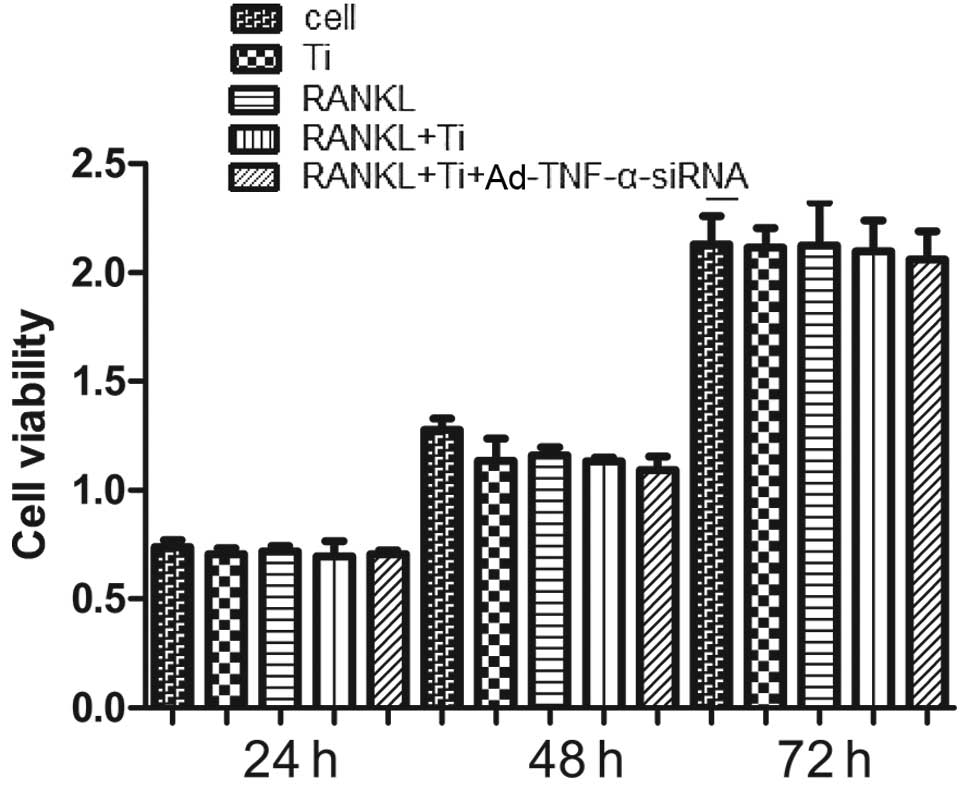
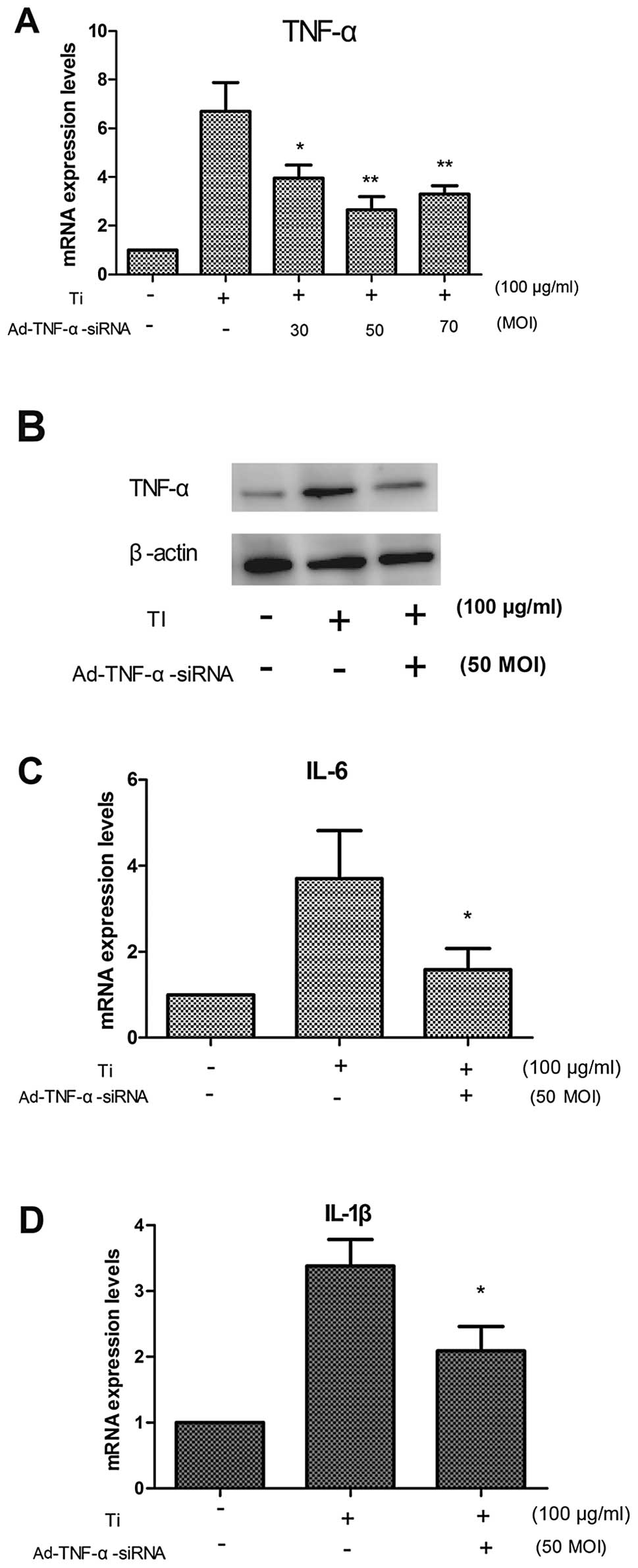
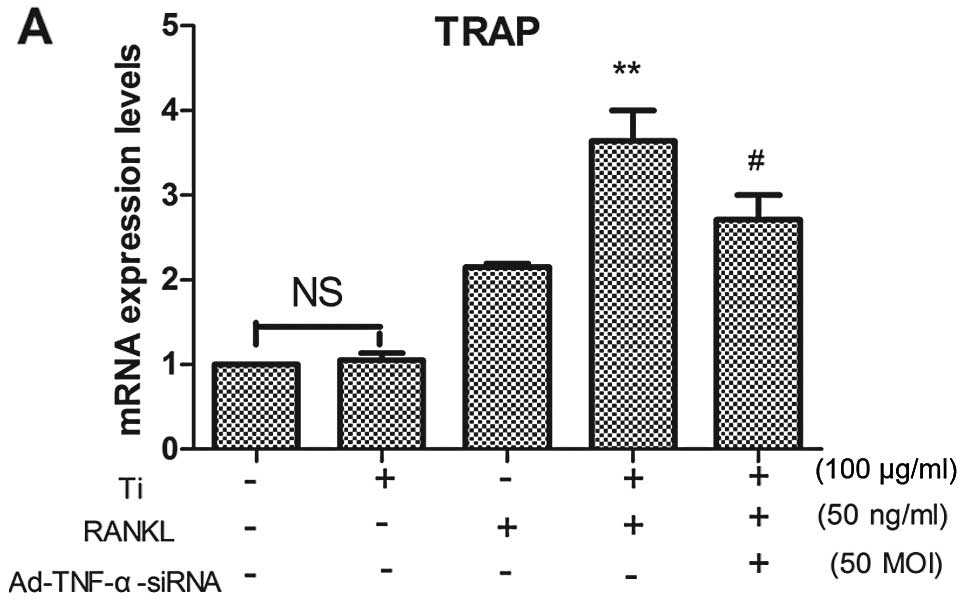
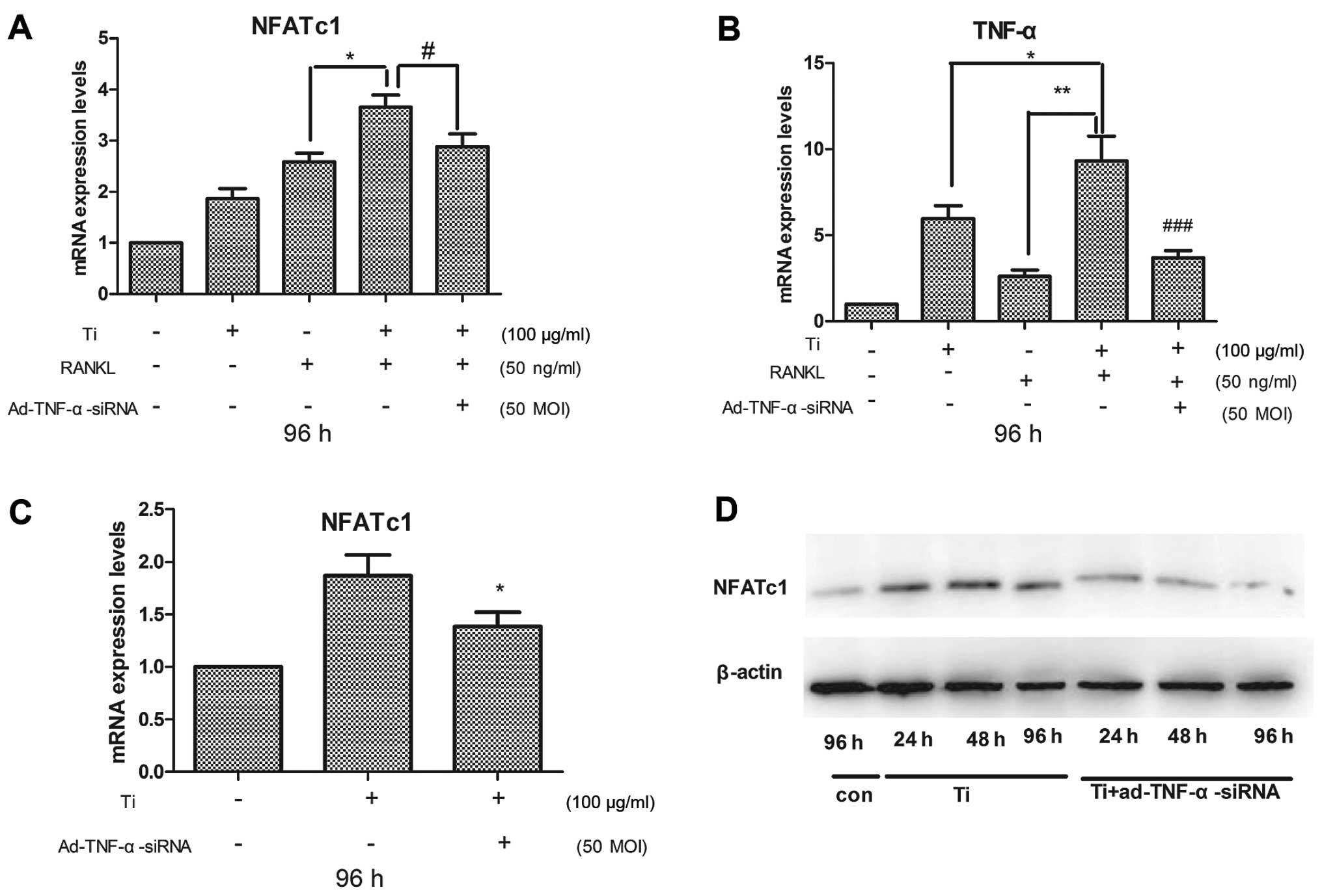
|
1
|
Harris WH: The problem is osteolysis. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 311:46–53. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldring SR, Clark CR and Wright TM: The
problem in total joint arthroplasty: aseptic loosening. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 75:799–801. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A and Ohashi H: Wear
and osteolysis in total joint replacements. Acta Orthop Scand
Suppl. 278:1–16. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Friedman RJ, Black J, Galante JO, Jacobs
JJ and Skinner HB: Current concepts in orthopaedic biomaterials and
implant fixation. Instr Course Lect. 43:233–255. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harris WH: Wear and periprosthetic
osteolysis: the problem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 393:66–70. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jacobs JJ, Roebuck KA, Archibeck M, Hallab
NJ and Glant TT: Osteolysis: basic science. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
393:71–77. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ingham E and Fisher J: The role of
macrophages in osteolysis of total joint replacement. Biomaterials.
26:1271–1286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hallab NJ and Jacobs JJ: Biologic effects
of implant debris. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 67:182–188.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaufman AM, Alabre CI, Rubash HE and
Shanbhag AS: Human macrophage response to UHMWPE, TiAlV, CoCr, and
alumina particles: analysis of multiple cytokines using protein
arrays. J Biomed Mater Res A. 84:464–474. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shanbhag AS, Jacobs JJ, Black J, Galante
JO and Glant TT: Cellular mediators secreted by Interfacial
membranes obtained at revision total hip arthroplasty. J
Arthroplasty. 10:498–506. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimble RB, Srivastava S, Ross FP,
Matayoshi A and Pacifici R: Estrogen deficiency increases the
ability of stromal cells to support murine osteoclastogenesis via
an interleukin-1and tumor necrosis factor-mediated stimulation of
macrophage colony-stimulating factor production. J Biol Chem.
271:28890–28897. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mori T, Miyamoto T, Yoshida H, Asakawa M,
Kawasumi M, Kobayashi T, et al: IL-1β and TNFα-initiated IL-6-STAT3
pathway is critical in mediating inflammatory cytokines and RANKL
expression in inflammatory arthritis. Int Immunol. 23:701–712.
2011.
|
|
14
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, et al: Osteoprotegerin (OPG)
ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and
activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quinn JM, Elliott J, Gillespie MT and
Martin TJ: A combination of osteoclast differentiation factor and
macrophage-colony stimulating factor is sufficient for both human
and mouse osteoclast formation in vitro. Endocrinology.
139:4424–4427. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi
K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, et al: Osteoclast differentiation
factor is a ligand for
osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is
identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:3597–3602.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba
T, Murata S, Sato K, et al: T-cell-mediated regulation of
osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and
IFN-gamma. Nature. 408:600–605. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goater JJ, O’Keefe RJ, Rosier RN, et al:
Efficacy of ex vivo OPG gene therapy in preventing wear debris
induced osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 20:169–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SS, Sharma AR, Choi BS, Jung JS, Chang
JD, Park S, et al: The effect of TNFα secreted from macrophages
activated by titanium particles on osteogenic activity regulated by
WNT/BMP signaling in osteoprogenitor cells. Biomaterials.
33:4251–4263. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Glass DA II, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M,
Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, et al:
Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls
osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 8:751–764. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, Sigler
RE, Faugere MC, Bouxsein ML, et al: Essential role of beta-catenin
in postnatal bone acquisition. J Biol Chem. 280:21162–21168. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grimaud E, Soubigou L, Couillaud S,
Coipeau P, Moreau A, Passuti N, et al: Receptor activator of
nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) ratio is
increased in severe osteolysis. Am J Pathol. 163:2021–2031. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gori F, Hofbauer L, Dunstan CR, Spelsberg
TC, Khosla S and Riggs BL: The expression of osteoprotegerin and
RANK ligand and the support of osteoclast formation by
stromal-osteoblast lineage cells is developmentally regulated.
Endocrinology. 141:4768–4776. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao Z, Li P, Zhang Q, et al: Tumor
necrosis factor-increases circulating osteoclast precursor numbers
by promoting their proliferation and differentiation in the bone
marrow through up-regulation of c-Fms expression. J Biol Chem.
281:11846–11855. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang YH, Heulsmann A, Tondravi MM, et al:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) stimulates RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis via coupling of TNF type 1 receptor and RANK
signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 276:563–568. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abu-Amer Y: Advances in osteoclast
differentiation and function. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr
Metabol Disord. 5:347–355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Teitelbaum S: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamashita T, Yao Z, Li F, et al: NF-kappaB
p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)
and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor
differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1. J Biol Chem.
282:18245–18253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Boyce BF and Xing L: Functions of
RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 473:139–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yao Z, Xing L and Boyce BF: NF-κB p100
limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent
mechanism. J Clin Invest. 119:3024–3034. 2009.
|
|
32
|
Fullerb K and Murphy C: TNF alpha potently
activates osteoclasts, through a direct action independent of and
strongly synergistic with RANKL. Endocrinology. 143:1108–1118.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kobayashi K, Takahashi N, Jimi E, Udagawa
N, Takami M, Kotake S, et al: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of
the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med. 191:275–286. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gallo J, Raska M, Mrazek F and Petrek M:
Bone remodeling, particle disease and individual susceptibility to
periprosthetic osteolysis. Physiol Res. 57:339–349. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hikiji H, Shin WS, Koizumi T, Takato T,
Susami T, Koizumi Y, et al: Peroxynitrite production by TNF-alpha
and IL-1beta: implication for suppression of osteoblastic
differentiation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 278:E1031–E1037.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gilbert L, He X, Farmer P, Boden S,
Kozlowski M, Rubin J, et al: Inhibition of osteoblast
differentiation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Endocrinology.
141:3956–3964. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurokouchi K, Kambe F, Yasukawa K, Izumi
R, Ishiguro N, Iwata H and Seo H: TNF-alpha increases expression of
IL-6 and ICAM-1 genes through activation of NF-kappaB in
osteoblast-like ROS17/2.8 cells. J Bone Miner Res. 13:1290–1299.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, Edwards J and
Teitelbaum SL: Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated osteoclastogenesis is
mediated by tumor necrosis factor via its P55 receptor. J Clin
Invest. 100:1557–1565. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abu-Amer Y, Ross FP, McHugh KP, Livolsi A,
Peyron JF and Teitelbaum SL: Tumor necrosis factor-α activation of
nuclear transcription factor-κB in marrow macrophages is mediated
by c-Src tyrosine phosphorylation of IκBα. J Biol Chem.
273:29417–29423. 1998.
|
|
40
|
Kudo O, Fujikawa Y, Itonaga I, Sabokbar A,
Torisu T and Athanasou NA: Proinflammatory cytokine
(TNF-alpha/IL-1alpha) induction of human osteoclast formation. J
Pathol. 198:220–227. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rakshit DS, Ly K, Sengupta TK, Nestor BJ,
Sculco TP, Ivashkiv LB and Purdue PE: Wear debris inhibition of
anti-osteoclastogenic signaling by interleukin-6 and
interferon-gamma. Mechanistic insights and implications for
periprosthetic osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 88:788–799. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
von Knoch M, Jewison DE, Sibonga JD,
Sprecher C, Morrey BF, Loer F, et al: The effectiveness of
polyethylene versus titanium particles in inducing osteolysis in
vivo. J Orthop Res. 22:237–243. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SS, Woo CH, Chang JD and Kim JH: Roles
of Rac and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in the intracellular
signalling in response to titanium particles. Cell Signal.
15:339–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng H, Yu X, Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby
P: RANKL stimulates inducible nitricoxide synthase expression and
nitric oxide production in developing osteoclasts. An autocrine
negative feedback mechanism triggered by RANKL induced
interferon-beta via NF-kappaB that restrains osteoclastogenesis and
bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 281:15809–15820. 2006.
|
|
45
|
Asagiri M and Takayanagi H: The molecular
understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 40:251–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Takayanagi H: The role of NFAT in
osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1116:227–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, et al: Induction and activation of the
transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in
terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Taki N, Tatro JM, Lowe R, Goldberg VM and
Greenfield EM: Comparison of the roles of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α in
cell culture and murine models of aseptic loosening. Bone.
40:1276–1283. 2007.
|
|
49
|
Yamanaka Y, Abu-Amer W, Foglia D, Otero J,
Clohisy JC and Abu-Amer Y: NFAT2 is an essential mediator of
orthopedic particle-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Orthop Res.
26:1577–1584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lam J, Takeshita S, Barker JE, Kanagawa O,
Ross FP and Teitelbaum SL: TNF-alpha induces osteoclastogenesis by
direct stimulation of macrophages exposed to permissive levels of
RANK ligand. J Clin Invest. 106:1481–1488. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Matsuo K, Galson DL, Zhao C, Peng L,
Laplace C, Wang KZ, et al: Nuclear factor of activated T-cells
(NFAT) rescues osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos. J
Biol Chem. 279:26475–26480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hofbauer LC, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR,
Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL and Khosla S: Interleukin-1beta and tumor
necrosis factoralpha, but not interleukin-6, stimulate
osteoprotegerin ligand gene expression in human osteoblastic cells.
Bone. 25:255–259. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Crotti TN, Smith MD, Findlay DM, Zreiqat
H, Ahern MJ, Weedon H, et al: Factors regulating osteoclast
formation in human tissues adjacent to peri-implant bone loss:
expression of receptor activator NFkappaB, RANK ligand and
osteoprotegerin. Biomaterials. 25:565–573. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Arai F, Miyamoto T, Ohneda O, Inada T,
Sudo T, Brasel K, Miyata T, et al: Commitment and differentiation
of osteoclast precursor cells by the sequential expression of c-Fms
and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB (RANK) receptors. J
Exp Med. 190:1741–1754. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bucay N, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR, Morony S,
Tarpley J, Capparelli C, et al: Osteoprotegerin-deficient mice
develop early onset osteoporosis and arterial calcification. Genes
Dev. 12:1260–1268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Burgess TL, Qian Y, Kaufman S, Ring BD,
Van G, Capparelli C, et al: The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL)
directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 145:527–538.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nakagawa N, Kinosaki M, Yamaguch K, Shima
N, Yasuda H, Yano K, et al: RANK is the essential signaling
receptor for osteoclast differentiation factor in
osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 253:395–400. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Nestor BJ and
Sculco TP: The central role of wear debris in periprosthetic
osteolysis. HSS J. 2:102–113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S and Okada Y:
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation.
Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:325–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Peruzzi B, Cappariello A, Del Fattore A,
Rucci N, De Benedetti F and Teti A: c-Src and IL-6 inhibit
osteoblast differentiation and integrate IGFBP5 signalling. Nat
Commun. 3:6302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Abbas S, Zhang YH, Clohisy JC and Abu-Amer
Y: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits pre-osteoblast
differentiation through its type-1 receptor. Cytokine. 22:33–41.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Harada S and Rodan GA: Control of
osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature.
423:349–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kramer I, Halleux C, Keller H, Pegurri M,
Gooi JH, Weber PB, et al: Osteocyte Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is
required for normal bone homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol. 30:3071–3085.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kamiya N, Ye L, Kobayashi T, et al: BMP
signaling negatively regulates bone mass through sclerostin by
inhibiting the canonical Wnt pathway. Development. 135:3801–3811.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Thomas GP, Baker SU, Eisman JA and
Gardiner EM: Changing RANKL/OPG mRNA expression in differentiating
murine primary osteoblasts. J Endocrinol. 170:451–460. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sabokbar A and Rushton N: Role of
inflammatory mediators and adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis
of aseptic loosening in total hip arthroplasties. J Arthroplasty.
10:810–816. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kim KJ, Rubash HE, Wilson SC, D’Antonio JA
and McClain EJ: A histologic and biochemical comparison of the
interface tissues in cementless and cemented hip prostheses. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 287:142–152. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Al-Saffar N, Khwaja HA, Kadoya Y and
Revell PA: Assessment of the role of GM-CSF in the cellular
transformation and the development of erosive lesions around
orthopaedic implants. Am J Clin Pathol. 105:628–639.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang W, Ferguson DJ, Quinn JM, Simpson AH
and Athanasou NA: Biomaterial particle phagocytosis by
bone-resorbing osteoclasts. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 79:849–856. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gallo J, Kamínek P, Tichá V, Riháková P
and Ditmar R: Particle disease. A comprehensive theory of
periprosthetic osteolysis: a review. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ
Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 146:21–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Archibeck MJ, Jacobs JJ, Roebuck KA and
Glant TT: The basic science of periprosthetic osteolysis. Instr
Course Lect. 50:185–195. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Schwarz E, Lu P, Goater J, Benz E, Kollias
G, Rosier R, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha/nuclear
transcription factor-kappaB signaling in periprosthetic osteolysis.
J Orthop Res. 18:472–480. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu JW, Konttinen YT, Lassus J, Natah S,
Ceponis A, Solovieva S, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) in loosening of total hip replacement (THR). Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 14:643–648. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Evans CH, Ghivizzani SC and Robbins PD:
Orthopedic gene therapy in 2008. Mol Ther. 17:231–244. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Bandara G, Robbins PD, Georgescu HI,
Mueller GM, Glorioso JC and Evans CH: Gene transfer to
synoviocytes: prospects for gene treatment of arthritis. DNA Cell
Biol. 11:227–231. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bandara G, Mueller GM, Galea-Lauri J,
Tindal MH, Georgescu HI, Suchanek MK, et al: Intraarticular
expression of biologically active interleukin 1-receptor-antagonist
protein by ex vivo gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:10764–10768. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM and
Hannon GJ: Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step
of RNA interference. Nature. 409:363–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bao JJ, Zhang WW and Kuo MT: Adenoviral
delivery of recombinant DNA into transgenic mice bearing
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hum Gene Ther. 7:355–365. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ali M, Lemoine NR and Ring CJ: The use of
DNA viruses as vectors for gene therapy. Gene Ther. 1:367–384.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Smith AE: Viral vectors in gene therapy.
Annu Rev Microbiol. 49:807–838. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|