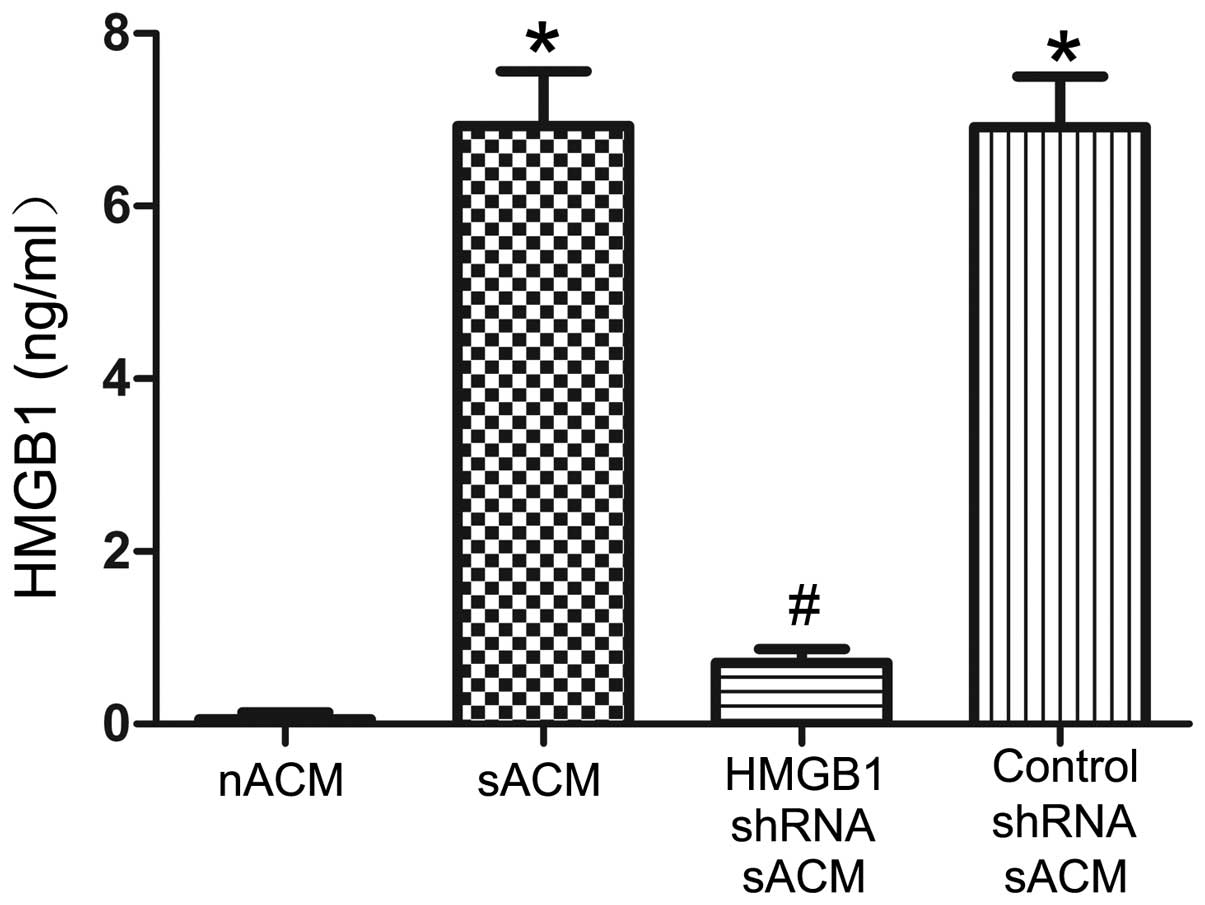
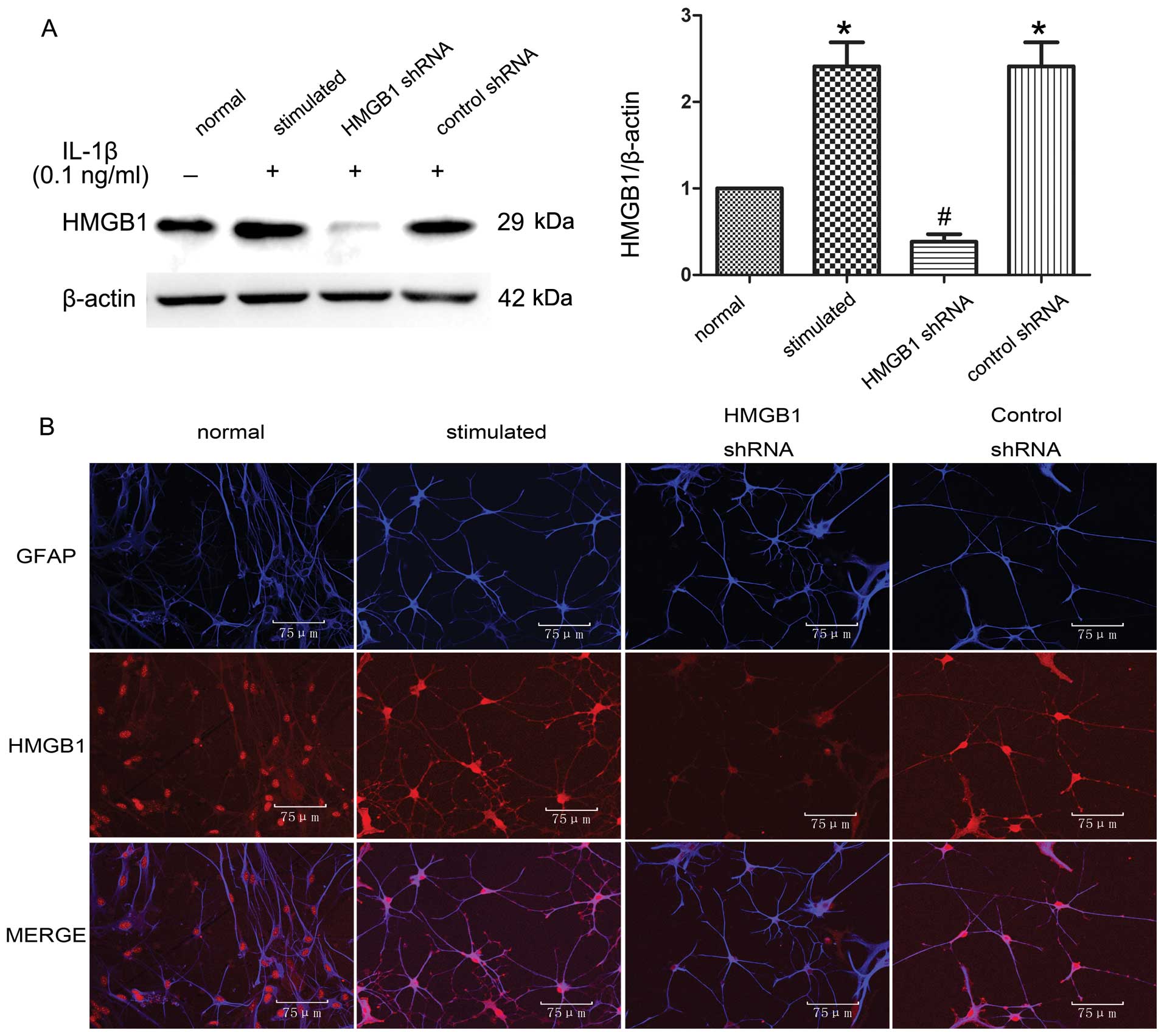
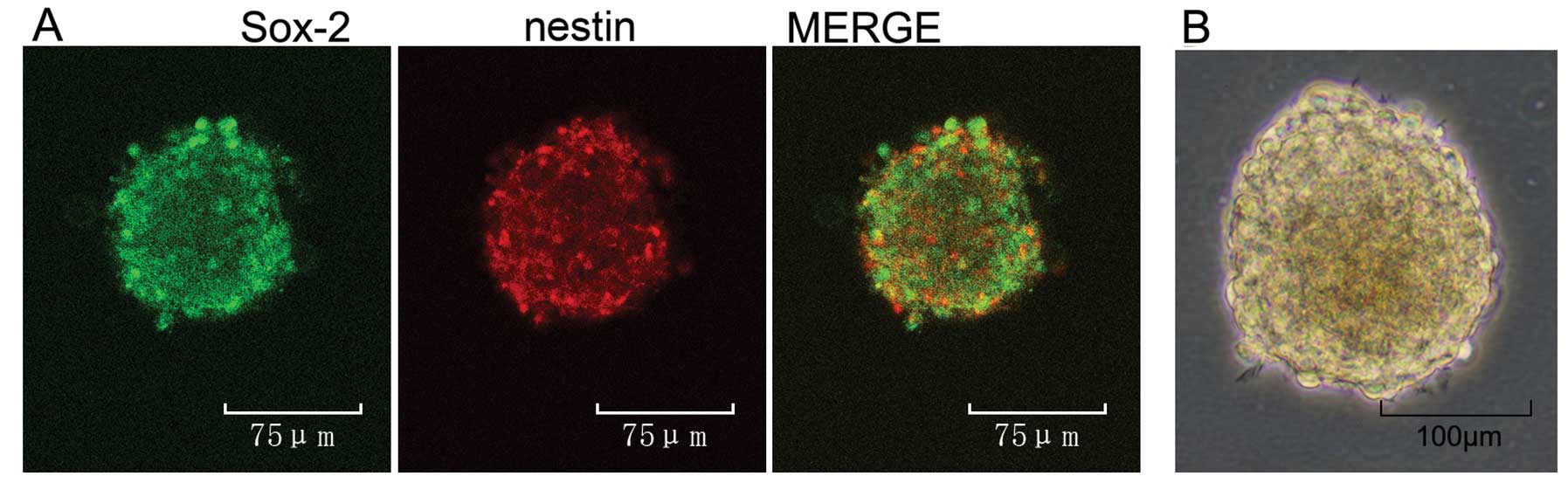
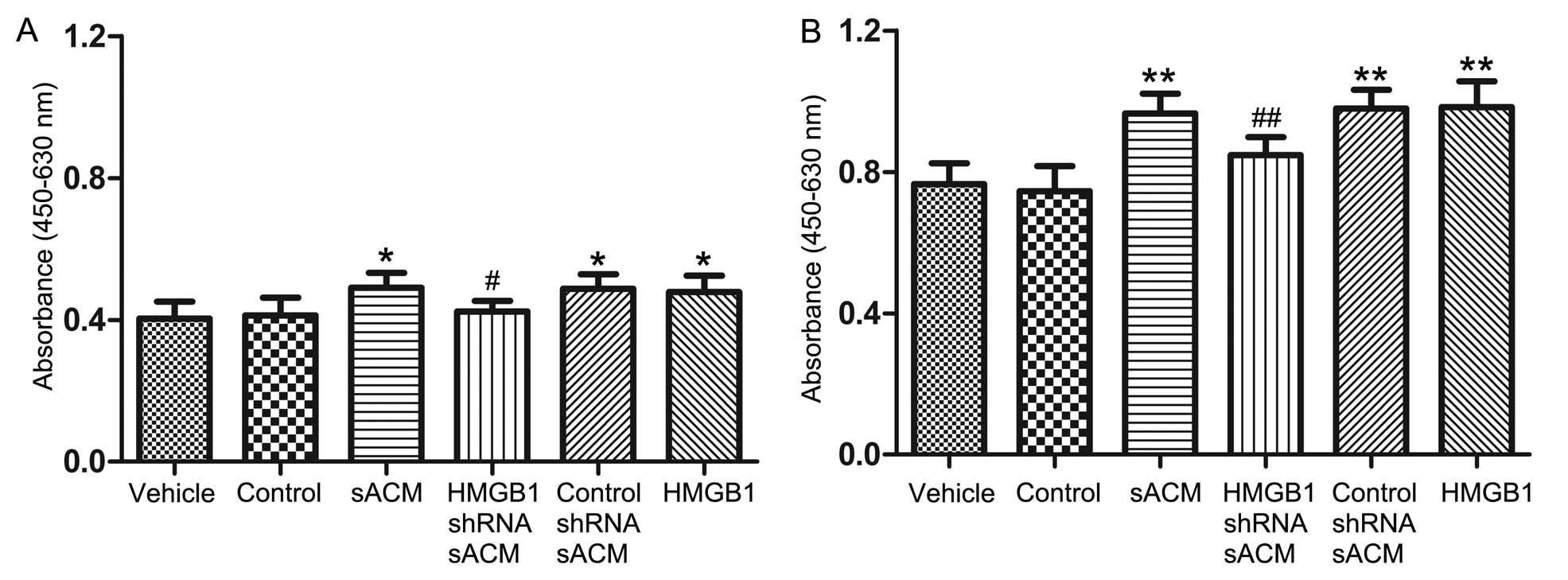
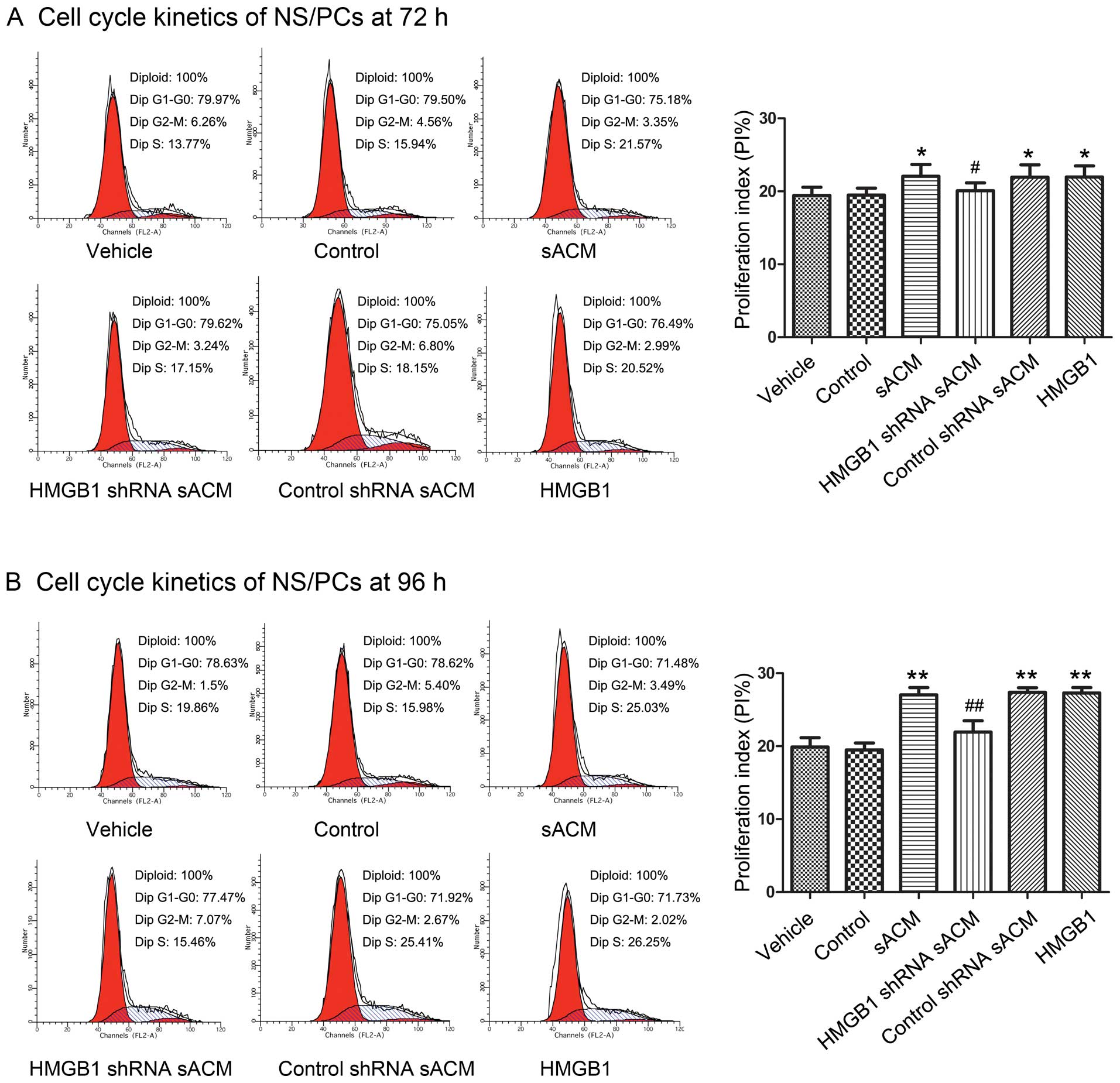
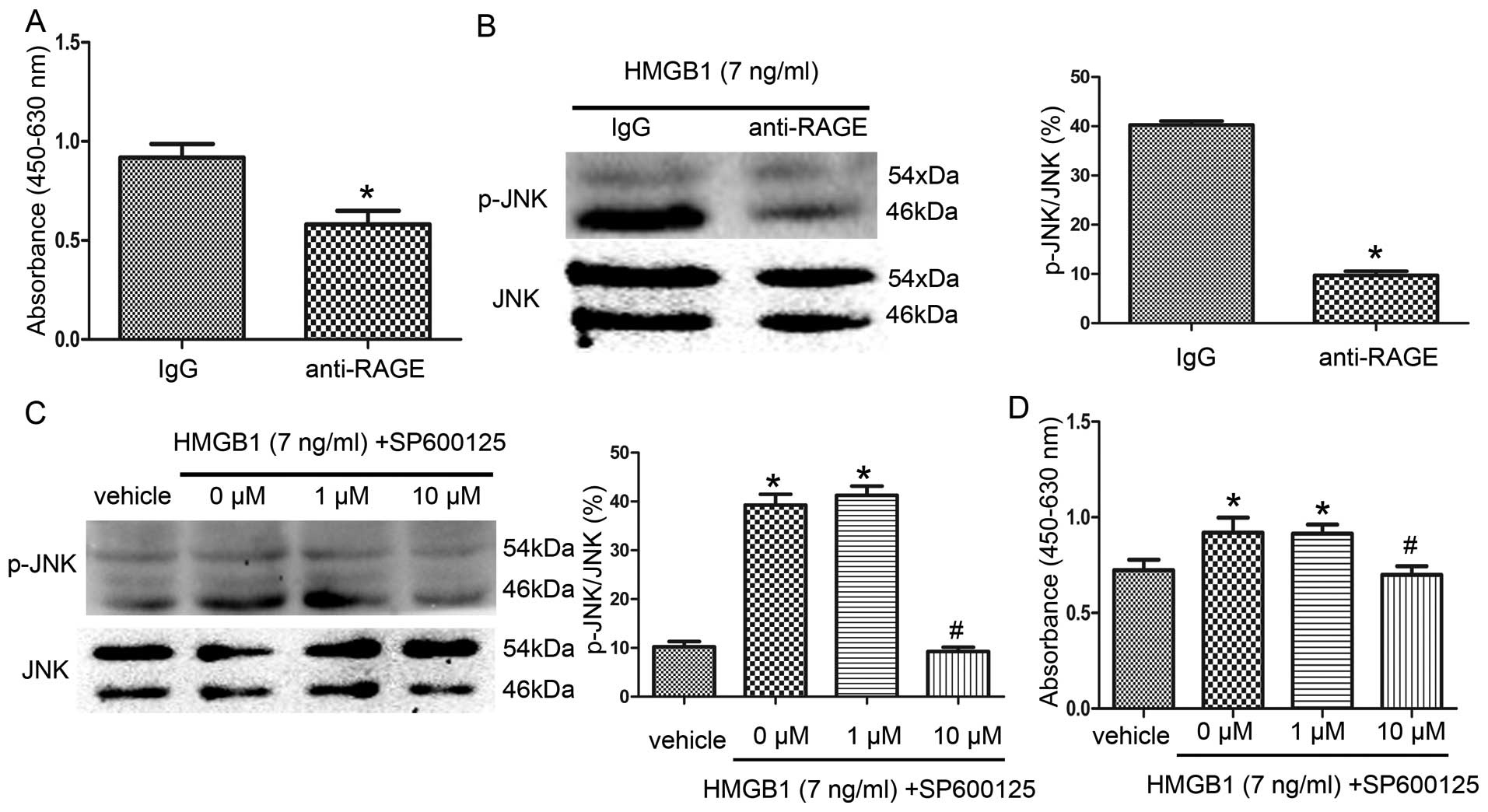
|
1
|
Go HS, Shin CY, Lee SH, et al: Increased
proliferation and gliogenesis of cultured rat neural progenitor
cells by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 16:365–376. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee C, Hu J, Ralls S, et al: The molecular
profiles of neural stem cell niche in the adult subventricular
zone. PLoS One. 7:e505012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao X, Li LP, Qin XH, et al: Astrocytic
adenosine 5′-triphosphate release regulates the proliferation of
neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Stem Cells.
31:1633–1643. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Guo Y, Wei Q, Huang Y, Xia W, Zhou Y and
Wang S: The effects of astrocytes on differentiation of neural stem
cells are influenced by knock-down of the glutamate transporter,
GLT-1. Neurochem Int. 63:498–506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao W, Wang Y, Shi W, et al: The
expression of FBP1 after traumatic brain injury and its role in
astrocyte proliferation. J Mol Neurosci. 51:687–694. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sukumari-Ramesh S, Alleyne CH Jr and
Dhandapani KM: Astrocyte-specific expression of survivin after
intracerebral hemorrhage in mice: a possible role in reactive
gliosis? J Neurotrauma. 29:2798–2804. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hayakawa K, Pham LD, Katusic ZS, Arai K
and Lo EH: Astrocytic high-mobility group box 1 promotes
endothelial progenitor cell-mediated neurovascular remodeling
during stroke recovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:7505–7510.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JB, Lim CM, Yu YM and Lee JK:
Induction and subcellular localization of high-mobility group box-1
(HMGB1) in the postischemic rat brain. J Neurosci Res.
86:1125–1131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayakawa K, Arai K and Lo EH: Role of ERK
map kinase and CRM1 in IL-1β-stimulated release of HMGB1 from
cortical astrocytes. Glia. 58:1007–1015. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sawa H, Ueda T, Takeyama Y, et al:
Blockade of high mobility group box-1 protein attenuates
experimental severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol.
12:7666–7670. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valdes-Ferrer SI, Rosas-Ballina M,
Olofsson PS, et al: High-mobility group box 1 mediates persistent
splenocyte priming in sepsis survivors: evidence from a murine
model. Shock. 40:492–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Achouiti A, van der Meer AJ, Florquin S,
et al: High-mobility group box 1 and the receptor for advanced
glycation end products contribute to lung injury during
Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Crit Care. 17:R2962013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Agnello D, Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ and
Ghezzi P: HMGB-1, a DNA-binding protein with cytokine activity,
induces brain TNF and IL-6 production, and mediates anorexia and
taste aversion. Cytokine. 18:231–236. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu H, Yao YM, Ding LH, et al: High
mobility group box-1 protein acts as a coactivator of nuclear
factor of activated T cells-2 in promoting interleukin-2
transcription. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:641–648. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JB, Sig Choi J, Yu YM, et al: HMGB1, a
novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and
delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J Neurosci.
26:6413–6421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei C, Lin S, Zhang C, et al:
High-mobility group box1 protein promotes neuroinflammation after
intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Neuroscience. 228:190–199. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laird MD, Shields JS, Sukumari-Ramesh S,
et al: High mobility group box protein-1 promotes cerebral edema
after traumatic brain injury via activation of toll-like receptor
4. Glia. 62:26–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SW, Lim CM, Kim JB, et al:
Extracellular HMGB1 released by NMDA treatment confers neuronal
apoptosis via RAGE-p38 MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Neurotox Res.
20:159–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hayakawa K, Nakano T, Irie K, et al:
Inhibition of reactive astrocytes with fluorocitrate retards
neurovascular remodeling and recovery after focal cerebral ischemia
in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hayakawa K, Miyamoto N, Seo JH, et al:
High-mobility group box 1 from reactive astrocytes enhances the
accumulation of endothelial progenitor cells in damaged white
matter. J Neurochem. 125:273–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guazzi S, Strangio A, Franzi AT and
Bianchi ME: HMGB1, an architectural chromatin protein and
extracellular signalling factor, has a spatially and temporally
restricted expression pattern in mouse brain. Gene Expr Patterns.
3:29–33. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhao X, Kuja-Panula J, Rouhiainen A, Chen
YC, Panula P and Rauvala H: High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1;
amphoterin) is required for zebrafish brain development. J Biol
Chem. 286:23200–23213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meneghini V, Bortolotto V, Francese MT, et
al: High-mobility group box-1 protein and β-amyloid oligomers
promote neuronal differentiation of adult hippocampal neural
progenitors via receptor for advanced glycation end
products/nuclear factor-κB axis: relevance for Alzheimer’s disease.
J Neurosci. 33:6047–6059. 2013.
|
|
24
|
Nakagomi T, Taguchi A, Fujimori Y, et al:
Isolation and characterization of neural stem/progenitor cells from
post-stroke cerebral cortex in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 29:1842–1852.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen J, Xie L, Mao X, et al: Neurogenesis
after primary intracerebral hemorrhage in adult human brain. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:1460–1468. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Itoh T, Imano M, Nishida S, et al:
Exercise increases neural stem cell proliferation surrounding the
area of damage following rat traumatic brain injury. J Neural
Transm. 118:193–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Louis SA, Mak CK and Reynolds BA: Methods
to culture, differentiate, and characterize neural stem cells from
the adult and embryonic mouse central nervous system. Methods Mol
Biol. 946:479–506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen J, Guo Y, Cheng W, et al: High
glucose induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation of adult rat
neural stem cells following in vitro ischemia. BMC Neurosci.
14:242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meneghini V, Francese MT, Carraro L and
Grilli M: A novel role for the Receptor for Advanced Glycation
End-products in neural progenitor cells derived from adult
SubVentricular Zone. Mol Cell Neurosci. 45:139–150. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Taguchi A, Blood DC, del Toro G, et al:
Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and
metastases. Nature. 405:354–360. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bao Y, Qin L, Kim E, et al: CD36 is
involved in astrocyte activation and astroglial scar formation. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 32:1567–1577. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jeong SR, Kwon MJ, Lee HG, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor reduces astrocytic scar formation and
promotes axonal growth beyond glial scars after spinal cord injury.
Exp Neurol. 233:312–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kawano H, Kimura-Kuroda J, Komuta Y, et
al: Role of the lesion scar in the response to damage and repair of
the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 349:169–180. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brambilla R, Morton PD, Ashbaugh JJ,
Karmally S, Lambertsen KL and Bethea JR: Astrocytes play a key role
in EAE pathophysiology by orchestrating in the CNS the inflammatory
response of resident and peripheral immune cells and by suppressing
remyelination. Glia. 62:452–467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palumbo R, Sampaolesi M, De Marchis F, et
al: Extracellular HMGB1, a signal of tissue damage, induces
mesoangioblast migration and proliferation. J Cell Biol.
164:441–449. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Limana F, Germani A, Zacheo A, et al:
Exogenous high-mobility group box 1 protein induces myocardial
regeneration after infarction via enhanced cardiac
C-kit+cell proliferation and differentiation. Circ Res.
97:e73–e83. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang X, Fu S, Wang Y, et al:
Interleukin-1β mediates proliferation and differentiation of
multipotent neural precursor cells through the activation of
SAPK/JNK pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci. 36:343–354. 2007.
|
|
38
|
Kim J, Wan CK, S JOC, Shaikh SB and
Nicholson LF: The role of receptor for advanced glycation end
products (RAGE) in neuronal differentiation. J Neurosci Res.
90:1136–1147. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshida H, Mimura J, Imaizumi T, et al:
Edaravone and carnosic acid synergistically enhance the expression
of nerve growth factor in human astrocytes under
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Neurosci Res. 69:291–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koyama Y, Maebara Y, Hayashi M, Nagae R,
Tokuyama S and Michinaga S: Endothelins reciprocally regulate
VEGF-A and angiopoietin-1 production in cultured rat astrocytes:
implications on astrocytic proliferation. Glia. 60:1954–1963. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kuric E, Wieloch T and Ruscher K: Dopamine
receptor activation increases glial cell line-derived neurotrophic
factor in experimental stroke. Exp Neurol. 247:202–208. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Modi KK, Sendtner M and Pahan K:
Up-regulation of ciliary neurotrophic factor in astrocytes by
aspirin: implications for remyelination in multiple sclerosis. J
Biol Chem. 288:18533–18545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tian Y, Liu Y, Chen X, et al: AMN082
promotes the proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor
cells with influence on phosphorylation of MAPK signaling pathways.
Neurochem Int. 57:8–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gage FH and Temple S: Neural stem cells:
generating and regenerating the brain. Neuron. 80:588–601. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|