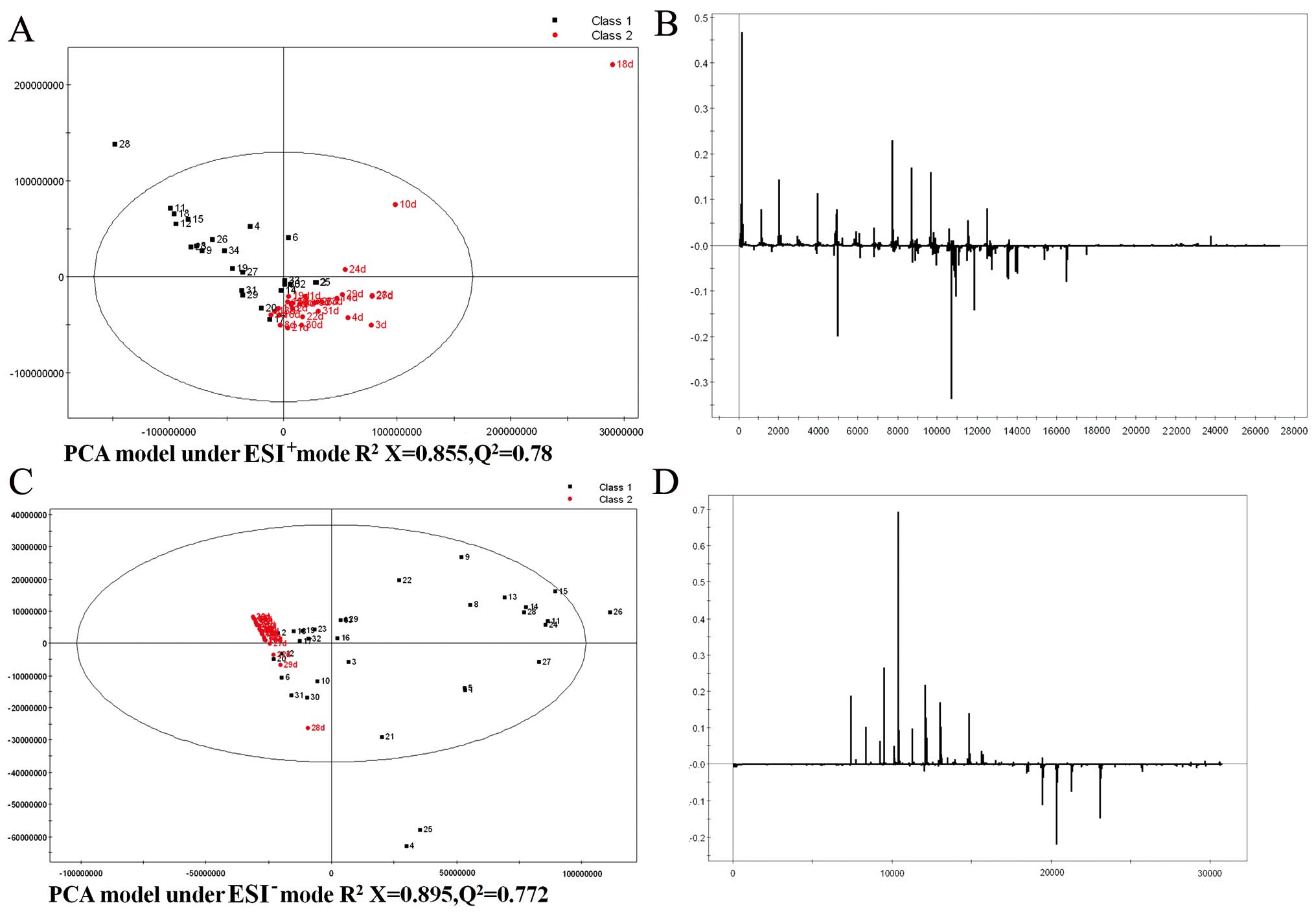
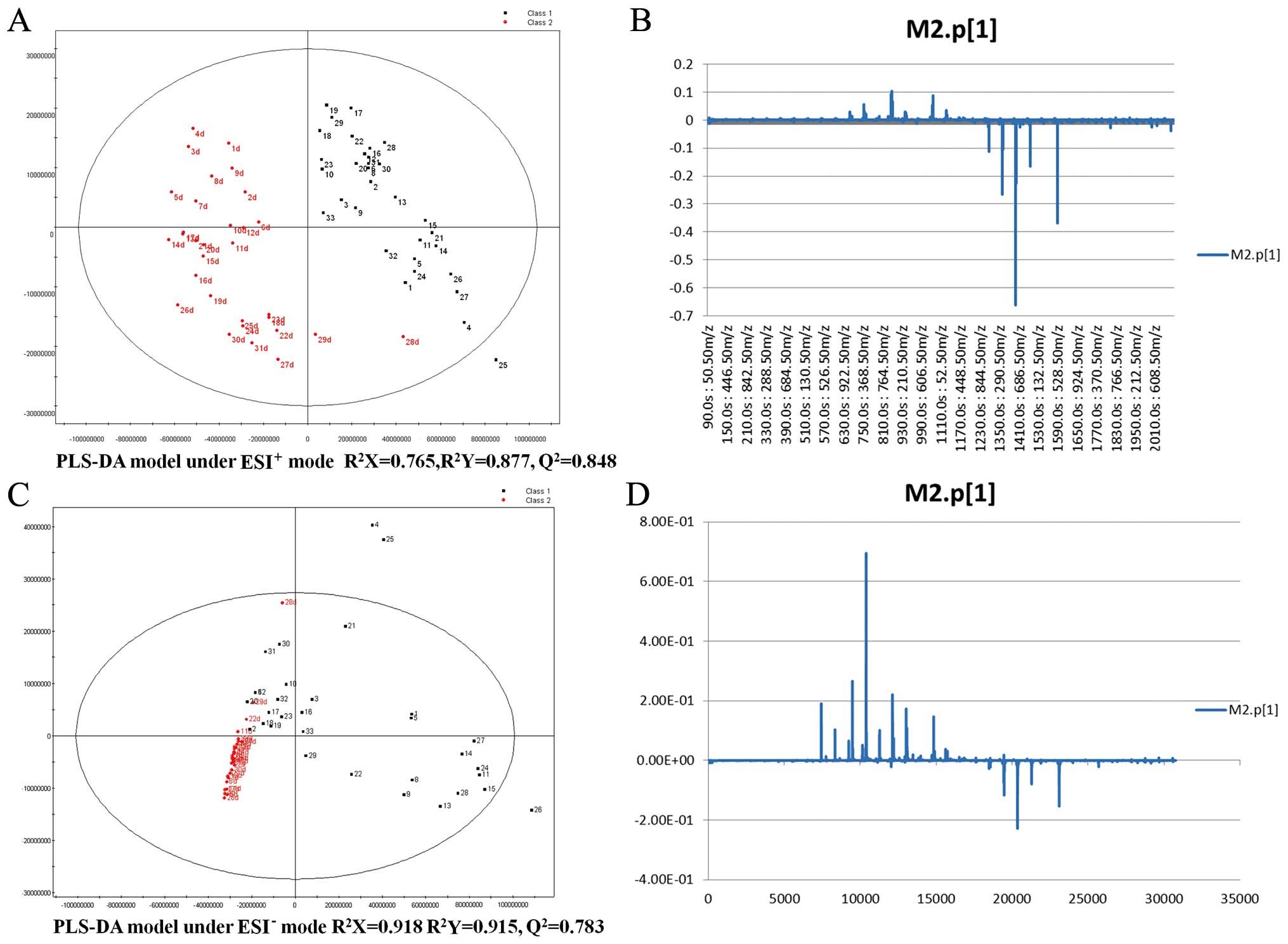
|
1
|
Kaplan MM and Gershwin ME: Primary biliary
cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 353:1261–1273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prince M, Chetwynd A, Newman W, Metcalf JV
and James OF: Survival and symptom progression in a geographically
based cohort of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: Follow-up
for up to 28 years. Gastroenterology. 123:1044–1051. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim WR, Lindor KD, Locke GR III, Therneau
TM, Homburger HA, Batts KP, Yawn BP, Petz JL, Melton LJ III and
Dickson ER: Epidemiology and natural history of primary biliary
cirrhosis in a US community. Gastroenterology. 119:1631–1636. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Zuin M, Podda M and
Gershwin ME: Genetics and geoepidemiology of primary biliary
cirrhosis: Following the footprints to disease etiology. Semin
Liver Dis. 25:265–280. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He XS, Ansari AA, Ridgway WM, Coppel RL
and Gershwin ME: New insights to the immunopathology and autoimmune
responses in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cell Immunol. 239:1–13.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu C, Deng C, Song G, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li
X, Li P, Zhang F and Li Y: Prevalence of autoimmune liver disease
related autoantibodies in Chinese patients with primary biliary
cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 56:3357–3363. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bogdanov M, Matson WR, Wang L, Matson T,
Saunders-Pullman R, Bressman SS and Flint Beal M: Metabolomic
profiling to develop blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease.
Brain. 131:389–396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, et
al: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in
prostate cancer progression. Nature. 457:910–914. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Kong H, Guan Y, Yang J, Gu J, Yang
S and Xu G: Plasma phospholipid metabolic profiling and biomarkers
of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on high-performance liquid
chromatography/electrospray mass spectrometry and multivariate
statistical analysis. Anal Chem. 77:4108–4116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sabatine MS, Liu E, Morrow DA, Heller E,
McCarroll R, Wiegand R, Berriz GF, Roth FP and Gerszten RE:
Metabolomic identification of novel biomarkers of myocardial
ischemia. Circulation. 112:3868–3875. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heazell AE, Brown M, Worton SA and Dunn
WB: Review: The effects of oxygen on normal and preeclamptic
placental tissue -insights from metabolomics. Placenta. 32(Suppl
2): S119–S124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Barr J, Caballería J, Martínez-Arranz I,
et al: Obesity-dependent metabolic signatures associated with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression. J Proteome Res.
11:2521–2532. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kalhan SC, Guo L, Edmison J, Dasarathy S,
McCullough AJ, Hanson RW and Milburn M: Plasma metabolomic profile
in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 60:404–413. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Puri P, Wiest MM, Cheung O, et al: The
plasma lipidomic signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Hepatology. 50:1827–1838. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tokushige K, Hashimoto E, Kodama K, et al:
Serum metabolomic profile and potential biomarkers for severity of
fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol.
48:1392–1400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trottier J, Białek A, Caron P, Straka RJ,
Heathcote J, Milkiewicz P and Barbier O: Metabolomic profiling of
17 bile acids in serum from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis
and primary sclerosing cholangitis: A pilot study. Dig Liver Dis.
44:303–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Heathcote EJ: Management of primary
biliary cirrhosis. The American Association for the Study of Liver
Diseases practice guidelines. Hepatology. 31:1005–1013. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin P, Zhao X, Li Q, Wang J, Li J and Xu
G: Metabonomics study of intestinal fistulas based on
ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-TOF mass
spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF MS). J Proteome Res. 5:2135–2143. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
User’s Guide to SIMCA-P, SIMCA-P version
11.0. Umetrics AB; Umeå, Sweden: pp. 3972005
|
|
20
|
Ramm GA, Shepherd RW, Hoskins AC, et al:
Fibrogenesis in pediatric cholestatic liver disease: Role of
taurocholate and hepatocyte-derived monocyte chemotaxis protein-1
in hepatic stellate cell recruitment. Hepatology. 49:533–544. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Allen K, Jaeschke H and Copple BL: Bile
acids induce inflammatory genes in hepatocytes: A novel mechanism
of inflammation during obstructive cholestasis. Am J Pathol.
178:175–186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cipriani S, Mencarelli A, Chini MG,
Distrutti E, Renga B, Bifulco G, Baldelli F, Donini A and Fiorucci
S: The bile acid receptor GPBAR-1 (TGR5) modulates integrity of
intestinal barrier and immune response to experimental colitis.
PLoS One. 6:e256372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McMahan RH, Wang XX, Cheng LL, et al: Bile
acid receptor activation modulates hepatic monocyte activity and
improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biol Chem.
288:11761–11770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Renga B, Mencarelli A, Cipriani S, D’Amore
C, Carino A, Bruno A, Francisci D, Zampella A, Distrutti E and
Fiorucci S: The bile acid sensor FXR is required for
immune-regulatory activities of TLR-9 in intestinal inflammation.
PLoS One. 8:e544722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bremer J: Carnitine - metabolism and
functions. Physiol Rev. 63:1420–1480. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bowyer BA, Miles JM, Haymond MW and
Fleming CR: L-carnitine therapy in home parenteral nutrition
patients with abnormal liver tests and low plasma carnitine
concentrations. Gastroenterology. 94:434–438. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amodio P, Angeli P, Merkel C, Menon F and
Gatta A: Plasma carnitine levels in liver cirrhosis: Relationship
with nutritional status and liver damage. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem.
28:619–626. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krähenbühl S and Reichen J: Carnitine
metabolism in patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology.
25:148–153. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sonne S, Shekhawat PS, Matern D, Ganapathy
V and Ignatowicz L: Carnitine deficiency in OCTN2−/−
newborn mice leads to a severe gut and immune phenotype with
widespread atrophy, apoptosis and a proinflammatory response. PLoS
One. 7:e477292012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Thangasamy T, Subathra M, Sittadjody S,
Jeyakumar P, Joyee AG, Mendoza E and Chinnakkanu P: Role of
L-carnitine in the modulation of immune response in aged rats. Clin
Chim Acta. 389:19–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chiricolo M, Lenzi M, Bianchi F,
Franceschi C, Bartolini G, Orlandi M, Tomasi V and Licastro F:
Immune dysfunction in primary biliary cirrhosis. II. Increased
production of prostaglandin E. Scand J Immunol. 30:363–367. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Licastro F, Lenzi M, Chiricolo M, Davis
LJ, Cassani F, Bianchi F and Franceschi C: Immune dysfunction in
primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC): I. Increased sensitivity of PHA
stimulated lymphocyte cultures to indomethacin. J Clin Lab Immunol.
23:19–23. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hayashi N, Yamamoto H, Hiraoka N, et al:
Differential expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in human bile
duct epithelial cells and bile duct neoplasm. Hepatology.
34:638–650. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yao C, Sakata D, Esaki Y, Li Y, Matsuoka
T, Kuroiwa K, Sugimoto Y and Narumiya S: Prostaglandin E2-EP4
signaling promotes immune inflammation through Th1 cell
differentiation and Th17 cell expansion. Nat Med. 15:633–640. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aoki T, Nishimura M, Matsuoka T, et al:
PGE(2)-EP(2) signalling in endothelium is activated by haemodynamic
stress and induces cerebral aneurysm through an amplifying loop via
NF-κB. Br J Pharmacol. 163:1237–1249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oga T, Matsuoka T, Yao C, et al:
Prostaglandin F(2alpha) receptor signaling facilitates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis independently of transforming
growth factor-beta. Nat Med. 15:1426–1430. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ricciotti E and FitzGerald GA:
Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:986–1000. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fattahi MJ and Mirshafiey A:
Prostaglandins and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis (Egypt).
2012:2393102012.
|
|
39
|
Lima IV, Bastos LF, Limborço-Filho M,
Fiebich BL and de Oliveira AC: Role of prostaglandins in
neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Mediators
Inflamm. 2012:9468132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bell LN, Wulff J, Comerford M, Vuppalanchi
R and Chalasani N: Serum metabolic signatures of primary biliary
cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Liver Int.
35:263–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sasaki M, Ikeda H, Sato Y and Nakanuma Y:
Proinflammatory cytokine-induced cellular senescence of biliary
epithelial cells is mediated via oxidative stress and activation of
ATM pathway: A culture study. Free Radic Res. 42:625–632. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|