and
involvement in vascular cytoskeleton reconstruction. Heliyon.
10(e32022)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mamiya T, Kanamori F, Yokoyama K, Ota A,
Karnan S, Uda K, Araki Y, Maesawa S, Yoshikawa K and Saito R: Long
noncoding RNA profile of the intracranial artery in patients with
moyamoya disease. J Neurosurg. 138:709–716. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kanamori F, Yokoyama K, Ota A, Yoshikawa
K, Karnan S, Maruwaka M, Shimizu K, Ota S, Uda K, Araki Y, et al:
Transcriptome-wide analysis of intracranial artery in patients with
moyamoya disease showing upregulation of immune response, and
downregulation of oxidative phosphorylation and DNA repair.
Neurosurg Focus. 51(E3)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fukui M: Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis
(‘moyamoya’ disease). Research committee on spontaneous occlusion
of the circle of Willis (Moyamoya disease) of the ministry of
health and welfare, Japan. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 99
(Suppl):238–240. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ye F, Niu X, Liang F, Dai Y, Liang J, Li
J, Wu X, Zheng H, Qi T and Sheng W: RNF213 loss-of-function
promotes pathological angiogenesis in moyamoya disease via the
Hippo pathway. Brain. 146:4674–4689. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Takagi Y, Kikuta K, Sadamasa V, Nozaki K
and Hashimoto N: Caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in middle cerebral
arteries in patients with moyamoya disease. Neurosurgery.
59:894–900. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhao D, Meng Y, Dian Y, Zhou Q, Sun Y, Le
J, Zeng F, Chen X, He Y and Deng G: Molecular landmarks of tumor
disulfidptosis across cancer types to promote disulfidptosis-target
therapy. Redox Biol. 68(102966)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Miyamoto S, Yoshimoto T, Hashimoto N,
Okada Y, Tsuji I, Tominaga T, Nakagawara J and Takahashi JC:
Effects of extracranial-intracranial bypass for patients with
hemorrhagic moyamoya disease: Results of the Japan adult moyamoya
trial. Stroke. 45:1415–1421. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Han C, Jia Y, Wang J, Ge W and
Duan L: Proteomic profiling of exosomes from hemorrhagic moyamoya
disease and dysfunction of mitochondria in endothelial cells.
Stroke. 52:3351–3361. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Honne K, Hallgrímsdóttir I, Wu C, Sebro R,
Jewell NP, Sakurai T, Iwamoto M, Minota S and Jawaheer D: A
longitudinal genome-wide association study of anti-tumor necrosis
factor response among Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 18(12)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Anuraga G, Lang J, Xuan DTM, Ta HDK, Jiang
JZ, Sun Z, Dey S, Kumar S, Singh A, Kajla G, et al: Integrated
bioinformatics approaches to investigate alterations in
transcriptomic profiles of monkeypox infected human cell line
model. J Infect Public Health. 17:60–69. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lane JM, Liang J, Vlasac I, Anderson SG,
Bechtold DA, Bowden J, Emsley R, Gill S, Little MA, Luik AI, et al:
Genome-wide association analyses of sleep disturbance traits
identify new loci and highlight shared genetics with
neuropsychiatric and metabolic traits. Nat Genet. 49:274–281.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Diercks AH, Podolskaia IS, Murray TA, Jahn
AN, Mai D, Liu D, Amon LM, Nakagawa Y, Shimano H, Aderem A and Gold
ES: Oxysterol binding protein regulates the resolution of
TLR-induced cytokine production in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci
U S A. 121(e2406492121)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bouchard L, Faucher G, Tchernof A,
Deshaies Y, Marceau S, Lescelleur O, Biron S, Bouchard C, Pérusse L
and Vohl MC: Association of OSBPL11 gene polymorphisms with
cardiovascular disease risk factors in obesity. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 17:1466–1472. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Weng R, Ren S, Su J, Ni W, Yang C, Gao X,
Xiao W, Zhang X, Jiang H, Guan Y, et al: 18F-FDG PET and a
classifier algorithm reveal a characteristic glucose metabolic
pattern in adult patients with moyamoya disease and vascular
cognitive impairment. Brain Imaging Behav. 17:185–199.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kalay Yildizhan I, Gökpınar İli E,
Onoufriadis A, Kocyigit P, Kesidou E, Simpson MA, McGrath JA,
Kutlay NY and Kundakci N: New homozygous missense MSMO1 mutation in
two siblings with SC4MOL deficiency presenting with psoriasiform
dermatitis. Cytogenet Genome Res. 160:523–530. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu P, Wu M, Chen H and Xu J, Wu M, Li M,
Qian F and Xu J: Bioinformatics analysis of hepatitis C virus
genotype 2a-induced human hepatocellular carcinoma in Huh7 cells.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:191–202. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Simigdala N, Gao Q, Pancholi S,
Roberg-Larsen H, Zvelebil M, Ribas R, Folkerd E, Thompson A, Bhamra
A, Dowsett M and Martin LA: Cholesterol biosynthesis pathway as a
novel mechanism of resistance to estrogen deprivation in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
18(58)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He P, Sun L, Zhu D, Zhang H, Zhang L, Guo
Y, Liu S, Zhou J, Xu X and Xie P: Knock-down of endogenous
bornavirus-like nucleoprotein 1 inhibits cell growth and induces
apoptosis in human oligodendroglia cells. Int J Mol Sci.
17(435)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cao R, Zhang Z, Tian C, Sheng W, Dong Q
and Dong M: Down-regulation of MSMO1 promotes the development and
progression of pancreatic cancer. J Cancer. 13:3013–3021.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tapryal N, Chakraborty A, Saha K, Islam A,
Pan L, Hosoki K, Sayed IM, Duran JM, Alcantara J, Castillo V, et
al: The DNA glycosylase NEIL2 is protective during SARS-CoV-2
infection. Nat Commun. 14(8169)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chakraborty A, Wakamiya M, Venkova-Canova
T, Pandita RK, Aguilera-Aguirre L, Sarker AH, Singh DK, Hosoki K,
Wood TG, Sharma G, et al: Neil2-null mice accumulate oxidized DNA
bases in the transcriptionally active sequences of the genome and
are susceptible to innate inflammation. J Biol Chem.
290:24636–24648. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sayed IM, Sahan AZ, Venkova T, Chakraborty
A, Mukhopadhyay D, Bimczok D, Beswick EJ, Reyes VE, Pinchuk I,
Sahoo D, et al: Helicobacter pylori infection downregulates the DNA
glycosylase NEIL2, resulting in increased genome damage and
inflammation in gastric epithelial cells. J Biol Chem.
295:11082–11098. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sarker AH, Chatterjee A, Williams M, Lin
S, Havel C, Jacob P III, Boldogh I, Hazra TK, Talbot P and Hang B:
NEIL2 protects against oxidative DNA damage induced by sidestream
smoke in human cells. PLoS One. 9(e90261)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ye F, Liu J, Wang H, Chen X, Cheng Q and
Chen H: Cervical carcinoma risk associate with genetic
polymorphisms of NEIL2 gene in Chinese population and its
significance as predictive biomarker. Sci Rep.
10(5136)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|