Introduction
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an acquired
autoimmune disorder characterized by an isolated platelet count of
<100x109/l in the absence of any other identifiable
cause (1). The underlying
mechanisms include increased platelet destruction and impaired
platelet production, due to autoreactive antibodies and T-cell
dysregulation (2). ITP can present
with asymptomatic thrombocytopenia or progress to clinically
notable bleeding, particularly if platelet count is
<30x109/l (1,3).
Severe bleeding events, such as gastrointestinal or intracranial
bleeding, are rare but can be life-threatening (1).
Epidemiologically, ITP affects ~3-4 per 100,000
individuals annually, particularly women and adults >60 years of
age (1). Beyond the immediate risk
of hemorrhage, patients with ITP frequently experience a
considerable disease burden, including fatigue, psychological
distress, and treatment-related adverse effects such as
corticosteroid-related metabolic disturbances, all of which
collectively impair their quality of life (4).
First-line treatments for ITP, including
corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), can achieve
rapid platelet responses but are limited by short-term efficacy
(lasting only days to a few weeks) and notable adverse effects,
such as weight gain, glucose intolerance, mood changes and
infusion-related reactions including headache, fever and rash
(3). Consequently, numerous
patients either relapse as platelet counts decrease or discontinue
therapy because of cumulative toxicity, therefore requiring
second-line treatment. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs)
have become the key second-line option for stimulating
megakaryopoiesis and enhancing platelet production (5). These agents have demonstrated
favorable efficacy and enable the tapering or discontinuation of
corticosteroids (6,7).
To the best of our knowledge, to date, four TPO-RAs
have been approved for ITP treatment in China, the European Union
and United States. These include the peptide-based agent
romiplostim and the non-peptidic small molecules eltrombopag,
avatrombopag and hetrombopag (8).
Unlike romiplostim, the three non-peptidic oral agents can be
self-administered at home, which has driven their widespread
adoption in routine ITP care (6,7).
However, as the treatment durations and exposure in patients
increase, the overall safety profile of non-peptidic TPO-RAs
long-term remains unclear. Furthermore, elevations in hepatic
enzyme levels have emerged as an important safety concern (9). Considering the lack of synthesized
evidence, the present study conducted a meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the potential hepatic risks of
non-peptidic TPO-RAs in ITP.
Materials and methods
Literature search
The present meta-analysis was designed and conducted
in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic
reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 guidelines and methodological
guidelines of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of
Interventions (10,11). In line with these standards, the
present study protocol was prospectively registered in the
International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews
(registration no. CRD420251084782; https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD420251084782).
The present study comprehensively searched PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), Web of Science
(https://webofscience.clarivate.cn)
and the Chinese Medical Association Journal Database (CMAJD;
https://www.yiigle.com/index) from
database inception to June 2, 2025.
The search strategy combined medical subject
headings and free-text terms, including ‘immune thrombocytopenia’,
‘immune thrombocytopenic purpura’, ‘idiopathic thrombocytopenia’,
‘idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura’, ‘ITP’, ‘eltrombopag’,
‘avatrombopag’, ‘hetrombopag’, ‘liver function tests’, ‘hepatic
enzyme’, ‘transaminases’, ‘alanine aminotransferase’ (ALT),
‘aspartate aminotransferase’ (AST) and ‘randomized controlled
trial’.
The reference lists of eligible studies were
manually screened to identify additional trials. If the outcome
data were incomplete, the corresponding authors were contacted
through e-mail for clarification. Filters were not used during the
search process.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows: i) RCT design;
ii) enrolled patients diagnosed with ITP according to the American
Society of Hematology guidelines (12); iii) treatment duration of >1
week; and iv) at least one hepatic enzyme outcome was reported
(ALT, AST or transaminase levels). The exclusion criteria were as
follows: i) Duplicate publications reporting the same data; ii)
articles not published in English or Chinese; and iii) records
lacking full-text access; and iv) studies lacking a control
group.
Data extraction
All search results were imported into EndNote X9
(Clarivate Plc) for reference management. Duplicate records were
identified, electronically removed and verified manually. In total,
two investigators screened the remaining titles and abstracts,
excluding articles that clearly failed to meet the pre-specified
inclusion criteria. The full texts of potentially relevant studies
were retrieved and reviewed in detail based on the inclusion and
exclusion criteria.
After identifying all the eligible studies, two
investigators independently extracted the following information
using a standardized data extraction form, including the first
author, year of publication, study design, sample size, participant
characteristics, intervention and control regimens (drug and
treatment duration) and reported hepatic enzyme outcomes. Upon the
completion of data extraction, the two datasets were cross-checked
for consistency. Discrepancies were addressed through consensus
discussions with arbitration by a third investigator, if
necessary.
Quality analysis
Methodological quality was assessed using the
Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias (RoB) tool (version 2.0)
(13). A total of two
investigators independently assessed each RCT across the following
seven key domains: i) Random sequence generation; ii) allocation
concealment; iii) participants and personnel blinding; iv) outcome
assessment blinding; v) incomplete outcome data; vi) selective
outcome reporting; and vii) other potential sources of bias, such
as baseline imbalances or inappropriate analytical methods. For
each domain, signaling questions were answered according to the RoB
2.0 algorithm and rated as ‘low risk’, ‘unclear risk’ or ‘high
risk’. Discrepancies between investigators were resolved by
discussion and if consensus was not achieved, a third investigator
was consulted. All quality assessments were conducted without
blinding to study authorship or journal of publication and the
final ratings were presented in tables or graphs to inform the
interpretation of the pooled estimates.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using Review Manager
(version 5.4.1; The Cochrane Collaboration). Dichotomous outcomes
were pooled as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs. The statistical
significance of pooled effect sizes was assessed using the Z-test.
Inter-study heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran s Q test
and quantified using the I2 statistic. A
DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model was applied to all the
meta-analyses, with effect sizes synthesized using the inverse
variance method, as recommended by the Cochrane Handbook for
Systematic Reviews of Interventions. If I2 was >50%,
planned subgroup or sensitivity analyses were to be used to explore
potential sources of heterogeneity; however, these analyses were
not performed in the present study because all pooled results
demonstrated low heterogeneity (I² <30%). Publication bias was
evaluated using Egger s test. All pre-specified primary and
subgroup meta-analyses were presented as forest plots to ensure
transparency and facilitate interpretation. Presenting these
results, including overall results from all included studies,
duration-specific (≥6 weeks), adult-only (enrolling participants
>18 years of age), agent-specific and severe transaminase
analyses, allowed for clear visualization of study-level effect
sizes and heterogeneity, consistent with the Cochrane
recommendations for reporting meta-analyses. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Study selection
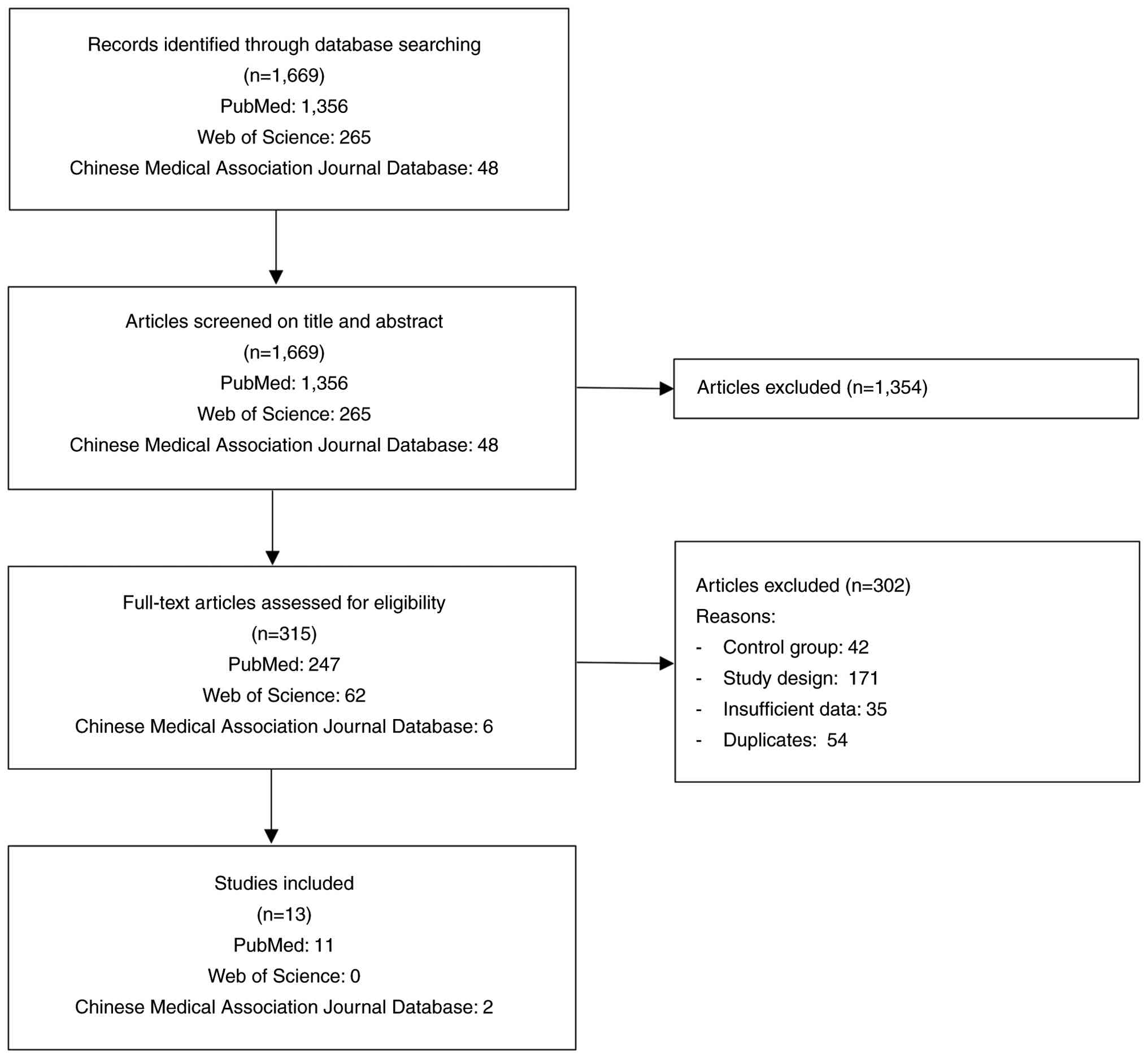
Database searches yielded 1,669 records, including
48 studies from the CMAJD. After screening the titles and
abstracts, 1,354 records were excluded, leaving 315 articles for
full-text review. Of these, 302 articles were excluded due to
non-randomized study designs, lack of hepatic enzyme outcomes,
absence of an appropriate control group or overlapping patient
populations. Ultimately, the present meta-analysis included 13 RCTs
(14-26),
all of which were publicly available, with 11 studies identified
from PubMed and two studies identified from the CMAJD (Fig. 1). These studies were published in
the period of 2007-2024.
Study characteristics
Of the included studies, 12 were conducted at
multiple centers (14-25),
including five that involved multinational collaboration (14-16,18,24).
Single-country multicenter studies were conducted in Japan
(17), the United States (23), China (19,20,22,25)
and Canada (21). A total of 11
trials used a double-blind design (14-20,22-25),
while the remaining two trials were conducted using an open-label
design (21,26). Furthermore, two studies were
published in Chinese (20,26) and the remaining studies were
published in English. The enrolled population predominantly
included adults aged 18-85 years (14-17,19-26),
with one trial exclusively focusing on pediatric patients aged 1-17
years (18), in which written
informed consent was obtained from the parents or legal guardians
of all participating children. The participants exhibited all the
clinical subtypes of ITP, including newly diagnosed, persistent and
chronic ITP. The interventions assessed included eltrombopag (n=9),
avatrombopag (n=2) and hetrombopag (n=2). The comparator groups
received placebo treatment (n=10), recombinant human thrombopoietin
(n=2) or IVIG (n=1). The treatment duration varied from 1 week to 6
months. In total, 1,480 patients were included, with 1,034 in the
intervention arm (including 63 pediatric patients) and 446 in the
control arm (including 29 pediatric patients). All the included
studies reported hepatic enzyme elevation events, defined as
increases in ALT and/or AST. Detailed characteristics of the
included studies are presented in Table I.
 | Table IStudy characteristics. |
Table I
Study characteristics.
| A, Eltrombopag |
|---|
| | | Elevations in
hepatic enzymes | Severe transaminase
elevation | |
|---|
| First author,
year | Study design | Country | Study duration | Population
(intervention/control) | Comparator | Intervention
group | Control group | Intervention
group | Control group | (Refs.) |
|---|
| Bussel et
al, 2007 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | 13 countries | 6 weeks | 117 (88/29) | Placebo | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | (14) |
| Bussel et
al, 2009 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | 23 countries | 6 weeks | 114 (76/38) | Placebo | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | (15) |
| Cheng et al,
2011 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | 23 countries | 6 months | 197 (135/62) | Placebo | 17 | 6 | 9 | 2 | (16) |
| Tomiyama et
al, 2012 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | Japan | 6 weeks | 23 (15/8) | Placebo | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | (17) |
| Grainger et
al, 2015 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | 12 countries | 13 weeks | 92 (63/29) | Placebo | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 | (18) |
| Yang et al,
2017 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | China | 8 weeks | 155 (104/51) | Placebo | 13 | 6 | 1 | 1 | (19) |
| Huang et al,
2018 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | China | 6 weeks | 35 (17/18) | Placebo | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | (20) |
| Arnold et
al, 2020 | Multicenter,
randomized, open-label and controlled | Canada | 4 weeks | 74 (38/36) | IVIG | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | (21) |
| Mei et al,
2021(1) | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and controlled | China | 2 weeks | 96 (48/48) | rhTPO | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | (22) |
| B,
Avatrombopag |
| | | Elevations in
hepatic enzymes | Severe transaminase
elevation | |
| First author,
year | Study design | Country | Study duration | Population
(intervention/control) | Comparator | Intervention
group | Control group | Intervention
group | Control group | (Refs.) |
| Bussel et
al, 2014 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | United States | 4 weeks | 64 (59/5) | Placebo | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | (23) |
| Jurczak et
al, 2018 | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | 11 countries | 6 months | 49 (32/17) | Placebo | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | (24) |
| C, Hetrombopag |
| | | Elevations in
hepatic enzymes | Severe transaminase
elevation | |
| First author,
year | Study design | Country | Study duration | Population
(intervention/control) | Comparator | Intervention
group | Control group | Intervention
group | Control group | (Refs.) |
| Mei et al,
2021(2) | Multicenter,
randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled | China | 10 weeks | 424 (339/85) | Placebo | 24 | 8 | 0 | 0 | (25) |
| Sun et al,
2024 | Single institution,
randomized and controlled | China | 1 week | 40 (20/20) | rhTPO | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | (26) |
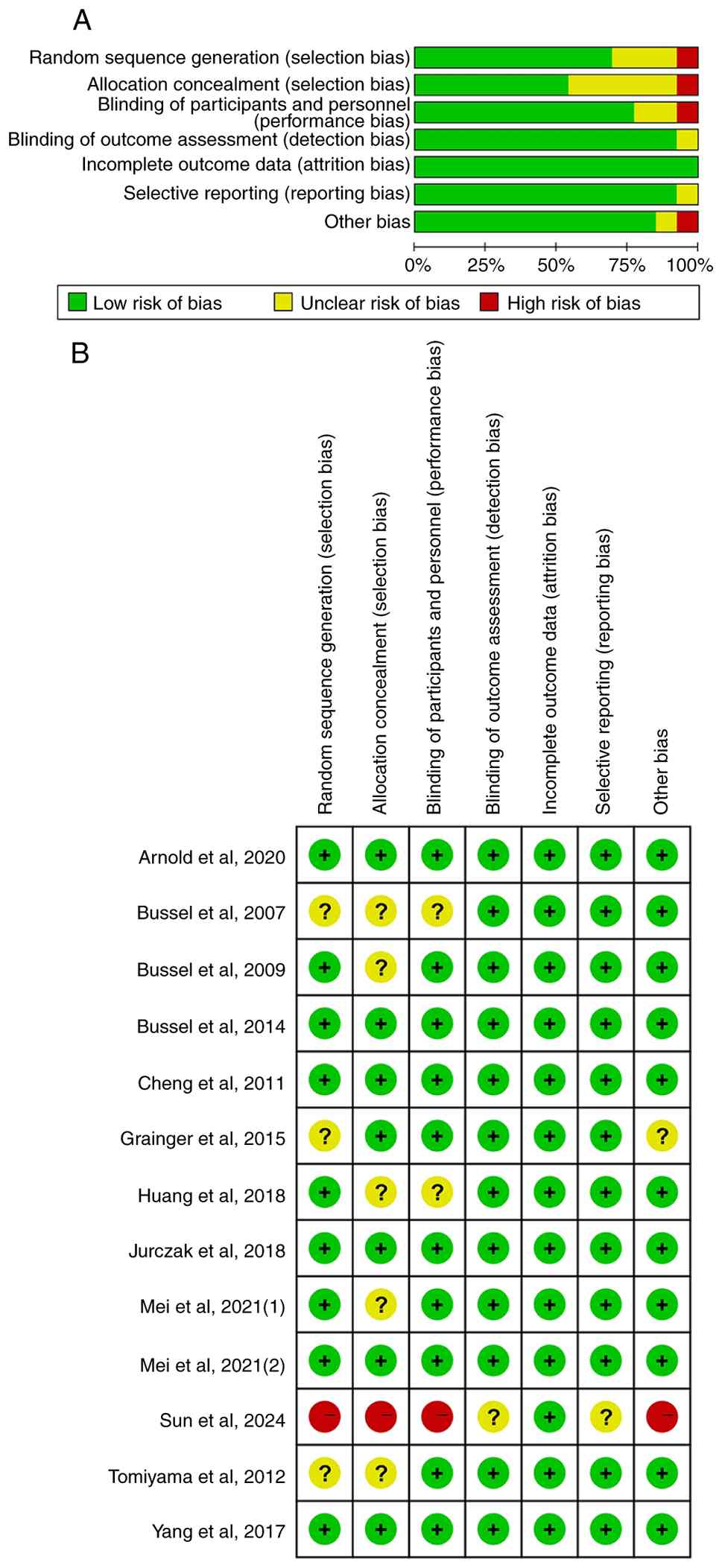
With regards to study quality, six trials were rated
as having a ‘low risk’ of bias, six as having an ‘unclear risk’ and
one study was deemed to have a ‘high risk’, mainly due to
deficiencies in random sequence generation, allocation concealment
and blinding of participants and personnel. A summary of the bias
assessment across the studies is presented in Fig. 2.
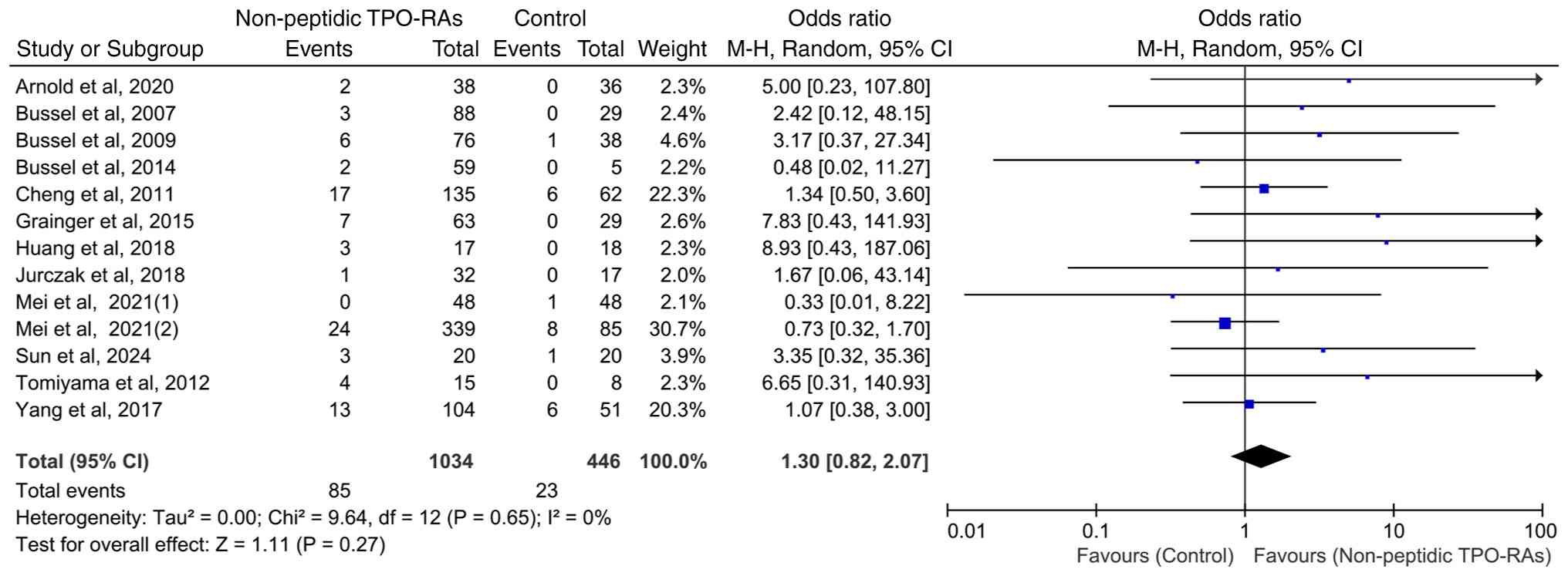
Hepatic enzyme elevation events on
total non-peptidic TPO-RAs
Heterogeneity testing indicated a high level of
consistency across the 13 included studies (χ2=9.64;
P=0.65; I2=0%), suggesting no significant inter-study
variability. Hepatic enzyme elevation events occurred in 8.22%
(85/1,034) of patients receiving non-peptidic TPO-RAs for ITP
compared with 5.16% (23/446) patients in the control group.
Although the event rate was higher in the intervention group, a
pooled analysis revealed no statistically significant increase in
the risk of hepatic enzyme elevation events with non-peptidic
TPO-RAs compared with that in the controls (OR=1.30; 95% CI,
0.82-2.07; P=0.27; Fig. 3).
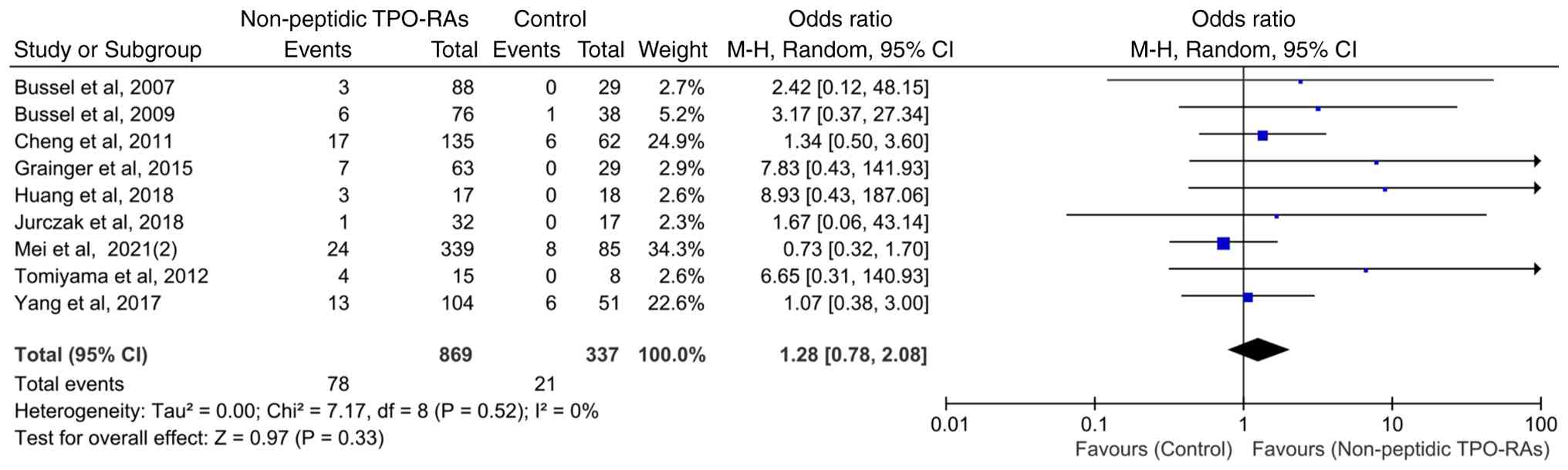
Hepatic enzyme elevation events in
patients treated for ≥6 weeks
To assess the potential impact of treatment duration
on hepatic enzyme elevation events, nine studies with a treatment
duration of ≥6 weeks were analyzed. The heterogeneity among these
studies was low (χ2=7.17; P=0.52; I2=0%),
indicating good consistency among the trials. The pooled analysis
demonstrated that compared with that in the control group,
non-peptidic TPO-RA treatment lasting ≥6 weeks was not associated
with a statistically significant increase in the incidence of
hepatic enzyme elevation events (OR=1.28; 95% CI, 0.78-2.08;
P=0.33; Fig. 4).
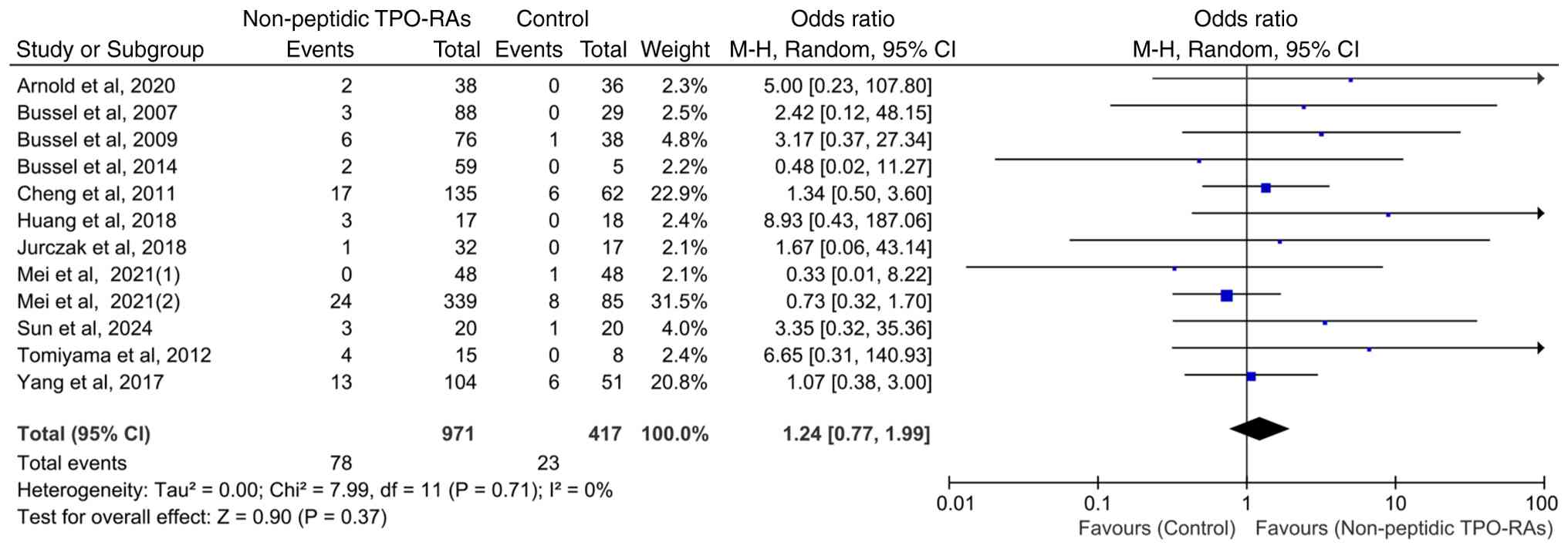
Hepatic enzyme elevation events in
adult patients
Of the 13 included RCTs, 12 exclusively enrolled
adult participants. To ensure population homogeneity, separate
analyses were conducted on all adult cohorts. The pooled results
demonstrated no significant difference in the incidence of hepatic
enzyme elevation events between patients treated with non-peptidic
TPO-RAs and those in the control group (OR=1.24; 95% CI, 0.77-1.99;
P=0.37), with no observed heterogeneity among studies
(χ2=7.99; P=0.71; I2=0%; Fig. 5). Owing to the inclusion of only
one pediatric study, no separate analysis was performed on cohorts
of children.
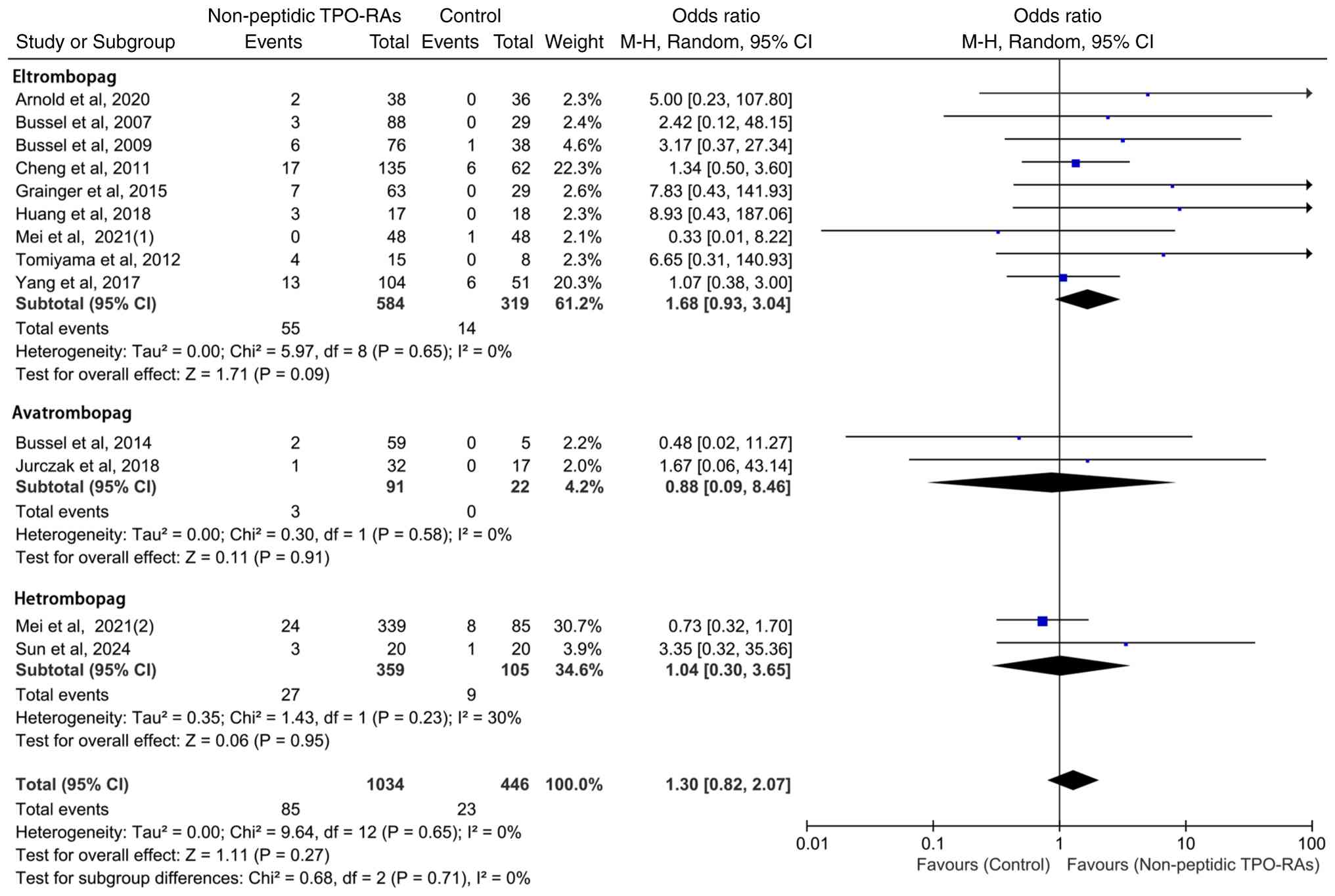
Subgroup analysis of hepatic enzyme
elevation events by individual TPO-RAs
To facilitate comparison, the subgroup results for
eltrombopag, avatrombopag and hetrombopag are presented within a
single integrated forest plot, which allows for clear visualization
of the ORs and 95% CIs whilst avoiding unnecessary fragmentation
into multiple figures. Based on this layout, a subgroup analysis
was performed to further assess the hepatic safety profiles of
individual non-peptidic TPO-RAs. Eltrombopag (OR=1.68; 95% CI:
0.93-3.04; P=0.09) and hetrombopag (OR=1.04; 95% CI: 0.30-3.65;
P=0.95) demonstrated a trend toward increased risk when compared
with the control group, whereas avatrombopag (OR=0.88; 95% CI:
0.09-8.46; P=0.91) exhibited a trend toward reduced risk (Fig. 6). Notably, no statistically
significant differences in hepatic enzyme elevation events were
observed between any of the agents and their respective
controls.
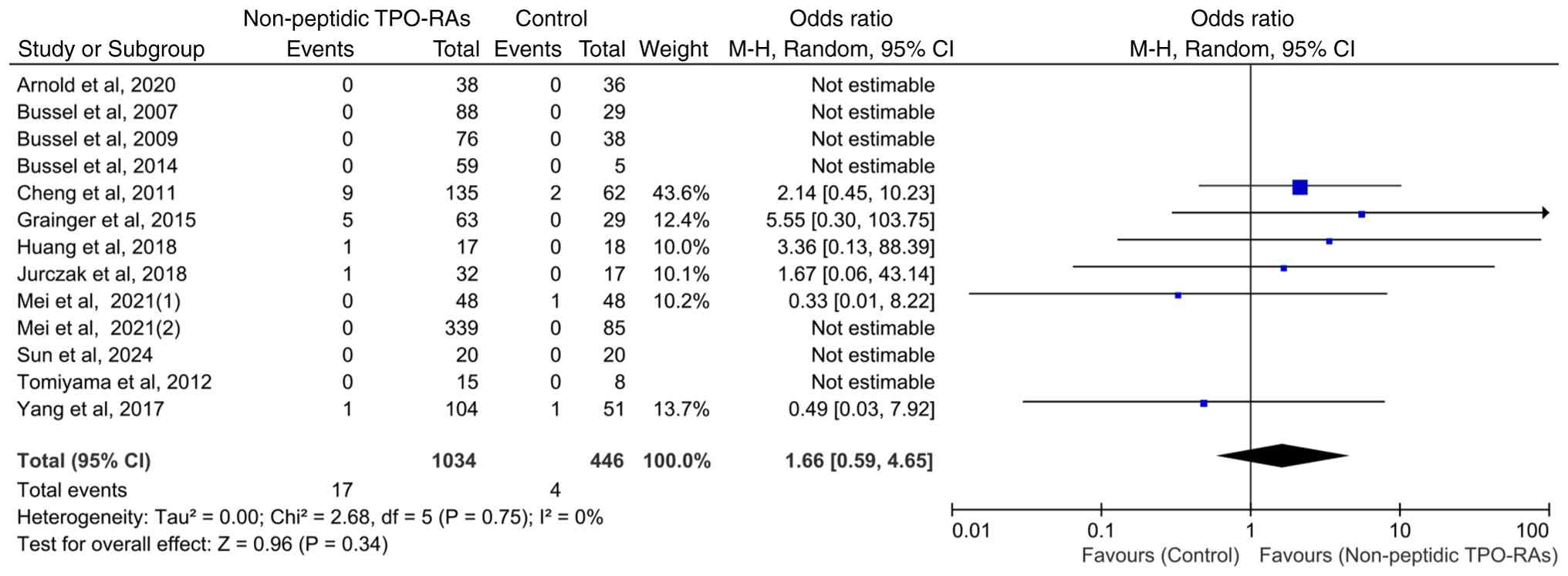
Incidence of severe transaminase
elevation with non-peptidic TPO-RAs
All 13 included studies reported whether severe
transaminase elevation events (defined as hepatic enzyme levels ≥3
times the upper limit of normal) occurred as an outcome, but only
six studies documented actual events, while the remaining studies
reported zero events. Heterogeneity among studies was low
(χ2=2.68; P=0.75; I2=0%). The incidence of
severe transaminase elevation events was 1.64% (17/1,034) in the
intervention group and 0.90% (4/446) in the control group. However,
no statistically significant differences were observed between the
groups (OR=1.66; 95% CI: 0.59-4.65; P=0.34; Fig. 7).
Publication bias
Egger s test indicated statistically
significant asymmetry (P=0.02), suggesting the presence of
small-study effects. However, heterogeneity across studies was
minimal (I²=0%), indicating that this asymmetry was unlikely to
materially influence the pooled estimates.
Discussion
The present meta-analysis of 13 RCTs demonstrated
that non-peptidic TPO-RAs used to treat patients with ITP did not
result in a significantly increased incidence of hepatic enzyme
elevation events compared with that in the control group, with
minimal heterogeneity across studies. This finding was consistent
across studies comprising adult populations, a longer treatment
duration (≥6 weeks) and each individual agent (eltrombopag,
avatrombopag and hetrombopag). Furthermore, no significant
differences were observed in the incidence of severe transaminase
elevation events between the intervention and control groups. These
findings indicated that non-peptidic TPO-RAs were not associated
with a clinically notable increase in the risk of hepatic enzyme
abnormalities.
Hepatic enzyme elevation is classified as an adverse
event of interest in the context of non-peptidic TPO-RA therapy
(24,25). This concern stems from the fact
that these agents are metabolized in the liver and that hepatic
enzyme abnormalities have been reported in previous clinical trials
and post-marketing surveillance (27-32).
The present meta-analysis demonstrated that the incidence of
hepatic enzyme elevation events during non-peptidic TPO-RA
treatments for ITP (8.22%) was higher compared with that in the
control group (5.16%). However, the difference was not
statistically significant. In addition, the findings revealed that
severe transaminase elevation events were rare in both cohorts and
occurred at comparable rates in the intervention and control groups
(1.64 vs. 0.90% respectively). These findings suggest that although
hepatic enzyme elevation events were more frequent in the
intervention group, severe transaminase elevation events were rare
and should not necessarily be attributed to non-peptidic TPO-RA
therapy.
To examine whether longer exposure influences
hepatic safety, a separate analysis of patients treated for ≥6
weeks was conducted. This analysis likewise showed no significant
increase in hepatic enzyme elevation events in the TPO-RA group.
Data from long-term studies and real-world observations reinforce
the notion that hepatic events may not be time-dependent. The open
label Eltrombopag eXTENded Dosing trial (median exposure of ~2
years to eltrombopag) showed that prolonged therapy remained
generally safe and well-tolerated without new safety issues
emerging over time (33). Another
previous retrospective cohort study of 85 patients with ITP on
eltrombopag found hepatic enzyme elevations in 11.8% patients but
no notable association between the occurrence of these elevations
and the duration of eltrombopag therapy or cumulative dose
(34). This suggests that the
susceptibility to non-peptidic TPO-RA-associated hepatic effects
may depend on patient-specific factors (such as underlying liver
conditions or metabolic risk factors) rather than the treatment
duration. This same previous study demonstrated that comorbid type
2 diabetes or pre-existing hepatobiliary disease was associated
with higher risk of mild liver test elevation, whereas treatment
duration was not (34). Therefore,
evaluation of pre-existing liver disease and metabolic risk factors
before therapy may be more important than treatment duration in
predicting subsequent hepatic effects.
The pathophysiology and prognosis of ITP differ
between adults and children, such that abnormalities in liver
function and metabolic disorders are more prevalent in adults
(35). Consequently, adults may
face a greater risk of drug-related hepatic complications during
non-peptidic TPO-RA therapy. A separate analysis restricted to
adult cohorts was conducted and found no significant increase in
the incidence of hepatic enzyme elevation events. However, given
the availability of only one small pediatric trial, the present
study was unable to perform a comparative analysis of the incidence
of hepatic events in adults and children. This may represent an
important area for future investigation to clarify potential
age-related differences in hepatic responses to non-peptidic TPO-RA
therapy.
Despite shared hepatic metabolism, variability in
metabolic pathways among non-peptidic TPO-RAs may influence hepatic
safety profiles. Among the oral agents, eltrombopag exhibits the
most pronounced hepatic safety signals, and post-marketing
pharmacovigilance studies have suggested that it may be associated
with a higher frequency of liver-related adverse events, with
clinical trials reporting hepatic enzyme elevations in 8-15% of
patients (16,19,27).
By contrast, avatrombopag appears to be associated with a lower
incidence of hepatotoxicity, especially with short-term use. In
trials with avatrombopag, ALT elevations were observed in only 1-4%
treated patients, similar to those treated with placebo (0-2%) and
were reversible (36). Although
the longer use (~6 months) of avatrombopag may result in slightly
more frequent mild liver enzyme increases, no serious liver injury
events have been attributed to avatrombopag, which is frequently
described as having ‘no known hepatotoxicity signals’ as opposed to
eltrombopag (27). These findings
exhibit some similarity to those observed in the subgroup analysis.
Although statistical significance was not reached, eltrombopag
(OR=1.68; 95% CI, 0.93-3.04) exhibited a trend toward an increased
risk of hepatic enzyme elevation, whereas avatrombopag (OR=0.88;
95% CI, 0.09-8.46) exhibited a slightly reduced risk compared with
the control group. The wide 95% CI for avatrombopag reflects the
limited sample size and small number of events, resulting in
statistical imprecision rather than true heterogeneity. This
interpretation is supported by the low I2 value observed
and underscores the need for additional trials with avatrombopag to
provide more precise estimates. Nevertheless, this particular
result may indirectly support the clinical rationale for the
preferential use of avatrombopag in the management of
thrombocytopenia in patients with underlying chronic liver disease
(36). In addition, given the
increase in the incidence of hepatic events in the TPO-RA therapy
group overall (8.22 vs. 5.16%) and the eltrombopag-specific trend,
closer monitoring may be warranted in patients with pre-existing
liver disease or other hepatic vulnerabilities when prescribing
non-peptidic TPO-RAs.
The present study has several limitations. First,
the strict eligibility criteria led to a relatively small sample
size and the included trials varied in treatment duration and
choice of control arm, which may have introduced residual bias
despite low statistical heterogeneity. In addition, because the
longest treatment duration among the included studies was only 6
months, the present findings do not capture the hepatic safety
profile of prolonged, multi-year therapy with non-peptidic TPO-RAs.
The current evidence base in pediatric populations is also limited
and further studies specifically focusing on children are
warranted. The lack of standardized definitions for liver outcome
measures across trials (apart from severe transaminase elevation
events, which were uniformly defined as ≥3 times the upper limit of
normal) may hinder comparability, highlighting the need for uniform
criteria in future research to enhance the validity and clinical
applicability of the findings. Numerous trials did not provide
standardized information on the ethnic composition of the
participants and none reported analyses stratified by ethnicity,
limiting the generalizability of the present findings. Future
studies should report and analyze ethnicity more explicitly to
address this gap. The present study also fully acknowledges the
potential clinical importance of comorbidities, as well as more
refined subgrouping based on parameters such as sex, baseline
platelet counts, or comorbid liver disease. However, the relatively
short period since the clinical introduction of non-peptidic
TPO-Ras, beginning in 2007, as first reported in the pivotal
eltrombopag trial (14), and the
limited number and scope of currently available trials mean that
such data were not sufficiently reported to allow meaningful
meta-regression. This represents an inherent limitation of the
evidence base at present. Future studies should place greater
emphasis on patient heterogeneity, particularly comorbidity burden
and long-term treatment effects.
Overall, the present meta-analysis indicated that
the use of non-peptidic TPO-RAs does not increase the risk of
hepatic enzyme abnormalities during treatments for ITP, suggesting
a favorable hepatic safety profile. This finding provides
clinically relevant reassurance for physicians when prescribing
non-peptidic TPO-RAs, as long as appropriate liver function
monitoring is maintained. From a clinical perspective, this
provides evidence to support the continued use of TPO-RAs as
effective therapeutic options in practice.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: The present study was supported by the Suqian Sci &
Tech Project (grant no. K202428).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors contributions
SZ and JL designed the present study. RW, TL, YJ,
JY, TN, CD and SL collected the data. NS, RW and TL performed the
data analysis and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and
approved the final version of the manuscript. NS and SZ confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Cooper N and Ghanima W: Immune
thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 381:945–955. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Audia S, Mahévas M, Samson M, Godeau B and
Bonnotte B: Pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmun Rev.
16:620–632. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gafter-Gvili A: Current approaches for the
diagnosis and management of immune thrombocytopenia. Eur J Intern
Med. 108:18–24. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cooper N, Kruse A, Kruse C, Watson S,
Morgan M, Provan D, Ghanima W, Arnold DM, Tomiyama Y, Santoro C, et
al: Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) World Impact Survey (I-WISh):
Impact of ITP on health-related quality of life. Am J Hematol.
96:199–207. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bussel J, Kulasekararaj A, Cooper N, Verma
A, Steidl U, Semple JW and Will B: Mechanisms and therapeutic
prospects of thrombopoietin receptor agonists. Semin Hematol.
56:262–278. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pulanić D, Bátorová A, Bodó I, Červinek L,
Ionita I, Lissitchkov T, Melikyan A and Podolak-Dawidziak M: Use of
thrombopoietin receptor agonists in adults with immune
thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and Central European expert
consensus. Ann Hematol. 102:715–727. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lassandro G, Palladino V, Vecchio GCD,
Palmieri VV, Corallo PC, Faienza MF and Giordano P: Thrombopoietin
receptor agonists in children with immune thrombocytopenia: A new
therapeutic era. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets.
21:397–406. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gebetsberger J, Streif W and Dame C:
Update on the use of thrombopoietin-receptor agonists in
pediatrics. Hamostaseologie. 44:316–325. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lucchesi A, Lovrencic B, McDonald V,
Newland A, Morgan M, Eriksson D, Wilson K, Giordano G, Carli G,
Geldman E, et al: Treatment preferences towards
thrombopoietin-receptor agonists for immune thrombocytopenia and
experience of disease (TRAPeze): Italy cohort. Hematology.
28(2253069)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J,
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA*(eds): Cochrane handbook for
systematic reviews of interventions. Version 6.5. Cochrane,
Alberta, 2024. Available from: http://www.cochrane.org/handbook.
|
|
12
|
George JN, Woolf SH, Raskob GE, Wasser JS,
Aledort LM, Ballem PJ, Blanchette VS, Bussel JB, Cines DB, Kelton
JG, et al: Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A practice
guideline developed by explicit methods for the American society of
hematology. Blood. 88:3–40. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG,
Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge
SM, et al: RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 366(l4898)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bussel JB, Cheng G, Saleh MN, Psaila B,
Kovaleva L, Meddeb B, Kloczko J, Hassani H, Mayer B, Stone NL, et
al: Eltrombopag for the treatment of chronic idiopathic
thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 357:2237–2247.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bussel JB, Provan D, Shamsi T, Cheng G,
Psaila B, Kovaleva L, Salama A, Jenkins JM, Roychowdhury D, Mayer
B, et al: Effect of eltrombopag on platelet counts and bleeding
during treatment of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet.
373:641–648. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cheng G, Saleh MN, Marcher C, Vasey S,
Mayer B, Aivado M, Arning M, Stone NL and Bussel JB: Eltrombopag
for management of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (RAISE): A
6-month, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet. 377:393–402.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tomiyama Y, Miyakawa Y, Okamoto S,
Katsutani S, Kimura A, Okoshi Y, Ninomiya H, Kosugi H, Nomura S,
Ozaki K, et al: A lower starting dose of eltrombopag is efficacious
in Japanese patients with previously treated chronic immune
thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 10:799–806. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Grainger JD, Locatelli F,
Chotsampancharoen T, Donyush E, Pongtanakul B, Komvilaisak P,
Sosothikul D, Drelichman G, Sirachainan N, Holzhauer S, et al:
Eltrombopag for children with chronic immune thrombocytopenia
(PETIT2): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial.
Lancet. 386:1649–1658. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang R, Li J, Jin J, Huang M, Yu Z, Xu X,
Zhang X and Hou M: Multicentre, randomised phase III study of the
efficacy and safety of eltrombopag in Chinese patients with chronic
immune thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 176:101–110.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang YT, Liu XF, Chen YF, Fu RF, Liu W,
Zhang L and Yang RC: The efficacy and safety of eltrombopag in
Chinese patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Zhonghua Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 39:32–36. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Arnold DM, Heddle NM, Cook RJ, Hsia C,
Blostein M, Jamula E, Sholzberg M, Lin Y, Kassis J, Larratt L, et
al: Perioperative oral eltrombopag versus intravenous
immunoglobulin in patients with immune thrombocytopenia: A
non-inferiority, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Haematol.
7:e640–e648. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mei H, Xu M, Yuan G, Zhu F, Guo J, Huang
R, Qin J, Lv T, Qin F, Cai H, et al: A multicentre double-blind,
double-dummy, randomised study of recombinant human thrombopoietin
versus eltrombopag in the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia in
Chinese adult patients. Br J Haematol. 195:781–789. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bussel JB, Kuter DJ, Aledort LM, Kessler
CM, Cuker A, Pendergrass KB, Tang S and McIntosh J: A randomized
trial of avatrombopag, an investigational thrombopoietin-receptor
agonist, in persistent and chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Blood.
123:3887–3894. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jurczak W, Chojnowski K, Mayer J, Krawczyk
K, Jamieson BD, Tian W and Allen LF: Phase 3 randomised study of
avatrombopag, a novel thrombopoietin receptor agonist for the
treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol.
183:479–490. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mei H, Liu X, Li Y, Zhou H, Feng Y, Gao G,
Cheng P, Huang R, Yang L, Hu J, et al: A multicenter, randomized
phase III trial of hetrombopag: A novel thrombopoietin receptor
agonist for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia. J Hematol
Oncol. 14(37)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun Q, Wang H, Chen L, Shao J, Zhang W,
Zhou F and Jian X: Effect analysis of recombinant human
thrombopoietin and herombopag on immune function in patients with
primary immune thrombocytopenia. Int J Blood Transfus Hematol.
47:503–511. 2024.
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Li Y and Zhuang W: Safety analysis
of romiplostim, eltrombopag, and avatrombopag post-market approval:
A pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting
system. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 26(46)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Deng Y, Madatian A, Wire MB, Bowen C, Park
JW, Williams D, Peng B, Schubert E, Gorycki F, Levy M and Gorycki
PD: Metabolism and disposition of eltrombopag, an oral, nonpeptide
thrombopoietin receptor agonist, in healthy human subjects. Drug
Metab Dispos. 39:1734–1746. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nomoto M, Pastino G, Rege B, Aluri J,
Ferry J and Han D: Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics,
pharmacogenomics, safety, and tolerability of avatrombopag in
healthy Japanese and white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev.
7:188–195. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zheng L, Liang MZ, Zeng XL, Li CZ, Zhang
YF, Chen XY, Zhu X and Xiang AB: Safety, pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of hetrombopag olamine, a novel TPO-R agonist, in
healthy individuals. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 121:414–422.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li F, Lin H, Feng S, Cai L, Zhang L, Feng
S, Liu X, Chen Z, Zou Q, Wu Y, et al: A phase I, single-sequence,
open-label study to evaluate the drug-drug interaction between
hetrombopag and cyclosporine in healthy Chinese subjects. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 89:2160–2167. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wong RSM, Saleh MN, Khelif A, Salama A,
Portella MSO, Burgess P and Bussel JB: Safety and efficacy of
long-term treatment of chronic/persistent ITP with eltrombopag:
Final results of the EXTEND study. Blood. 130:2527–2536.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Saleh MN, Bussel JB, Cheng G, Meyer O,
Bailey CK, Arning M and Brainsky A: EXTEND Study Group. Safety and
efficacy of eltrombopag for treatment of chronic immune
thrombocytopenia: Results of the long-term, open-label EXTEND
study. Blood. 121:537–545. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang P and Miao W: Eltrombopag-induced
liver dysfunction during the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia
and its risk factors. Ann Palliat Med. 10:6419–6424.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Despotovic JM and Grimes AB: Pediatric
ITP: Is it different from adult ITP? Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 2018:405–411. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Terrault N, Chen YC, Izumi N, Kayali Z,
Mitrut P, Tak WY, Allen LF and Hassanein T: Avatrombopag before
procedures reduces need for platelet transfusion in patients with
chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia. Gastroenterology.
155:705–718. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|