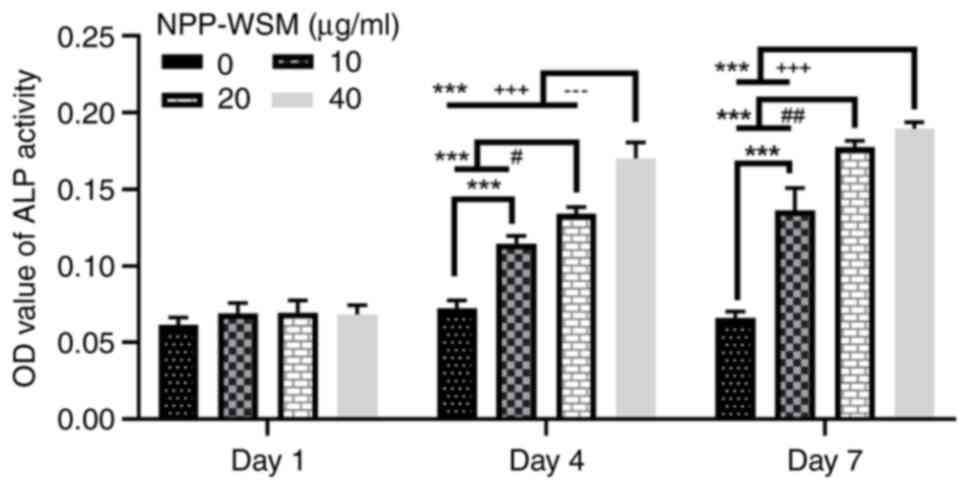
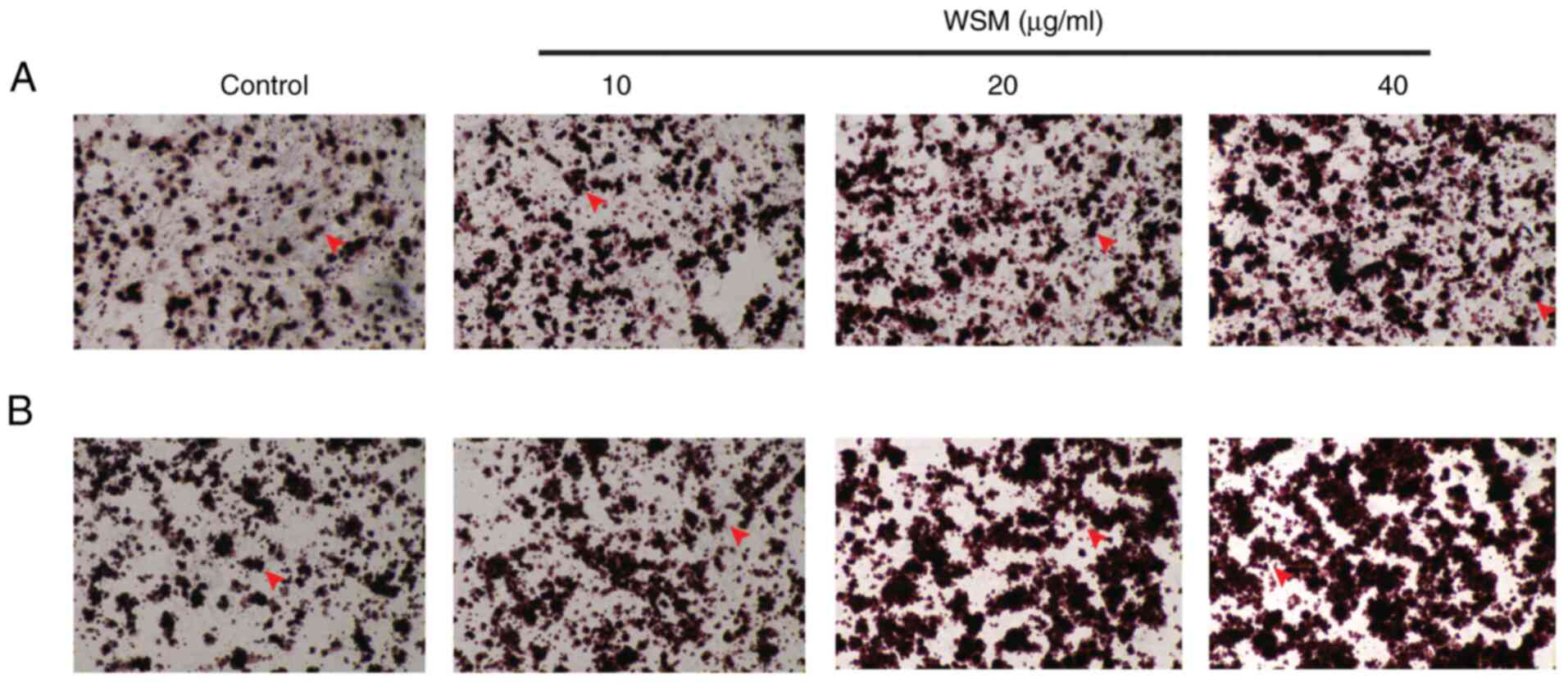
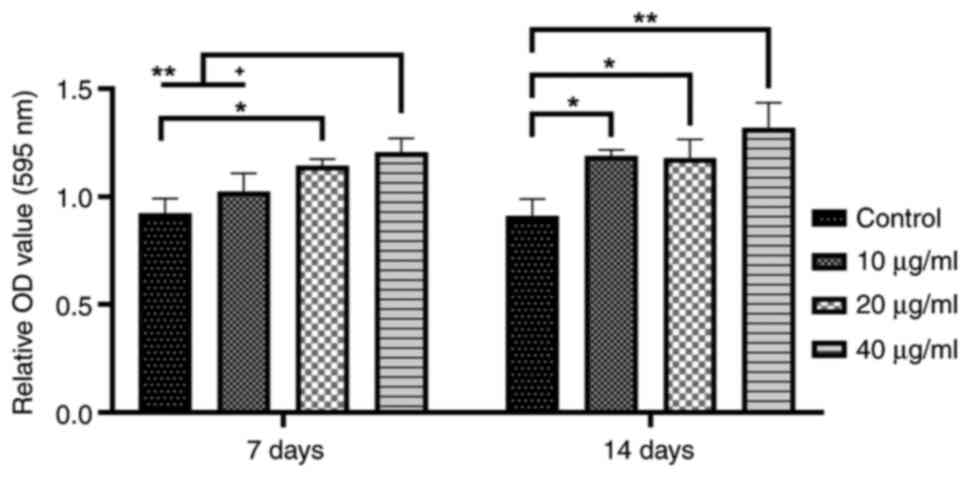
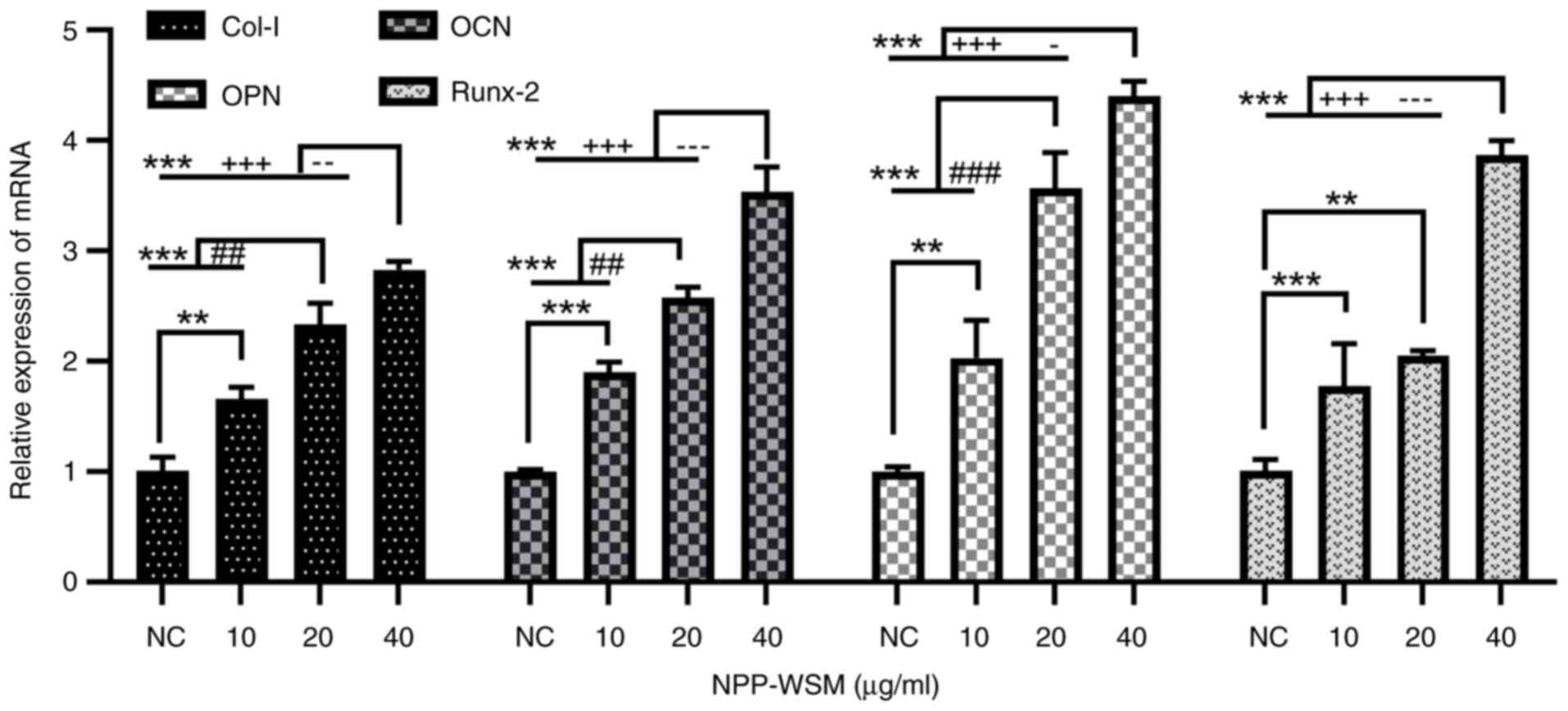
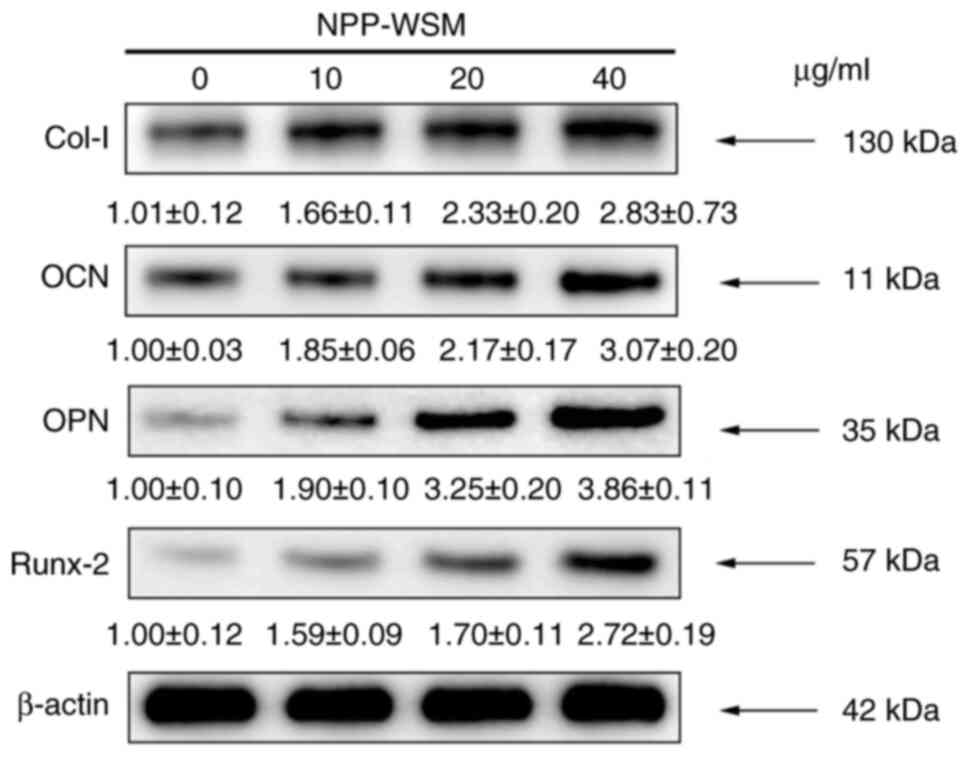
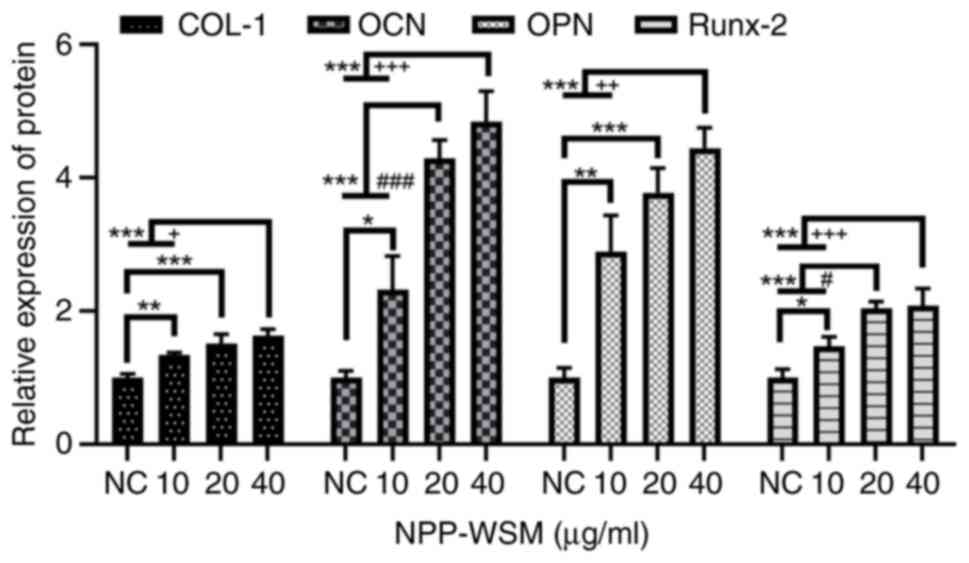
|
1
|
Cuif JP, Dauphin Y, Luquet G, Medjoubi K,
Somogyi A and Perez-Huerta A: Revisiting the organic template model
through the microstructural study of shell development in Pinctada
margaritifera, the polynesian pearl oyster. Minerals.
8(370)2018.
|
|
2
|
Farre B, Brunelle A, Laprévote O, Cuif JP,
Williams CT and Dauphin Y: Shell layers of the black-lip pearl
oyster Pinctada margaritifera: Matching microstructure and
composition. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 159:131–139.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ma Y, Qiao L and Feng Q: In-vitro study on
calcium carbonate crystal growth mediated by organic matrix
extracted from fresh water pearls. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
32:1963–1970. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Almeida MJ, Milet C, Peduzzi J, Pereira L,
Haigle J, Barthelemy M and Lopez E: Effect of water-soluble matrix
fraction extracted from the nacre of Pinctada maxima on the
alkaline phosphatase activity of cultured fibroblasts. J Exp Zool.
288:327–334. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Li S, Yao S, Si W, Cai L, Pan H,
Hou J, Yang W, Da J, Jiang B, et al: Ultra-performance liquid
chromatography of amino acids for the quality assessment of pearl
powder. J Sep Sci. 38:1552–1560. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chiu HF, Hsiao SC, Lu YY, Han YC, Shen YC,
Venkatakrishnan K and Wang CK: Efficacy of protein rich pearl
powder on antioxidant status in a randomized placebo-controlled
trial. J Food Drug Anal. 26:309–317. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen X, Peng LH, Chee SS, Shan YH, Liang
WQ and Gao JQ: Nanoscaled pearl powder accelerates wound repair and
regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev Ind Pharm.
45:1009–1016. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang JX, Li SR, Yao S, Bi QR, Hou JJ, Cai
LY, Han SM, Wu WY and Guo DA: Anticonvulsant and sedative-hypnotic
activity screening of pearl and nacre (mother of pearl). J
Ethnopharmacol. 181:229–235. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ansari N and Sims NA: The cells of bone
and their interactions. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 262:1–25.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dai R, Liu M, Xiang X, Xi Z and Xu H:
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts: An important switch of tumour cell
dormancy during bone metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
41(316)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jurisic V, Terzic T, Pavlovic S, Colovic N
and Colovic M: Elevated TNF-alpha and LDH without parathormone
disturbance is associated with diffuse osteolytic lesions in
leukemic transformation of myelofibrosis. Pathol Res Pract.
204:129–132. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yao Z, Getting SJ and Locke IC: Regulation
of TNF-induced osteoclast differentiation. Cells.
11(132)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Akdis M, Aab A, Altunbulakli C, Azkur K,
Costa RA, Crameri R, Duan S, Eiwegger T, Eljaszewicz A, Ferstl R,
et al: Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming
growth factor β, and TNF-α: Receptors, functions, and roles in
diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 138:984–1010. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhao Y, Sun Q and Huo B: Focal adhesion
regulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and
osteoblasts. Biomater Transl. 2:312–322. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nahle S, Lutet-Toti C, Namikawa Y, Piet
MH, Brion A, Peyroche S, Suzuki M, Marin F and Rousseau M: Organic
matrices of calcium carbonate biominerals improve osteoblastic
mineralization. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 26:539–549. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jin C, Zhao JY, Liu XJ and Li JL:
Expressions of shell matrix protein genes in the pearl sac and its
correlation with pearl weight in the first 6 months of pearl
formation in Hyriopsis cumingii. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 21:240–249.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Commission CP and Commission SP:
Pharmacopoeia of the people's Republic of China 2015. (No Title),
2015.
|
|
18
|
Huang F, Deng CM and Fu Z: GC-MS
determination of microamounts of organic chemical compositions in
nacre powder of Hyriopsis cumingii Lea. Phs Test Chem Anal.
46:300–302. 2010.
|
|
19
|
He JF, Deng Q, Pu YH, Liao B and Zeng M:
Amino acids composition analysis of pearl powder and pearl layer
powder. Food Ind. 37:270–273. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Berland S, Ma Y, Marie A, Andrieu JP,
Bedouet L and Feng Q: Proteomic and profile analysis of the
proteins laced with aragonite and vaterite in the freshwater mussel
Hyriopsis cumingii shell biominerals. Protein Pept Lett.
20:1170–1180. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Green DW, Kwon HJ and Jung HS: Osteogenic
potency of nacre on human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cells.
38:267–272. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jurisic V, Srdic-Rajic T, Konjevic G,
Bogdanovic G and Colic M: TNF-α induced apoptosis is accompanied
with rapid CD30 and slower CD45 shedding from K-562 cells. J Membr
Biol. 239:115–122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim JM, Lin C, Stavre Z, Greenblatt MB and
Shim JH: Osteoblast-osteoclast communication and bone homeostasis.
Cells. 9(2073)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li S, Liu G and Hu S: Osteoporosis:
Interferon-gamma-mediated bone remodeling in osteoimmunology. Front
Immunol. 15(1396122)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jurisic V: Multiomic analysis of cytokines
in immuno-oncology. Expert Rev Proteomics. 17:663–674.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lan TJ, Luo X, Mo MY, Chen ZX, Luo F, Han
SY, Liu P, Liang ZX, Zhang T, Li TY, et al: Hydrolyzed seawater
pearl tablet modulates the immunity via attenuating Th1/Th2
imbalance in an immunosuppressed mouse model. J Tradit Chin Med.
41:397–405. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Loh XJ, Young DJ, Guo H, Tang L, Wu Y,
Zhang G, Tang C and Ruan H: Pearl powder-an emerging material for
biomedical applications: A review. Materials (Basel).
14(2797)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Luo W, Chen Y, Chen C and Ren G: The
proteomics of the freshwater pearl powder: Insights from
biomineralization to biomedical application. J Proteomics.
265(104665)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang W, Xu P, Cheng Y, Yang Y, Mao Q and
Chen Z: Preparation of a nanopearl powder/C-HA (chitosan-hyaluronic
acid)/rhBMP-2 (recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2)
composite artificial bone material and a preliminary study of its
effects on MC3T3-E1 cells. Bioengineered. 13:14368–14381.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pei J, Wang Y, Zou X, Ruan H, Tang C, Liao
J, Si G and Sun P: Extraction, purification, bioactivities and
application of matrix proteins from pearl powder and nacre powder:
A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 9(649665)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li X, Xu P, Cheng Y, Zhang W, Zheng B and
Wang Q: Nano-pearl powder/chitosan-hyaluronic acid porous composite
scaffold and preliminary study of its osteogenesis mechanism. Mater
Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 111(110749)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Du X, Li D, Ao R and Yu B and Yu
B: Three dimensionally printed pearl powder/poly-caprolactone
composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.
29:1686–1700. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li SG, Guo ZL, Tao SY, Han T, Zhou J, Lin
WY, Guo X, Li CX, Diwas S and Hu XW: In vivo study on osteogenic
efficiency of nHA/gel porous scaffold with nacre water-soluble
matrix. Tissue Cell. 88(102347)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
de Muizon CJ, Iandolo D, Nguyen DK,
Al-Mourabit A and Rousseau M: Organic matrix and secondary
metabolites in nacre. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 24:831–842.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Evans JS: The biomineralization proteome:
Protein complexity for a complex bioceramic assembly process.
Proteomics. 19(e1900036)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Han S, Huang D, Lan T, Wu Y, Wang Y, Wei
J, Zhang W, Ou Y, Yan Q, Liu P, et al: Therapeutic effect of
seawater pearl powder on UV-induced photoaging in mouse skin. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021(9516427)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wu Y, Ding Z, Ren H, Ji M and Yan Y:
Preparation, characterization and in vitro biological evaluation of
a novel pearl powder/poly-amino acid composite as a potential
substitute for bone repair and reconstruction. Polymers (Basel).
11(831)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Du X, Yu B, Pei P, Ding H, Yu B and Zhu Y:
3D printing of pearl/CaSO4 composite scaffolds for bone
regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 6:499–509. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qiu-Hua M and Pu X: Research progress of
pearl/nacer in bone tissue repair. J Oral Sci Res. 32:311–333.
2016.
|
|
41
|
Yang X, Li Y, Liu X, He W, Huang Q and
Feng Q: Nanoparticles and their effects on differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Transl. 1:58–68. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang YL, Chang CH, Huang CC, Kao WMW, Liu
WC and Liu HW: Osteogenic activity of nanonized pearl powder/poly
(lactide-co-glycolide) composite scaffolds for bone tissue
engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 24:979–985. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rico-Llanos GA, Borrego-González S,
Moncayo-Donoso M, Becerra J and Visser R: Collagen type I
biomaterials as scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Polymers
(Basel). 13(588)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu M, Tao J, Guo H, Tang L, Zhang G, Tang
C, Zhou H, Wu Y, Ruan H and Loh XJ: Efficacy of water-soluble pearl
powder components extracted by a CO2 supercritical
extraction system in promoting wound healing. Materials (Basel).
14(4458)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dai J.P, Chen J, Bei Y.F, Han B.X, Guo S.B
and Jiang L.L: Effects of pearl powder extract and its fractions on
fibroblast function relevant to wound repair. Pharm Biol.
48:122–127. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cheng Y, Zhang W, Fan H and Xu P:
Water-soluble nano-pearl powder promotes MC3T3-E1 cell
differentiation by enhancing autophagy via the MEK/ERK signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:993–1000. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|