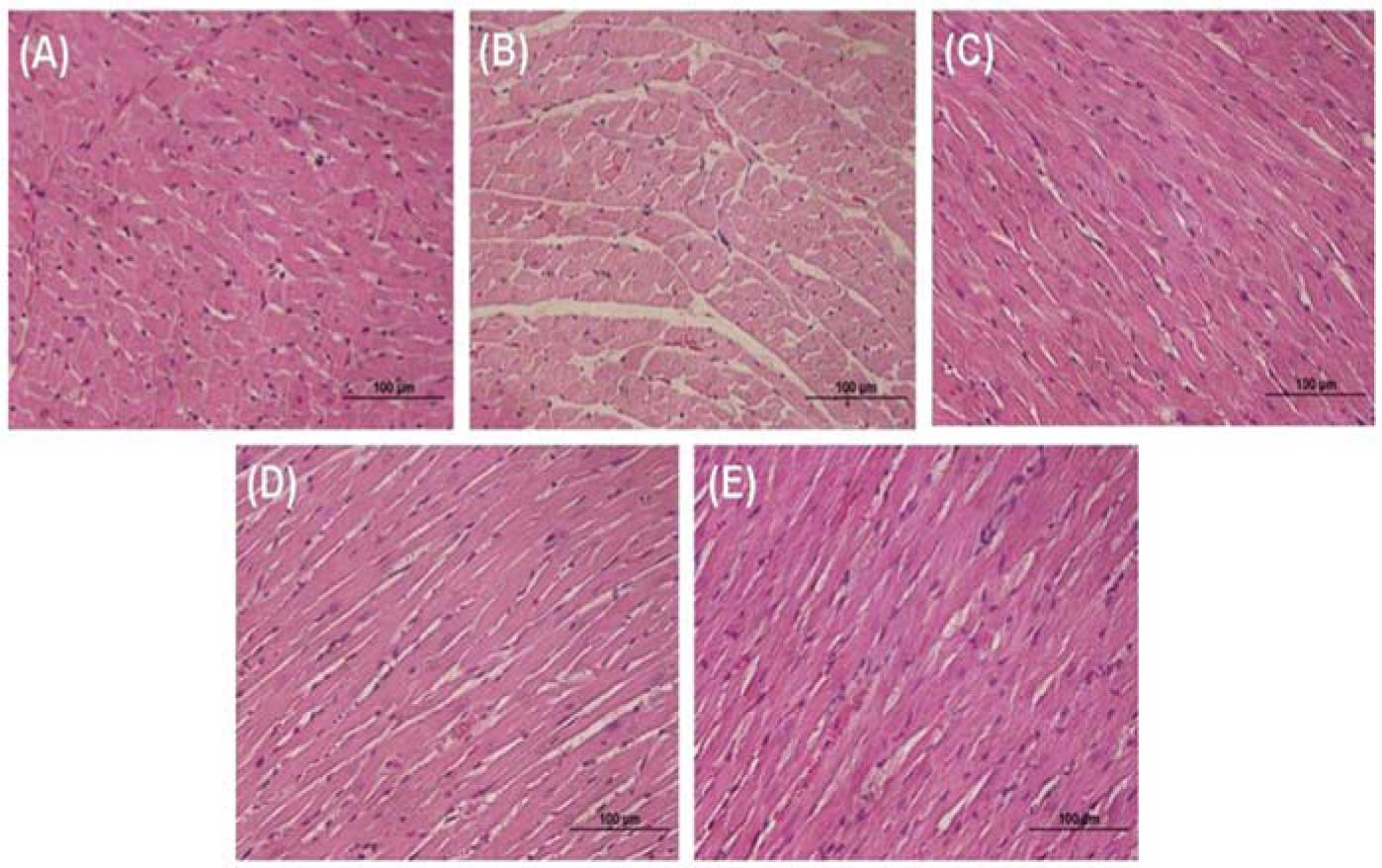
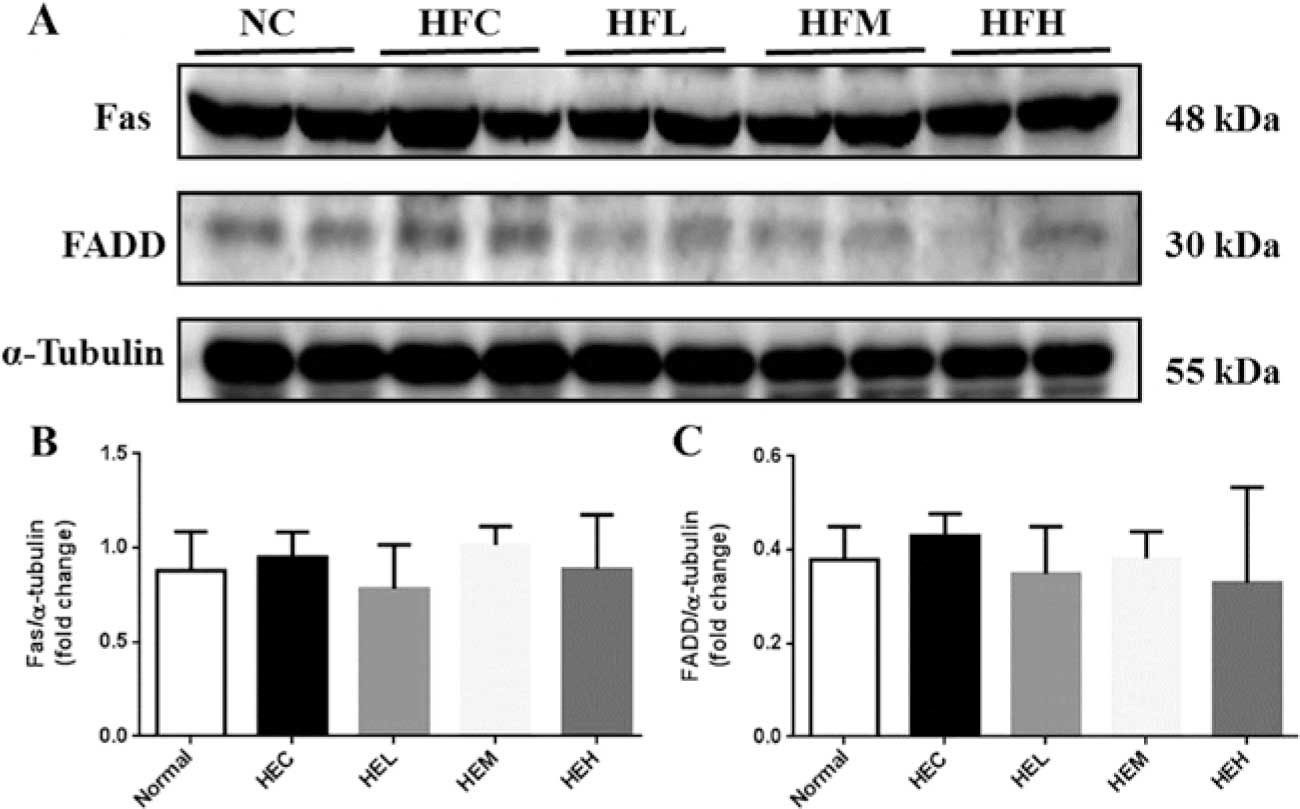
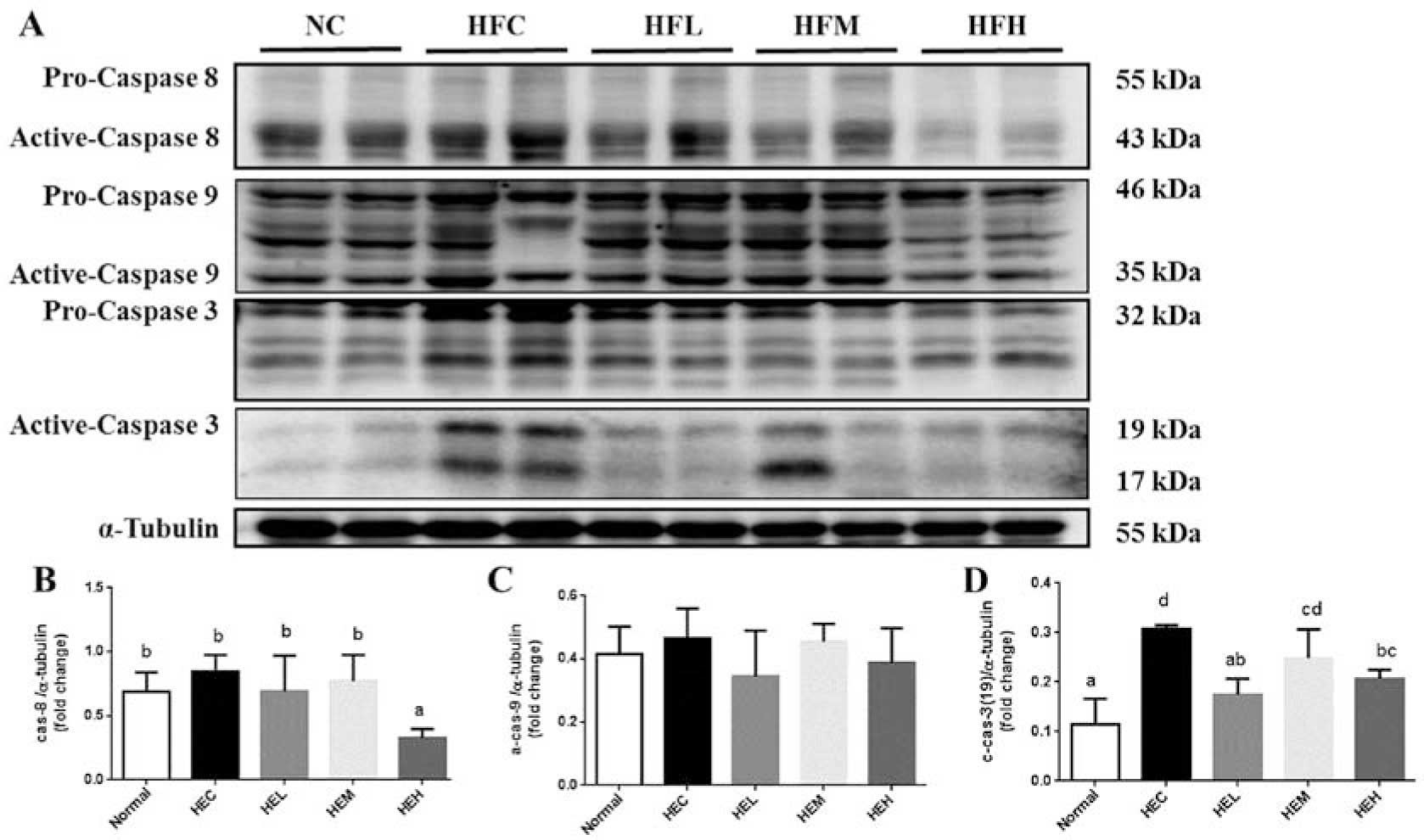
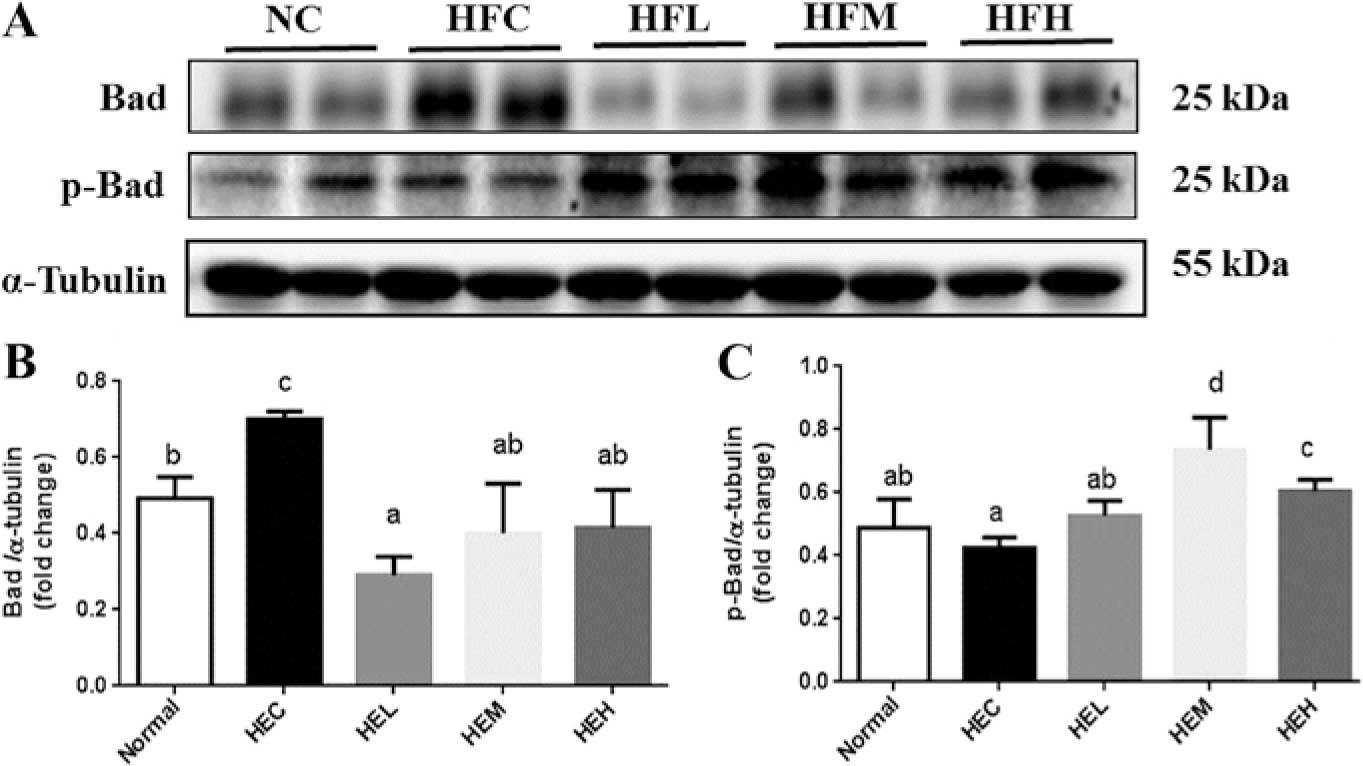
|
1
|
Jang H, Conklin DJ and Kong M: Piecewise
nonlinear mixed-effects models for modeling cardiac function and
assessing treatment effects. Comput Methods Programs Biomed.
110:240–252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Subramanian S, Turner MS, Ding Y,
Goodspeed L, Wang S, Buckner JH, O'Brien K, Getz GS, Reardon CA and
Chait A: Increased levels of invariant natural killer T lymphocytes
worsens metabolic abnormalities and atherosclerosis in obese mice.
J Lipid Res. 54:2831–2841. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Younce CW, Burmeister MA and Ayala JE:
Exendin-4 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of
SERCA2a. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 304:C508–C518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun W, Zhang Z, Chen Q, Yin X, Fu Y, Zheng
Y, Cai L, Kim KS, Kim KH, Tan Y and Kim YH: Magnolia extract
(BL153) protection of heart from lipid accumulation caused cardiac
oxidative damage, inflammation, and cell death in high fat diet fed
mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:2058492014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hua Y, Zhang Y, Dolence J, Shi GP, Ren J
and Nair S: Cathepsin K knockout mitigates high fat diet-induced
cardiac hypertrophy and contractile dysfunction. Diabetes.
62:498–509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Li SY, Liu Y, Sigmon VK, McCort A and Ren
J: High fat diet enhances visceral advanced glycation end products,
nuclear O-Glc-Nac modification, p38 mitogen activated protein
kinase activation and apoptosis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 7:448–454.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barouch LA, Gao D, Chen L, Miller KL, Xu
W, Phan AC, Kittleson MM, Minhas KM, Berkowitz DE, Wei C and Hare
JM: Cardiac myocyte apoptosis is associated with increased DNA
damage and decreased survival in murine models of obesity. Circ
Res. 98:119–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee SD, Chu CH, Huang EJ, Lu MC, Liu JY,
Liu CJ, Hsu HH, Lin JA, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Roles of insulin-like
growth factor II in cardiomyoblast apoptosis and in hypertensive
rat heart with abdominal aorta ligation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 291:E306–E314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haunstetter A and Izumo S: Apoptosis:
basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ
Res. 82:1111–1129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Narula J, Haider N, Arbustini E and
Chandrashekhar Y: Mechanisms of disease: apoptosis in heart
failure-seeing hope in death. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med.
3:681–688. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN
and Walsh K: Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and
protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse heart. Circ.
101:660–667. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Athanasiou A, Clarke AB, Turner AE,
Kumaran NM, Vakilpour S, Smith PA, Bagiokou D, Bradshaw TD,
Westwell AD, Fang L, Lobo DN, Constantinescu CS, Calabrese V,
Loesch A, Alexander SP, Clothier RH, Kendall DA and Bates TE:
Cannabinoid receptor agonists are mitochondrial inhibitors: a
unified hypothesis of how cannabinoids modulate mitochondrial
function and induce cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
364:131–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SD, Tzang BS, Kuo WW, Lin YM, Yang AL,
Chen SH, Tsai FJ, Wu FL, Lu MC and Huang CY: Cardiac fas
receptor-dependent apoptotic pathway in obese Zucker rats. Obesity.
15:2407–2415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu MC, Tzang BS, Kuo WW, Wu FL, Chen YS,
Tsai CH, Huang CY and Lee SD: More activated cardiac
mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway in obese Zucker rats.
Obesity. 15:2634–2642. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bishopric NH, Andreka P, Slepak T and
Webster KA: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in the cardiac
myocyte. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 1:141–150. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ren J, Samson WK and Sowers JR:
Insulin-like growth factor I as a cardiac hormone: physiological
and pathophysiological implications in heart disease. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 31:2049–2061. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vincent AM and Feldman EL: Control of cell
survival by IGF signaling pathways. Growth Horm IGF Res.
12:193–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP,
Ley K, Chin WW and Liao JK: Interaction of oestrogen receptor with
the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature.
407:538–541. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Yuan M, Bradley KM, Dong F,
Anversa P and Ren J: Insulin-like growth factor 1 alleviates high
fat diet-induced myocardial contractile dysfunction: role of
insulin signaling and mitochondrial function. Hypertension.
59:680–693. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang HT, Liu CF, Tsai TH, Chen YL, Chang
HW, Tsai CY, Leu S, Zhen YY, Chai HT, Chung SY, Chua S, Yen CH and
Yip HK: Effect of obesity reduction on preservation of heart
function and attenuation of left ventricular remodeling, oxidative
stress and inflammation in obese mice. J Transl Med. 10:1452012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang Y, Wang X, Wang J, Wu F, Sui Y, Yang
L and Wang Z: Lactobacillus plantarum strains as potential
probiotic cultures with cholesterol-lowering activity. J Dairy Sci.
96:2746–2753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park DY, Ahn YT, Park SH, Huh CS, Yoo SR,
Yu R, Sung MK, McGregor RA and Choi MS: Supplementation of
Lactobacillus curvatus HY7601 and Lactobacillus plantarum KY1032 in
diet-induced obese mice is associated with gut microbial changes
and reduction in obesity. PLoS One. 8:e594702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sanchez M, Darimont C, Drapeau V,
Emady-Azar S, Lepage M, Rezzonico E, Ngom-Bru C, Berger B, Philippe
L, Ammon-Zuffrey C, Leone P, Chevrier G, St-Amand E, Marette A,
Dore J and Tremblay A: Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus
CGMCC1.3724 supplementation on weight loss and maintenance in obese
men and women. Br J Nutr. 111:1507–1519. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Agerholm-Larsen L, Raben A, Haulrik N,
Hansen AS, Manders M and Astrup A: Effect of 8 week intake of
probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular
diseases. Eur J Clin Nutr. 54:288–297. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Azzout-Marniche D, Chaumontet C, Nadkarni
NA, Piedcoq J, Fromentin G, Tome D and Even PC: Food intake and
energy expenditure are increased in high fat-sensitive but not in
high carbohydrate-sensitive obesity prone rats. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Barbo-da-Silva S, Fraulob-Aquino JC, Lopes
JR, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA and Aguila MB: Weight cycling enhances
adipose tissue inflammatory responses in male mice. PLoS One.
7:e398372012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Park JE, Oh SH and Cha YS: Lactobacillus
plantarum LG42 isolated from gajami sik-hae decreases body and fat
pad weights in diet-induced obese mice. J Appl Microbiol.
116:145–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fåk F1 and Bäckhed F: Lactobacillus
reuteri prevents diet-induced obesity, but not atherosclerosis, in
a strain dependent fashion in Apoe−/− mice. PLoS One.
7:e468372012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jung SP, Lee KM, Kang JH, Yun SI, Park HO,
Moon Y and Kim JY: Effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 on
overweight and obese adults: A randomized, double-blind clinical
trial. Korean J Fam Med. 34:80–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanida M, Imanishi K, Akashi H, Kurata Y,
Chonan O, Naito E, Kunihiro S, Kawai M, Kato-Kataoka A and
Shibamoto T: Injection of Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota
affects autonomic nerve activities in a tissue-specific manner, and
regulates glucose and lipid metabolism in rats. J Diabetes
Investig. 5:153–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fortuno MA, Ravassa S, Fortuno A, Zalba G
and Diez J: Cardiomyocyte apoptotic cell death in arterial
hypertension: mechanisms and potential management. Hypertension.
38:1406–1412. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McGowan BS, Ciccimaro EF, Chan TO and
Feldman AM: The balance between proapoptotic and anti-apoptotic
pathways in the failing myocardium. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 3:191–206.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Brown GC and Borutaite V: Nitric oxide,
cytochrome c and mitochondria. Biochem Soc Symp. 66:17–25.
1999.
|
|
34
|
Torella D, Rota M, Nurzynska D, Musso E,
Monsen A, Shiraishi I, Zias E, Walsh K, Rosenzweig A, Sussman MA,
Urbanek K, Nadal-Ginard B, Kajstura J, Anversa P and Leri A:
Cardiac stem cell and myocyte aging, heart failure, and
insulin-like growth factor-1 overexpression. Circ Res. 94:514–524.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Palmen M, Daemen MJ, Bronsaer R, Dassen
WR, Zandbergen HR, Kockx M, Smits JF, van der Zee R and Doevendans
PA: Cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction is impaired in
IGF-1 deficient mice. Circ Res. 50:516–524. 2001.
|
|
36
|
Wellen KE and Hotamisligil GS:
Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 115:1111–1119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Heilbronn LK and Campbell LV: Adipose
tissue macrophages, low grade inflammation and insulin resistance
in human obesity. Curr Pharm Design. 14:1225–1230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu S, Zhi H, Hou X, Cohen RA and Jiang B:
IкBβ attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular inflammation
and fibrosis in mice. Hypertension. 58:310–316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li JJ and Chen JL: Inflammation may be a
bridge connecting hypertension and atherosclerosis. Med Hypotheses.
64:925–929. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA,
Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S, Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley
RE and Gewirtz AT: Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in
mice lacking toll-like receptor 5. Science. 328:228–231. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ebel B, Lemetais G, Beney L, Cachon R,
Sokol H, Langella P and Gervais P: Impact of probiotics on risk
factors for cardiovascular diseases. A review. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 54:175–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Toral M, Gomez-Guzman M, Jimenez R, Romero
M, Sanchez M, Utrilla MP, Garrido-Mesa N, Rodriguez-Cabezas ME,
Olivares M, Galvez J and Duarte J: The probiotic Lactobacillus
coryniformis CECT5711 reduces the vascular pro-oxidant and
pro-inflammatory status in obese mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 127:33–45.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sobol KV, Belostotskaya GB and Nesterov
VP: The effect of probiotics and their metabolic products on
cardiovascular system cells in vitro. Dokl Biol Sci. 436:9–12.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin PP, Hsieh YM, Kuo WW, Lin YM, Yeh YL,
Lin CC, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Huang CY and Tsai CC: Probiotic-fermented
purple sweet potato yogurt activates compensatory IGF-IR/PI3K/Akt
survival pathways and attenuates cardiac apoptosis in the hearts of
spontaneously hypertensive rat. Int J Mol Med. 32:1319–1328.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|