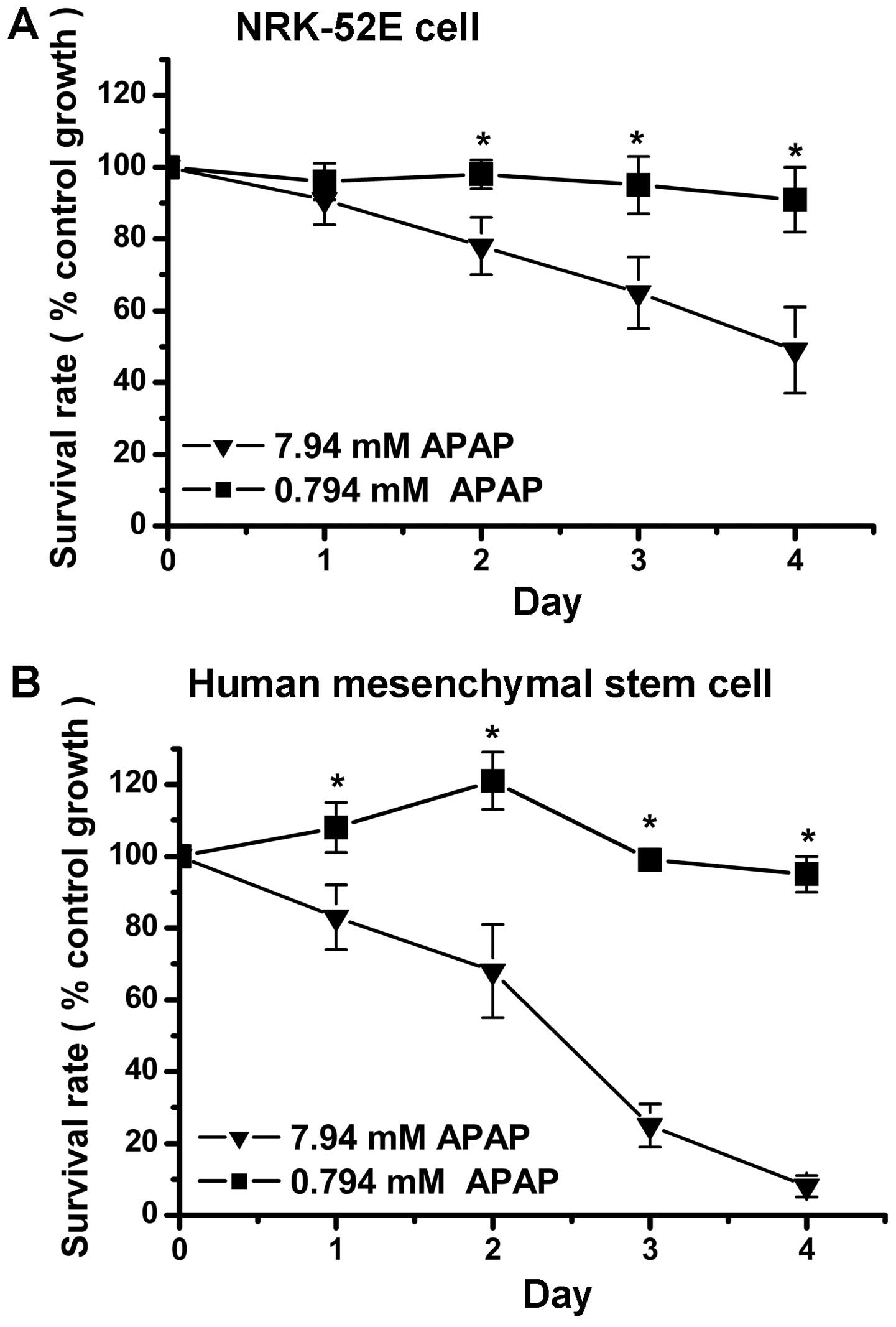
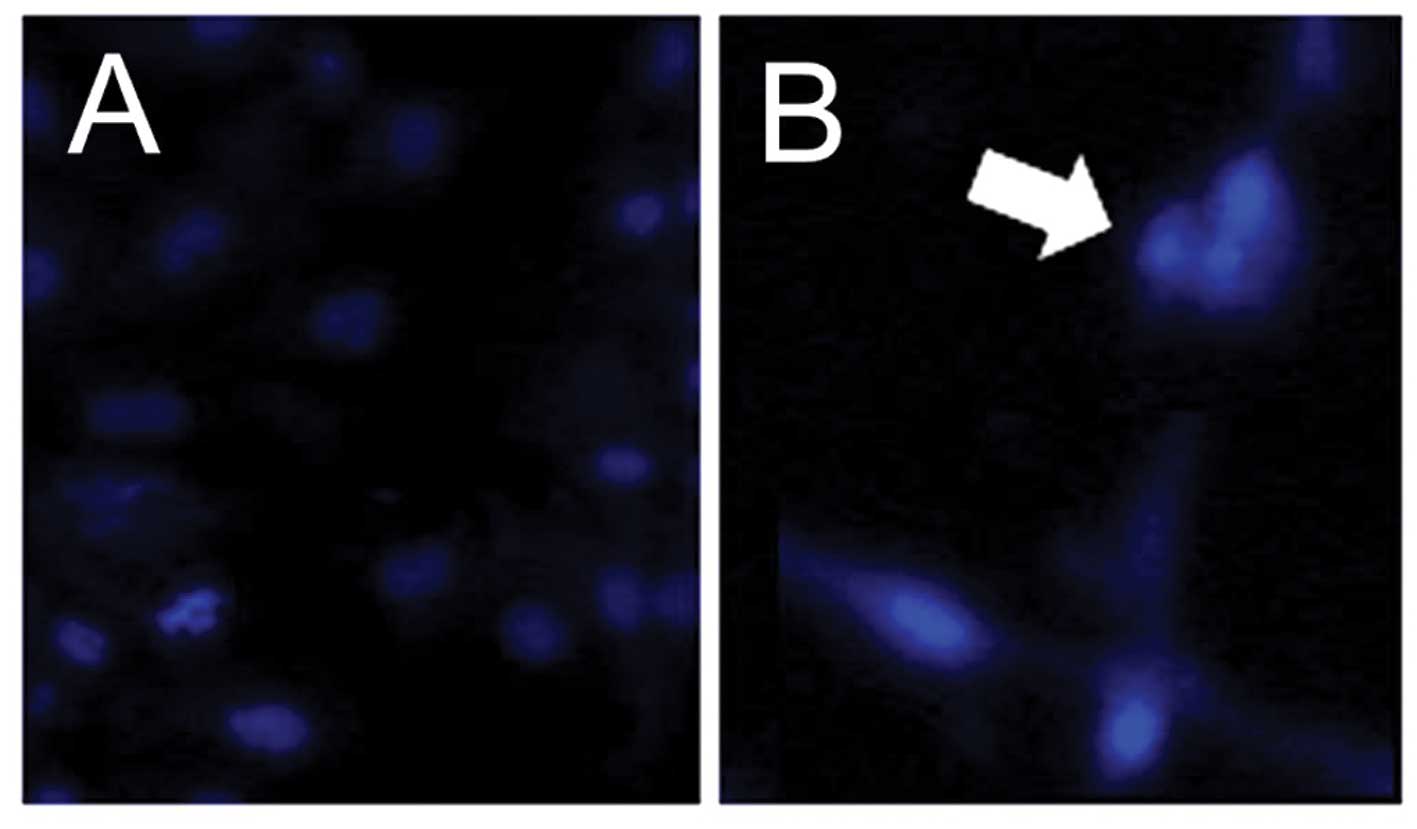
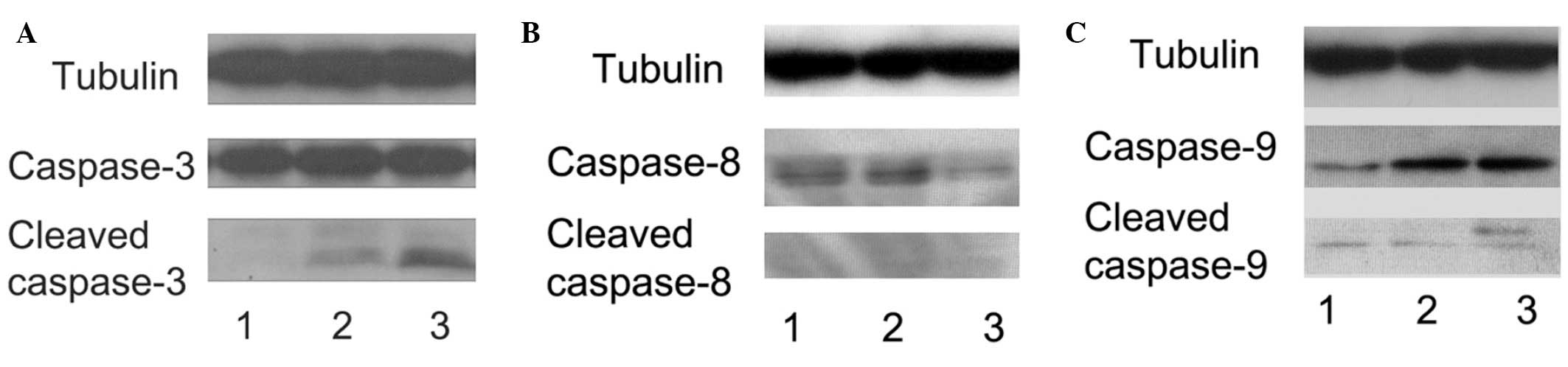
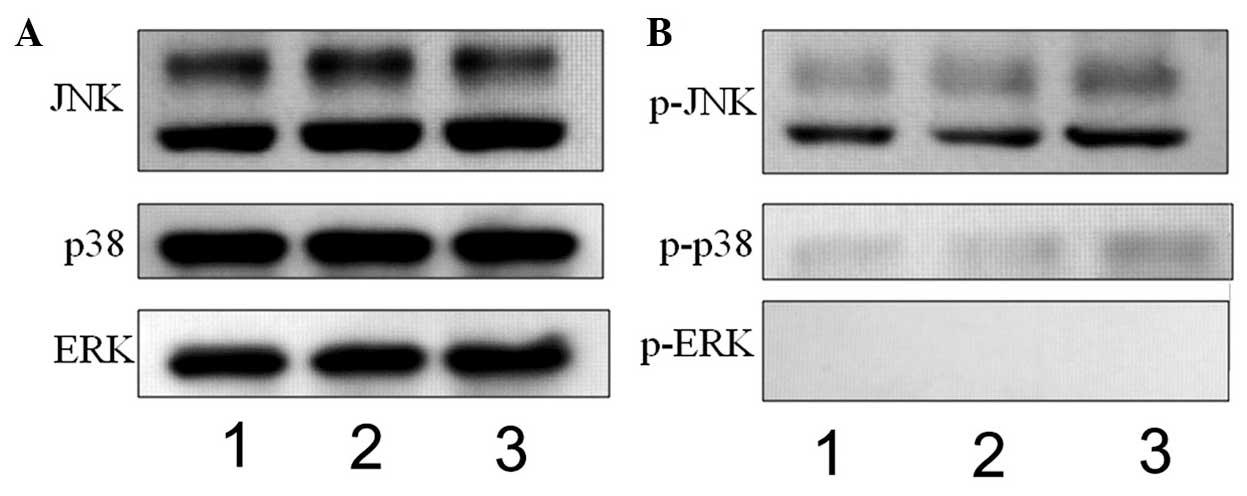
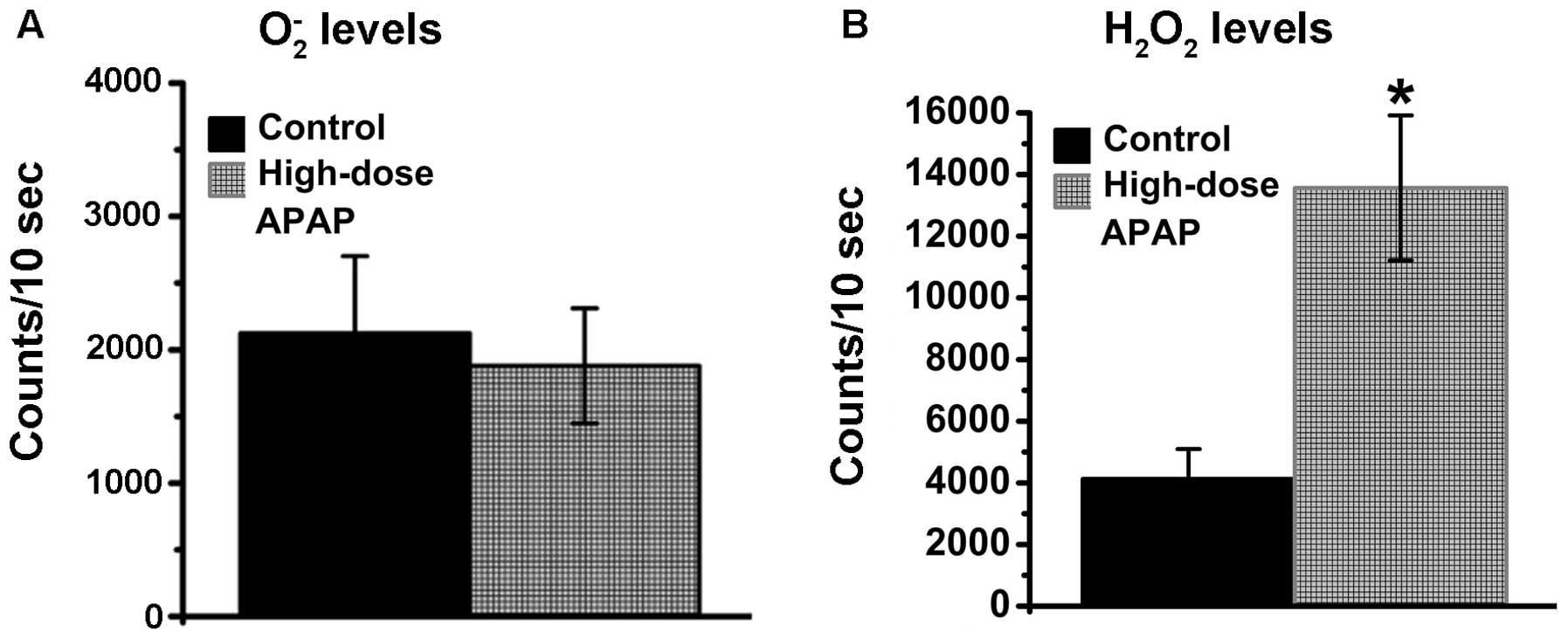
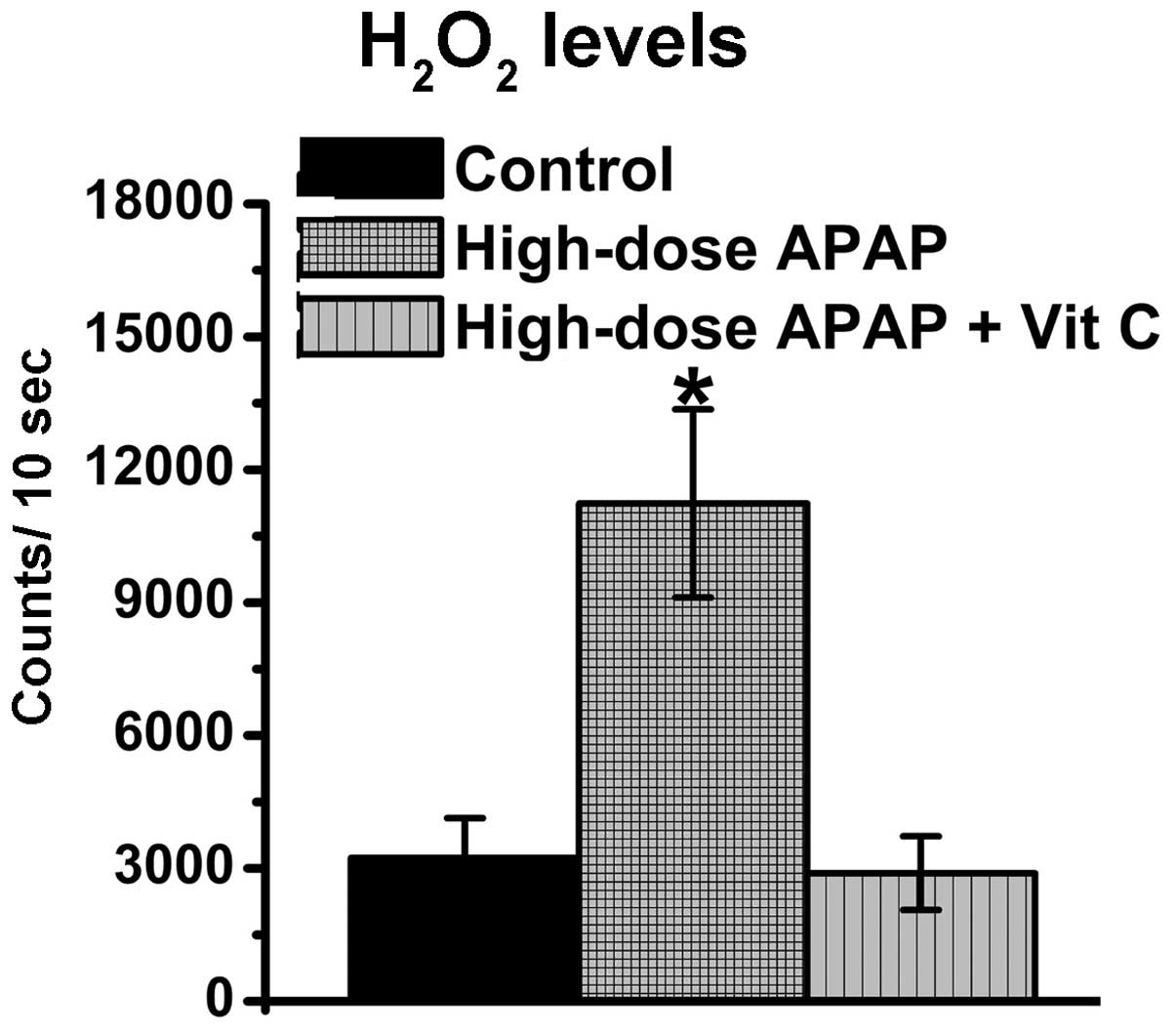
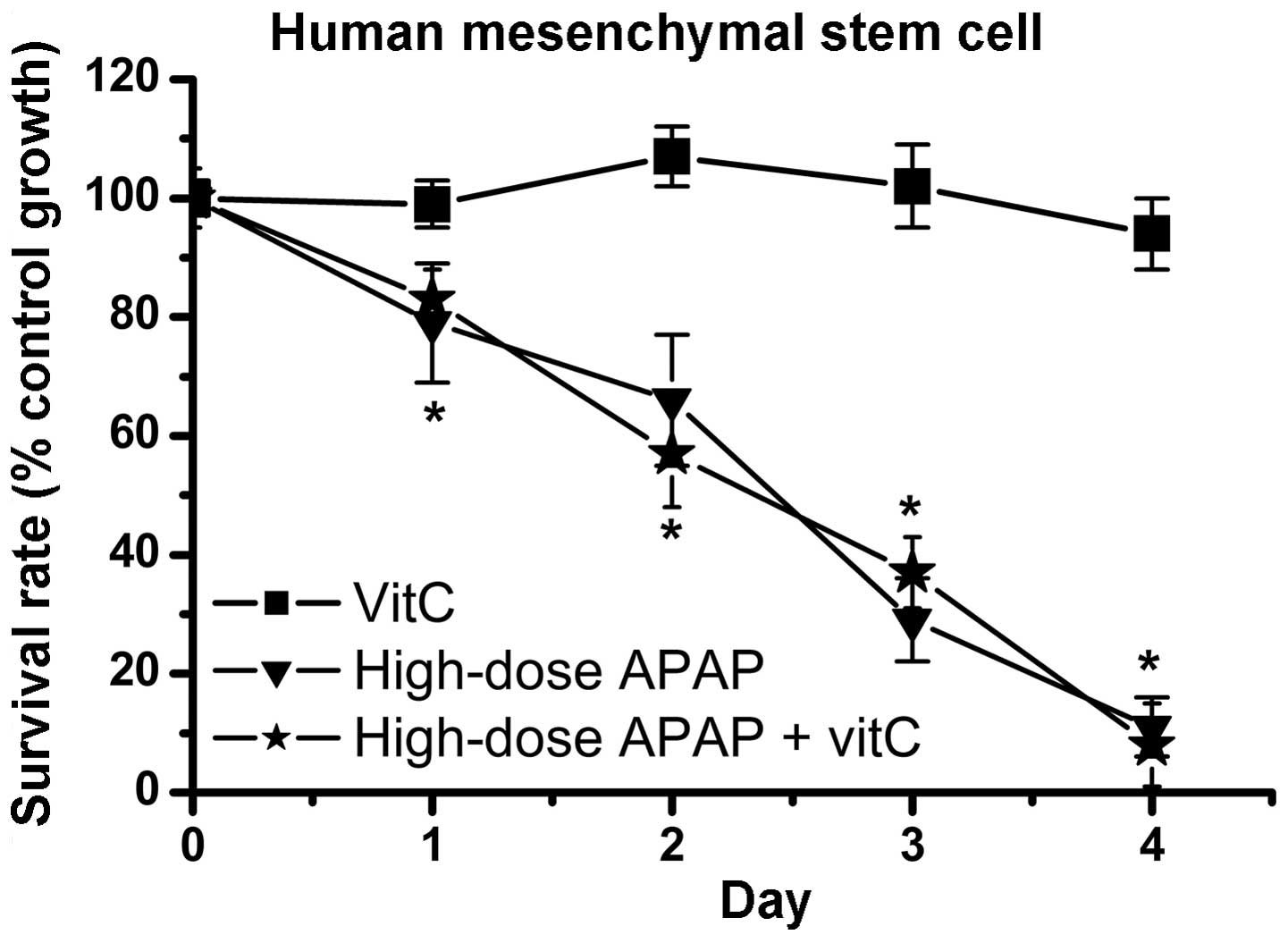
|
1
|
Cuzzolin L, Antonucci R and Fanos V:
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) efficacy and safety in the newborn.
Curr Drug Metab. 14:178–185. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Klotz U: Paracetamol (acetaminophen) - a
popular and widely used nonopioid analgesic. Drug Res. 62:355–359.
2012.
|
|
3
|
Section on Clinical Pharmacology
Therapeutics, Committee on Drugs; Sullivan JE and Farrar HC: Fever
and antipyretic use in children. Pediatrics. 127:580–587. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rumack BH: Acetaminophen misconceptions.
Hepatology. 40:10–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hawton K, Bergen H, Simkin S, et al:
Impact of different pack sizes of paracetamol in the United Kingdom
and Ireland on intentional overdoses: a comparative study. BMC
Public Health. 11:4602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hawton K, Townsend E, Deeks J, et al:
Effects of legislation restricting pack sizes of paracetamol and
salicylate on self poisoning in the United Kingdom: before and
after study. BMJ. 322:1203–1207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Daly FF, Fountain JS, Murray L, Graudins A
and Buckley NA; Panel of Australian and New Zealand clinical
toxicologists: Guidelines for the management of paracetamol
poisoning in Australia and New Zealand - explanation and
elaboration. A consensus statement from clinical toxicologists
consulting to the Australasian poisons information centres. Med J
Aust. 188:296–301. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Young RJ: Dextropropoxyphene overdosage.
Pharmacological considerations and clinical management. Drugs.
26:70–79. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simkin S, Hawton K, Kapur N and Gunnell D:
What can be done to reduce mortality from paracetamol overdoses? A
patient interview study. QJM. 105:41–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
McGill MR, Li F, Sharpe MR, et al:
Circulating acylcarnitines as biomarkers of mitochondrial
dysfunction after acetaminophen overdose in mice and humans. Arch
Toxicol. 88:391–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P and Sil PC:
Acetaminophen induced renal injury via oxidative stress and
TNF-alpha production: therapeutic potential of arjunolic acid.
Toxicology. 268:8–18. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chandrasekaran VR, Wan CH, Liu LL, Hsu DZ
and Liu MY: Effect of sesame oil against acetaminophen-induced
acute oxidative hepatic damage in rats. Shock. 30:217–221.
2008.
|
|
13
|
Galal RM, Zaki HF, Seif El-Nasr MM and
Agha AM: Potential protective effect of honey against
paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Iran Med. 15:674–680.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abdul Hamid Z, Budin SB, Wen Jie N, Hamid
A, Husain K and Mohamed J: Nephroprotective effects of Zingiber
zerumbet Smith ethyl acetate extract against paracetamol-induced
nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.
13:176–185. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kheradpezhouh E, Panjehshahin MR, Miri R,
et al: Curcumin protects rats against acetaminophen-induced
hepatorenal damages and shows synergistic activity with N-acetyl
cysteine. Eur J Pharmacol. 628:274–281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Anoush M, Eghbal MA, Fathiazad F, Hamzeiy
H and Kouzehkonani NS: The protective effects of garlic extract
against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and glutathione
depletion. Pak J Biol Sci. 12:765–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mehrpour O, Shadnia S and Sanaei-Zadeh H:
Late extensive intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine can
reverse hepatic failure in acetaminophen overdose. Hum Exp Toxicol.
30:51–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Blackford MG, Felter T, Gothard MD and
Reed MD: Assessment of the clinical use of intravenous and oral
N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acute acetaminophen poisoning
in children: a retrospective review. Clin Ther. 33:1322–1330. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai CL, Chang WT, Weng TI, Fang CC and
Walson PD: A patient-tailored N-acetylcysteine protocol for acute
acetaminophen intoxication. Clin Ther. 27:336–341. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Amaral SS, Oliveira AG, Marques PE, et al:
Altered responsiveness to extracellular ATP enhances acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity. Cell Commun Signal. 11:102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Badmann A, Langsch S, Keogh A, Brunner T,
Kaufmann T and Corazza N: TRAIL enhances paracetamol-induced liver
sinusoidal endothelial cell death in a Bim- and Bid-dependent
manner. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Badmann A, Keough A, Kaufmann T, Bouillet
P, Brunner T and Corazza N: Role of TRAIL and the pro-apoptotic
Bcl-2 homolog Bim in acetaminophen-induced liver damage. Cell Death
Dis. 2:e1712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McGill MR, Yan HM, Ramachandran A, Murray
GJ, Rollins DE and Jaeschke H: HepaRG cells: a human model to study
mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Hepatology. 53:974–982.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao X, Cong X, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L and
Peng J: Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, shows remarkable
protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in
vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Lett. 214:69–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mobasher MA, Gonzalez-Rodriguez A,
Santamaria B, et al: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B modulates
GSK3β/Nrf2 and IGFIR signaling pathways in acetaminophen-induced
hepatotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6262013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yu YL, Yiang GT, Chou PL, et al: Dual role
of acetaminophen in promoting hepatoma cell apoptosis and kidney
fibroblast proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 9:2077–2084. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gopi KS, Reddy AG, Jyothi K and Kumar BA:
Acetaminophen-induced hepato- and nephrotoxicity and amelioration
by silymarin and Terminalia chebula in rats. Toxicol Int. 17:64–66.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Hady RH, Mahmoud MM
and Farrag MM: The potential protective role of alpha-lipoic acid
against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicology.
243:261–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cermik H, Taslipinar MY, Aydin I, et al:
The relationship between N-acetylcysteine, hyperbaric oxygen, and
inflammation in a rat model of acetaminophen-induced
nephrotoxicity. Inflammation. 36:1145–1152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ucar F, Taslipinar MY, Alp BF, et al: The
effects of N-acetylcysteine and ozone therapy on oxidative stress
and inflammation in acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity model. Ren
Fail. 35:640–647. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liang YL, Zhang ZH, Liu XJ, et al:
Melatonin protects against apoptosis-inducing factor
(AIF)-dependent cell death during acetaminophen-induced acute liver
failure. PLoS One. 7:e519112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ni HM,
Ding WX and Jaeschke H: Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a
critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte
necrosis in mice. Hepatology. 58:2099–2108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahmad ST, Arjumand W, Nafees S, et al:
Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats
by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation.
Toxicol Lett. 208:149–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Inkielewicz-Stepniak I and Knap N: Effect
of exposure to fluoride and acetaminophen on oxidative/nitrosative
status of liver and kidney in male and female rats. Pharmacol Rep.
64:902–911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Slitt AM, Dominick PK, Roberts JC and
Cohen SD: Effect of ribose cysteine pretreatment on hepatic and
renal acetaminophen metabolite formation and glutathione depletion.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96:487–494. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yousef MI, Omar SA, El-Guendi MI and
Abdelmegid LA: Potential protective effects of quercetin and
curcumin on paracetamol-induced histological changes, oxidative
stress, impaired liver and kidney functions and haematotoxicity in
rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:3246–3261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
De-Giorgio F, Lodise M, Chiarotti M,
d’Aloja E, Carbone A and Valerio L: Possible fatal acetaminophen
intoxication with atypical clinical presentation. J Forensic Sci.
58:1397–1400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brusilow SW and Cooper AJ: Encephalopathy
in acute liver failure resulting from acetaminophen intoxication:
new observations with potential therapy. Crit Care Med.
39:2550–2553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Posadas I, Santos P and Cena V:
Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB
activation. PLoS One. 7:e501602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Posadas I, Vellecco V, Santos P,
Prieto-Lloret J and Cena V: Acetaminophen potentiates
staurosporine-induced death in a human neuroblastoma cell line. Br
J Pharmacol. 150:577–585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jaeschke H: Comments on ‘glycogen synthase
kinase-3 mediates acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma
cells’. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 314:1401–1402; author reply
1403–1404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Macanas-Pirard P, Yaacob NS, Lee PC,
Holder JC, Hinton RH and Kass GE: Glycogen synthase kinase-3
mediates acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 313:780–789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bilir A, Guneri AD and Altinoz MA:
Acetaminophen and DMSO modulate growth and gemcitabine cytotoxicity
in FM3A breast cancer cells in vitro. Neoplasma. 51:460–464.
2004.
|
|
44
|
Thiele K, Kessler T, Arck P, Erhardt A and
Tiegs G: Acetaminophen and pregnancy: short- and long-term
consequences for mother and child. J Reprod Immunol. 97:128–139.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wilkes JM, Clark LE and Herrera JL:
Acetaminophen overdose in pregnancy. South MedJ. 98:1118–1122.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tsunekawa Y, Kikkawa T and Osumi N:
Asymmetric inheritance of Cyclin D2 maintains proliferative neural
stem/progenitor cells: A critical event in brain development and
evolution. Dev Growth Differ. 56:349–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Di Bernardo J, Maiden MM, Jiang G,
Hershenson MB and Kunisaki SM: Paracrine regulation of fetal lung
morphogenesis using human placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal
cells. J Surg Res. 190:255–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dambrot C, Buermans HP, Varga E, et al:
Strategies for rapidly mapping proviral integration sites and
assessing cardiogenic potential of nascent human induced
pluripotent stem cell clones. Exp Cell Res. 327:297–306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yiang GT, Chen YH, Chou PL, Chang WJ, Wei
CW and Yu YL: The NS3 protease and helicase domains of Japanese
encephalitis virus trigger cell death via caspase-dependent and
-independent pathways. Mol Med Rep. 7:826–830. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu YL, Su KJ, Chen CJ, et al: Synergistic
anti-tumor activity of isochaihulactone and paclitaxel on human
lung cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 227:213–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wei CW, Hu CC, Tang CH, Lee MC and Wang
JJ: Induction of differentiation rescues HL-60 cells from Rana
catesbeiana ribonuclease-induced cell death. FEBS Lett.
531:421–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen KH, Li PC, Lin WH, Chien CT and Low
BH: Depression by a green tea extract of alcohol-induced oxidative
stress and lipogenesis in rat liver. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
75:1668–1676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lin BR, Yu CJ, Chen WC, et al: Green tea
extract supplement reduces D-galactosamine-induced acute liver
injury by inhibition of apoptotic and proinflammatory signaling. J
Biomed Sci. 16:352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Chou PL, et al: The
cytotoxic protein can induce autophagocytosis in addition to
apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. In Vivo. 26:403–409.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Hu SC, Chen MH, Wang JJ
and Wei CW: PKC and MEK pathways inhibit caspase-9/-3-mediated
cytotoxicity in differentiated cells. FEBS Lett. 582:881–885. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tang CH, Hu CC, Wei CW and Wang JJ:
Synergism of Rana catesbeiana ribonuclease and IFN-gamma triggers
distinct death machineries in different human cancer cells. FEBS
Lett. 579:265–270. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang AY, Lian LH, Jiang YZ, Wu YL and Nan
JX: Gentiana manshurica Kitagawa prevents acetaminophen-induced
acute hepatic injury in mice via inhibiting JNK/ERK MAPK pathway.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:384–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Win S, Than TA, Han D, Petrovic LM and
Kaplowitz N: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent acute liver
injury from acetaminophen or tumor necrosis factor (TNF) requires
mitochondrial Sab protein expression in mice. J Biol Chem.
286:35071–35078. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen JY, Zhang L, Zhang H, Su L and Qin
LP: Triggering of p38 MAPK and JNK signaling is important for
oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial death
pathway in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Phytother Res.
28:1468–1478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu X, Ye F, Xiong H, et al: IL-1β
upregulates IL-8 production in human Müller cells through
activation of the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Inflammation. 37:1486–1495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Levanon D, Manov I and Iancu TC:
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effects of
acetaminophen and N-acetylcysteine on the surface morphology of
Hep3B hepatoma cells in vitro. Ultrastruct Pathol. 28:3–14.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Manov I, Hirsh M and Iancu TC:
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and mechanisms of its protection by
N-acetylcysteine: a study of Hep3B cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
53:489–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kumari A and Kakkar P: Lupeol protects
against acetaminophen-induced oxidative stress and cell death in
rat primary hepatocytes. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1781–1789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Okokon JE, Nwafor PA, Charles U, Dar A and
Choudhary MI: Antioxidative burst and hepatoprotective effects of
ethanol root extract of Hippocratea africana against
paracetamol-induced liver injury. Pharm Biol. 51:872–880. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lee NH, Seo CS, Lee HY, et al:
Hepatoprotective and antioxidative activities of Cornus officinalis
against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:8049242012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Olaleye MT, Akinmoladun AC, Ogunboye AA
and Akindahunsi AA: Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective
property of leaf extracts of Boerhaavia diffusa Linn against
acetaminophen-induced liver damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:2200–2205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nkosi CZ, Opoku AR and Terblanche SE: In
vitro antioxidative activity of pumpkin seed (Cucurbita pepo)
protein isolate and its in vivo effect on alanine transaminase and
aspartate transaminase in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in low
protein fed rats. Phytother Res. 20:780–783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bhattacharjee R and Sil PC: The protein
fraction of Phyllanthus niruri plays a protective role against
acetaminophen induced hepatic disorder via its antioxidant
properties. Phytother Res. 20:595–601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Needleman SM: Safety of rapid intravenous
of infusion acetaminophen. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 26:235–238.
2013.
|
|
70
|
Engstrom Ruud L, Wilhelms DB, Eskilsson A,
et al: Acetaminophen reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced fever by
inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2. Neuropharmacology. 71:124–129. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zuppa AF, Hammer GB, Barrett JS, et al:
Safety and population pharmacokinetic analysis of intravenous
acetaminophen in neonates, infants, children, and adolescents with
pain or fever. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 16:246–261. 2011.
|
|
72
|
Boulares AH, Zoltoski AJ, Stoica BA,
Cuvillier O and Smulson ME: Acetaminophen induces a
caspase-dependent and Bcl-XL sensitive apoptosis in human hepatoma
cells and lymphocytes. Pharmacol Toxicol. 90:38–50. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ghanizadeh A: Acetaminophen may mediate
oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in autism. Med Hypotheses.
78:3512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang C, Blough ER, Arvapalli R, et al:
Metabolic syndrome-induced tubulointerstitial injury: role of
oxidative stress and preventive effects of acetaminophen. Free
Radic Biol Med. 65:1417–1426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Fouad AA, Al-Mulhim AS, Jresat I and Gomaa
W: Therapeutic role of telmisartan against acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 693:64–71. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Choi J, Park KH, Kim SZ, Shin JH and Jang
SI: The ameliorative effects of L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylate
on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Molecules.
18:3467–3478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kumari A and Kakkar P: Lupeol prevents
acetaminophen-induced in vivo hepatotoxicity by altering the
Bax/Bcl-2 and oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial signaling
cascade. Life Sci. 90:561–570. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ji L, Jiang P, Lu B, Sheng Y, Wang X and
Wang Z: Chlorogenic acid, a dietary polyphenol, protects
acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:1911–1919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Nafisi S, Heidari R, Ghaffarzadeh M, et
al: Cytoprotective effects of silafibrate, a newly-synthesised
siliconated derivative of clofibrate, against acetaminophen-induced
toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol.
65:169–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Colle D, Arantes LP, Gubert P, et al:
Antioxidant properties of Taraxacum officinaleleaf extract are
involved in the protective effect against hepatoxicity induced by
acetaminophen in mice. J Med Food. 15:549–556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhao YL, Zhou GD, Yang HB, et al: Rhein
protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal toxicity.
Food Chem Toxicol. 49:1705–1710. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lu Y, Sun J, Petrova K, et al:
Metabolomics evaluation of the effects of green tea extract on
acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Chem Toxicol.
62:707–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yakubu N, Oboh G and Olalekan AA:
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective properties of tofu (curdle
soymilk) against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in rats.
Biotechnol Res Int. 2013:2301422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Prescott LF, Park J, Ballantyne A,
Adriaenssens P and Proudfoot AT: Treatment of paracetamol
(acetaminophen) poisoning with N-acetylcysteine. Lancet. 2:432–434.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Allameh A, Vansoun EY and Zarghi A: Role
of glutathione conjugation in protection of weanling rat liver
against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Mech Ageing Dev.
95:71–79. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|