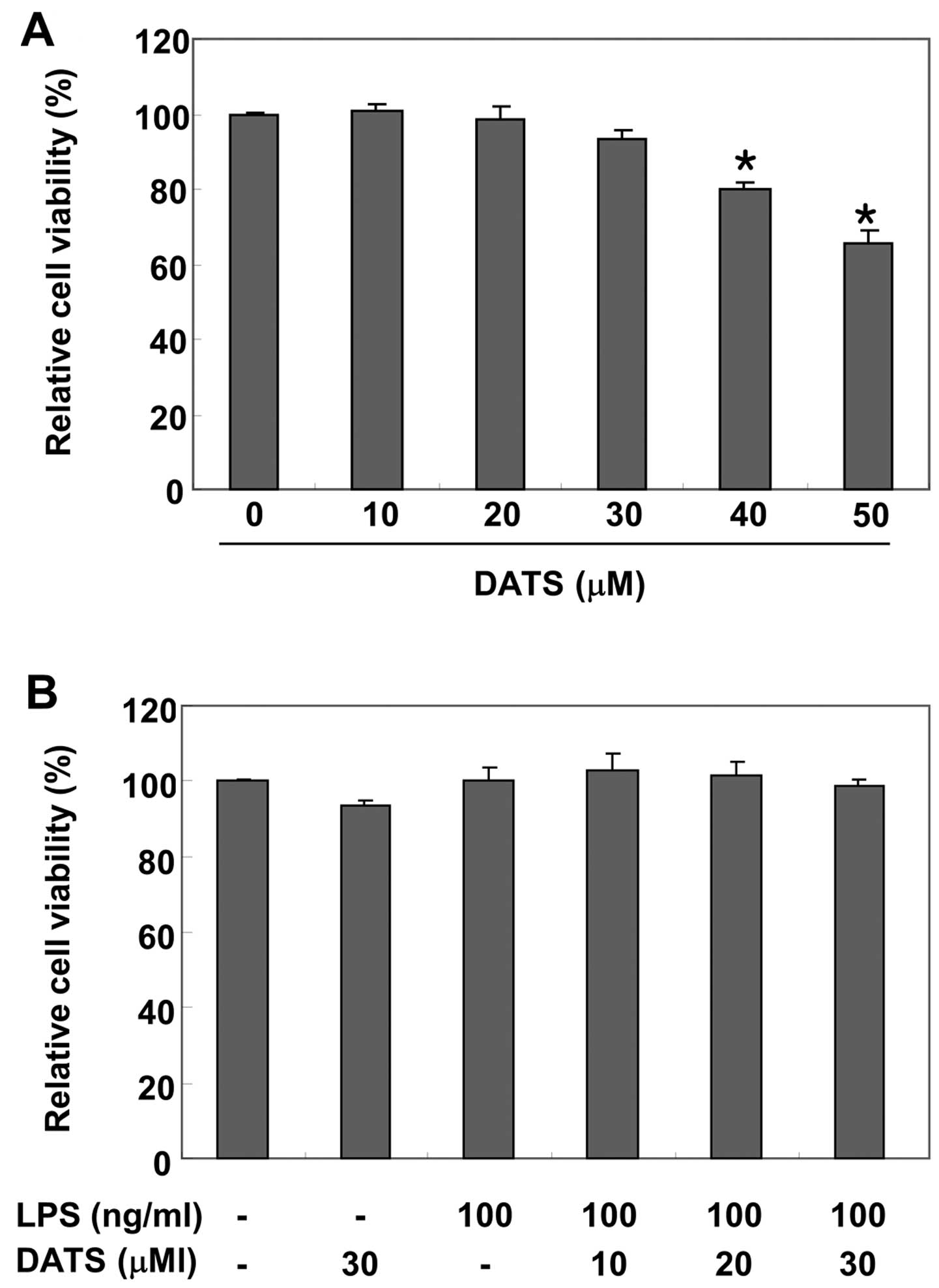
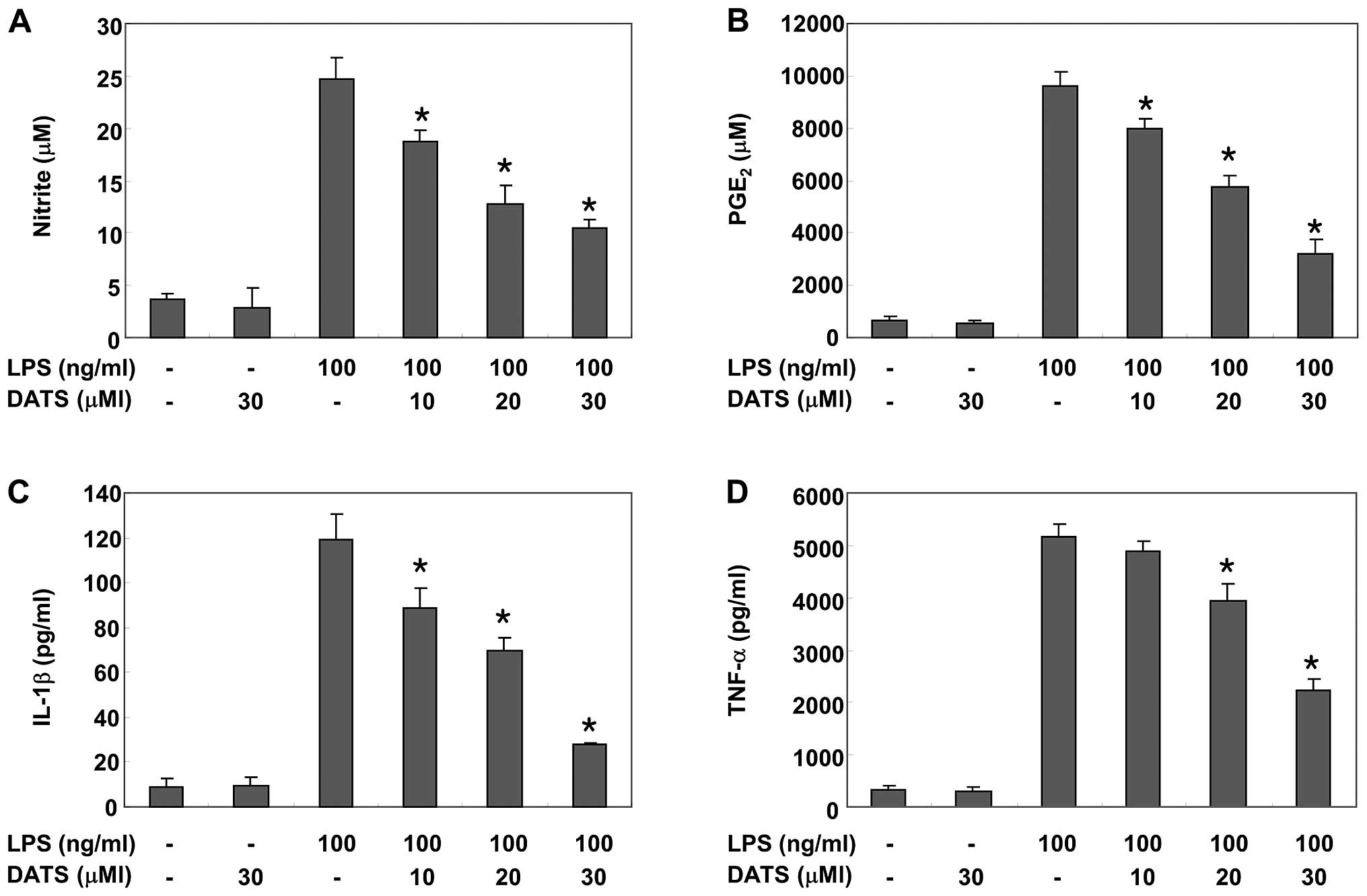
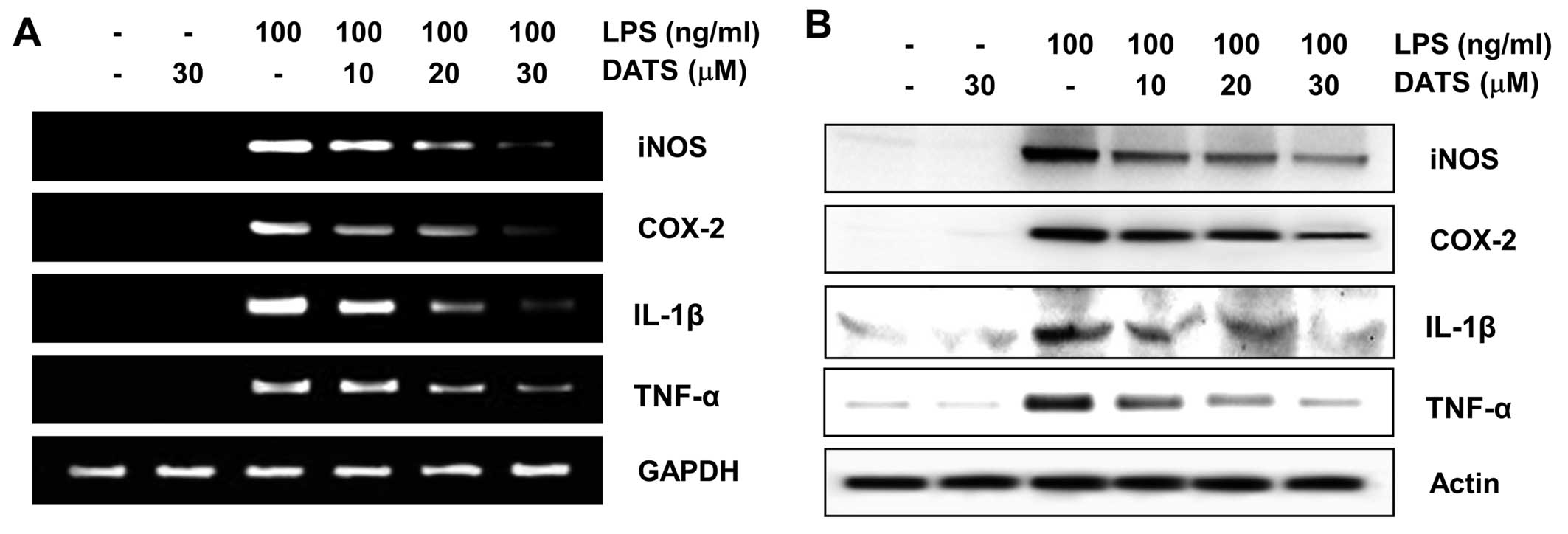
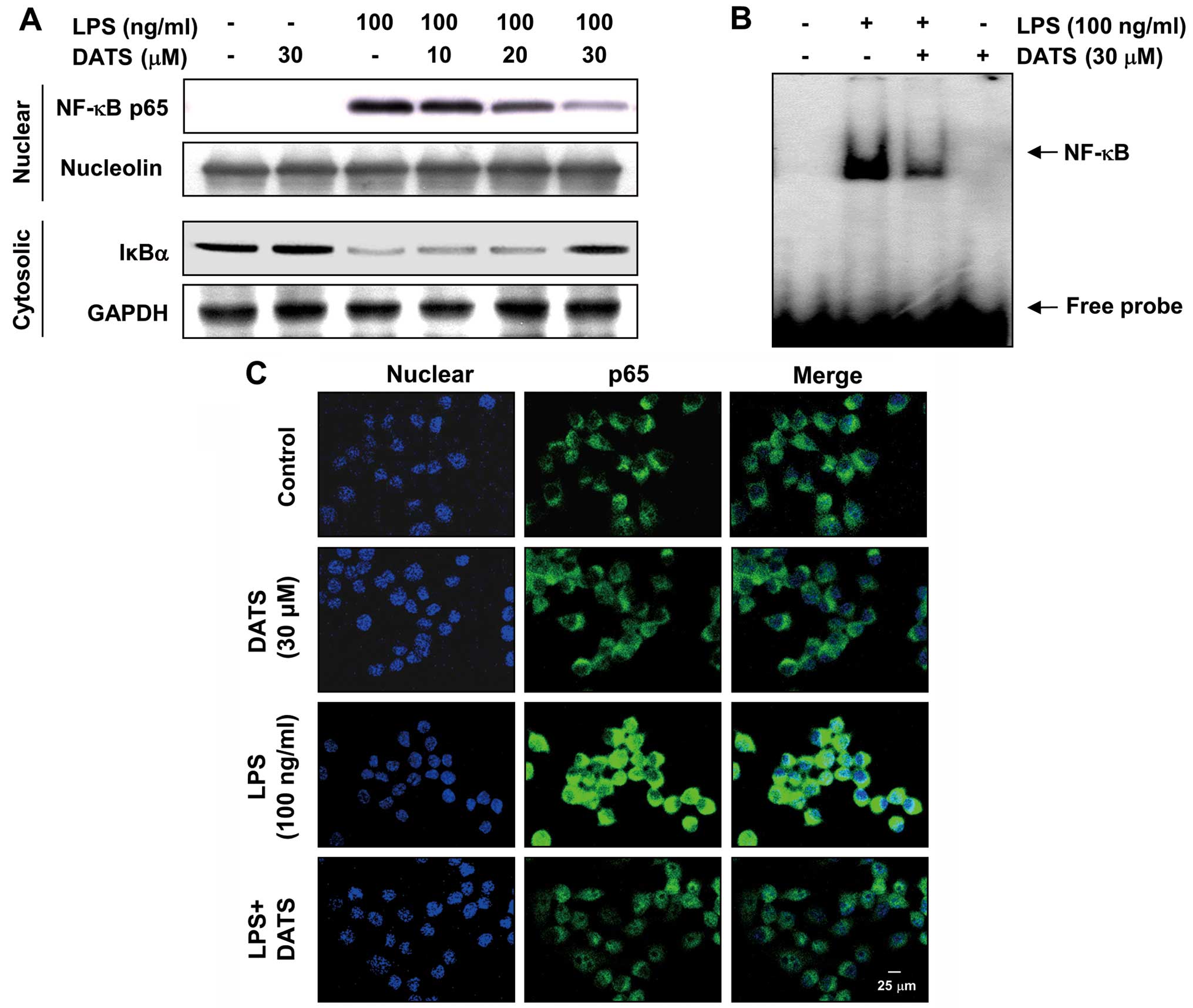
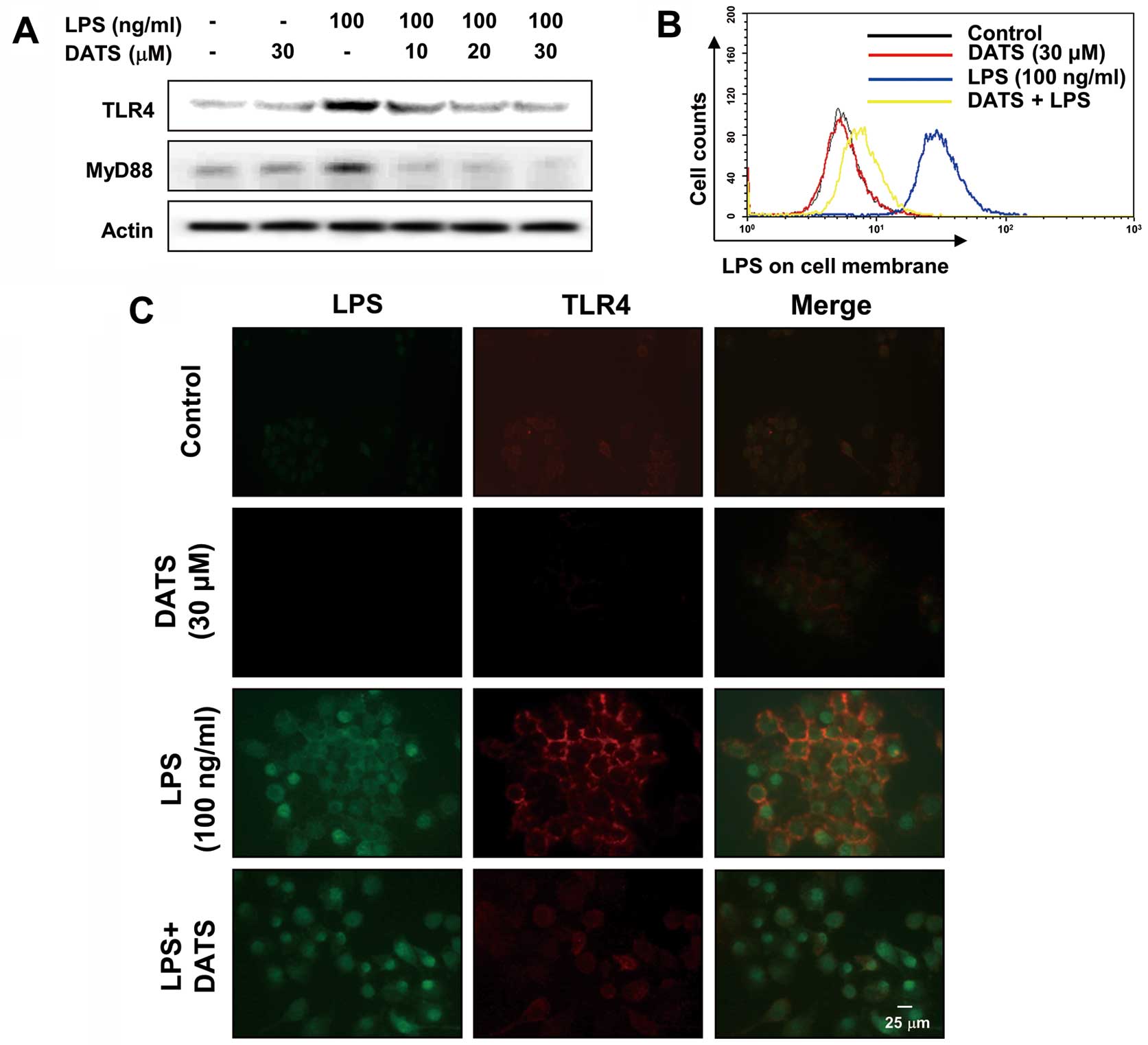
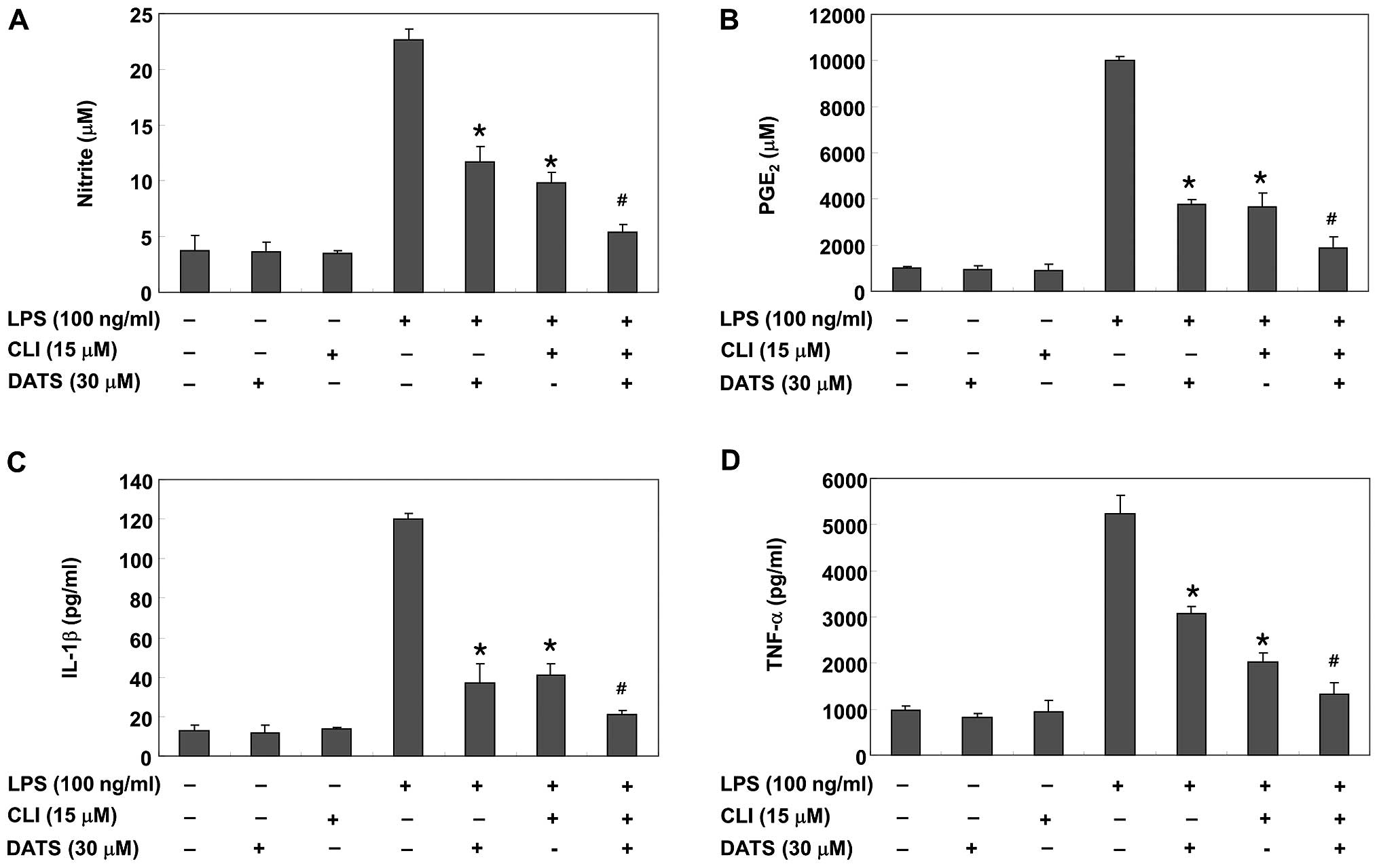
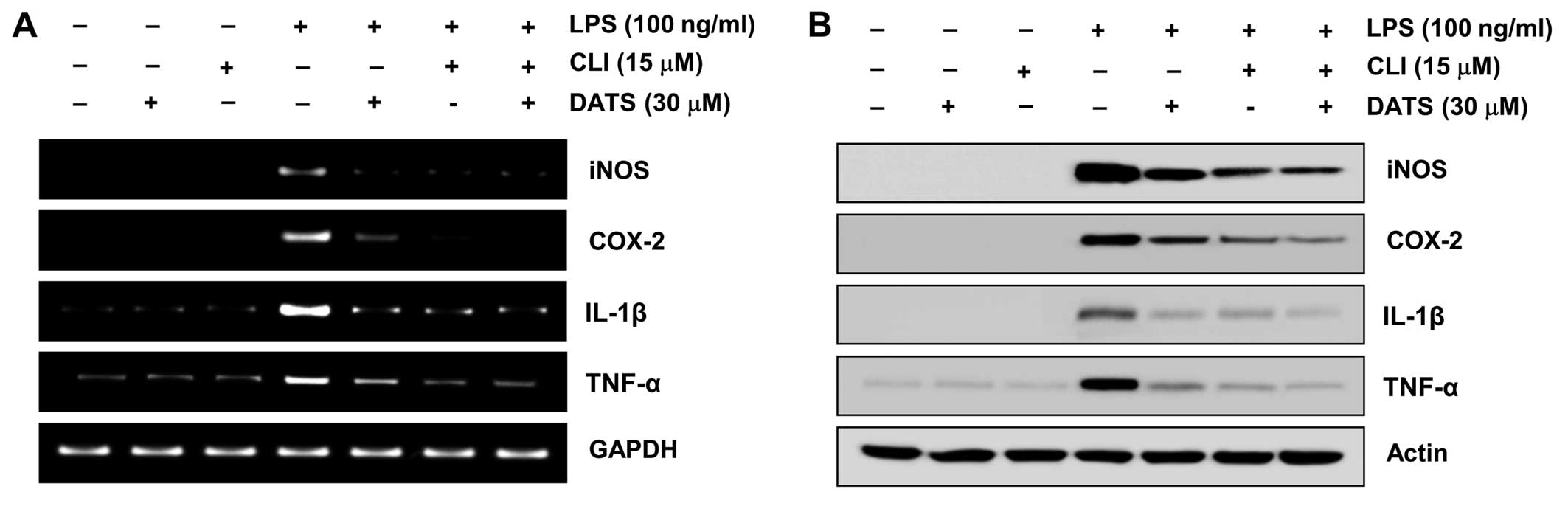
|
1
|
Lind L: Circulating markers of
inflammation and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 169:203–214.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bertolini A, Ottani A and Sandrini M: Dual
acting anti-inflammatory drugs: a reappraisal. Pharmacol Res.
44:437–450. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanno S, Shouji A, Tomizawa A, Hiura T,
Osanai Y, Ujibe M, Obara Y, Nakahata N and Ishikawa M: Inhibitory
effect of naringin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxin
shock in mice and nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Life Sci. 78:673–681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van
Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C,
Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B and Beutler B:
Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations
in Tlr4 gene. Science. 282:2085–2088. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Microbial
recognition by Toll-like receptors. J Dermatol Sci. 34:73–82. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shuto T, Kato K, Mori Y, Viriyakosol S,
Oba M, Furuta T, Okiyoneda T, Arima H, Suico MA and Kai H:
Membrane-anchored CD14 is required for LPS-induced TLR4 endocytosis
in TLR4/MD-2/CD14 overexpressing CHO cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 338:1402–1409. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chan ED and Riches DW: IFN-gamma + LPS
induction of iNOS is modulated by ERK, JNK/SAPK, and p38(mapk) in a
mouse macrophage cell line. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
280:C441–C450. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hattori Y, Hattori S and Kasai K:
Lipopolysaccharide activates Akt in vascular smooth muscle cells
resulting in induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase through
nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 481:153–158.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anwar MA, Basith S and Choi S: Negative
regulatory approaches to the attenuation of Toll-like receptor
signaling. Exp Mol Med. 45:e112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Datla P, Kalluri MD, Basha K, Bellary A,
Kshirsagar R, Kanekar Y, Upadhyay S, Singh S and Rajagopal V:
9,10-dihydro-2,5-dime-thoxyphenanthrene-1,7-diol, from Eulophia
ochreata, inhibits inflammatory signalling mediated by Toll-like
receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 160:1158–1170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tattelman E: Health effects of garlic. Am
Fam Physician. 72:103–106. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moyad MA: Bladder cancer recurrence: Part
II. What do I tell my patients about lifestyle changes and dietary
supplements? Curr Opin Urol. 13:379–383. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yi L and Su Q: Molecular mechanisms for
the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol.
57:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Padiya R and Banerjee SK: Garlic as an
anti-diabetic agent: recent progress and patent reviews. Recent Pat
Food Nutr Agric. 5:105–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Capasso A: Antioxidant action and
therapeutic efficacy of Allium sativum L. Molecules. 18:690–700.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iciek M, Kwiecień I and Włodek L:
Biological properties of garlic and garlic-derived organosulfur
compounds. Environ Mol Mutagen. 50:247–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lea MA: Organosulfur compounds and cancer.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 401:147–154. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Amagase H, Petesch BL, Matsuura H, Kasuga
S and Itakura Y: Intake of garlic and its bioactive components. J
Nutr. 131:955S–962S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen C, Pung D, Leong V, Hebbar V, Shen G,
Nair S, Li W and Kong AN: Induction of detoxifying enzymes by
garlic organosulfur compounds through transcription factor Nrf2:
effect of chemical structure and stress signals. Free Radic Biol
Med. 37:1578–1590. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukao T, Hosono T, Misawa S, Seki T and
Ariga T: The effects of allyl sulfides on the induction of phase II
detoxification enzymes and liver injury by carbon tetrachloride.
Food Chem Toxicol. 42:743–749. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu KL, Chen HW, Wang RY, Lei YP, Sheen LY
and Lii CK: DATS reduces LPS-induced iNOS expression, NO
production, oxidative stress, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7
macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 54:3472–3478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Na HK, Kim EH, Choi MA, Park JM, Kim DH
and Surh YJ: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells through ROS-mediated activation of JNK and AP-1.
Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1241–1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
You S, Nakanishi E, Kuwata H, Chen J,
Nakasone Y, He X, Liu X, Zhang S, Zhang B and Hou DX: Inhibitory
effects and molecular mechanisms of garlic organosulfur compounds
on the production of inflammatory mediators. Mol Nutr Food Res.
57:2049–2060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kyung J, Kim D, Park D, Yang YH, Choi EK,
Lee SP, Kim TS, Lee YB and Kim YB: Synergistic anti-inflammatory
effects of Laminaria japonica fucoidan and Cistanche tubulosa
extract. Lab Anim Res. 28:91–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SH, Kim DW, Eom SA, Jun SY, Park M,
Kim DS, Kwon HJ, Kwon HY, Han KH, Park J, Hwang HS, Eum WS and Choi
SY: Suppression of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
(TPA)-induced skin inflammation in mice by transduced Tat-Annexin
protein. BMB Rep. 45:354–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Joh EH and Kim DH: Lancemaside A inhibits
lipopolysac-charide-induced inflammation by targeting LPS/TLR4
complex. J Cell Biochem. 111:865–871. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aggarwal BB and Natarajan K: Tumor
necrosis factors: developments during the last decade. Eur Cytokine
Netw. 7:93–124. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brennan FM and McInnes IB: Evidence that
cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest.
118:3537–3545. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blatteis CM, Li S, Li Z, Perlik V and
Feleder C: Signaling the brain in systemic inflammation: the role
of complement. Front Biosci. 9:915–931. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai AP, Ouyang Q and Hu RW: Diallyl
trisulfide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in
inflammed mucosa of ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 50:1426–1431.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee HJ, Lee HG, Choi KS, Surh YJ and Na
HK: Diallyl trisulfide suppresses dextran sodium sulfate-induced
mouse colitis: NF-κB and STAT3 as potential targets. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 437:267–273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuo WW, Wang WJ, Tsai CY, Way CL, Hsu HH
and Chen LM: Diallyl trisufide (DATS) suppresses high
glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting JNK/NFκB
signaling via attenuating ROS generation. Int J Cardiol.
168:270–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Yang JS, Ma CY, Lu
HF, Tang NY, Hsia TC, Ho HC and Chung JG: Diallyl sulfide, diallyl
disulfide, and diallyl trisulfide inhibit migration and invasion in
human colon cancer colo 205 cells through the inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-2, -7, and -9 expressions. Environ Toxicol.
28:479–488. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Akira S and Takeda K: Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:499–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie
AG, Jefferies CA, Mansell AS, Brady G, Brint E, Dunne A, Gray P,
Harte MT, McMurray D, Smith DE, Sims JE, Bird TA and O’Neill LA:
Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4
signal transduction. Nature. 413:78–83. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jawan B, Kao YH, Goto S, Pan MC, Lin YC,
Hsu LW, Nakano T, Lai CY, Sun CK, Cheng YF, Tai MH, Eng HL, Wang
CS, Huang CJ, Lin CR and Chen CL: Propofol pretreatment attenuates
LPS-induced granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
production in cultured hepatocytes by suppressing MAPK/ERK activity
and NF-kappaB translocation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 229:362–373.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jung JS, Shin KO, Lee YM, Shin JA, Park
EM, Jeong J, Kim DH, Choi JW and Kim HS: Anti-inflammatory
mechanism of exogenous C2 ceramide in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
microglia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1016–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee JY, Ye J, Gao Z, Youn HS, Lee WH, Zhao
L, Sizemore N and Hwang DH: Reciprocal modulation of Toll-like
receptor-4 signaling pathways involving MyD88 and
phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase/AKT by saturated and polyunsaturated
fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 278:37041–37051. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Islam MA, Cinar MU, Uddin MJ, Tholen E,
Tesfaye D, Looft C and Schellander K: Expression of Toll-like
receptors and downstream genes in lipopolysaccharide-induced
porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 146:62–73.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cario E and Podolsky DK: Differential
alteration in intestinal epithelial cell expression of toll-like
receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4 in inflammatory bowel disease. Infect
Immun. 68:7010–7017. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ii M, Matsunaga N, Hazeki K, Nakamura K,
Takashima K, Seya T, Hazeki O, Kitazaki T and Iizawa Y: A novel
cyclohexene derivative, ethyl
(6R)-6-[N-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)sulfamoyl]
cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate (TAK-242), selectively inhibits
toll-like receptor 4-mediated cytokine production through
suppression of intracellular signaling. Mol Pharmacol.
69:1288–1295. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Takashima K, Matsunaga N, Yoshimatsu M,
Hazeki K, Kaisho T, Uekata M, Hazeki O, Akira S, Iizawa Y and Ii M:
Analysis of binding site for the novel small-molecule TLR4 signal
transduction inhibitor TAK-242 and its therapeutic effect on mouse
sepsis model. Br J Pharmacol. 157:1250–1262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|