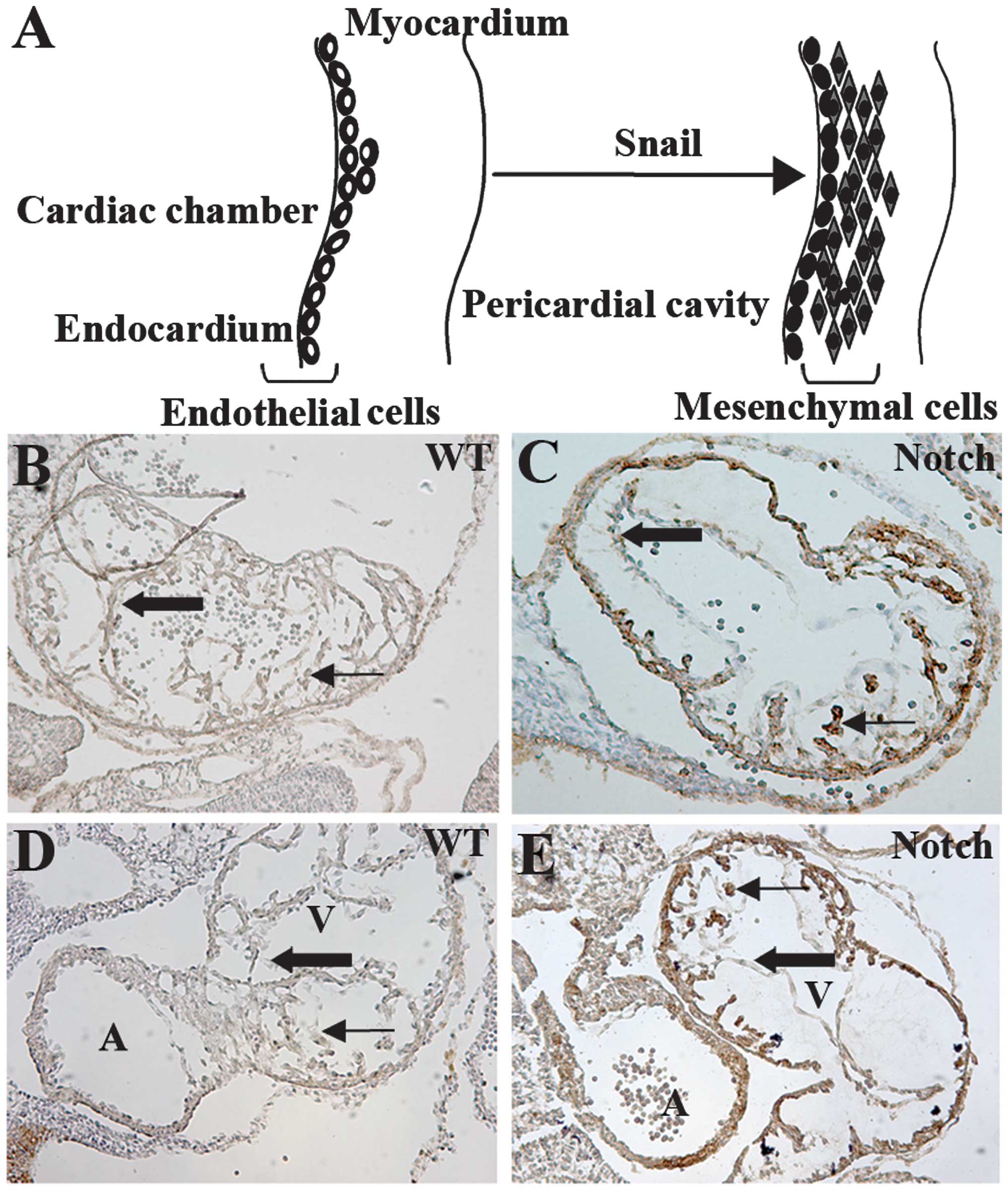
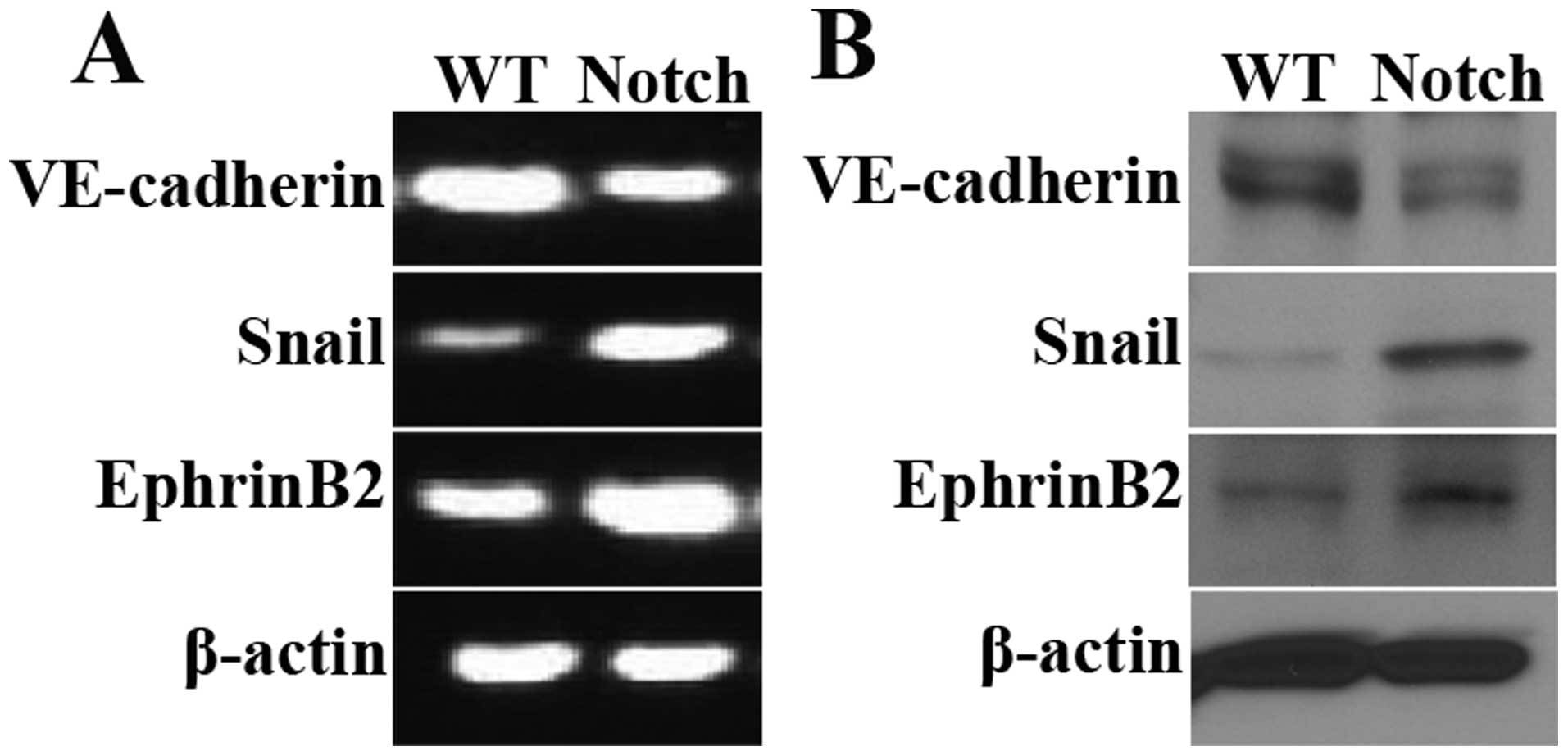
|
1
|
Kovacic JC, Mercader N, Torres M, Boehm M
and Fuster V: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal and
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: from cardiovascular
development to disease. Circulation. 125:1795–1808. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, et
al: Endothelial-to- mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac
fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garcia J, Sandi MJ, Cordelier P, et al:
Tie1 deficiency induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO
Rep. 13:431–439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arciniegas E, Neves CY, Carrillo LM,
Zambrano EA and Ramírez R: Endothelial-mesenchymal transition
occurs during embryonic pulmonary artery development. Endothelium.
12:193–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Markwald RR, Fitzharris TP and Smith WN:
Structural analysis of endocardial cytodifferentiation. Dev Biol.
42:160–180. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Markwald RR, Fitzharris TP and Manasek FJ:
Structural development of endocardial cushions. Am J Anat.
148:85–119. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Arciniegas E, Frid MG, Douglas IS and
Stenmark KR: Perspectives on endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
potential contribution to vascular remodeling in chronic pulmonary
hypertension. Am J Physiol. 293:L1–L8. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J and Bertram JF: Review:
Endothelial-myofibroblast transition, a new player in diabetic
renal fibrosis. Nephrology (Carlton). 15:507–512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu H, Zaidi M, Struve J, et al: Abnormal
fibrillin-1 expression and chronic oxidative stress mediate
endothelial mesenchymal transition in a murine model of systemic
sclerosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 300:C550–C556. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kizu A, Medici D and Kalluri R:
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition as a novel mechanism for
generating myofibroblasts during diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol.
175:1371–1373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoshimatsu Y and Watabe T: Roles of TGF-β
signals in endothelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac
fibrosis. Int J Inflam. 2011:7240802011.
|
|
12
|
Armstrong EJ and Bischoff J: Heart valve
development: endothelial cell signaling and differentiation. Circ
Res. 95:459–470. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
High FA, Jain R, Stoller JZ, et al: Murine
Jagged1/Notch signaling in the second heart field orchestrates Fgf8
expression and tissue-tissue interactions during outflow tract
development. J Clin Invest. 119:1986–1996. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Garside VC, Chang AC, Karsan A and
Hoodless PA: Co-ordinating Notch, BMP, and TGF-β signaling during
heart valve development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:2899–2917.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fu Y, Chang A, Chang L, et al:
Differential regulation of transforming growth factor beta
signaling pathways by Notch in human endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 284:19452–19462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lewis J: Notch signalling. A short cut to
the nucleus. Nature. 393:304–305. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gridley T: Notch signaling in vascular
development and physiology. Development. 134:2709–2718. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gridley T: Notch signaling during vascular
development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:5377–5378. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fortini ME and Artavanis-Tsakonas S: The
suppressor of hairless protein participates in notch receptor
signaling. Cell. 79:273–282. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tun T, Hamaguchi Y, Matsunami N, Furukawa
T, Honjo T and Kawaichi M: Recognition sequence of a highly
conserved DNA binding protein RBP-J kappa. Nucleic Acids Res.
22:965–971. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, et al: Notch
signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes
Dev. 14:1343–1352. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Noseda M, McLean G, Niessen K, et al:
Notch activation results in phenotypic and functional changes
consistent with endothelial-to-mesenchymal transformation. Circ
Res. 94:910–917. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grieskamp T, Rudat C, Lüdtke TH, Norden J
and Kispert A: Notch signaling regulates smooth muscle
differentiation of epicardium-derived cells. Circ Res. 108:813–823.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chang AC, Fu Y, Garside VC, et al: Notch
initiates the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the
atrioventricular canal through autocrine activation of soluble
guanylyl cyclase. Dev Cell. 21:288–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Noseda M, Fu Y, Niessen K, et al: Smooth
muscle alpha-actin is a direct target of Notch/CSL. Circ Res.
98:1468–1470. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Penton AL, Leonard LD and Spinner NB:
Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:450–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duarte A, Hirashima M, Benedito R, et al:
Dosage-sensitive requirement for mouse Dll4 in artery development.
Genes Dev. 18:2474–2478. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krebs LT, Shutter JR, Tanigaki K, Honjo T,
Stark KL and Gridley T: Haploinsufficient lethality and formation
of arteriovenous malformations in Notch pathway mutants. Genes Dev.
18:2469–2473. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xue Y, Gao X, Lindsell CE, et al:
Embryonic lethality and vascular defects in mice lacking the Notch
ligand Jagged1. Hum Mol Genet. 8:723–730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
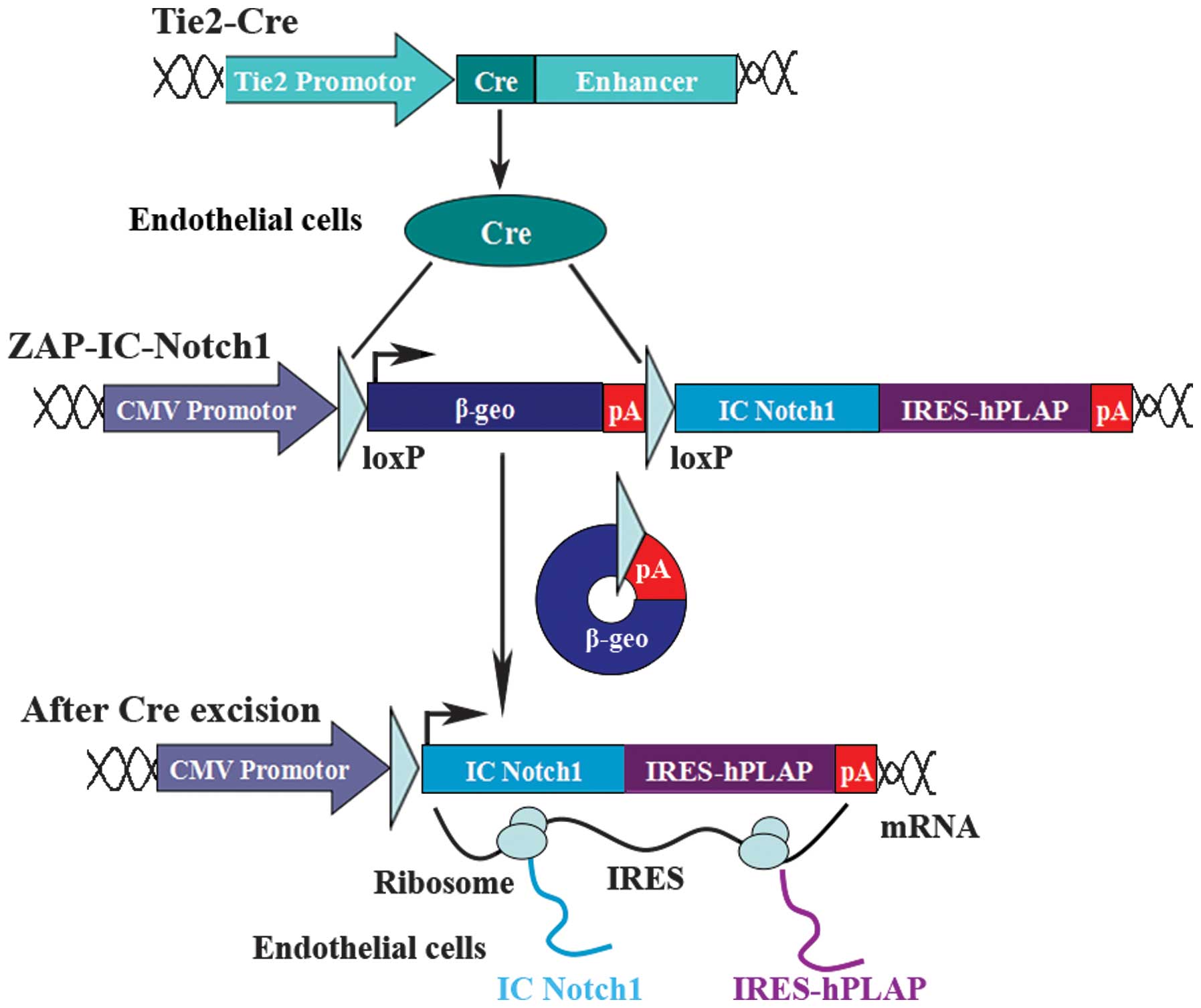
Liu J and Lobe CG: Cre-conditional
expression of constitutively active Notch1 in transgenic mice.
Genesis. 45:259–265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kisanuki YY, Hammer RE, Miyazaki J,
Williams SC, Richardson JA and Yanagisawa M: Tie2-Cre transgenic
mice: a new model for endothelial cell-lineage analysis in vivo.
Dev Biol. 230:230–242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lobe CG, Koop KE, Kreppner W, Lomeli H,
Gertsenstein M and Nagy A: Z/AP, a double reporter for cre-mediated
recombination. Dev Biol. 208:281–292. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Kanki Y, Okada Y, et al: A +220
GATA motif mediates basal but not endotoxin-repressible expression
of the von Willebrand factor promoter in Hprt-targeted transgenic
mice. J Thromb Haemost. 7:1384–1392. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baldwin HS, Shen HM, Yan HC, et al:
Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31):
alternatively spliced, functionally distinct isoforms expressed
during mammalian cardiovascular development. Development.
120:2539–2553. 1994.
|
|
35
|
Eisenberg LM and Markwald RR: Molecular
regulation of atrioventricular valvuloseptal morphogenesis. Circ
Res. 77:1–6. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nieto MA, Sargent MG, Wilkinson DG and
Cooke J: Control of cell behavior during vertebrate development by
Slug, a zinc finger gene. Science. 264:835–839. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bolós V, Peinado H, Pérez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: a comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, et al:
Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular
development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular
morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 13:295–306.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gerety SS and Anderson DJ: Cardiovascular
ephrinB2 function is essential for embryonic angiogenesis.
Development. 129:1397–1410. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Niessen K and Karsan A: Notch signaling in
the developing cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol. 293:C1–C11.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fischer A, Schumacher N, Maier M, Sendtner
M and Gessler M: The Notch target genes Hey1 and Hey2 are required
for embryonic vascular development. Genes Dev. 18:901–911. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Uyttendaele H, Ho J, Rossant J and
Kitajewski J: Vascular patterning defects associated with
expression of activated Notch4 in embryonic endothelium. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:5643–5648. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kang Y and Massague J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Iso T, Hamamori Y and Kedes L: Notch
signaling in vascular development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
23:543–553. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Garg V, Muth AN, Ransom JF, et al:
Mutations in NOTCH1 cause aortic valve disease. Nature.
437:270–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eldadah ZA, Hamosh A, Biery NJ, et al:
Familial tetralogy of fallot caused by mutation in the jagged1
gene. Hum Mol Genet. 10:163–169. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li L, Krantz ID, Deng Y, et al: Alagille
syndrome is caused by mutations in human Jagged1, which encodes a
ligand for Notch1. Nat Genet. 16:243–251. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Oka C, Nakano T, Wakeham A, et al:
Disruption of the mouse RBP-J kappa gene results in early embryonic
death. Development. 121:3291–3301. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Timmerman LA, Grego-Bessa J, Raya A, et
al: Notch promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac
development and oncogenic transformation. Genes Dev. 18:99–115.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Donovan J, Kordylewska A, Jan YN and Utset
MF: Tetralogy of fallot and other congenital heart defects in Hey2
mutant mice. Curr Biol. 12:1605–1610. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Murray SA and Gridley T: Snail family
genes are required for left-right asymmetry determination, but not
neural crest formation, in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:10300–10304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vestweber D: VE-cadherin: the major
endothelial adhesion molecule controlling cellular junctions and
blood vessel formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:223–232.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cheng JC, Chang HM and Leung PC:
Transforming growth factor-β1 inhibits trophoblast cell invasion by
inducing Snail-mediated down-regulation of vascular
endothelial-cadherin protein. J Biol Chem. 288:33181–33192.
2013.
|
|
58
|
Pérez-Pomares JM and de la Pompa JL:
Signaling during epicardium and coronary vessel development. Circ
Res. 109:1429–1442. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
del Monte G, Casanova JC, Guadix JA, et
al: Differential Notch signaling in the epicardium is required for
cardiac inflow development and coronary vessel morphogenesis. Circ
Res. 108:824–836. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Iso T, Maeno T, Oike Y, et al:
Dll4-selective Notch signaling induces ephrinB2 gene expression in
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 341:708–714. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|