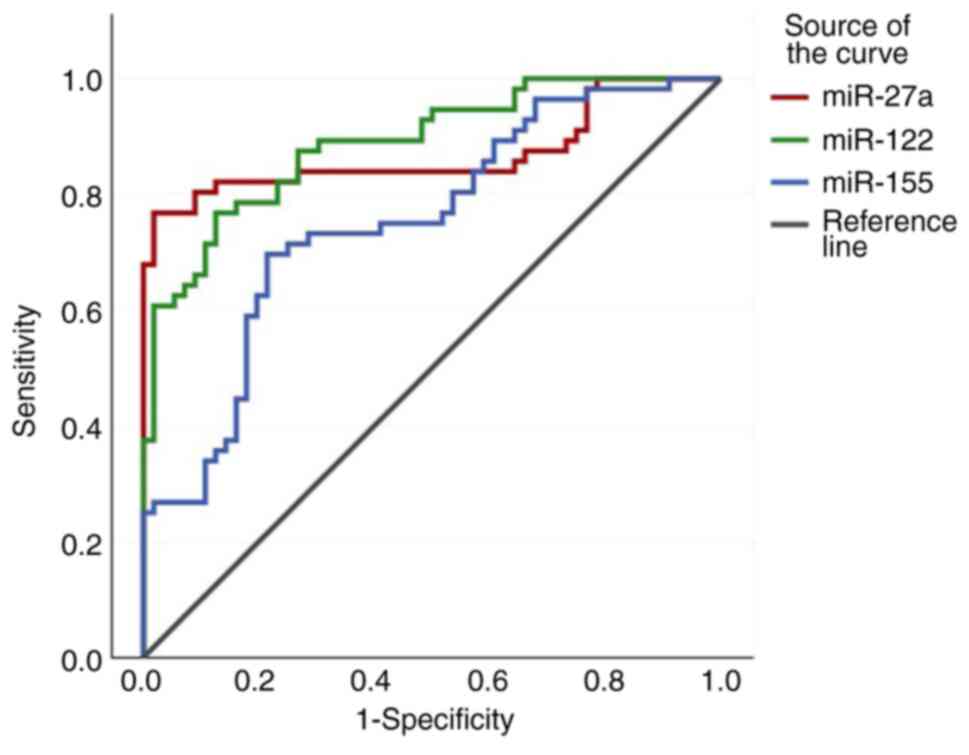
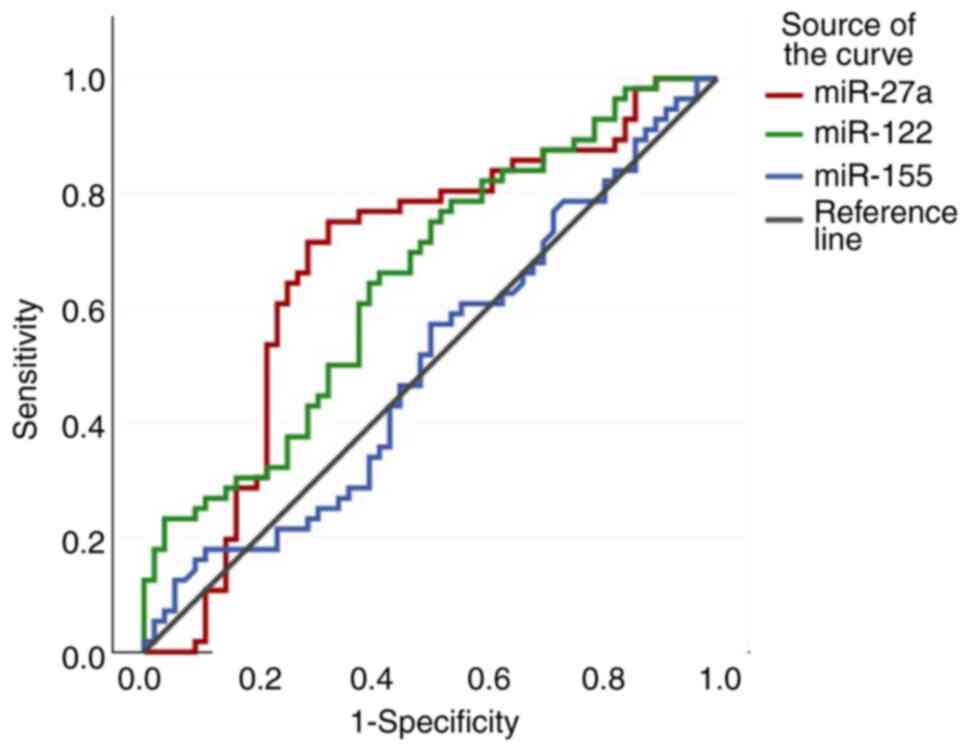
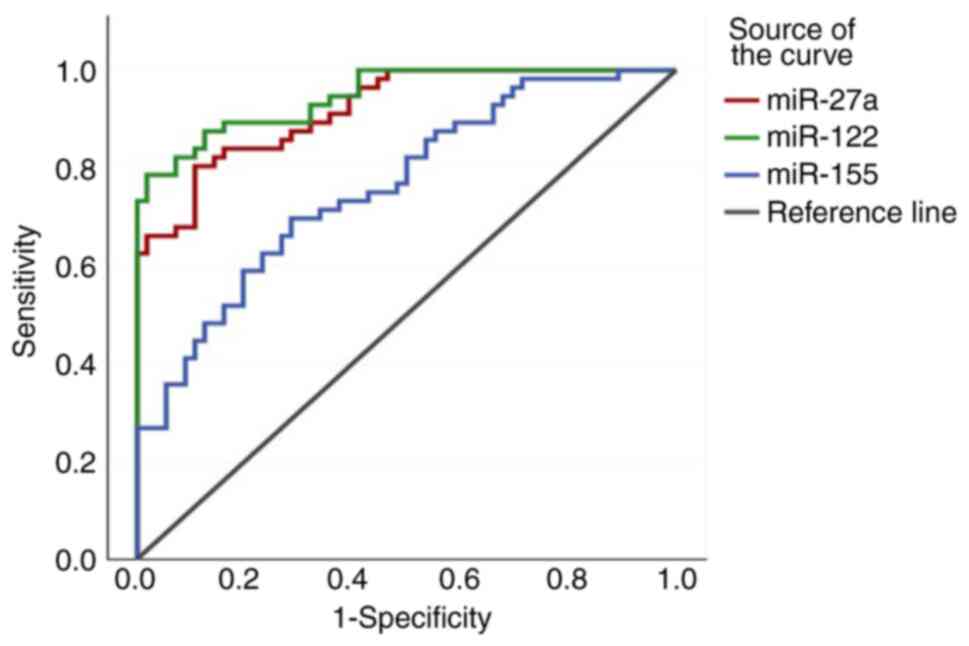
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Malvia S, Bagadi SA, Dubey US and Saxena
S: Epidemiology of breast cancer in Indian women. Asia Pac J Clin
Oncol. 13:289–295. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Momenimovahed Z and Salehiniya H:
Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for breast
cancer in the world. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 11:151–164.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Practice bulletin no 182: Hereditary
breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 130:e110–e126.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jafari SH, Saadatpour Z, Salmaninejad A,
Momeni F, Mokhtari M, Nahand JS, Rahmati M, Mirzaei H and Kianmehr
M: Breast cancer diagnosis: Imaging techniques and biochemical
markers. J Cell Physiol. 233:5200–5213. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang L: Early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Sensors (Basel). 17(1572)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, Sabir DK,
Taheri M and Ghafouri-Fard S: MicroRNA: A signature for cancer
progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 138(111528)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N and Kerin MJ:
Circulating microRNAs: Promising breast cancer biomarkers. Breast
Cancer Res. 13(402)2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ng EK, Li R, Shin VY, Jin HC, Leung CP, Ma
ES, Pang R, Chua D, Chu KM, Law WL, et al: Circulating microRNAs as
specific biomarkers for breast cancer detection. PLoS One.
8(e53141)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Giordano C, Accattatis FM, Gelsomino L,
Del Console P, Győrffy B, Giuliano M, Veneziani BM, Arpino G, De
Angelis C, De Placido P, et al: miRNAs in the box: Potential
diagnostic role for extracellular vesicle-packaged miRNA-27a and
miRNA-128 in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 24(15695)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ljepoja B, García-Roman J, Sommer AK,
Wagner E and Roidl A: MiRNA-27a sensitizes breast cancer cells to
treatment with selective estrogen receptor modulators. Breast Edinb
Scotl. 43:31–38. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Swellam M, Zahran RFK, Ghonem SA and
Abdel-Malak C: Serum MiRNA-27a as potential diagnostic nucleic
marker for breast cancer. Arch Physiol Biochem. 127:90–96.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Elghoroury EA, Abdelghafar EE, Kamel S,
Awadallah E, Shalaby A, El-Saeed GSM, Mahmoud E, Kamel MM, Abobakr
A and Yousef RN: Dysregulation of miR-122, miR-574 and miR-375 in
Egyptian patients with breast cancer. PLoS One.
19(e0298536)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ranjbari S, Rezayi M, Arefinia R,
Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH, Hatamluyi B and Pasdar A: A novel
electrochemical biosensor based on signal amplification of Au
HFGNs/PnBA-MXene nanocomposite for the detection of miRNA-122 as a
biomarker of breast cancer. Talanta. 255(124247)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li M, Zou X, Xia T, Wang T, Liu P, Zhou X,
Wang S and Zhu W: A five-miRNA panel in plasma was identified for
breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Med. 8:7006–7017. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ali SA, Abdulrahman ZFA and Faraidun HN:
Circulatory miRNA-155, miRNA-21 target PTEN expression and activity
as a factor in breast cancer development. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 66:44–50. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dziechciowska I, Dąbrowska M, Mizielska A,
Pyra N, Lisiak N, Kopczyński P, Jankowska-Wajda M and Rubiś B:
miRNA expression profiling in human breast cancer diagnostics and
therapy. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 45:9500–9525. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS and Tewari
M: Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum
using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods San
Diego Calif. 50:298–301. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Roth C, Rack B, Müller V, Janni W, Pantel
K and Schwarzenbach H: Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers
for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 12(R90)2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wu XJ, Li Y, Liu D, Zhao LD, Bai B and Xue
MH: miR-27a as an oncogenic microRNA of hepatitis B virus- related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:885–889.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ding L, Zhang S, Xu M, Zhang R, Sui P and
Yang Q: MicroRNA-27a contributes to the malignant behavior of
gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PH domain and
leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36(45)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saleh AA, Soliman SE, Habib MSE, Gohar SF
and Abo-Zeid GS: Potential value of circulatory microRNA122 gene
expression as a prognostic and metastatic prediction marker for
breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 46:2809–2818. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu X, Somlo G, Yu Y, Palomares MR, Li AX,
Zhou W, Chow A, Yen Y, Rossi JJ, Gao H, et al: De novo sequencing
of circulating miRNAs identifies novel markers predicting clinical
outcome of locally advanced breast cancer. J Transl Med.
10(42)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang B, Wang H and Yang Z: MiR-122
inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by
targeting IGF1R. PLoS One. 7(e47053)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fong MY, Zhou W, Liu L, Alontaga AY,
Chandra M, Ashby J, Chow A, O'Connor ST, Li S, Chin AR, et al:
Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in
premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat Cell Biol.
17:183–194. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hosseini Mojahed F, Aalami AH, Pouresmaeil
V, Amirabadi A, Qasemi Rad M and Sahebkar A: Clinical evaluation of
the diagnostic role of MicroRNA-155 in breast cancer. Int J
Genomics. 2020(9514831)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Swellam M, Zahran RFK, Abo El-Sadat Taha
H, El-Khazragy N and Abdel-Malak C: Role of some circulating MiRNAs
on breast cancer diagnosis. Arch Physiol Biochem. 125:456–464.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bašová P, Pešta M, Sochor M and Stopka T:
Prediction potential of serum miR-155 and miR-24 for relapsing
early breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18(2116)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM and
Callen DF: The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 21:1236–1243. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang S, Wang RH, Akagi K, Kim KA, Martin
BK and Cavallone L: Kathleen Cuningham Foundation Consortium for
Research into Familial Breast Cancer (kConFab). Haines DC, Basik M,
Mai P, et al: Tumor suppressor BRCA1 epigenetically controls
oncogenic microRNA-155. Nat Med. 17:1275–1282. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|