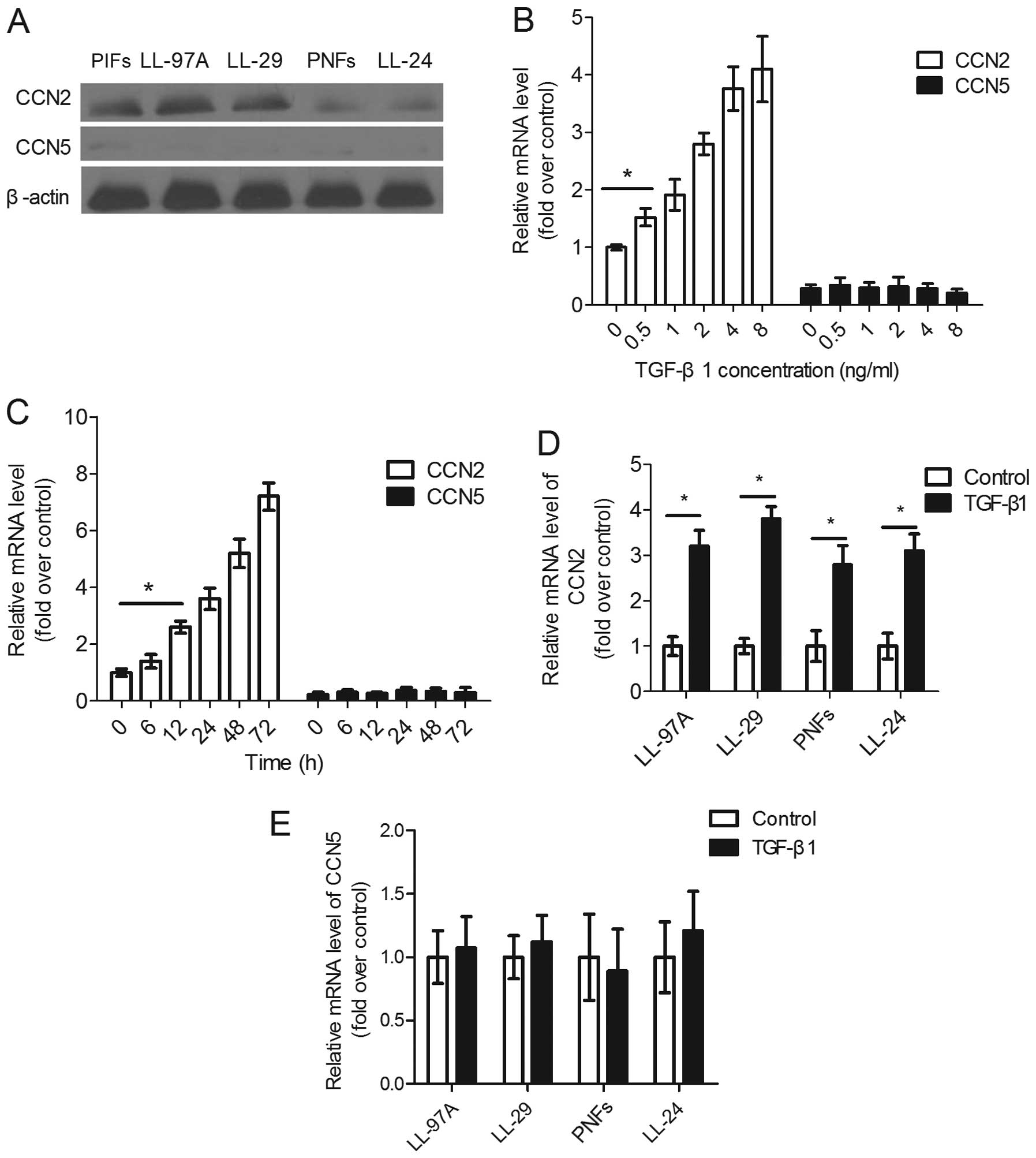
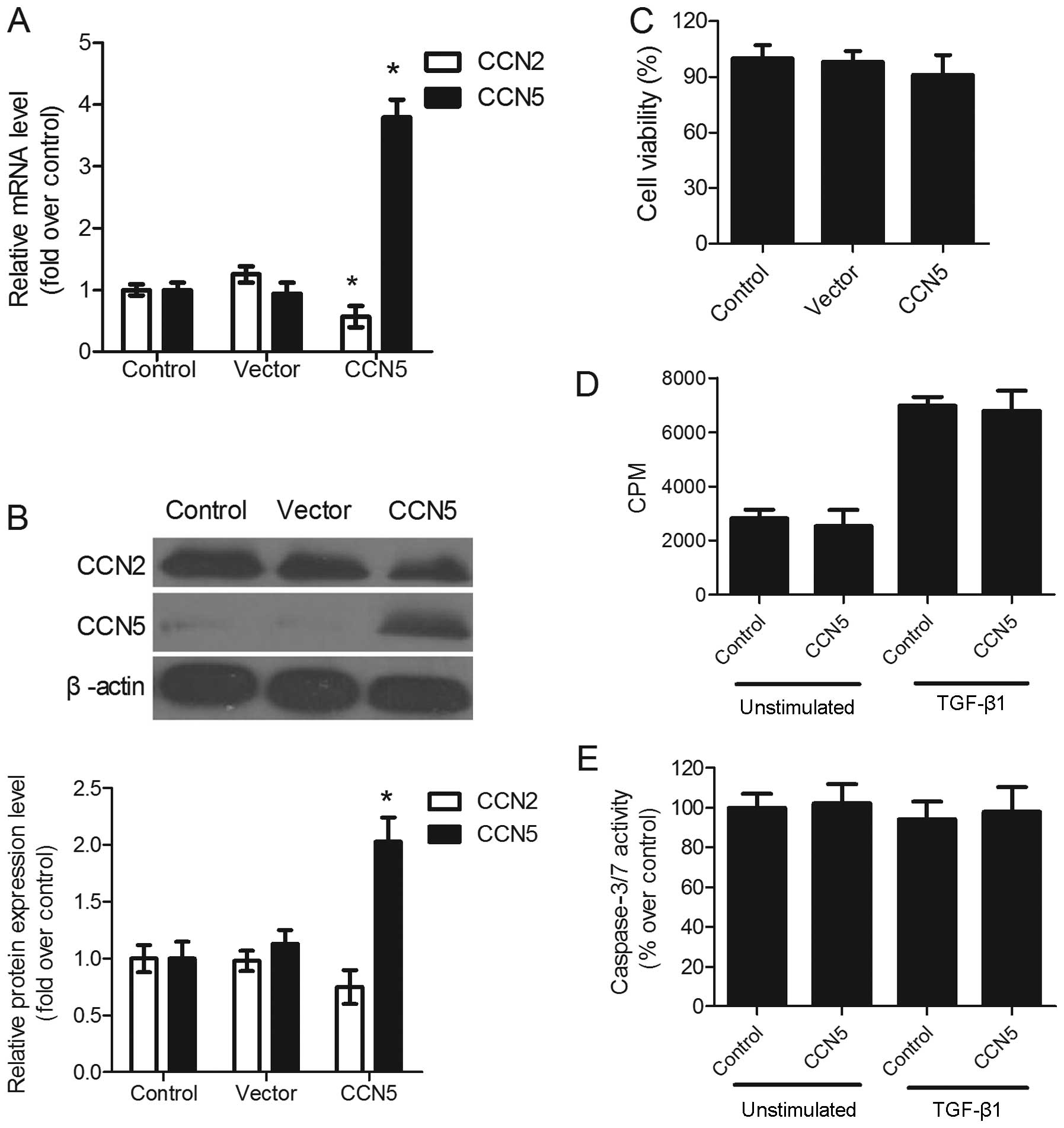
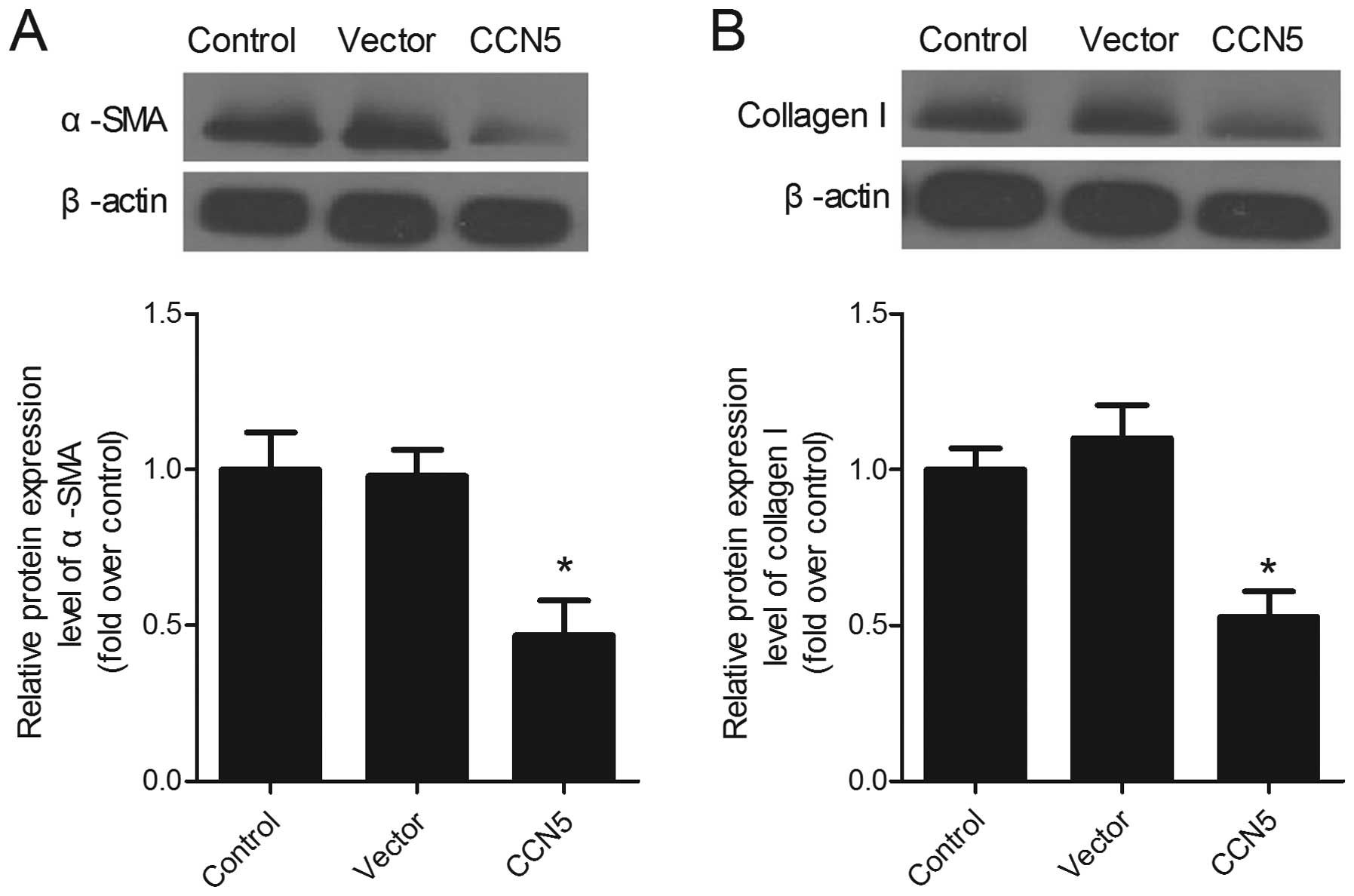
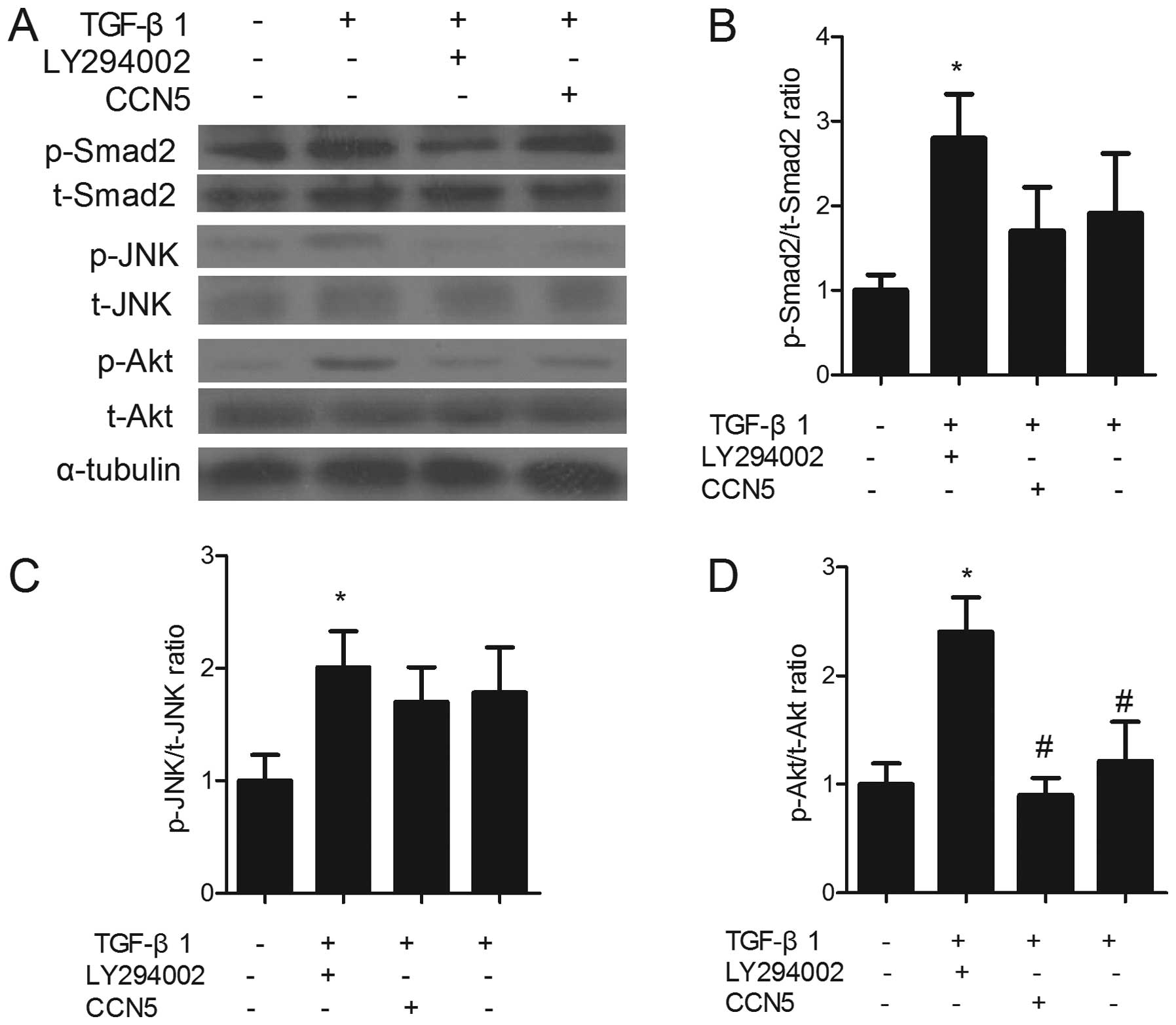
|
1
|
Huang LS, Berdyshev E, Mathew B, et al:
Targeting sphingosine kinase 1 attenuates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J. 27:1749–1760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scotton CJ and Chambers RC: Molecular
targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus. Chest.
132:1311–1321. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh SR and Hall IP: Airway
myofibroblasts and their relationship with airway myocytes and
fibroblasts. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 5:127–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Phan SH: The myofibroblast in pulmonary
fibrosis. Chest. 122:286S–289S. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kono M, Nakamura Y, Suda T, et al: Plasma
CCN2 (connective tissue growth factor; CTGF) is a potential
biomarker in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Clin Chim Acta.
412:2211–2215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fernandez IE and Eickelberg O: The impact
of TGF-β on lung fibrosis: from targeting to biomarkers. Proc Am
Thorac Soc. 9:111–116. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Fine A and Goldstein RH: The effect of
transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen
formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 262:3897–3902.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leask A and Abraham DJ: All in the CCN
family: essential matricellular signaling modulators emerge from
the bunker. J Cell Sci. 119:4803–4810. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Inadera H, Hashimoto S, Dong HY, et al:
WISP-2 as a novel estrogen-responsive gene in human breast cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 275:108–114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moussad EE and Brigstock DR: Connective
tissue growth factor: what’s in a name? Mol Genet Metab.
71:276–292. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Ponticos M, Holmes AM, Shi-wen X, et al:
Pivotal role of connective tissue growth factor in lung fibrosis:
MAPK-dependent transcriptional activation of type I collagen.
Arthritis Rheum. 60:2142–2155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brigstock DR: Connective tissue growth
factor (CCN2, CTGF) and organ fibrosis: lessons from transgenic
animals. J Cell Commun Signal. 4:1–4. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sonnylal S, Shi-Wen X, Leoni P, et al:
Selective expression of connective tissue growth factor in
fibroblasts in vivo promotes systemic tissue fibrosis. Arthritis
Rheum. 62:1523–1532. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu S, Shi-wen X, Abraham DJ and Leask A:
CCN2 is required for bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis in mice.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:239–246. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chambers RC, Leoni P, Blanc-Brude OP,
Wembridge DE and Laurent GJ: Thrombin is a potent inducer of
connective tissue growth factor production via proteolytic
activation of protease-activated receptor-1. J Biol Chem.
275:35584–35591. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bonniaud P, Martin G, Margetts PJ, et al:
Connective tissue growth factor is crucial to inducing a
profibrotic environment in ‘fibrosis-resistant’ BALB/c mouse lungs.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 31:510–516. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fritah A, Redeuilh G and Sabbah M:
Molecular cloning and characterization of the human WISP-2/CCN5
gene promoter reveal its upregulation by oestrogens. J Endocrinol.
191:613–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brigstock DR: The connective tissue growth
factor/cysteine-rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family.
Endocr Rev. 20:189–206. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leask A: Yin and Yang Part Deux: CCN5
inhibits the pro-fibrotic effects of CCN2. J Cell Commun Signal.
4:155–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoon PO, Lee MA, Cha H, et al: The
opposing effects of CCN2 and CCN5 on the development of cardiac
hypertrophy and fibrosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:294–303. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sabbah M, Prunier C, Ferrand N, et al:
CCN5, a novel transcriptional repressor of the transforming growth
factor β signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1459–1469.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ricci A, Cherubini E, Ulivieri A, et al:
Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase2 in human idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Physiol. 228:235–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Fritah A, Saucier C, De Wever O, et al:
Role of WISP-2/CCN5 in the maintenance of a differentiated and
noninvasive phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol.
28:1114–1123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuburai T, Suzuki M, Nagashima Y, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated transfer and overexpression of heme oxygenase 1
cDNA in lung prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via a
Fas-Fas ligand-independent pathway. Hum Gene Ther. 13:1945–1960.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Woessner JF Jr: The determination of
hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small
proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 93:440–447.
1961. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Milam JE, Keshamouni VG, Phan SH, et al:
PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit profibrotic phenotypes in human lung
fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L891–901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kolb M, Margetts PJ, Galt T, et al:
Transient transgene expression of decorin in the lung reduces the
fibrotic response to bleomycin. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:770–777. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Conte E, Fruciano M, Fagone E, et al:
Inhibition of PI3K prevents the proliferation and differentiation
of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: the role of class I
P110 isoforms. PLoS One. 6:e246632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park S and Lee EJ: Recent advances in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 74:1–6.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wójcik KA, Skoda M, Koczurkiewicz P, Sanak
M, Czyż J and Michalik M: Apigenin inhibits TGF-β1 induced
fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition in human lung fibroblast
populations. Pharmacol Rep. 65:164–172. 2013.
|
|
32
|
Wilkes MC, Mitchell H, Penheiter SG, et
al: Transforming growth factor-beta activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is independent of Smad2 and Smad3 and
regulates fibroblast responses via p21-activated kinase-2. Cancer
Res. 65:10431–10440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martin MM, Buckenberger JA, Jiang J, et
al: TGF-beta1 stimulates human AT1 receptor expression in lung
fibroblasts by cross talk between the Smad, p38 MAPK, JNK, and PI3K
signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
293:L790–L799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mason HR, Lake AC, Wubben JE, Nowak RA and
Castellot JJ Jr: The growth arrest-specific gene CCN5 is deficient
in human leiomyomas and inhibits the proliferation and motility of
cultured human uterine smooth muscle cells. Mol Hum Reprod.
10:181–187. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pennica D, Swanson TA, Welsh JW, et al:
WISP genes are members of the connective tissue growth factor
family that are up-regulated in wnt-1-transformed cells and
aberrantly expressed in human colon tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:14717–14722. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|