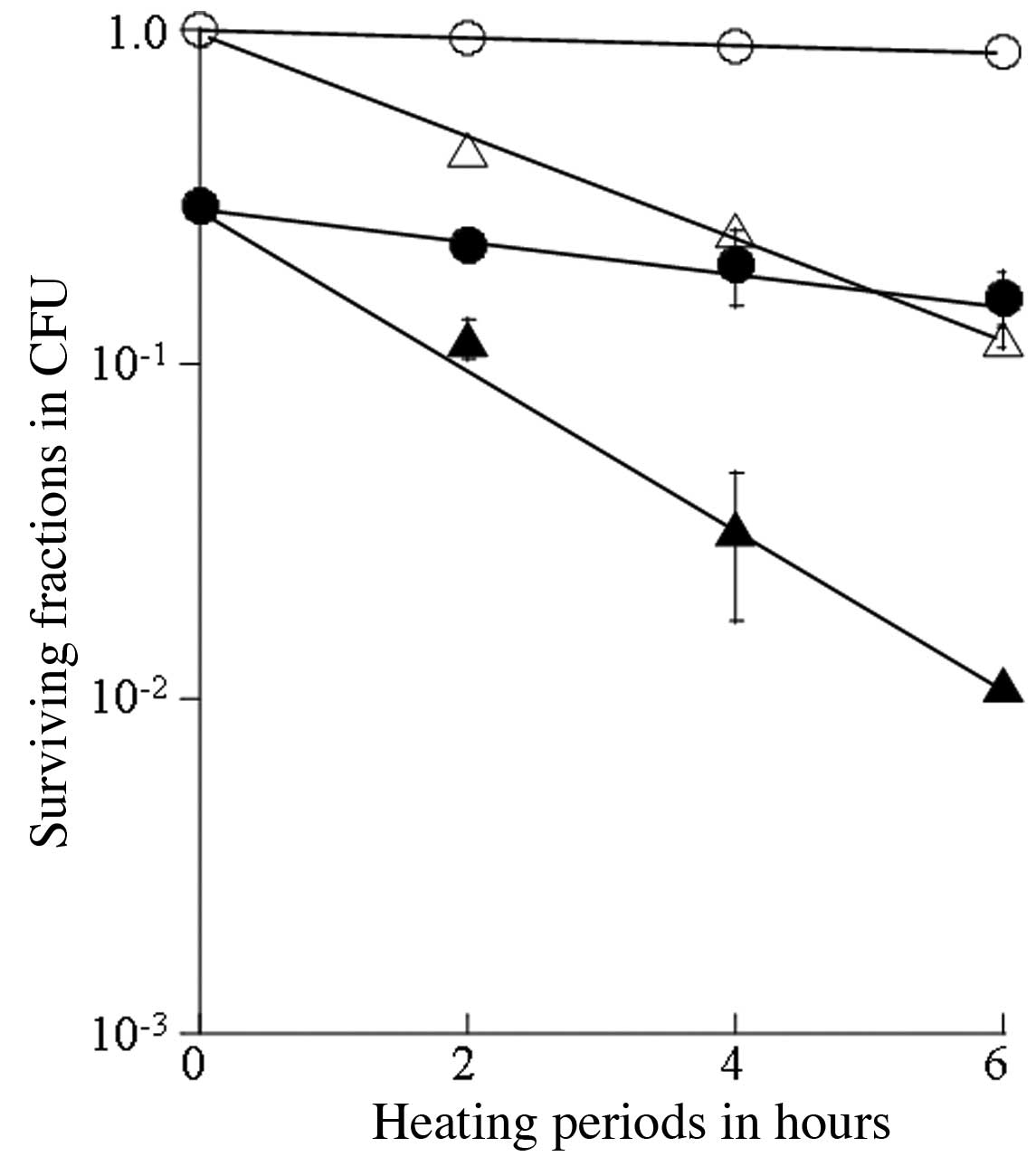
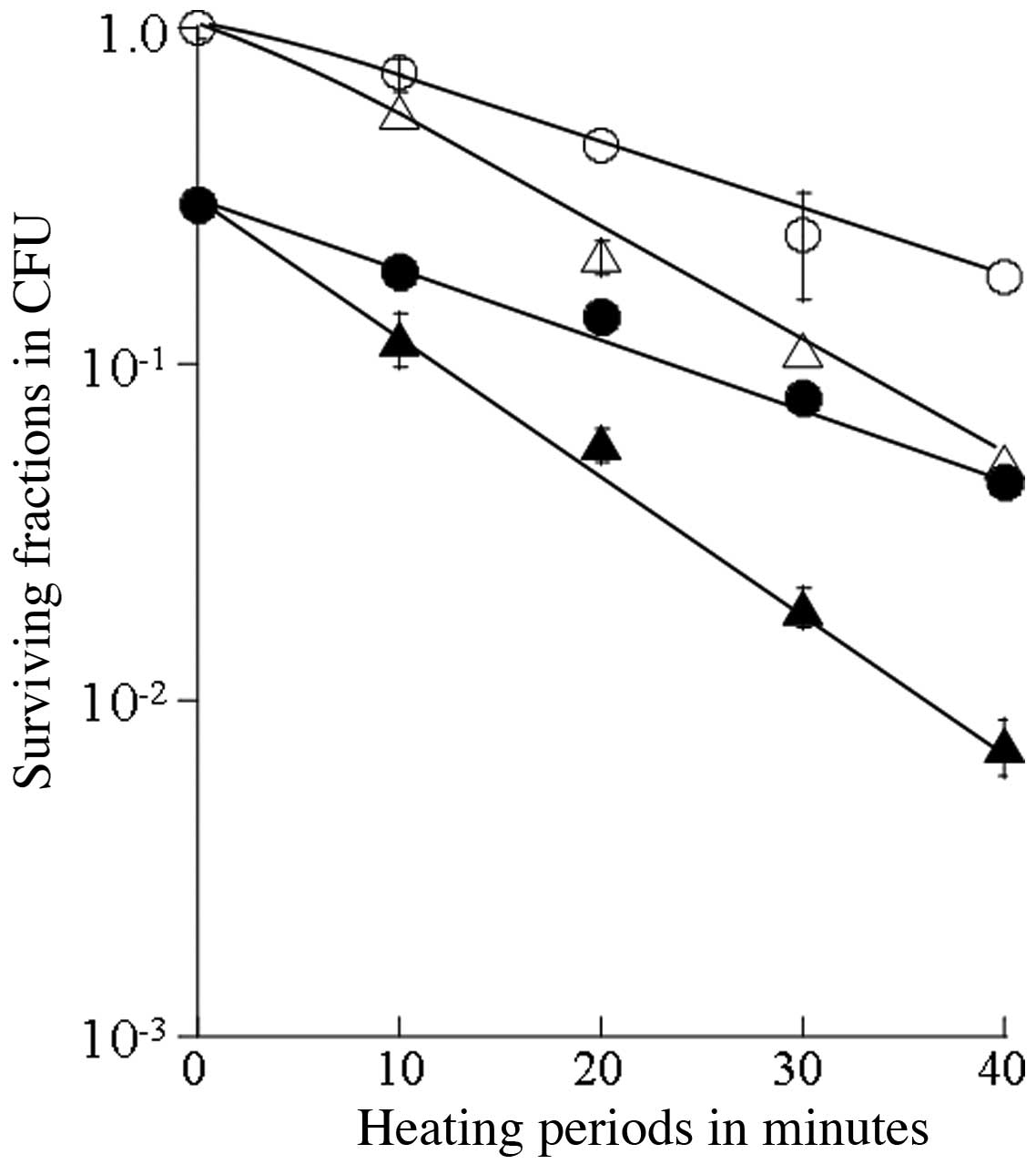
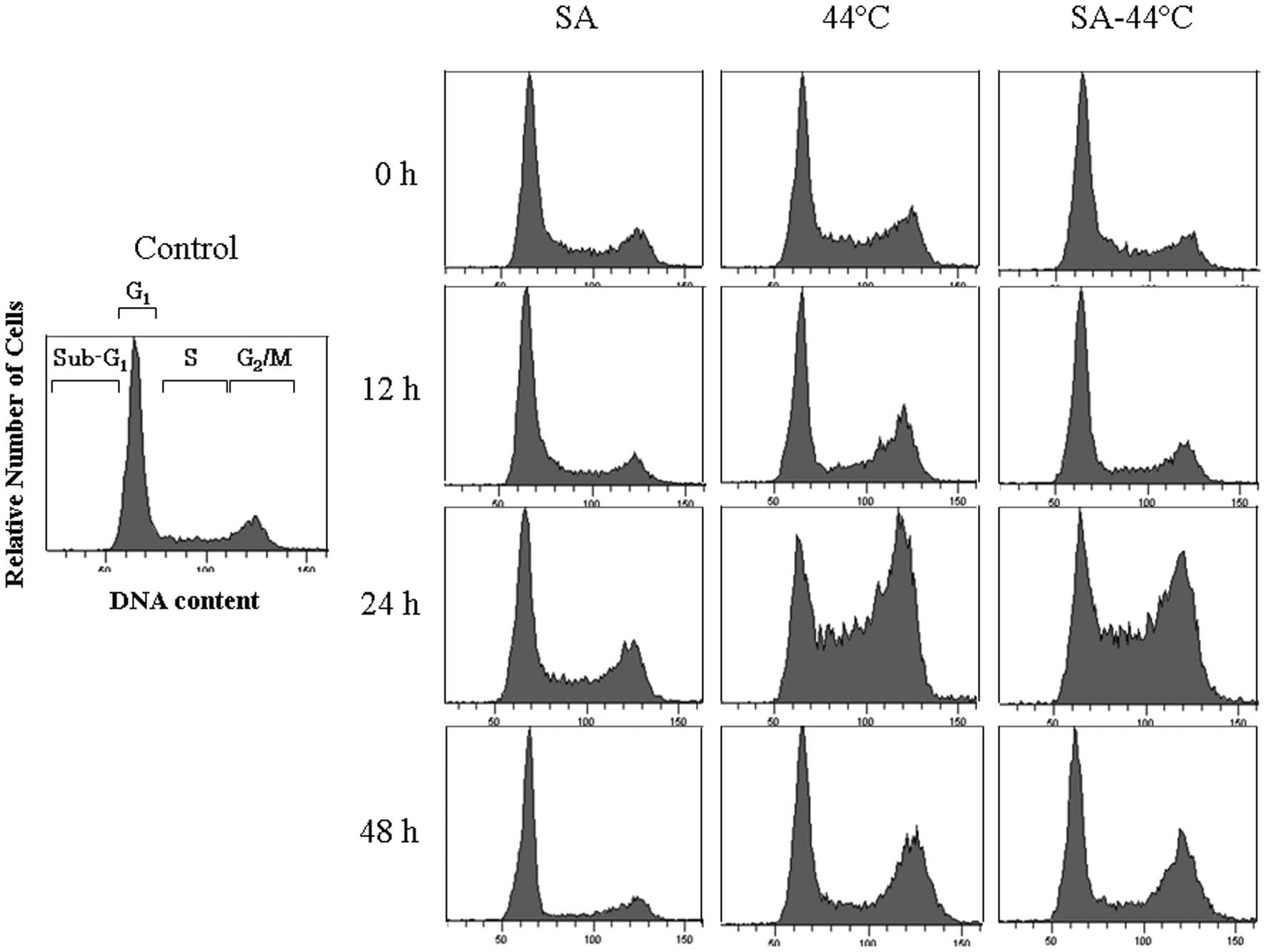
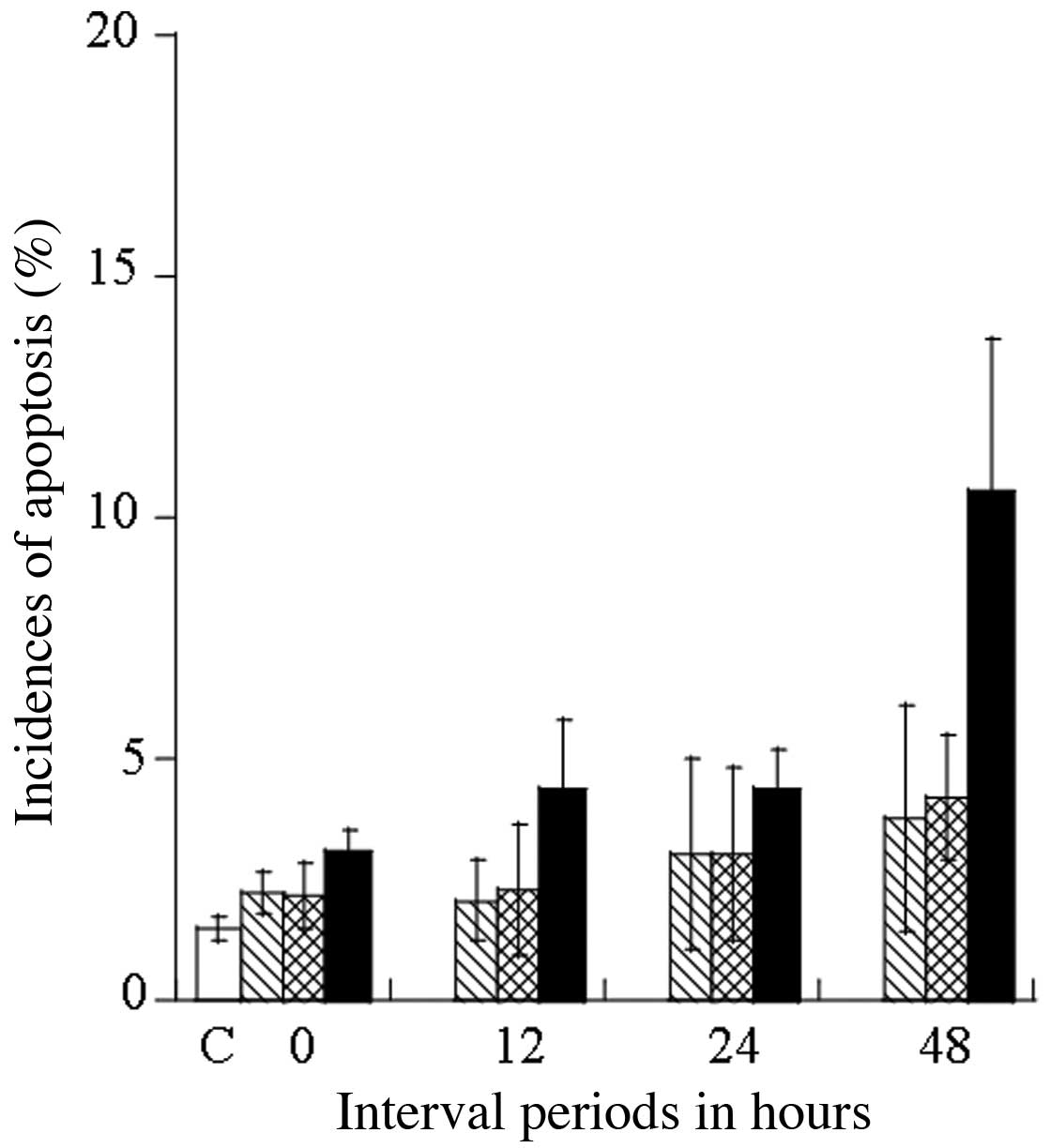
|
1
|
Wang NH, Taniguchi M, Tsuji D, Doi M,
Ohishi H, Yoza K and Baba K: Four guaianolides from Sinodielsia
yunnanensis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 51:68–70. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M and Baba K:
Anti-tumor actions of major component 3′-O-acetylhamaudol of
Angelica japonica roots through dual actions,
anti-angiogenesis and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte
activation. Cancer Lett. 265:84–97. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sugii M, Ohkita M, Taniguchi M, Baba K,
Kawai Y, Tahara C, Takaoka M and Matsumura Y: Xanthoangelol D
isolated from the roots of Angelica keiskei inhibits
endothelin-1 production through the suppression of nuclear
factor-kappaB. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:607–610. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Hayashi S, Hatashita M, Hayashi A,
Matsumoto H, Shioura H and Kitai R: Thermosensitization by
parthenolide in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells and p53- and
hsp72-independent apoptosis induction via the nuclear factor-κB
signal pathway. Int J Mol Med. 21:585–592. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayashi S, Sakurai H, Hayashi A, Tanaka Y,
Hatashita M and Shioura H: Inhibition of NF-κB by combination
therapy with parthenolide and hyperthermia and kinetics of
apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest in human lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 25:81–87. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Hayashi S, Koshiba K, Hatashita M, Sato T,
Jujo Y, Suzuki R, Tanaka Y and Shioura H: Thermosensitization and
induction of apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest via the MAPK cascade by
parthenolide, an NF-κB inhibitor, in human prostate cancer
androgen-independent cell lines. Int J Mol Med. 28:1033–1042.
2011.
|
|
7
|
Storer RD, Stein RB, Sina JF, DeLuca JG,
Allen HL and Bradley MO: Malignant transformation of preneoplastic
hamster epidermal cell line by the EJ c-Ha-ras-oncogene. Cancer
Res. 46:1458–1464. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cameron S, Levin L, Zoller M and Wigler M:
cAMP-independent control of sporulation, glycogen metabolism, and
heat shock resistance in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 53:555–566.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shirayama M, Kawakami K, Matsui Y, Tanaka
K and Toh-e A: MSI3, a multicopy suppressor of mutants
hyperactivated in the RAS-cAMP pathway, encodes a novel HSP70
protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet.
240:323–332. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mivechi NF and Giaccia AJ:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase acts as a negative regulator of
the heat shock response in NIH3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 55:5512–5519.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oh AS, Lorant LA, Holloway JN, Miller DL,
Kern FG and El-Ashry D: Hyperactivation of MAPK induces loss of
ERalpha expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol.
15:1344–1359. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barault L, Veyrie N, Jooste V, et al:
Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH
kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a
population-based series of colon cancers. Int J Cancer.
122:2255–2259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fecher LA, Amaravadi RK and Flaherty KT:
The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:183–189. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen KH, Weng MS and Lin JK: Tangeretin
suppresses IL-1beta-induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression
through inhibition of p38 MAPK, JNK, and AKT activation in human
lung carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:215–227. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang YQ, Jaganath I, Manikam R and Sekaran
SD: Phyllanthus suppresses prostate cancer cell, PC-3,
proliferation and induces apoptosis through multiple signalling
pathways (MAPKs, PI3K/Akt, NFκB, and hypoxia). Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:6095812013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cobb MH and Goldsmith EJ: How MAP kinases
are regulated. J Biol Chem. 270:14843–14846. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Robinson MJ and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:180–186. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB and Johnson
GL: Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a
three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev. 79:143–180.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mielke K and Herdegen T: JNK and p38
stresskinases - degenerative effectors of
signal-transduction-cascades in the nervous system. Prog Neurobiol.
61:45–60. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whitmarsh AJ and Davis RJ: Transcription
factor AP-1 regulation by mitogen-activated protein kinase signal
transduction pathways. J Mol Med (Berl). 74:589–607. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ip YT and Davis RJ: Signal transduction by
the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) - from inflammation to
development. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:205–219. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ahn KS, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: from clone to clinic. Curr Mol Med. 7:619–637. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Majumder PK and Sellers WR: Akt-regulated
pathways in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 24:7465–7474. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hayashi S, Kano E, Tsuji K,
Furukawa-Furuya M, Yoshikawa S, Hatashita M, Matsumoto H, Jin ZH,
Ohtsubo T and Kitai R: Modification of thermosensitivity and
chemosensitivity induced by combined treatments with hyperthermia
and adriamycin. Int J Mol Med. 8:417–422. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shioura H, Hayashi S, Matsumoto H, Kitai
R, Ohtsubo T, Nishida T, Zhang SW, Yoshida M, Ishii Y and Kano E:
The effects of combined treatments with low hyperthermia and
bleomycin on survivals of murine L cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
16:147–152. 1997.
|
|
28
|
Ohtsubo T, Saito H, Matsumoto H, Hayashi
S, Shioura H, Kitai R, Saito T and Kano E: In vitro effects of
hyperthermia combined with cisplatin or peplomycin on the human
maxillary carcinoma cell line IMC-2. Int J Hyperthermia. 13:59–67.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hayashi S, Hatashita M, Matsumoto H, Jin
ZH, Shioura H and Kano E: Modification of thermosensitivity by
amrubicin or amrubicinol in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells
and the kinetics of apoptosis and necrosis induction. Int J Mol
Med. 16:381–387. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mayo MW, Wang CY, Cogswell PC,
Rogers-Graham KS, Lowe SW, Der CJ and Baldwin AS Jr: Requirement of
NF-kappaB activation to suppress p53-independent apoptosis induced
by oncogenic Ras. Science. 278:1812–1815. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalra N, Seth K, Prasad S, Singh M, Pant
AB and Shukla Y: Theaflavins induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells is
mediated through induction of p53, down-regulation of NF-kappa B
and mitogen-activated protein kinases pathways. Life Sci.
80:2137–2146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vertrees RA, Das GC, Coscio AM, Xie J,
Zwischenberger JB and Boor PJ: A mechanism of hyperthermia-induced
apoptosis in ras-transformed lung cells. Mol Carcinog. 44:111–121.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Raffoul JJ, Wang Y, Kucuk O, Forman JD,
Sarkar FH and Hillman GG: Genistein inhibits radiation-induced
activation of NF-kappaB in prostate cancer cells promoting
apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle arrest. BMC Cancer. 6:1072006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vidya Priyadarsini R, Senthil Murugan R,
Maitreyi S, Ramalingam K, Karunagaran D and Nagini S: The flavonoid
quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53
induction and NF-κB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:84–91.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mogi M, Ozeki N, Nakamura H and Togari A:
Dual roles for NF-kappaB activation in osteoblastic cells by serum
deprivation: osteoblastic apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest. Bone.
35:507–516. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barbacid M: ras genes (Review). Annu Rev
Biochem. 56:779–827. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bos JL: ras oncogenes in human cancer: a
review (Review). Cancer Res. 49:4682–4689. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D
and Lowe SW: Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence
associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang W, Chen JX, Liao R, Deng Q, Zhou JJ,
Huang S and Sun P: Sequential activation of the MEK-extracellular
signal-regulated kinase and MKK3/6-p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways mediates oncogenic ras-induced premature
senescence. Mol Cell Biol. 22:3389–3403. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hingorani SR and Tuveson DA: Ras redux:
rethinking how and where Ras acts. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 13:6–13.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boguski MS and McCormick F: Proteins
regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 366:643–654. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benvenuti S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di
Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S, Siena S and Bardelli
A: Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs
the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal
growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res.
67:2643–2648. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Russo A, Rizzo S, Bronte G, Silvestris N,
Colucci G, Gebbia N, Bazan V and Fulfaro F: The long and winding
road to useful predictive factors for anti-EGFR therapy in
metastatic colorectal carcinoma: the KRAS/BRAF pathway. Oncology.
77(Suppl 1): 57–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pergolizzi RG, Kreis W, Rottach C, Susin M
and Broome JD: Mutational status of codons 12 and 13 of the N- and
K-ras genes in tissue and cell lines derived from primary and
metastatic prostate carcinomas. Cancer Invest. 11:25–32. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim-Kaneyama, Nose K and Shibanuma M:
Significance of nuclear relocalization of ERK1/2 in reactivation of
c-fos transcription and DNA synthesis in senescent fibroblasts. J
Biol Chem. 275:20685–20692. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Godeny MD and Sayeski PP: ANG II-induced
cell proliferation is dually mediated by c-Src/Yes/Fyn-regulated
ERK1/2 activation in the cytoplasm and PKCzeta-controlled ERK1/2
activity within the nucleus. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
291:C1297–C1307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cheung EC and Slack RS: Emerging role for
ERK as a key regulator of neuronal apoptosis. Sci STKE.
2004:PE452004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Aloyz RS, Bamji SX, Pozniak CD, Toma JG,
Atwal J, Kaplan DR and Miller FD: p53 is essential for
developmental neuron death as regulated by the TrkA and p75
neurotrophin receptors. J Cell Biol. 143:1691–1703. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leppä S and Bohmann D: Diverse functions
of JNK signaling and c-Jun in stress response and apoptosis.
Oncogene. 18:6158–6162. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shen HM and Liu ZG: JNK signaling pathway
is a key modulator in cell death mediated by reactive oxygen and
nitrogen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:928–939. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kim HJ, Chakravarti N, Oridate N, Choe C,
Claret FX and Lotan R: N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced
apoptosis triggered by reactive oxygen species is mediated by
activation of MAPKs in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells.
Oncogene. 25:2785–2794. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Rosner D, Stoneman V, Littlewood T,
McCarthy N, Figg N, Wang Y, Tellides G and Bennett M:
Interferon-gamma induces Fas trafficking and sensitization to
apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells via a PI3K- and
Akt-dependent mechanism. Am J Pathol. 168:2054–2063. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lu B, Wang L, Stehlik C, Medan D, Huang C,
Hu S, Chen F, Shi X and Rojanasakul Y: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt positively regulates Fas (CD95)-mediated apoptosis in
epidermal Cl41 cells. J Immunol. 176:6785–6793. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Aksamitiene E, Kiyatkin A and Kholodenko
BN: Cross-talk between mitogenic Ras/MAPK and survival PI3K/Akt
pathways: a fine balance. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:139–146. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ho AL and Sherman E: Clinical development
of kinase inhibitors for the treatment of differentiated thyroid
cancer. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 9:32–41. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu D and Xing M: Potent inhibition of
thyroid cancer cells by the MEK inhibitor PD0325901 and its
potentiation by suppression of the PI3K and NF-kappaB pathways.
Thyroid. 18:853–864. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Brzezianska E and Pastuszak-Lewandoska D:
A minireview: the role of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in thyroid
follicular cell-derived neoplasm (Review). Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 16:422–439. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|