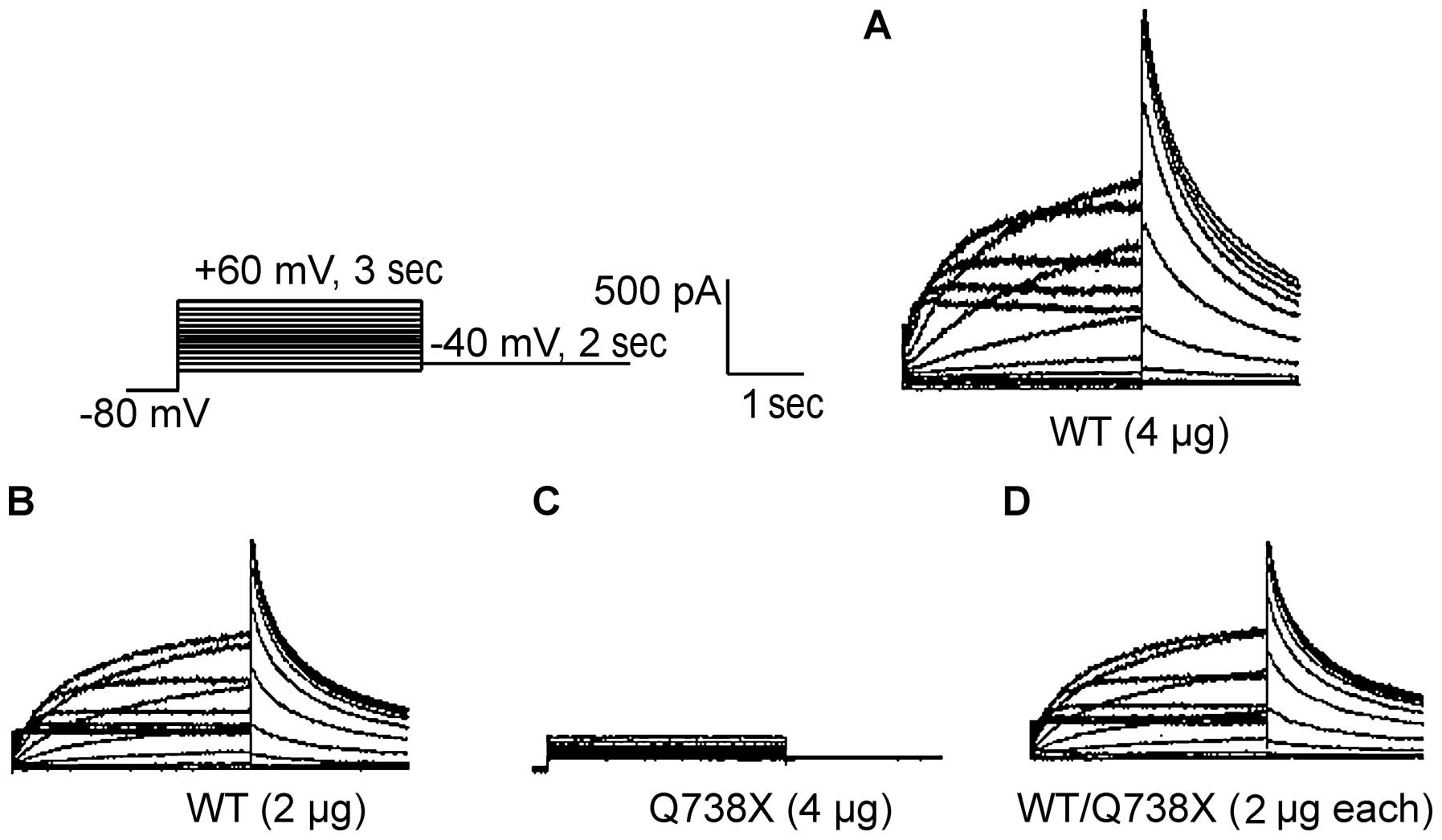
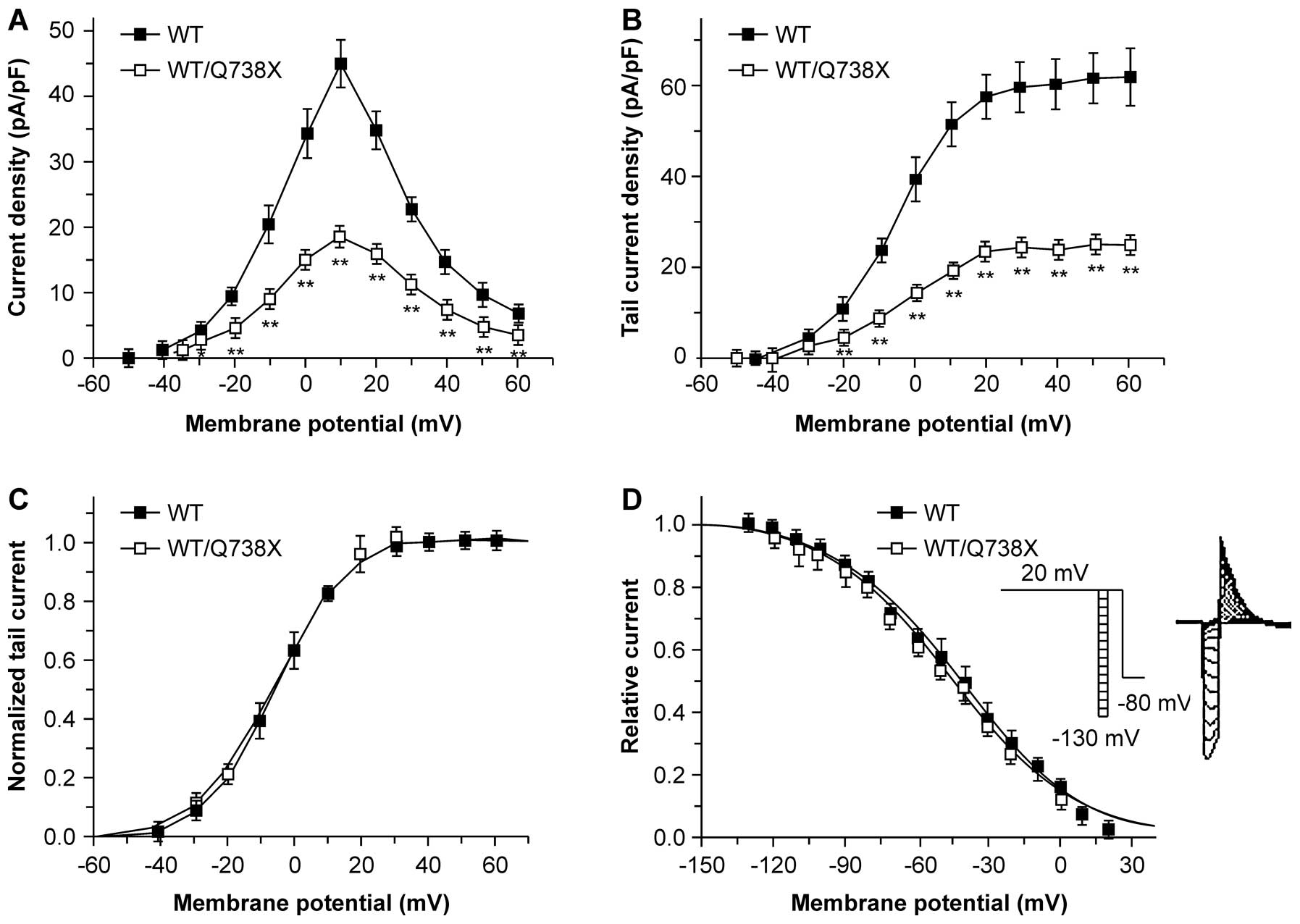
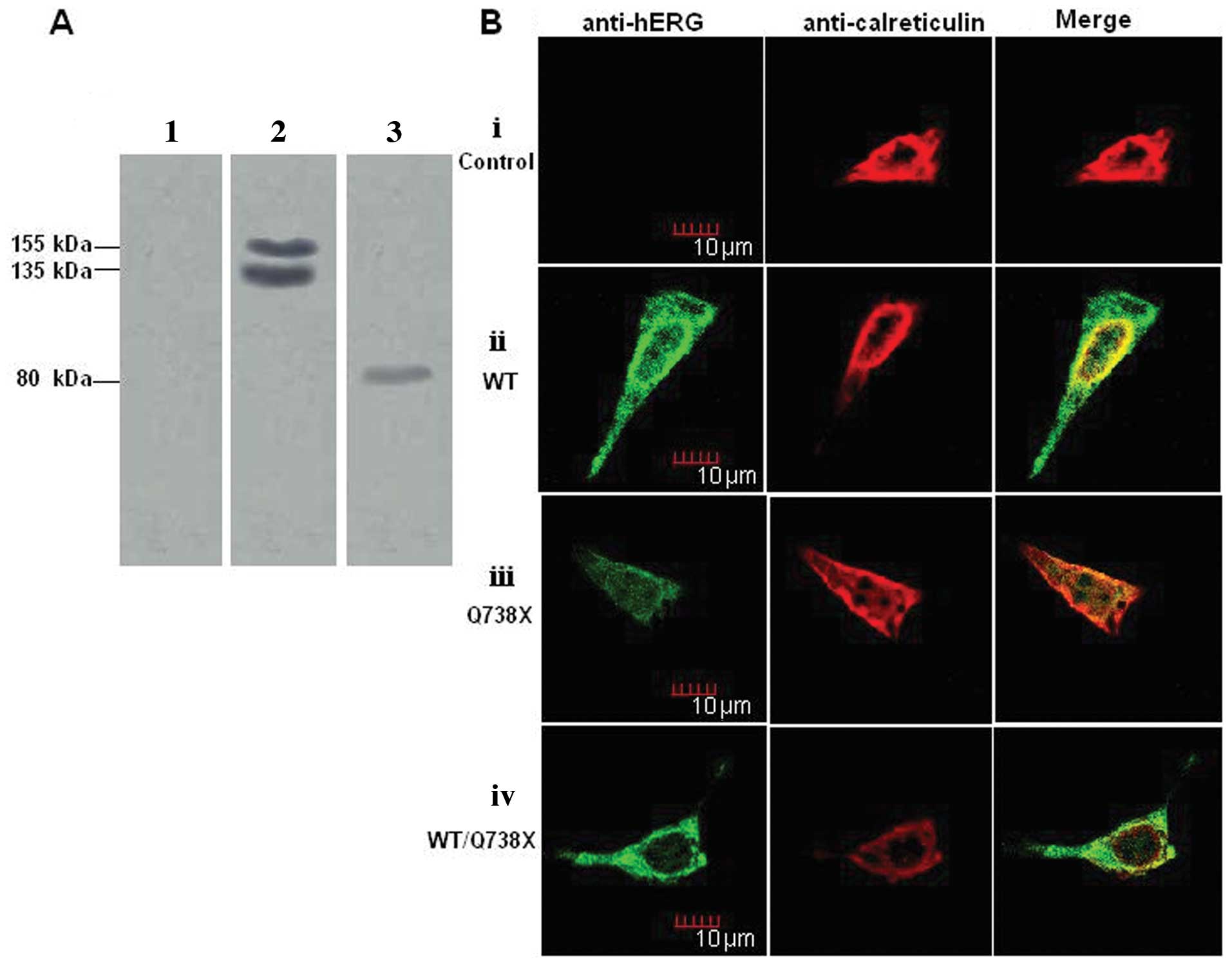
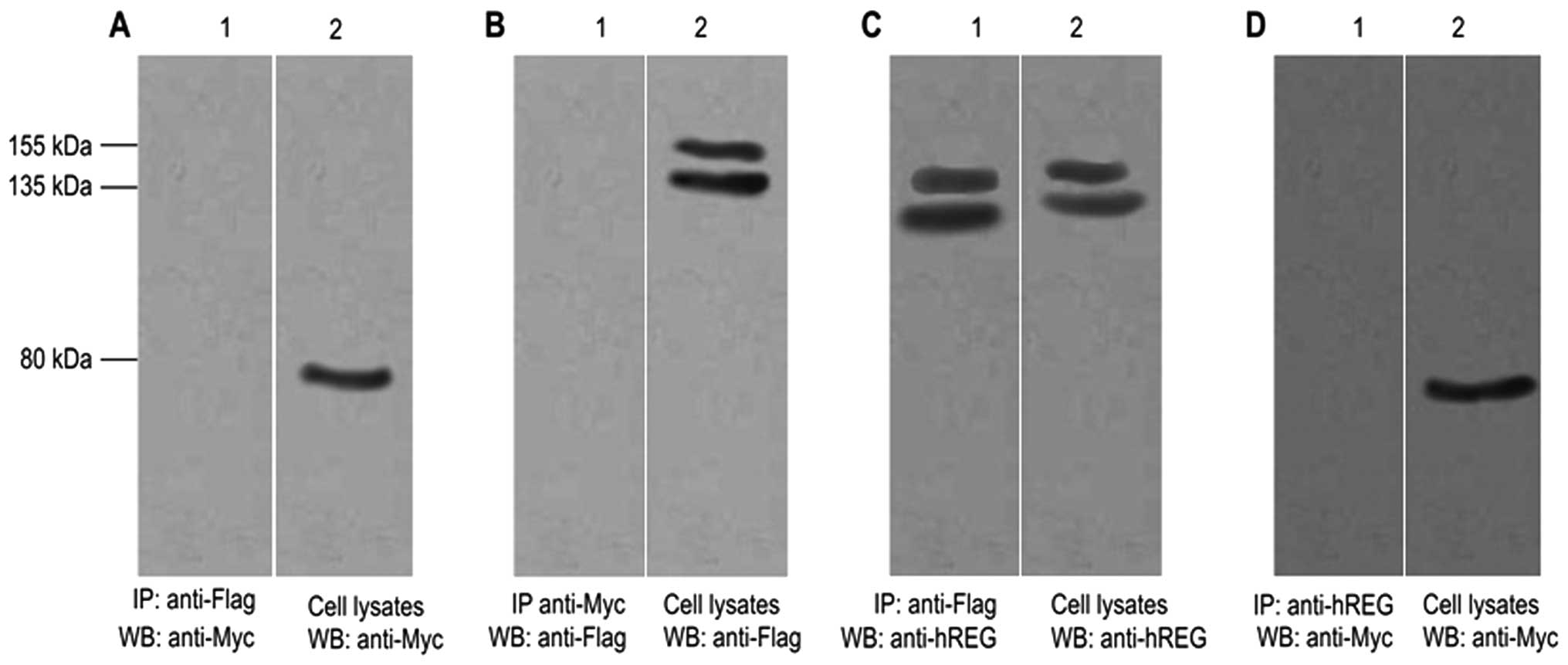
|
1
|
Priori SG, Barhanin J, Hauer RN, Haverkamp
W, Jongsma HJ, Kleber AG, McKenna WJ, Roden DM, Rudy Y, Schwartz K,
Schwartz PJ, Towbin JA and Wilde AM: Genetic and molecular basis of
cardiac arrhythmias: impact on clinical management parts I and II.
Circulation. 99:518–528. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Craft TM: Torsade de pointes after
astemizole overdose. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 292:6601986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mathews DR, McNutt B, Okerholm R, Flicker
M and McBride G: Torsades de pointes occurring in association with
terfenadine use. JAMA. 266:2375–2376. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anderson CL, Delisle BP, Anson BD, Kilby
JA, Will ML, Tester DJ, Gong Q, Zhou Z, Ackerman MJ and January CT:
Most LQT2 mutations reduce Kv11.1 (hERG) current by a class 2
(trafficking-deficient) mechanism. Circulation. 113:365–373. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gong Q, Keeney DR, Robinson JC and Zhou Z:
Defective assembly and trafficking of mutant HERG channels with
C-terminal truncations in long QT syndrome. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
37:1225–1233. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perrin MJ, Subbiah RN, Vandenberg JI and
Hill AP: Human ether-a-go-go related gene (hERG)
K+ channels: function and dysfunction. Prog Biophys Mol
Biol. 98:137–148. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Yasuda S, Hiramatsu S, Odashiro K,
Maruyama T, Tsuji K and Horie M: A family of hereditary long QT
syndrome caused by Q738X HERG mutation. Int J Cardiol. 144:69–72.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo J, Han SN, Liu JX, Zhang XM, Hu ZS,
Shi J, Zhang LR, Zhao ZZ and Zhang Z: The action of a novel
fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent antofloxacin hydrochloride on
human-ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel. Basic
Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 107:643–649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han S, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Duan Y, Zheng T,
Hu X, Zhang Z and Zhang L: Fluconazole inhibits hERG K+
channel by direct block and disruption of protein trafficking. Eur
J Pharmacol. 650:138–144. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takemasa H, Nagatomo T, Abe H, Kawakami K,
Igarashi T, Tsurugi T, Kabashima N, Tamura M, Okazaki M, Delisle
BP, January CT and Otsuji Y: Coexistence of hERG current block and
disruption of protein trafficking in ketoconazole-induced long QT
syndrome. Br J Pharmacol. 153:439–447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paulussen A, Yang P, Pangalos M,
Verhasselt P, Marrannes R, Verfaille C, Vandenberk I, Crabbe R,
Konings F, Luyten W and Armstrong M: Analysis of the human
KCNH2(HERG) gene: identification and characterization of a novel
mutation Y667X associated with long QT syndrome and a
non-pathological 9 bp insertion. Hum Mutat. 15:483–487. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aydar E and Palmer C: Functional
characterization of the C-terminus of the human
ether-a-go-go-related gene K+ channel (HERG). J
Physiol. 534:1–14. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson WH Jr, Yang P, Yang T, Lau YR,
Mostella BA, Wolff DJ, Roden DM and Benson DW: Clinical, genetic,
and biophysical characterization of a homozygous HERG mutation
causing severe neonatal long QT syndrome. Pediatr Res. 53:744–748.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Keating MT and Sanguinetti MC: Molecular
genetic insights into cardiovascular disease. Science. 272:681–685.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tseng GN: IKr: the hERG
channel. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 33:835–849. 2001.
|
|
16
|
Jenke M, Sanchez A, Monje F, Stuhmer W,
Weseloh RM and Pardo LA: C-terminal domains implicated in the
functional surface expression of potassium channels. EMBO J.
22:395–403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ficker E, Thomas D, Viswanathan PC, Dennis
AT, Priori SG, Napolitano C, Memmi M, Wible BA, Kaufman ES, Iyengar
S, Schwartz PJ, Rudy Y and Brown AM: Novel characteristics of a
misprocessed mutant HERG channel linked to hereditary long QT
syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 279:H1748–H1756.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao Y, Teng S, Li N, Zhang Y, Boyden PA
and Pu J: Aminoglycoside antibiotics restore functional expression
of truncated HERG channels produced by nonsense mutations. Heart
Rhythm. 6:553–560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Akhavan A, Atanasiu R, Noguchi T, Han W,
Holder N and Shrier A: Identification of the
cyclic-nucleotide-binding domain as a conserved determinant of
ion-channel cell-surface localization. J Cell Sci. 118:2803–2812.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lees-Miller JP, Duan Y, Teng GQ, Thorstad
K and Duff HJ: Novel gain-of-function mechanism in K+
channel-related long-QT syndrome: altered gating and selectivity in
the HERG1 N629D mutant. Circ Res. 86:507–513. 2000.
|