Introduction
Intussusception refers to the invagination of a
segment of the bowel into the lumen of an adjacent segment, which
can occur in all age groups. Intussusception is more common in the
pediatric population, with the ratio of child to adult cases being
~20:1(1). Adult intussusception is
often secondary to pathological conditions such as polyps, lipomas,
malignancies and Meckel's diverticulum (2,3).
Jejuno-jejunal intussusception in adults is a rare clinical entity
that often results from a pathological lead point, such as benign
or malignant neoplasms, and its diagnosis requires high clinical
suspicion (4-6).
Due to the non-specific nature of symptoms associated with
jejuno-jejunal intussusception and its low incidence rate, the
preoperative diagnosis remains challenging despite advancements in
imaging techniques. Previous reports have shown that tumors arising
in the horizontal (D3) and ascending (D4) portions of the duodenum
may lead to duodeno-duodenal intussusception (7-9).
However, the simultaneous occurrence of two tumors in these
segments, resulting in initial jejunum intussusception near the
Treitz ligament, is exceedingly rare. The current study presents
the case of a patient who underwent successful surgical
intervention for intussusception in the proximal jejunum near the
Treitz ligament. This report adheres to the Surgical Case Report
criteria (10).
Case report
In January 2023, a 54-year-old female presented to
Changzhi People's Hospital (Changzhi, China) with acute upper
abdominal pain that had persisted for 6 h, accompanied by referred
lumbar pain, nausea and vomiting. There were no indications of
fever, chills or jaundice. The abdominal pain presented as
persistent epigastric pain. A physical examination revealed
tenderness in the epigastric region but no palpable masses and
normal bowel sounds. Hematological analysis revealed a white blood
cell count of 8.16x109/l (reference range,
3.5-9.5x109/l), a red blood cell count of
4.19x1012/l (reference range, 3.8-5.1x1012/l)
and a neutrophil proportion of 75.6% (reference range, 40-75%).
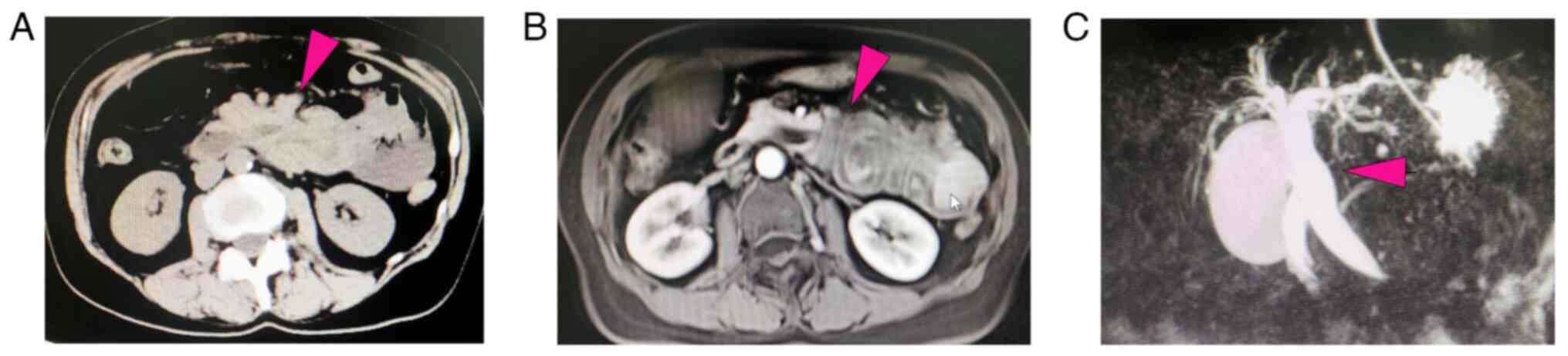
Computed tomography (CT) scans revealed signs of intestinal
obstruction in the left upper quadrant, suggesting Meckel's
diverticulum. Additionally, there was an enlarged gallbladder and
dilated bile ducts (common bile duct, gallbladder duct and
intrahepatic bile ducts) (Fig.
1A). To enhance diagnostic precision, an upper abdominal
enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan was performed,
revealing leftward displacement of the descending and horizontal
segments of the duodenum, deformation and dilation of the common
bile duct, and indications of intussusception at the proximal
jejunum (Fig. 1B). Magnetic
resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) was conducted to evaluate
the biliary system, revealing an enlarged gallbladder, dilation of
the common bile duct and leftward displacement of its distal
segment (Fig. 1C).
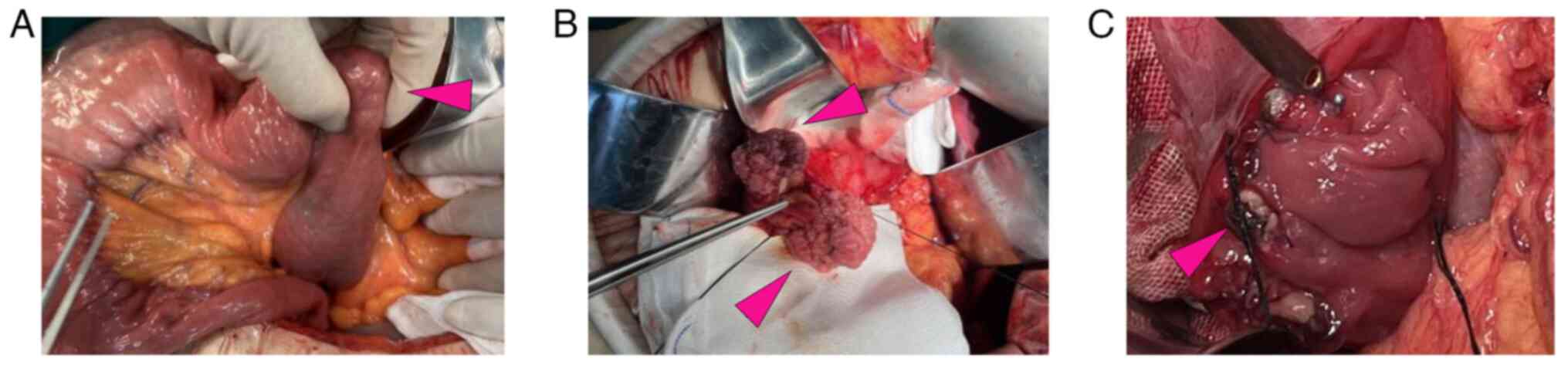
At 2 days post-admission, the patient underwent a
laparotomy due to the persistent epigastric pain and radiological
evidence of intestinal obstruction in the left upper abdomen, in
order to prevent progression to intestinal ischemia, perforation or
necrosis (Fig. 2). During the
operation, two large cauliflower-shaped tumors measuring 3.5x3x2.5
and 3x2.5x1.5 cm were observed in the D3 and D4 segments of the
duodenum, respectively, positioned at 3 and 9 o'clock. The lesions
were located ~7 cm distal to the duodenal papilla, without
involvement of the papillary region, and no direct invasion of the
pancreatic head or uncinate process was observed. A longitudinal
incision was made on the side wall of the duodenum to remove both
tumors along with ~1 cm of adjacent intestinal wall tissue
(Fig. 3). The displaced and
entrapped intestinal tract was successfully repositioned before
closing the duodenal incision and placing a drainage tube around
it. The intact sample was sent for pathological analysis.
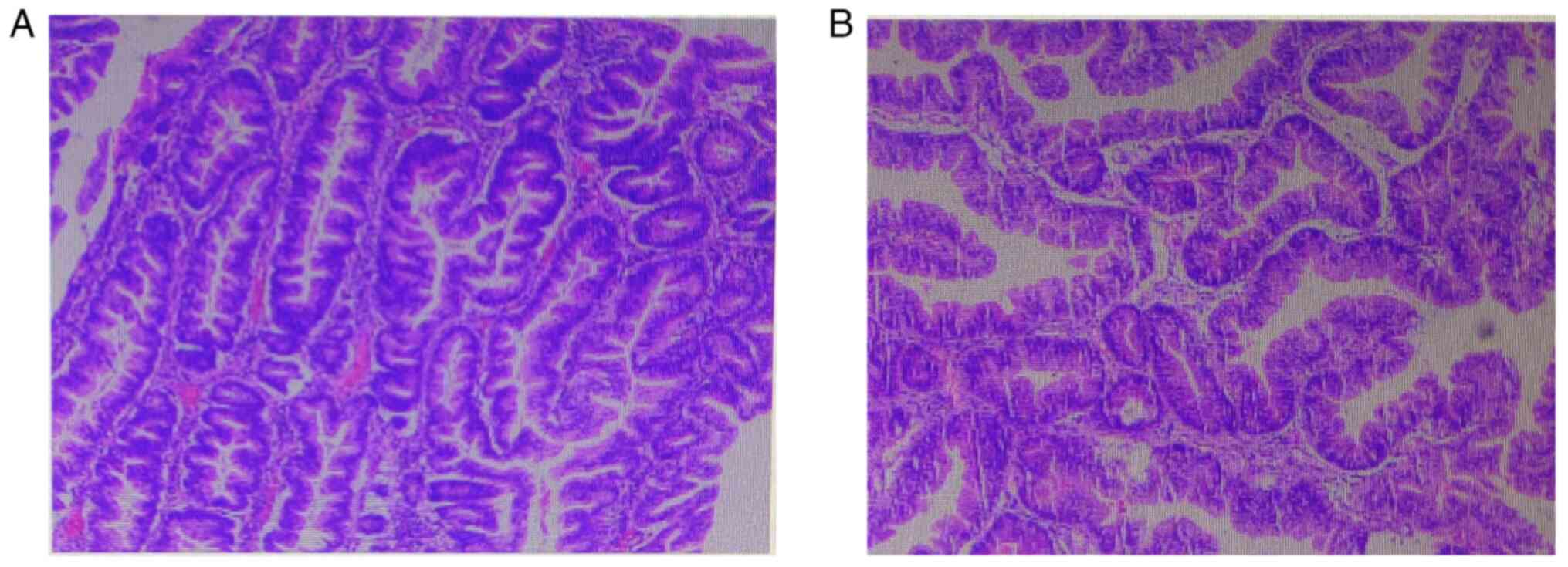
Tissues were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin
at room temperature for 24 h, sectioned at 4 µm, and stained with
hematoxylin and eosin at room temperature for 10 min each. Images
were captured using a Nikon Eclipse E100 light microscope (Nikon
Corporation) at x200 magnification. Histopathology results reported
a papillary tubular adenoma, localized high-grade epithelial
intraepithelial neoplasia and localized carcinoma in situ of
the mucosa (Fig. 3). Following
successful recovery, the patient was discharged from the
hospital.
Abdominal CT and gastroscopic examinations are being
performed at each follow-up visit, which have been planned at 3
months post-surgery, then every 6 months during the first year, and
annually thereafter. To date, the postoperative course has remained
uneventful, and the patient continues to be symptom-free, with no
evidence of recurrence on follow-up imaging.
Discussion
The present case is notable for two main reasons.
First, it underscores that an initial jejunum intussusception near
the Treitz ligament can be triggered by benign tumors in the D3 and
D4 segments of the duodenum, a finding not documented in previous
research, to the best of our knowledge. Second, while CT is the
primary imaging modality for adult intussusception, MRI may offer
complementary value in lesion characterization and in patients
where the avoidance of radiation is (11-13).
Primary intussusception occurs in the absence of a
point of invagination and is more common in children, with the
small intestine being most frequently affected. By contrast,
secondary intussusception arises from a lesion that acts as the
point of invagination. Although the underlying mechanism in adults
is not entirely clear, secondary intestinal intussusception is
believed to be triggered by a pathological lesion of the intestinal
wall that alters normal peristaltic activity, thus becoming a lead
point of invagination (2,14). In previously reported cases,
duodeno-jejunal intussusception typically involved the D2 segment
of the duodenum (15), whereas
duodeno-duodenal intussusception was observed in the D3 and D4
segments (8,9). However, synchronous tumors in the D3
and D4 segments are exceptionally rare but may disrupt duodenal
motility and precipitate jejunal intussusception near the ligament
of Treitz, highlighting the need for careful evaluation of
unexplained proximal small-bowel obstruction.
With the widespread adoption of CT, it has become
the most valuable imaging modality for diagnosing intussusception.
On CT images, a well-defined, smoothly contoured, sausage-shaped
mass is typically observed, consisting of two components, namely,
an inner intussusceptum and an outer intussuscipiens, with
eccentric areas of fat density representing the invaginated
mesenteric fat (16,17). Although previous studies have
confirmed the diagnostic superiority of CT for intestinal
intussusception (12,13), the present study findings indicate
that MRI, despite its greater cost and longer examination time, may
offer meaningful complementary value, especially in the
differential evaluation of soft-tissue pathology. Additionally,
since the distal portion (D3 and D4) of the duodenum is not within
the routine examination scope of gastroscopy, it is easily
misdiagnosed. The patient in the current case presented with a
series of clinical symptoms attributed to entrapment of the jejunal
loops at their proximal end, resulting in duodenal displacement and
subsequent biliary system displacement. This can lead to
obstruction of the distal bile duct, dilatation and obstruction of
the extrahepatic bile ducts, jaundice and mechanical obstruction of
the jejunum. Previous reports have indicated that involvement of
the junction of the pancreaticobiliary duct may cause obstructive
jaundice or acute pancreatitis (18,19).
Surgical treatment may be considered for patients with an unclear
diagnosis or severe symptoms (20,21).
The choice of the surgical plan depends mainly on the size of the
lesion and its relationship with the duodenal papilla (22). The duodenal papilla is closely
associated with the dilation of the common bile duct, making it
extremely important to predict the condition of the duodenal
papilla and develop a preoperative plan based on the degree of
biliary dilatation. MRCP imaging is of utmost importance in
diagnosing displacement and dilatation of the common bile duct
(23,24). Therefore, MRI is an extremely
important and effective diagnostic method for patients in which
there is difficulty in diagnosing intussusception.
The prognosis of intussusception depends mainly on
the causative factor of the lesion, and mortality from
intussusception in adults increases from 8.7% in benign causes to
52.4% in malignant causes (14).
Specifically, we highlight that this diagnosis warrants heightened
vigilance during postoperative surveillance, as it may indicate an
increased risk of recurrence or progression. Accordingly, we
emphasize the importance of individualized follow-up strategies,
including closer endoscopic and radiological monitoring.
In summary, this case underscores that synchronous
benign tumors originating in the D3 and D4 segments of the duodenum
may precipitate jejunal intussusception near the ligament of
Treitz, thereby emphasizing the complementary diagnostic utility of
MRI in such rare clinical scenarios. Intussusception involving the
proximal jejunum adjacent to the ligament of Treitz represents an
uncommon entity that should be considered in the differential
diagnosis when unexplained biliary displacement or dilatation is
encountered. MRI serves as a valuable modality for diagnostic
confirmation, and in patients with pronounced symptoms, surgical
intervention should be contemplated, with the operative strategy
tailored to the individual clinical context.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
LH performed the operation and wrote the manuscript.
LM participated in the study design and data interpretation. LM and
LH confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors agree
to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that
the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work (including the
provided data) are appropriately investigated and resolved. Both
authors have read and approved the final version of the
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
This study has been approved by the Ethics
Committees of Changzhi People's Hospital (Changzhi, China; approval
no. 2024K051).
Patient consent for publication
Informed written consent was obtained from the
patients for the publication of this report and any accompanying
images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Marsicovetere P, Ivatury SJ, White B and
Holubar SD: Intestinal intussusception: Etiology, diagnosis, and
treatment. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 30:30–39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Marinis A, Yiallourou A, Samanides L,
Dafnios N, Anastasopoulos G, Vassiliou I and Theodosopoulos T:
Intussusception of the bowel in adults: A review. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:407–411. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hong KD, Kim J, Ji W and Wexner SD: Adult
intussusception: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech
Coloproctol. 23:315–324. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kao YK and Chen JH: Adult Jejuno-jejunal
intussusception due to inflammatory fibroid polyp: A case report
and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore).
99(e22080)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cibulas MA, Carrillo EH, Lee SK and
Rosenthal AA: Jejuno-jejunal intussusception secondary to
recurrent/metastatic melanoma. Am Surg. 88:1024–1025.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sidharth M, Bains L, Bhatnagar P and
Mallya V: Jejuno-jejunal intussusception in an adult due to
inflammatory fibroid polyp: Tale of two unusual cases. Trop Doct.
55:267–269. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sahni M, Daga R, Jangir N, Singh S and
Sharma R: Management of a rare challenging case of duodenal
ampullary lipoma. Indian J Surg Oncol. 15 (Suppl 2):S322–S324.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Matsuura H, Saito A, Amano Y, Morishima K,
Sasanuma H, Lefor AK and Sata N: . Intussusception of the third
portion of the duodenum secondary to a primary duodenal malignancy:
A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 94(107085)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Varshney VK, Varshney B, Khera S and
Sureka B: Adenocarcinoma of the fourth portion of duodenum
presenting as intussusception: An unusual manifestation of rare
pathology. BMJ Case Rep. 14(e244034)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Agha RA, Franchi T, Sohrabi C, Mathew G
and Kerwan A: SCARE Group. The SCARE 2020 guideline: Updating
consensus surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int J Surg.
84:226–230. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tan KY, Tan SM, Tan AG, Chen CY, Chng HC
and Hoe MN: Adult intussusception: experience in Singapore. ANZ J
Surg. 73:1044–1047. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Takeuchi K, Tsuzuki Y, Ando T, Sekihara M,
Hara T, Kori T and Kuwano H: The diagnosis and treatment of adult
intussusception. J Clin Gastroenterol. 36:18–21. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
González-Carreró Sixto C, Baleato-González
S, García Palacios JD, Sánchez Bernal S, Junquera Olay S, Bravo
González M and García Figueiras R: Intestinal intussusception in
adults: Location, causes, symptoms, and therapeutic management.
Radiologia (Engl Ed). 65:213–221. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mohamed M, Elghawy K, Scholten D, Wilson K
and McCann M: Adult sigmoidorectal intussusception related to
colonic lipoma: A rare case report with an atypical presentation.
Int J Surg Case Rep. 10:134–137. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao B, Zhou X and Wang W: Duodenal
descending part-jejunum intussusception and upper gastrointestinal
bleeding caused by duodenal fibrolipoma: A case report. BMC Surg.
19(169)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chang CC, Chen YY, Chen YF, Lin CN, Yen HH
and Lou HY: Adult intussusception in Asians: Clinical
presentations, diagnosis, and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
22:1767–1771. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gayer G, Apter S, Hofmann C, Nass S,
Amitai M, Zissin R and Hertz M: Intussusception in adults: CT
diagnosis. Clin Radiol. 53:53–57. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schnedl WJ, Reisinger EC, Lipp RW,
Uggowitzer M, Mischinger HJ, Fickert P and Krejs GJ: . Biliary
obstruction due to duodenojejunal intussusception in Peutz-Jeghers
syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 23:220–223. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jeon SJ, Yoon SE, Lee YH, Yoon KH, Kim EA
and Juhng SK: Acute pancreatitis secondary to duodenojejunal
intussusception in Peutz-Jegher syndrome. Clin Radiol. 62:88–91.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Russel G and Postier Ronald A: Acute
abdomen. In: Sabisten text book of surgery. 18th Edition.
pp1180-1198, 2008.
|
|
21
|
Ademe Y, Seyoum N and Lemma R: Surgical
management of acute abdomen in adult patients: Experience from a
Private Hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci.
32:729–738. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yamamoto K, Iwasaki E and Itoi T: Insights
and updates on endoscopic papillectomy. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 14:435–444. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pavone P, Laghi A, Catalano C, Panebianco
V, Fabiano S and Passariello R: MRI of the biliary and pancreatic
ducts. Eur Radiol. 9:1513–1522. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fulcher AS, Turner MA and Capps GW: MR
cholangiography: Technical advances and clinical applications.
Radiographics. 19:25–41; discussion 41-4. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|