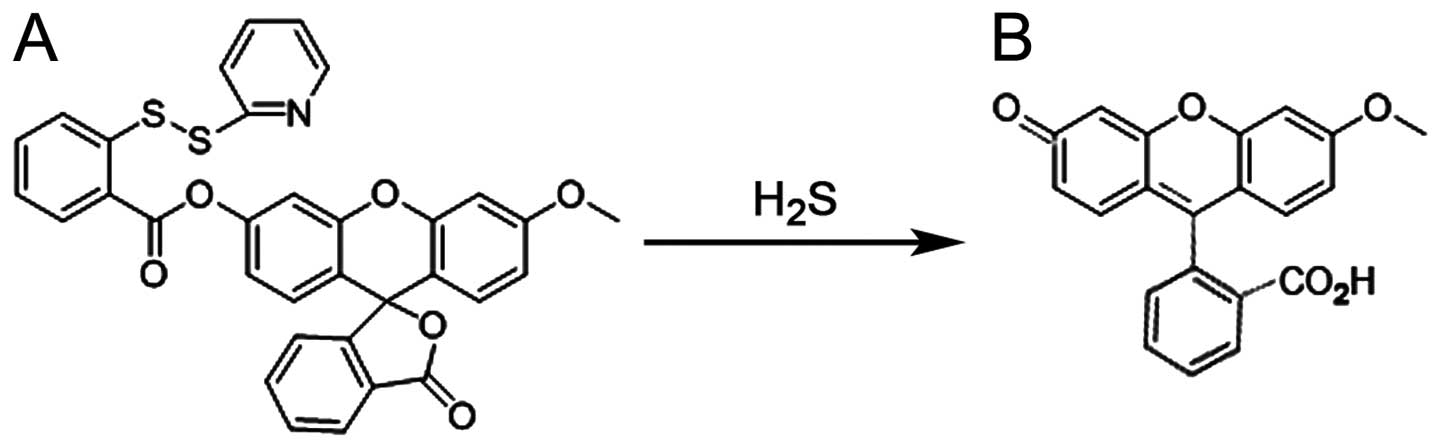
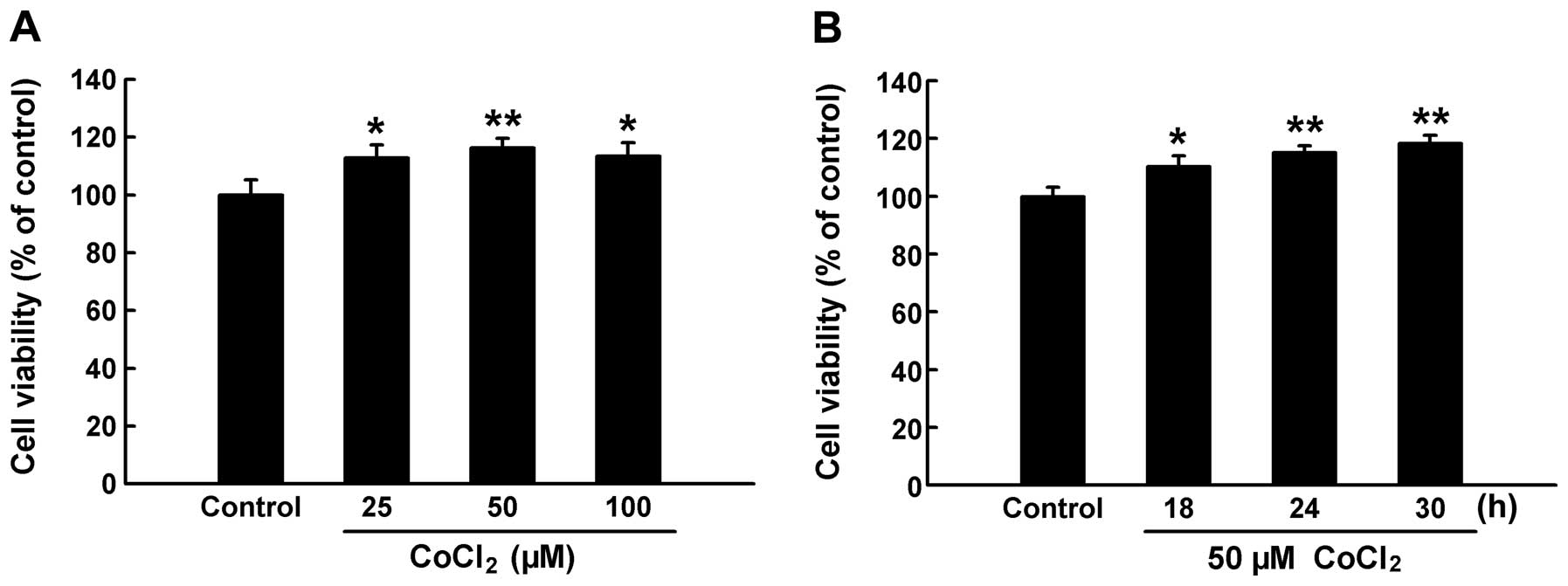
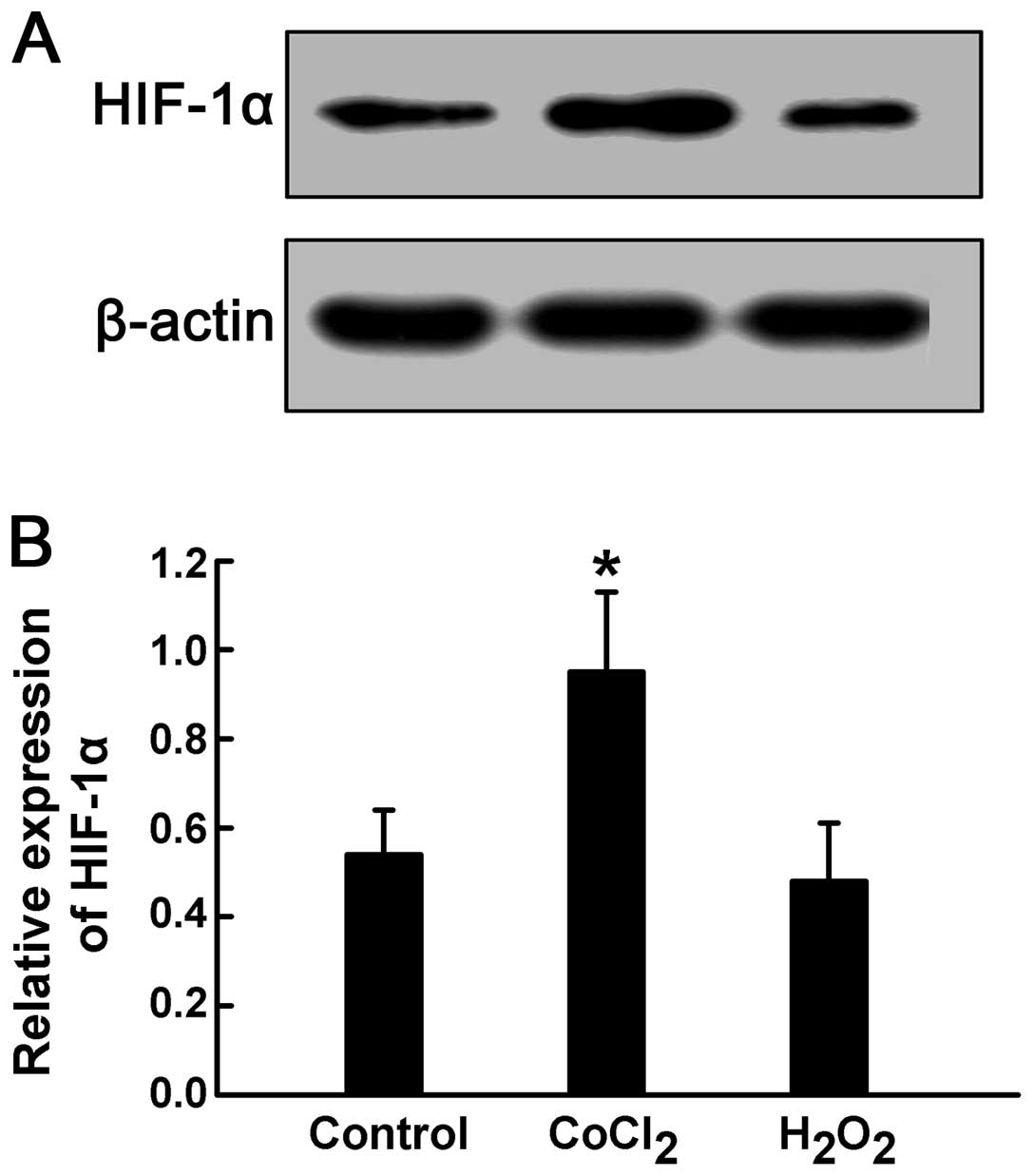
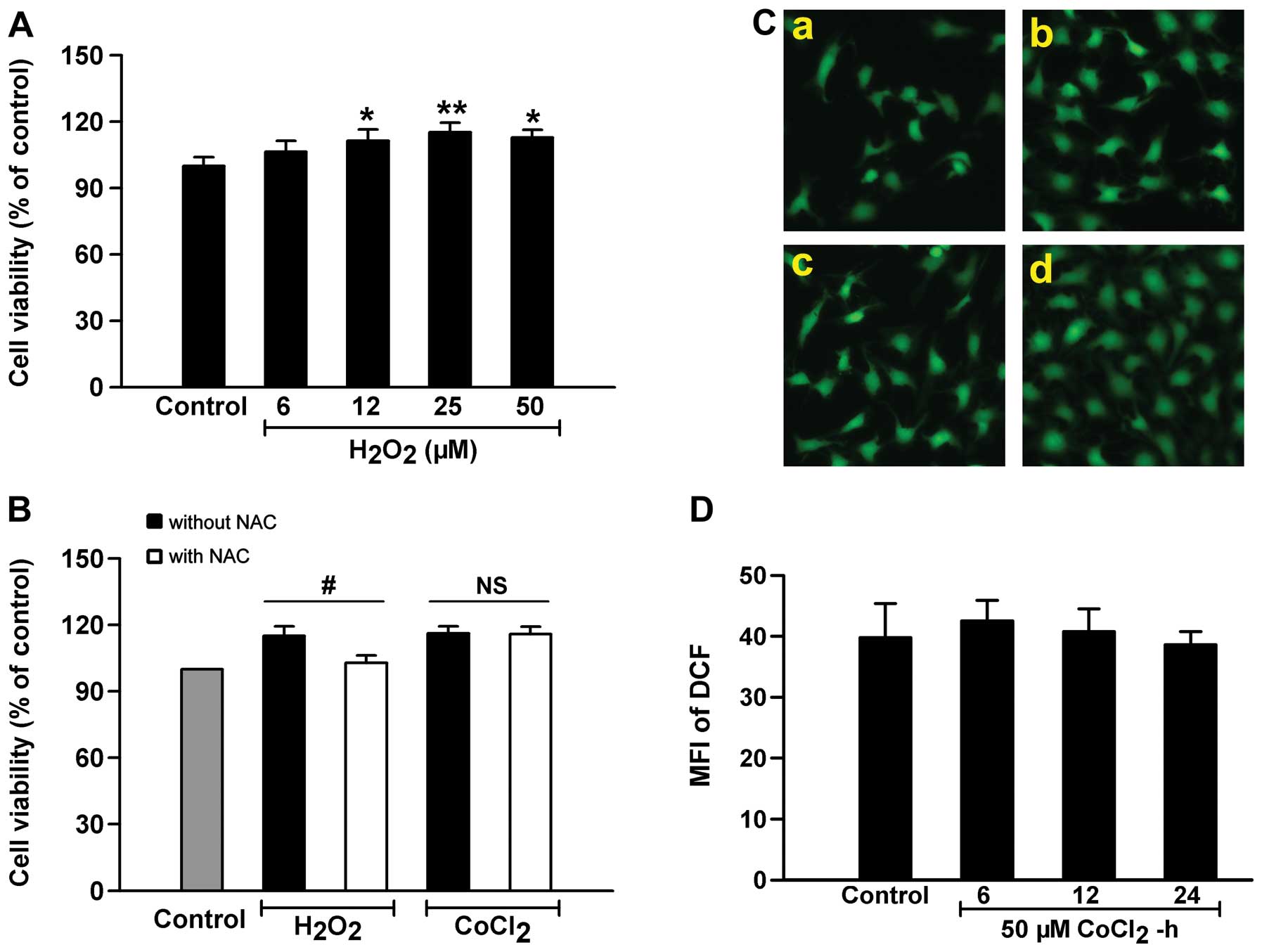
|
1
|
Schannwell CM, Steiner S and Strauer BE:
Diagnostics in pulmonary hypertension. J Physiol Pharmacol.
58(Suppl 5): 591–602. 2007.
|
|
2
|
Fredenburgh LE, Liang OD, Macias AA, et
al: Absence of cyclooxygenase-2 exacerbates hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension and enhances contractility of vascular
smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 117:2114–2122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ismail S, Sturrock A, Wu P, et al: NOX4
mediates hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells: the role of autocrine production of
transforming growth factor-β1 and insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L489–L499. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burdon RH, Gill V and Rice-Evans C:
Oxidative stress and tumour cell proliferation. Free Radic Res
Commun. 11:65–76. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Immenschuh S and Baumgart-Vogt E:
Peroxiredoxins, oxidative stress, and cell proliferation. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 7:768–777. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shimizu H, Hirose Y, Nishijima F,
Tsubakihara Y and Miyazaki H: ROS and PDGF-β receptors are
critically involved in indoxyl sulfate actions that promote
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 297:C389–C396. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Tsukagoshi H, Busch W and Benfey PN:
Transcriptional regulation of ROS controls transition from
proliferation to differentiation in the root. Cell. 143:606–616.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lakshminrusimha S, Russell JA, Wedgwood S,
et al: Superoxide dismutase improves oxygenation and reduces
oxidation in neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 174:1370–1377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zuckerbraun BS, Shiva S, Ifedigbo E, et
al: Nitrite potently inhibits hypoxic and inflammatory pulmonary
arterial hypertension and smooth muscle proliferation via xanthine
oxidoreductase-dependent nitric oxide generation. Circulation.
121:98–109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ruan CH, Dixon RA, Willerson JT and Ruan
KH: Prostacyclin therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Tex
Heart Inst J. 37:391–399. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pan TT, Feng ZN, Lee SW, Moore PK and Bian
JS: Endogenous hydrogen sulfide contributes to the cardioprotection
by metabolic inhibition preconditioning in the rat ventricular
myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 40:119–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang XY, Yang CT, Zheng DD, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cells against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Mol Cell Biochem. 363:419–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang C, Yang Z, Zhang M, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and
inflammation in HaCaT cells through inhibition of
ROS/NF-kappaB/COX-2 pathway. PLoS One. 6:e219712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang R: Physiological implications of
hydrogen sulfide: a whiff exploration that blossomed. Physiol Rev.
92:791–896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu LF, Pan TT, Neo KL, Yong QC and Bian
JS: Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates the delayed cardioprotection induced
by hydrogen sulfide preconditioning in isolated rat cardiomyocytes.
Pflugers Arch. 455:971–978. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin Hongfang J, Bailin Cong, Bin Zhao, et
al: Effects of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular
structural remodeling. Life Sci. 78:1299–1309. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu C, Liu F, Zhou X, et al: Effect of
protein kinase C on proliferation and apoptosis of T lymphocytes in
idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura children. Cell Mol Immunol.
2:197–203. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang C, Ling H, Zhang M, et al: Oxidative
stress mediates chemical hypoxia-induced injury and inflammation by
activating NF-kappab-COX-2 pathway in HaCaT cells. Mol Cells.
31:531–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y, Bhushan S, Yang C, et al:
Controllable hydrogen sulfide donors and the activity against
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. ACS Chem Biol. 8:1283–1290.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Pan J, Li S, et al: Capture and
visualization of hydrogen sulfide by a fluorescent probe. Angew
Chem Int Ed Engl. 50:10327–10329. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Coruzzi G, Venturi N and Spaggiari S:
Gastrointestinal safety of novel nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
drugs: selective COX-2 inhibitors and beyond. Acta Biomed.
78:96–110. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Badesch DB, Abman SH, Simonneau G, Rubin
LJ and McLaughlin VV: Medical therapy for pulmonary arterial
hypertension: updated ACCP evidence-based clinical practice
guidelines. Chest. 131:1917–1928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Simonneau G, Galie N, Rubin LJ, et al:
Clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 43:S5–S12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu M, Gong D, Lim M, Arutyunyan A, Groffen
J and Heisterkamp N: Lack of bcr and abr promotes hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension in mice. PLoS One. 7:e497562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Touyz RM: Reactive oxygen species,
vascular oxidative stress, and redox signaling in hypertension:
what is the clinical significance? Hypertension. 44:248–252. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Landmesser U, Dikalov S, Price SR, et al:
Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to uncoupling of endothelial
cell nitric oxide synthase in hypertension. J Clin Invest.
111:1201–1209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Booth EA, Flint RR, Lucas KL, Knittel AK
and Lucchesi BR: Estrogen protects the heart from
ischemia-reperfusion injury via COX-2-derived PGI2. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 52:228–235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dore S, Otsuka T, Mito T, et al: Neuronal
overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 increases cerebral infarction.
Ann Neurol. 54:155–162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kwak HJ, Park KM, Choi HE, Lim HJ, Park JH
and Park HY: The cardioprotective effects of zileuton, a
5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, are mediated by COX-2 via activation of
PKC delta. Cell Signal. 22:80–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Birnbaum Y, Ye Y, Rosanio S, et al:
Prostaglandins mediate the cardioprotective effects of atorvastatin
against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 65:345–355.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang Z, Yang C, Xiao L, et al: Novel
insights into the role of HSP90 in cytoprotection of H2S
against chemical hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cardiac myocytes.
Int J Mol Med. 28:397–403. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao W, Zhang J, Lu Y and Wang R: The
vasorelaxant effect of H2S as a novel endogenous gaseous
KATP channel opener. EMBO J. 20:6008–6016. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhatia M: Hydrogen sulfide as a
vasodilator. IUBMB Life. 57:603–606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng Y, Ndisang JF, Tang G, Cao K and
Wang R: Hydrogen sulfide-induced relaxation of resistance
mesenteric artery beds of rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H2316–H2323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shimizu K, Ogawa F, Hara T, et al:
Exogenous application of hydrogen sulfide donor attenuates
inflammatory reactions through the L-selectin-involved pathway in
the cutaneous reverse passive Arthus reaction. J Leukoc Biol.
93:573–584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang C, Du J, Bu D, Yan H, Tang X and
Tang C: The regulatory effect of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxic
pulmonary hypertension in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
302:810–816. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bearden SE, Beard RS Jr and Pfau JC:
Extracellular transsulfuration generates hydrogen sulfide from
homocysteine and protects endothelium from redox stress. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 299:H1568–H1576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang G, Sun X and Wang R: Hydrogen
sulfide-induced apoptosis of human aorta smooth muscle cells via
the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and caspase-3.
FASEB J. 18:1782–1784. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Du J, Hui Y, Cheung Y, et al: The possible
role of hydrogen sulfide as a smooth muscle cell proliferation
inhibitor in rat cultured cells. Heart Vessels. 19:75–80. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baskar R, Sparatore A, Del Soldato P and
Moore PK: Effect of S-diclofenac, a novel hydrogen sulfide
releasing derivative inhibit rat vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 594:1–8. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu B, Teng H, Yang G, Wu L and Wang R:
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the translational expression of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Br J Pharmacol. 167:1492–1505.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kai S, Tanaka T, Daijo H, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide inhibits hypoxia- but not anoxia-induced hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 activation in a von hippel-lindau- and
mitochondria-dependent manner. Antioxid Redox Signal. 16:203–216.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|