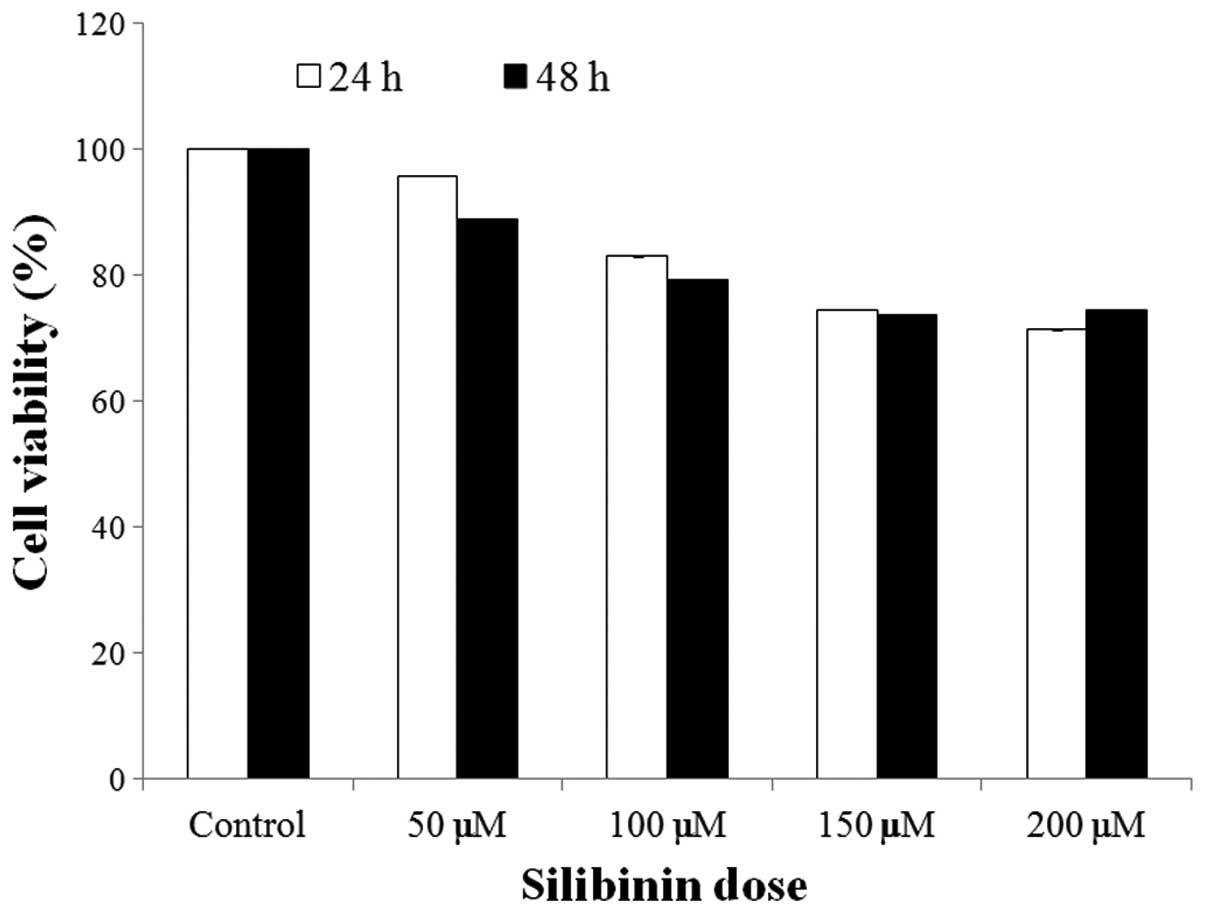
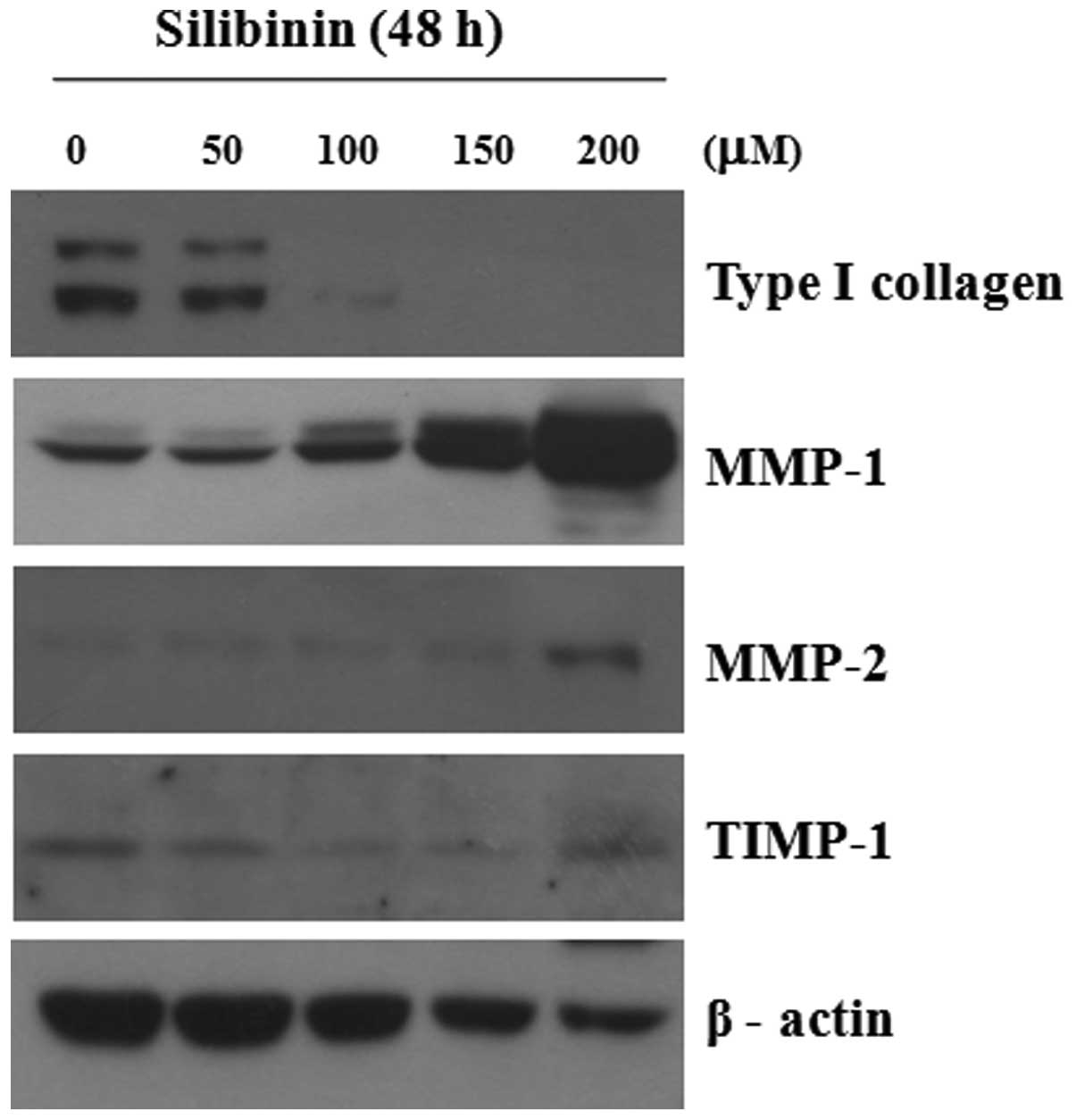
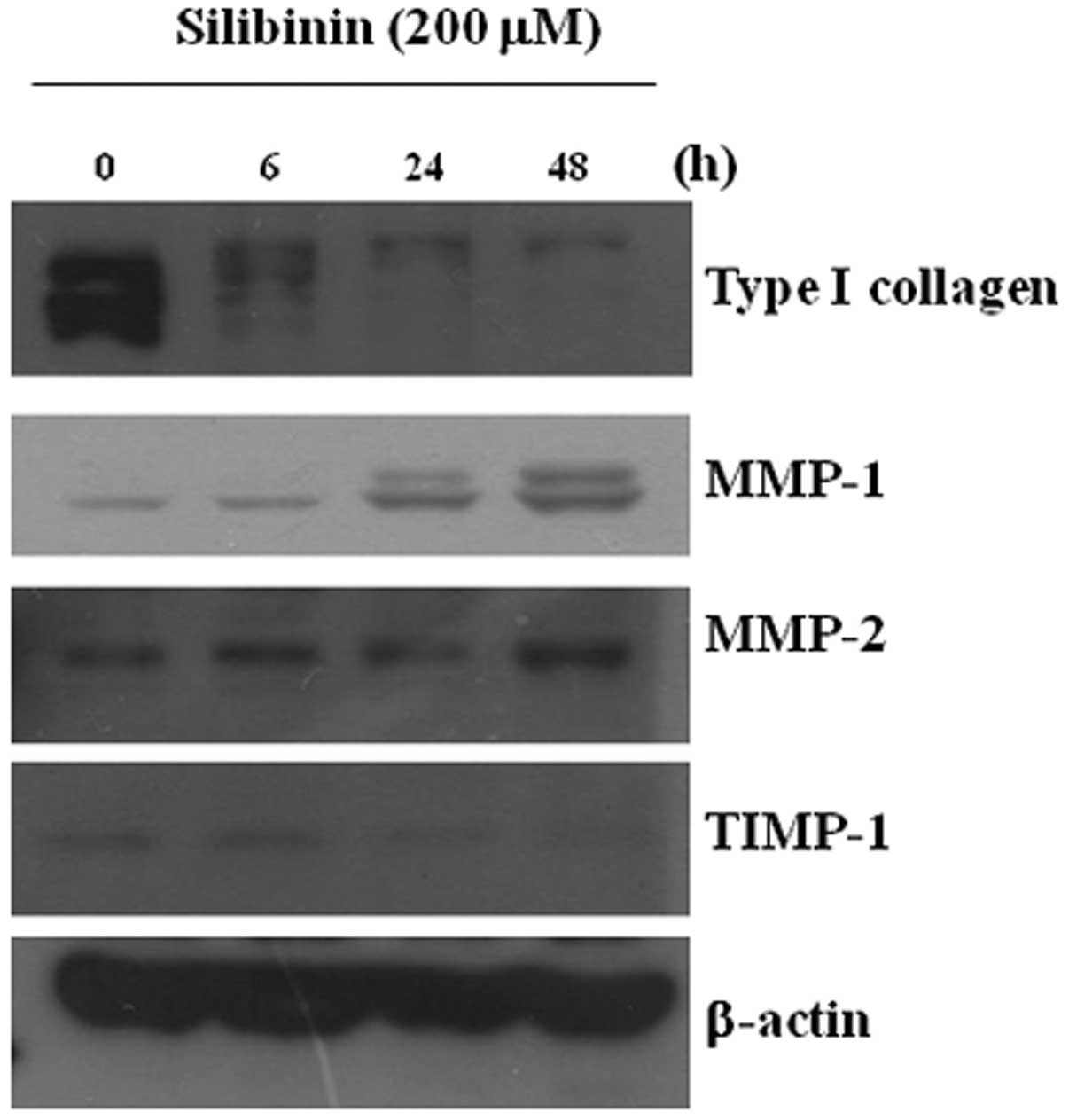
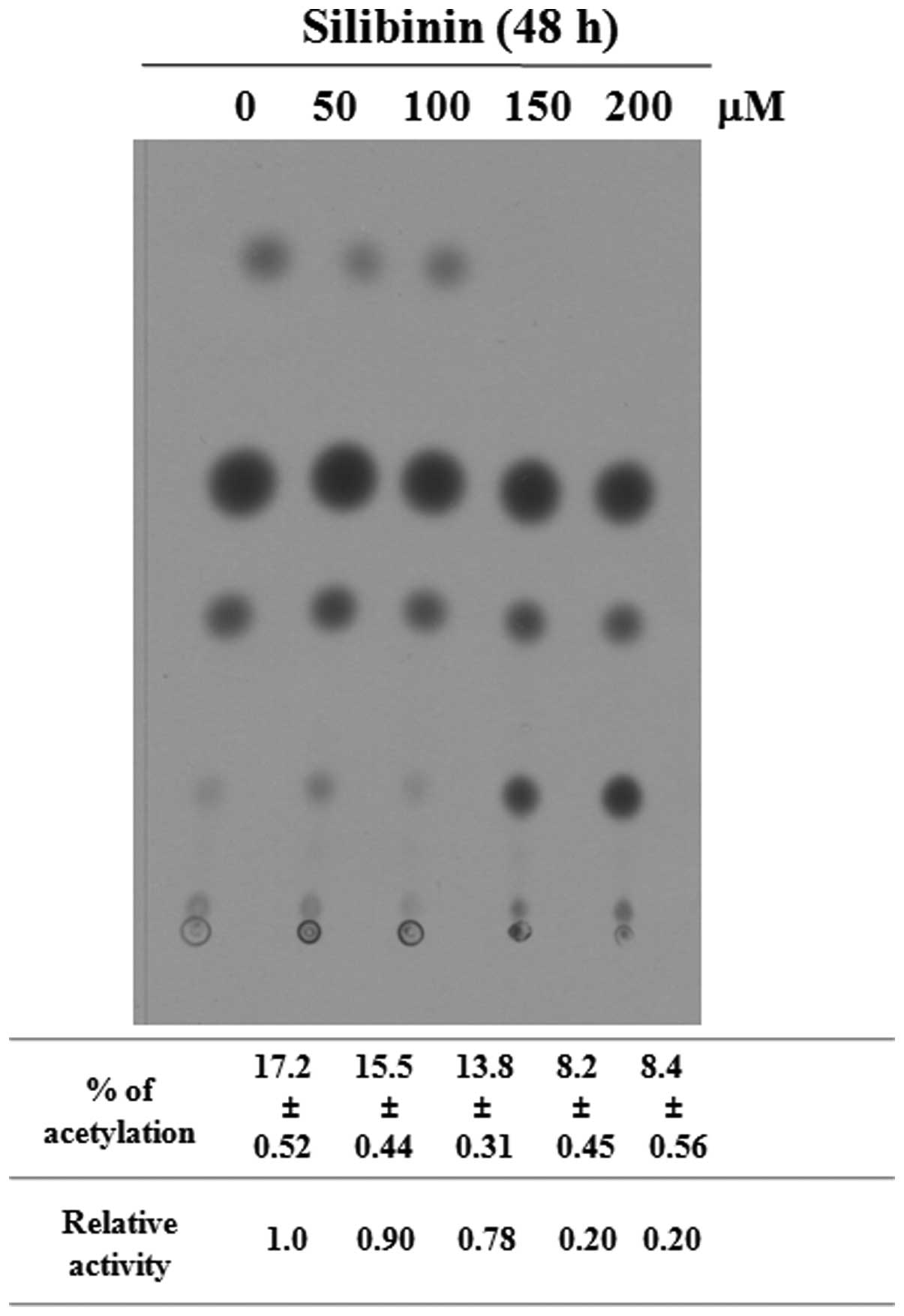
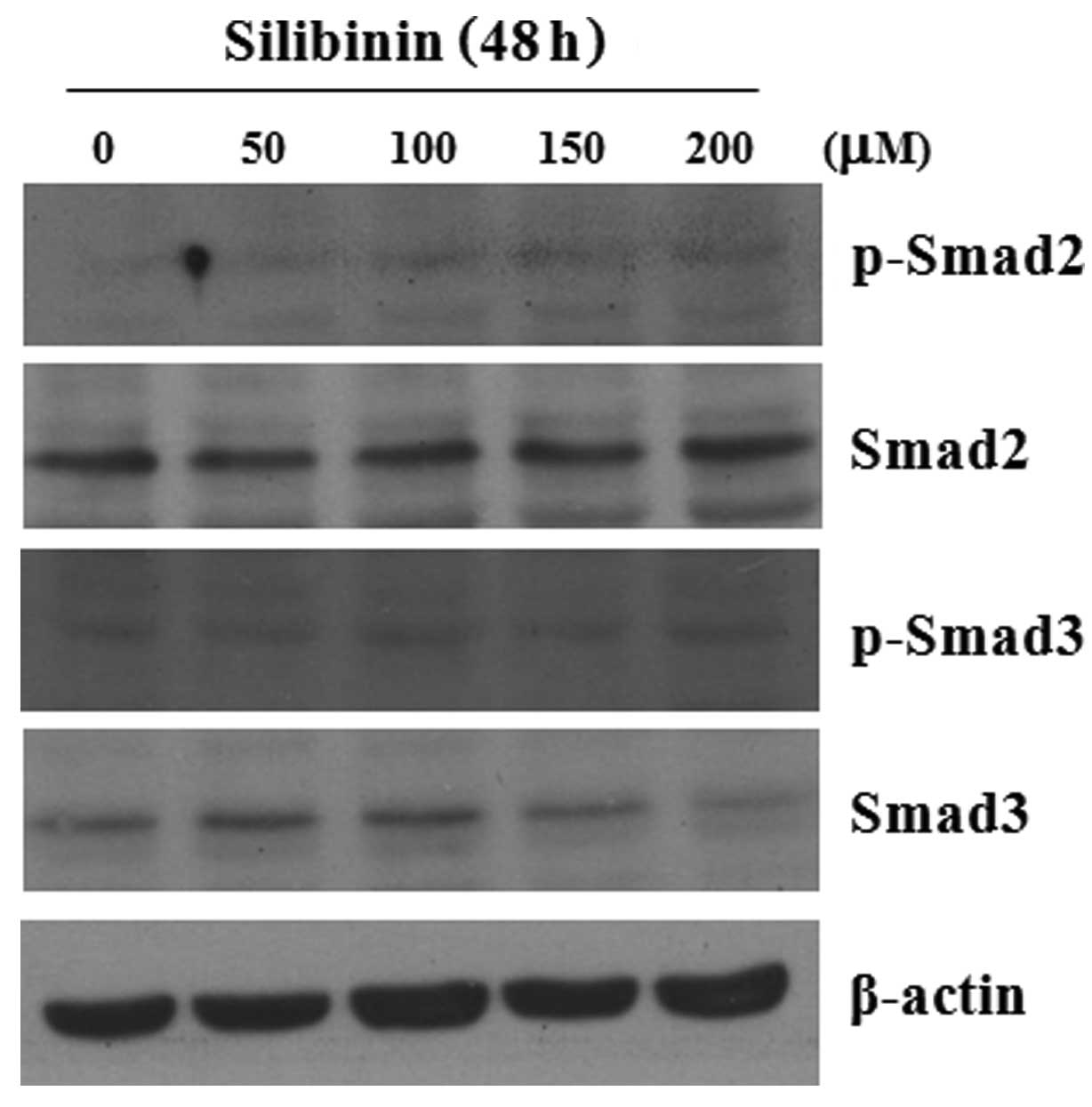
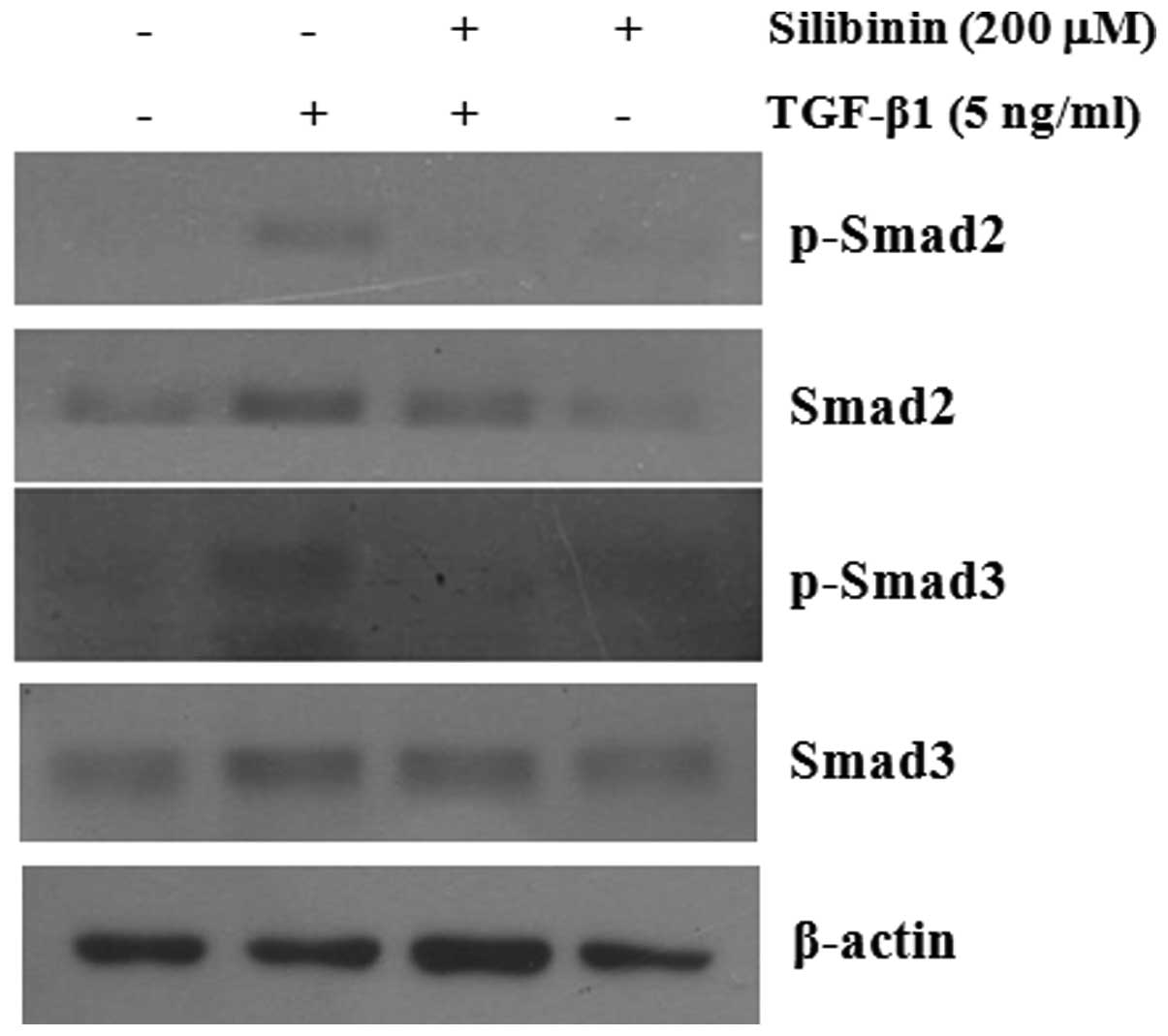
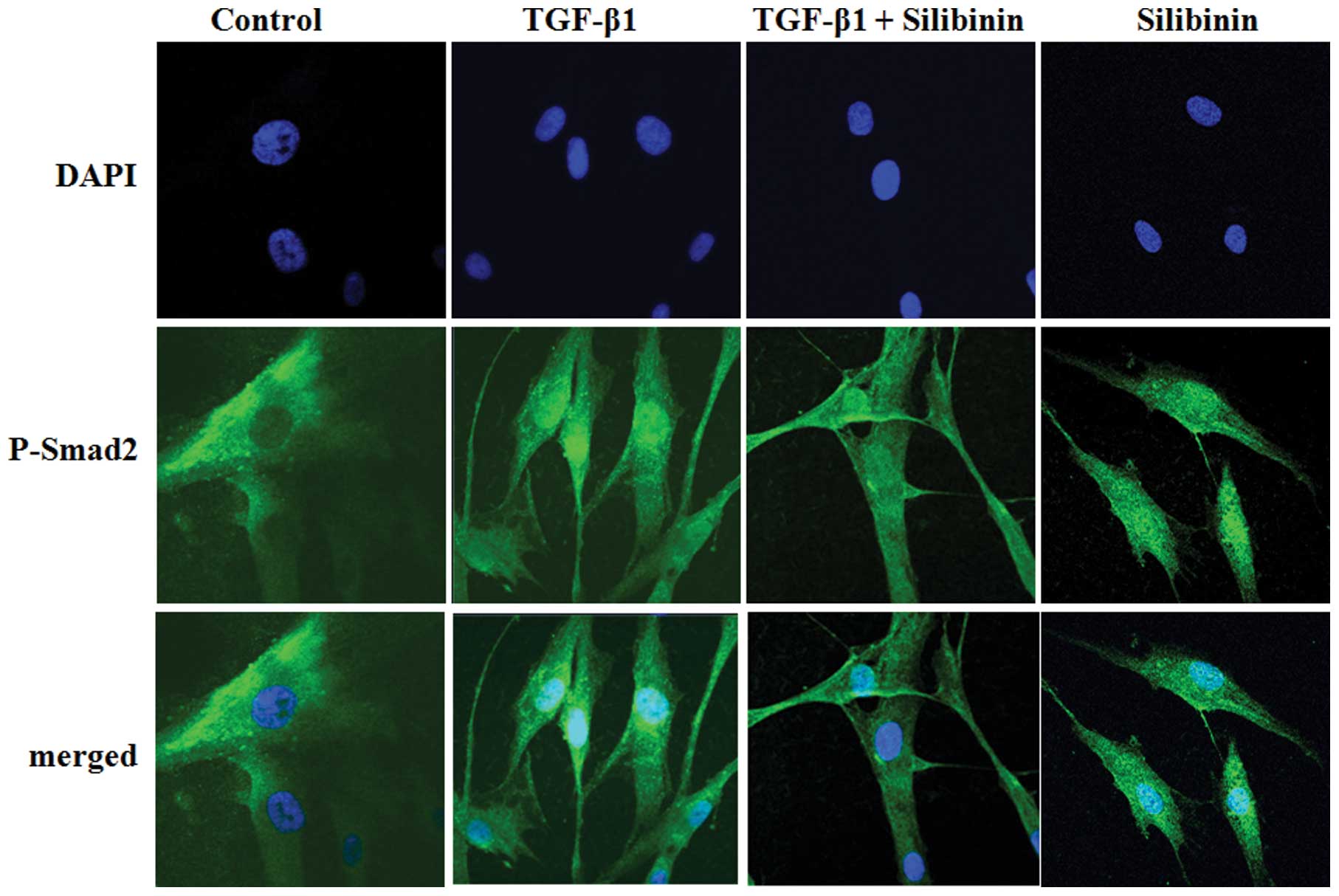
|
1
|
Ramasamy K and Agarwal R: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett. 269:352–362. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muriel P, Moreno MG, Hernández Mdel C,
Chávez E and Alcantar LK: Resolution of liver fibrosis in chronic
CCl4 administration in the rat after discontinuation of treatment:
effect of silymarin, silibinin, colchicine and trimethylcolchicinic
acid. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96:375–380. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh RP, Dhanalakshmi S, Agarwal C and
Agarwal R: Silibinin strongly inhibits growth and survival of human
endothelial cells via cell cycle arrest and downregulation of
survivin, Akt and NF-kappaB: implications for angioprevention and
antiangiogenic therapy. Oncogene. 24:1188–1202. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rahimi RA and Leof EB: TGF-beta signaling:
a tale of two responses. J Cell Biochem. 102:593–608. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie JL, Qi SH, Pan S, Xu YB, Li TZ, Liu XS
and Liu P: Expression of Smad protein by normal skin fibroblasts
and hypertrophic scar fibroblasts in response to transforming
growth factor beta1. Dermatol Surg. 34:1216–1225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zi Z, Chapnick DA and Liu X: Dynamics of
TGF-β/Smad signaling. FEBS Lett. 586:1921–1928. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Hsu YC, Chen MJ, Yu YM, Ko SY and Chang
CC: Suppression of TGF-β1/SMAD pathway and extracellular matrix
production in primary keloid fibroblasts by curcuminoids: its
potential therapeutic use in the chemoprevention of keloid. Arch
Dermatol Res. 302:717–724. 2010.
|
|
8
|
He S, Liu X, Yang Y, Huang W, Xu S, Yang
S, Zhang X and Roberts MS: Mechanisms of transforming growth factor
beta(1)/Smad signalling mediated by mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways in keloid fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 162:538–546.
2010.
|
|
9
|
Chin GS, Liu W, Peled Z, Lee TY,
Steinbrech DS, Hsu M and Longaker MT: Differential expression of
transforming growth factor-beta receptors I and II and activation
of Smad 3 in keloid fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 108:423–429.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ai W, Zhang Y, Tang QZ, Yan L, Bian ZY,
Liu C, Huang H, Bai X, Yin L and Li H: Silibinin attenuates cardiac
hypertrophy and fibrosis through blocking EGFR-dependent signaling.
J Cell Biochem. 110:1111–1122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi Y and Massagué J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moustakas A, Pardali K, Gaal A and Heldin
CH: Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling in regulation of cell growth
and differentiation. Immunol Lett. 82:85–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen HB, Rud JG, Lin K and Xu L: Nuclear
targeting of transforming growth factor-beta-activated Smad
complexes. J Biol Chem. 280:21329–21336. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Poncelet AC and Schnaper HW: Sp1 and Smad
proteins cooperate to mediate transforming growth factor-beta
1-induced alpha 2(I) collagen expression in human glomerular
mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 276:6983–6992. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ghosh AK, Yuan W, Mori Y and Varga J:
Smad-dependent stimulation of type I collagen gene expression in
human skin fibroblasts by TGF-beta involves functional cooperation
with p300/CBP transcriptional coactivators. Oncogene. 19:3546–3555.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen SJ, Ning H, Ishida W, Sodin-Semrl S,
Takagawa S, Mori Y and Varga J: The early-immediate gene EGR-1 is
induced by transforming growth factor-beta and mediates stimulation
of collagen gene expression. J Biol Chem. 281:21183–21197. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan W and Varga J: Transforming growth
factor-beta repression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in dermal
fibroblasts involves Smad3. J Biol Chem. 276:38502–38510. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|