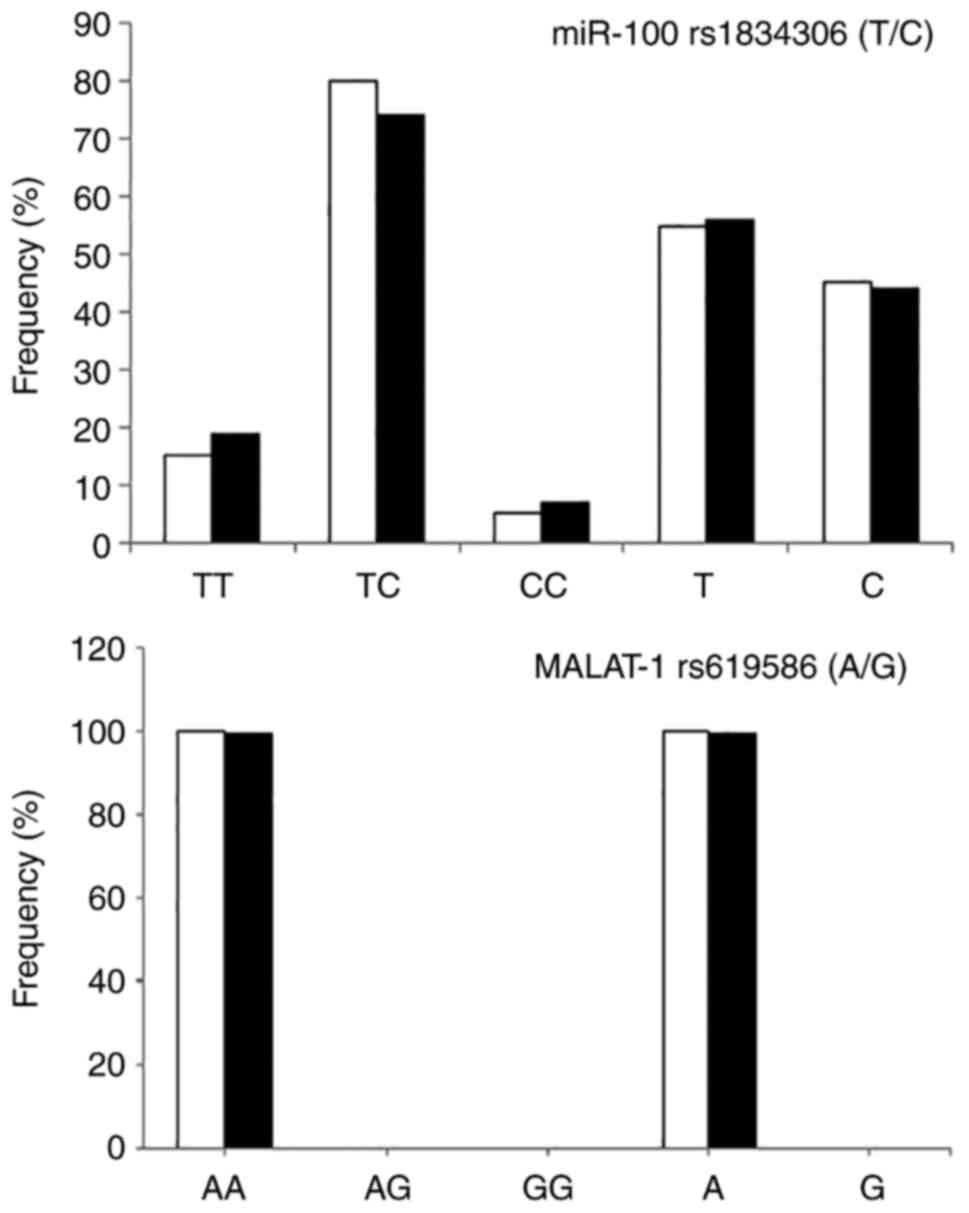
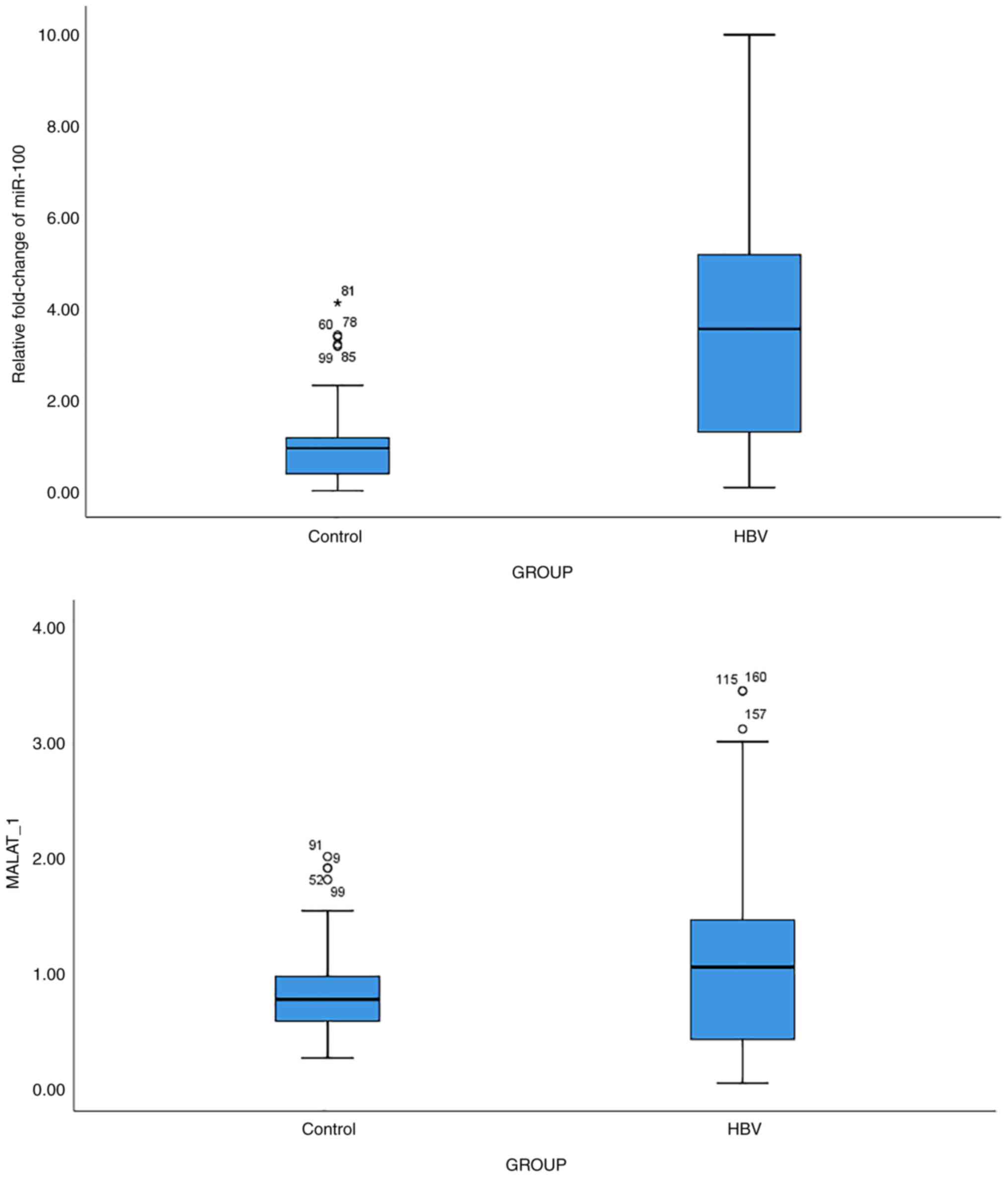
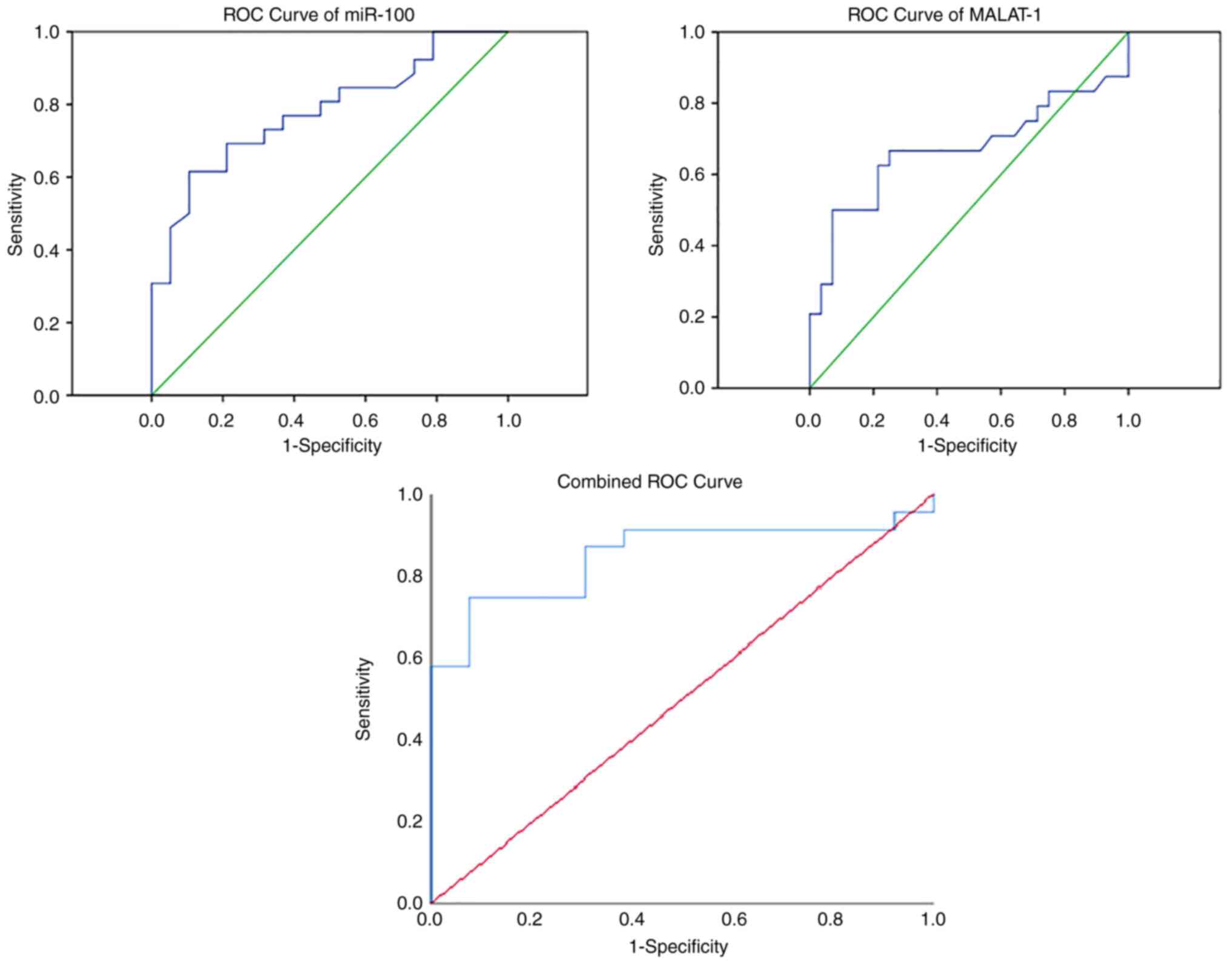
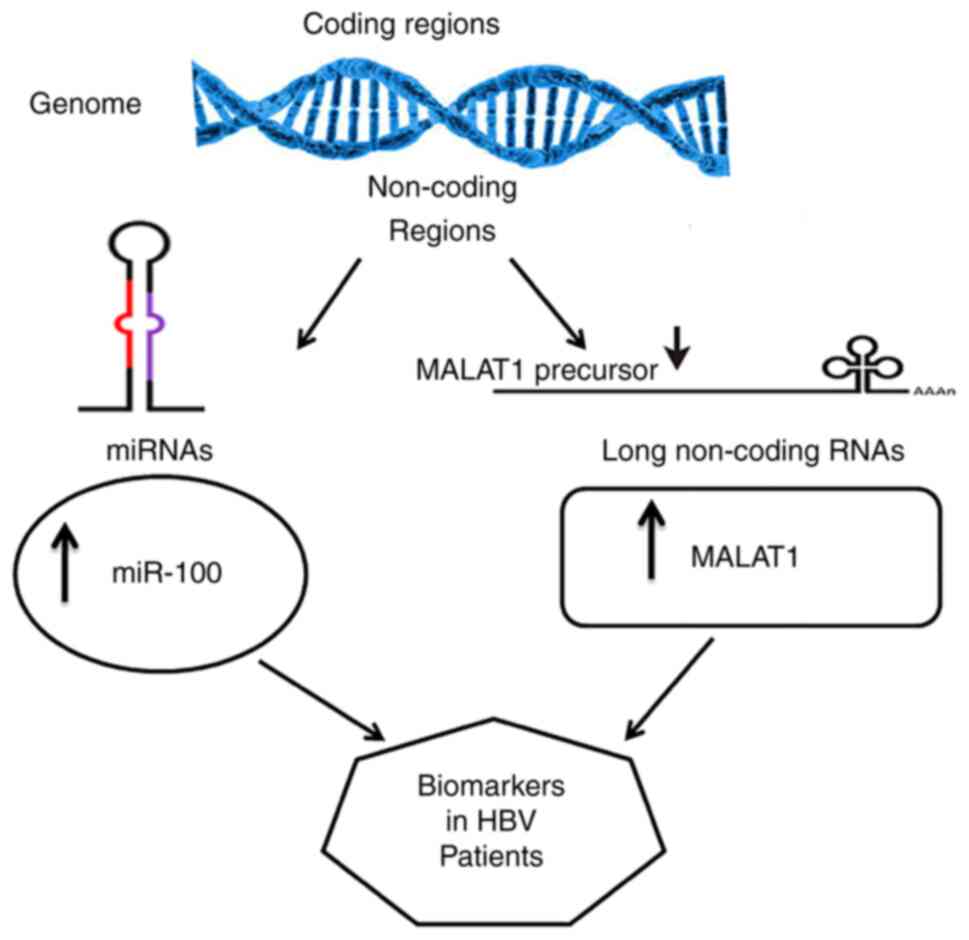
|
1
|
Ezbarami ZT, Hassani P, Tafreshi MZ and
Majd HA: A qualitative study on individual experiences of chronic
hepatitis B patients. Nurs Open. 4:310–318. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Asgari S, Chaturvedi N, Scepanovic P,
Hammer C, Semmo N, Giostra E, Müllhaupt B, Angus P, Thompson AJ,
Moradpour D and Fellay J: Human genomics of acute liver failure due
to hepatitis B virus infection: An exome sequencing study in liver
transplant recipients. J Viral Hepat. 26:271–277. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Revill P, Testoni B, Locarnini S and
Zoulim F: Global strategies are required to cure and eliminate HBV
infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:239–248.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Alavi M, Grebely J, Hajarizadeh B, Amin J,
Larney S, Law MG, George J, Degenhardt L and Dore GJ: Mortality
trends among people with hepatitis B and C: A population-based
linkage study, 1993-2012. BMC Infect Dis. 18(215)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cao MX, Jiang YP, Tang YL and Liang X: The
crosstalk between lncRNA and microRNA in cancer metastasis:
Orchestrating the epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity. Oncotarget.
8:12472–12483. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yamamura S, Imai-Sumida M, Tanaka Y and
Dahiya R: Interaction and cross-talk between non-coding RNAs. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 75:467–484. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tripathi R, Chakraborty P and Varadwaj PK:
Unraveling long non-coding RNAs through analysis of high-throughput
RNA-sequencing data. Noncoding RNA Res. 2:111–118. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bayoumi AS, Sayed A, Broskova Z, Teoh JP,
Wilson J, Su H, Tang YL and Kim IM: Crosstalk between long
non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci.
17(356)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kohlhapp FJ, Mitra AK, Lengyel E and Peter
ME: MicroRNAs as mediators and communicators between cancer cells
and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 34:5857–5868.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Deng K, Wang H, Guo X and Xia J: The
crosstalk between long, non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in gastric
cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:111–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Paneru B, Ali A, Al-Tobasei R, Kenney B
and Salem M: Crosstalk among lncRNAs, microRNAs and mRNAs in the
muscle ‘degradome’ of rainbow trout. Sci Rep.
8(8416)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qin C, Huang RY and Wang ZX: Potential
role of miR-100 in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Tumor
Biol. 36:1403–1409. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lin Y, Deng W, Pang J, Kemper T, Hu J, Yin
J, Zhang J and Lu M: The microRNA-99 family modulates hepatitis B
virus replication by promoting IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1
signaling-induced autophagy. Cell Microbiol. 19:1–15.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tan JY and Marques AC: miRNA-mediated
crosstalk between transcripts: The missing ‘linc’? Bioessays.
38:295–301. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
He RZ, Luo DX and Mo YY: Emerging roles of
lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes
Dis. 6:6–15. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bhat SA, Ahmad SM, Mumtaz PT, Malik AA,
Dar MA, Urwat U, Shah RA and Ganai NA: Long non-coding RNAs:
Mechanism of action and functional utility. Noncoding RNA Res.
1:43–50. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fernandes JCR, Acuña SM, Aoki JI,
Floeter-Winter LM and Muxel SM: Long non-coding RNAs in the
regulation of gene expression: Physiology and disease. Noncoding
RNA. 5(17)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Amodio N, Raimondi L, Juli G, Stamato MA,
Caracciolo D, Tagliaferri P and Tassone P: MALAT1: A druggable long
non-coding RNA for targeted anti-cancer approaches. J Hematol
Oncol. 11(63)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ren D, Li H, Li R, Sun J, Guo P, Han H,
Yang Y and Li J: Novel insight into MALAT-1 in cancer: Therapeutic
targets and clinical applications. Oncol Lett. 11:1621–1630.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sun Y and Ma L: New insights into long
non-coding RNA malat1 in cancer and metastasis. Cancers (Basel).
11(216)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao M, Wang S, Li Q, Ji Q, Guo P and Liu
X: Malat1: A long non-coding RNA highly associated with human
cancers. Oncol Lett. 16:19–26. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fareed M and Afzal M: Single nucleotide
polymorphism in genome-wide association of human population: A tool
for broad spectrum service. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 14:123–134.
2013.
|
|
23
|
Castellanos-Rubio A and Ghosh S:
Disease-associated SNPs in inflammation-related lncRNAs. Front
Immunol. 10(420)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Motawi TK, Mady AE, Shaheen S, Elshenawy
SZ, Talaat RM and Rizk SM: Genetic variation in microRNA-100
(miR-100) rs1834306 T/C associated with Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
infection: Correlation with expression level. Infect Genet Evol.
73:444–449. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fedeli U, Grande E, Grippo F and Frova L:
Mortality associated with hepatitis C and hepatitis B virus
infection: A nationwide study on multiple causes of death data.
World J Gastroenterol. 23:1866–1871. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lok AS, Zoulim F, Dusheiko G and Ghany MG:
Hepatitis B cure: From discovery to regulatory approval.
Hepatology. 66:1296–1313. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ahmadi A, Kaviani S, Yaghmaie M,
Pashaiefar H, Ahmadvand M, Jalili M, Alimoghaddam K, Eslamijouybari
M and Ghavamzadeh A: Altered expression of MALAT 1 lncRNA in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, correlation with cytogenetic
findings. Blood Res. 53:320–324. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Frías-Lasserre D and Villagra CA: The
importance of ncRNAs as epigenetic mechanisms in phenotypic
variation and organic evolution. Front Microbiol.
8(2483)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu M, Lin Z, Li X, Xin X, An J, Zheng Q,
Yang Y and Lu D: HULC cooperates with MALAT1 to aggravate liver
cancer stem cells growth through telomere repeat-binding factor 2.
Sci Rep. 6(36045)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Pan S, Liu L, Zhai X, Liu J, Wen J,
Zhang Y, Chen J, Shen H and Hu Z: A genetic variant in long
non-coding RNA HULC contributes to risk of HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. PLoS One.
7(e35145)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao K, Jin S, Wei B, Cao S and Xiong Z:
Association study of genetic variation of lncRNA MALAT1 with
carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res.
10:6257–6261. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Motawi TMK, El-Maraghy SA, Sabry D and
Mehana NA: The expression of long non-coding RNA genes is
associated with expression with polymorphisms of HULC rs7763881 and
MALAT1 rs619586 in hepatocellular carcinoma and HBV Egyptian
patients. J Cell Biochem. 120:14645–14656. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yuan LT, Chang JH, Lee HL, Yang YC, Su SC,
Lin CL, Yang SF and Chien MH: Genetic variants of lncRNA MALAT1
exert diverse impacts on the risk and clinicopathologic
characteristics of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin
Med. 8(1406)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang BG, Xu Q, Lv Z, Fang XX, Ding HX, Wen
J and Yuan Y: Association of twelve polymorphisms in three
onco-lncRNa genes with hepatocellular cancer risk and prognosis: A
case-control study. World J Gastroenterol. 24:2482–2490.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gong WJ, Peng JB, Yin JY, Li XP, Zheng W,
Xiao L, Tan LM, Xiao D, Chen YX, Li X, et al: Association between
well-characterized lung cancer lncRNA polymorphisms and
platinum-based chemotherapy toxicity in Chinese patients with lung
cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:581–590. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Q, Zhu W, Zhang B, Wu Y, Yan S, Yuan Y,
Zhang H, Li J, Sun K, Wang H and Yu T: The MALAT1 gene polymorphism
and its relationship with the onset of congenital heart disease in
Chinese. Biosci Rep. 38(BSR20171381)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhu R, Liu X and He Z: Long non-coding RNA
H19 and MALAT1 gene variants in patients with ischemic stroke in a
northern Chinese Han population. Mol Brain. 11(58)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang ML and Liu JX: MALAT1 rs619586
polymorphism functions as a prognostic biomarker in the management
of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 235:1700–1710.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Che D, Yang Y, Xu Y, Fang Z, Pi L, Fu L,
Zhou H, Tan Y, Lu Z, Li L, et al: The lncRNA MALAT1 rs619586 G
variant confers decreased susceptibility to recurrent miscarriage.
Front Physiol. 10(385)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Yamamoto Y, Arita
T, Shoda K, Hiramoto H, Hamada J, Itoh H, Fujita Y, Komatsu S, et
al: Plasma level of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1 is associated with liver damage and predicts
development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 107:149–154.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pan Y, Tong S, Cui R, Fan J, Liu C, Lin Y,
Tang J, Xie H, Lin P, Zheng T and Yu X: Long non-coding MALAT1
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate vimentin
expression by sponging miR-30a-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 50:108–120. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhao ZB, Chen F and Bai XF: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth
under hypoxia via sponging microRNA-200a. Yonsei Med J. 60:727–734.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang Z, Katsaros D, Biglia N, Shen Y, Fu
Y, Loo LWM, Jia W, Obata Y and Yu H: High expression of long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 in breast cancer is associated with poor
relapse-free survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 171:261–271.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu K, Ren Q and Zhao Y: . LncRNA MALAT1
overexpression promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of
gastric cancer by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Lett.
17:5335–5342. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Toraih EA, Ellawindy A, Fala SY, Al Ageeli
E, Gouda NS, Fawzy MS and Hosny S: Oncogenic long non-coding RNA
MALAT1 and HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed
Pharmacother. 102:653–669. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X, Ge Y,
Zhou L, Zhou C, Yuan Q and Yang M: Silencing of long non-coding RNA
MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration,
and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol
Chem. 290:3925–3935. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liu D, Zhu Y, Pang J, Weng X, Feng X and
Guo Y: Knockdown of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 inhibits growth and
motility of human hepatoma cells via modulation of miR-195. J Cell
Biochem. 119:1368–1380. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|