|
1
|
Eves PC, MacNeil S and Haycock JW:
alpha-Melanocyte stimulating hormone, inflammation and human
melanoma. Peptides. 27:444–452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yokota T, Nishio H, Kubota Y and Mizoguchi
M: The inhibitory effect of glabridin from licorice extracts on
melanogenesis and inflammation. Pigment Cell Res. 11:355–361. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eller MS, Ostrom K and Gilchrest BA: DNA
damage enhances melanogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:1087–1092. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong G and Pawelek J:
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone promotes activation of pre-existing
tyrosinase molecules in Cloudman S91 melanoma cells. Nature.
255:644–646. 1975. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Halaban R, Pomerantz SH, Marshall S and
Lerner AB: Tyrosinase activity and abundance in Cloudman melanoma
cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 230:383–387. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hunt G, Todd C, Cresswell JE and Thody AJ:
Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone and its analogue Nle4DPhe7
alpha-MSH affect morphology, tyrosinase activity and melanogenesis
in cultured human melanocytes. J Cell Sci. 107:205–211.
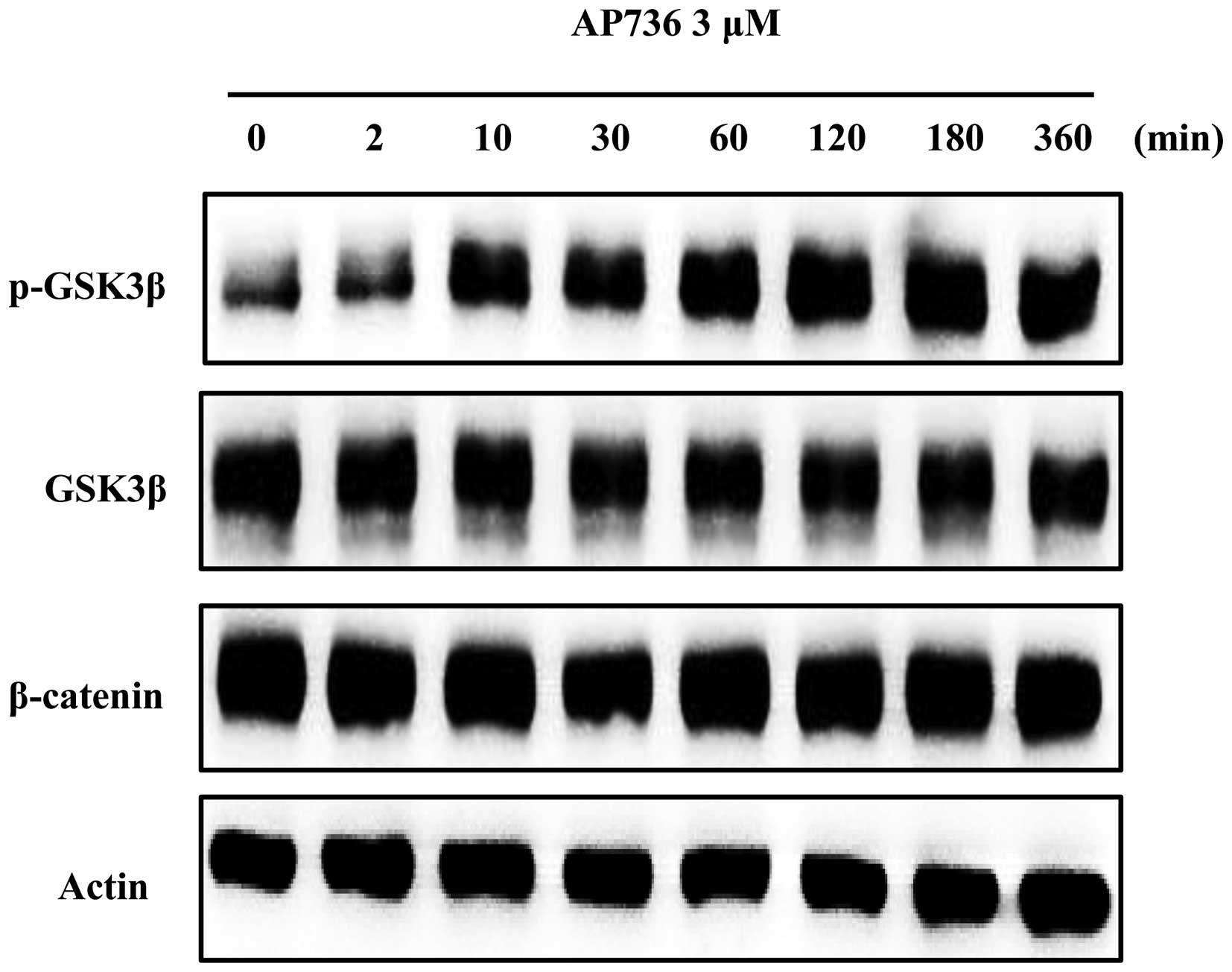
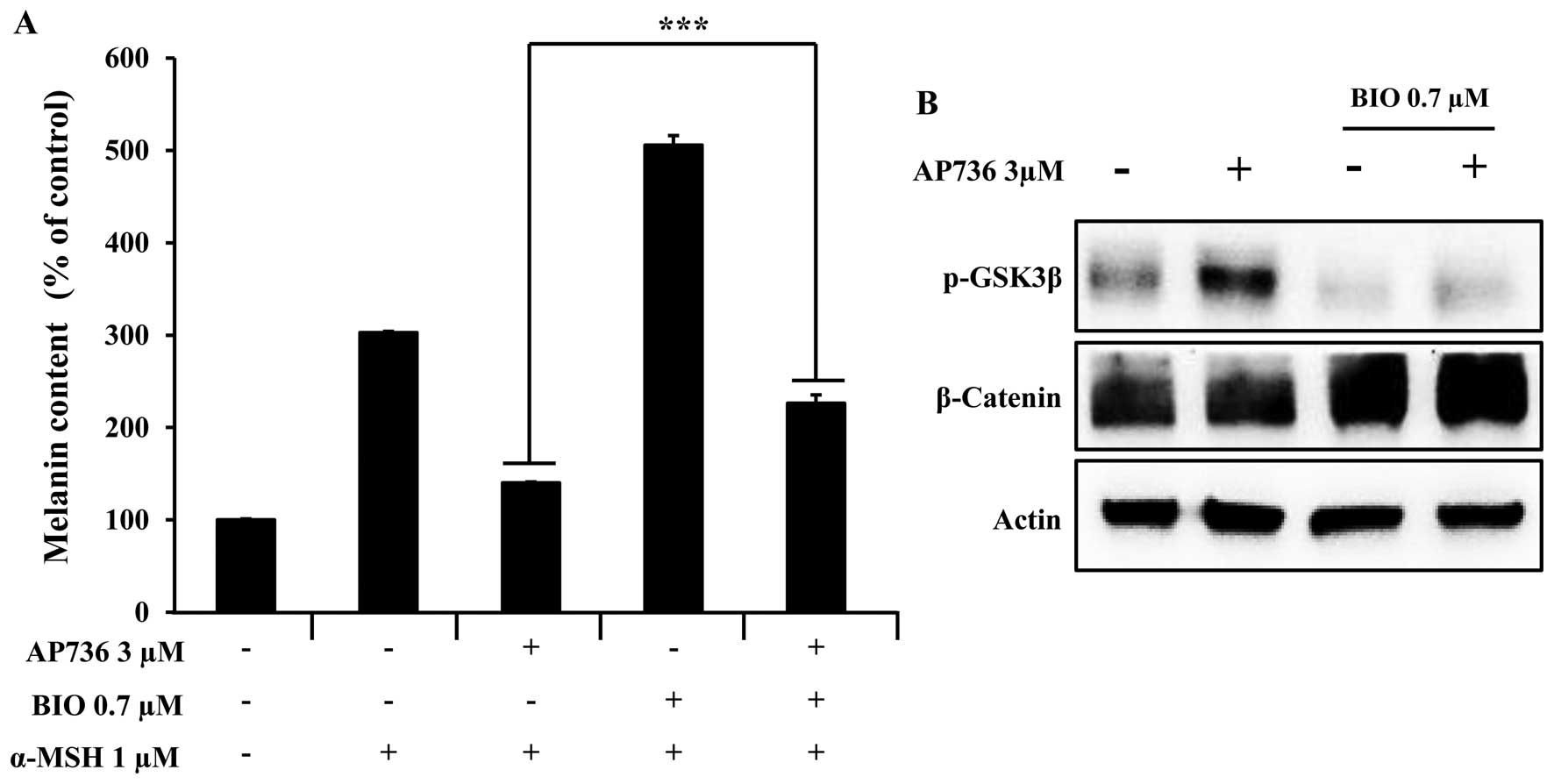
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanwar AJ, Dhar S and Kaur S: Treatment of
melasma with potent topical corticosteroids. Dermatology.
188:1701994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Körner A and Pawelek J: Mammalian
tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of
melanin. Science. 217:1163–1165. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boissy RE: Melanosome transfer to and
translocation in the keratinocyte. Exp Dermatol. 12(Suppl 2):
S52003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Buscà R, Bertolotto C, Ortonne JP and
Ballotti R: Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/p70(S6)-kinase pathway induces B16 melanoma cell
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 271:31824–31830. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Costin GE and Hearing VJ: Human skin
pigmentation: melanocytes modulate skin color in response to
stress. FASEB J. 21:976–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hearing VJ and Tsukamoto K: Enzymatic
control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J. 5:2902–2909.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung E, Lee J, Huh S, Lee J, Kim YS, Kim G
and Park D: Phloridzin-induced melanogenesis is mediated by the
cAMP signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2436–2440. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yasumoto K, Yokoyama K, Takahashi K,
Tomita Y and Shibahara S: Functional analysis of
microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in pigment
cell-specific transcription of the human tyrosinase family genes. J
Biol Chem. 272:503–509. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steingrímsson E, Moore KJ, Lamoreux ML,
Ferré-D'Amaré AR, Burley SK, Zimring DC, Skow LC, Hodgkinson CA,
Arnheiter H, Copeland NG, et al: Molecular basis of mouse
microphthalmia (mi) mutations helps explain their developmental and
phenotypic consequences. Nat Genet. 8:256–263. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tachibana M: MITF: A stream flowing for
pigment cells. Pigment Cell Res. 13:230–240. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vakhedi AS: Biological sutures in
ophthalmological microsurgery. Vestn Oftalmol. 5:27–31. 1976.In
Russian.
|
|
18
|
Jiménez-Cervantes C, Martínez-Esparza M,
Pérez C, Daum N, Solano F and García-Borrón JC: Inhibition of
melanogenesis in response to oxidative stress: transient
downregulation of melanocyte differentiation markers and possible
involvement of microphthalmia transcription factor. J Cell Sci.
114:2335–2344. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Corre S, Primot A, Sviderskaya E, Bennett
DC, Vaulont S, Goding CR and Galibert MD: UV-induced expression of
key component of the tanning process, the POMC and MC1R genes, is
dependent on the p-38-activated upstream stimulating factor-1
(USF-1). J Biol Chem. 279:51226–51233. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu M, Hemesath TJ, Takemoto CM, Horstmann
MA, Wells AG, Price ER, Fisher DZ and Fisher DE: c-Kit triggers
dual phosphorylations, which couple activation and degradation of
the essential melanocyte factor Mi. Genes Dev. 14:301–312.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu W, Gong L, Haddad MM, Bischof O,
Campisi J, Yeh ET and Medrano EE: Regulation of
microphthalmia-associated transcription factor MITF protein levels
by association with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme hUBC9. Exp
Cell Res. 255:135–143. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim DS, Hwang ES, Lee JE, Kim SY, Kwon SB
and Park KC: Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis
via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J
Cell Sci. 116:1699–1706. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Larue L and Delmas V: The WNT/Beta-catenin
pathway in melanoma. Front Biosci. 11:733–742. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Saint-Jeannet JP and Klein PS:
Wnt-frizzled signaling in neural crest formation. Trends Neurosci.
26:40–45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bellei B, Flori E, Izzo E, Maresca V and
Picardo M: GSK3beta inhibition promotes melanogenesis in mouse B16
melanoma cells and normal human melanocytes. Cell Signal.
20:1750–1761. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Giles RH, van Es JH and Clevers H: Caught
up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1653:1–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, van Wichen
D, de Weger R, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Clevers H: Constitutive
transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin-Tcf complex in APC-/-
colon carcinoma. Science. 275:1784–1787. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N,
Clevers H, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Activation of
beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in
beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wodarz A and Nusse R: Mechanisms of Wnt
signaling in development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 14:59–88. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes
Dev. 14:1837–1851. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg GH,
Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X and He X: Control of beta-catenin
phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell.
108:837–847. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Amit S, Hatzubai A, Birman Y, Andersen JS,
Ben-Shushan E, Mann M, Ben-Neriah Y and Alkalay I: Axin-mediated
CKI phosphorylation of beta-catenin at Ser 45: a molecular switch
for the Wnt pathway. Genes Dev. 16:1066–1076. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Latres E, Chiaur DS and Pagano M: The
human F box protein beta-Trcp associates with the Cul1/Skp1 complex
and regulates the stability of beta-catenin. Oncogene. 18:849–854.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee E, Salic A, Krüger R, Heinrich R and
Kirschner MW: The roles of APC and Axin derived from experimental
and theoretical analysis of the Wnt pathway. PLoS Biol. 1:E102003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takeda K, Yasumoto K, Takada R, Takada S,
Watanabe K, Udono T, Saito H, Takahashi K and Shibahara S:
Induction of melanocyte-specific microphthalmia-associated
transcription factor by Wnt-3a. J Biol Chem. 275:14013–14016. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schepsky A, Bruser K, Gunnarsson GJ,
Goodall J, Hallsson JH, Goding CR, Steingrimsson E and Hecht A: The
microphthalmia-associated transcription factor Mitf interacts with
beta-catenin to determine target gene expression. Mol Cell Biol.
26:8914–8927. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Parvez S, Kang M, Chung HS, Cho C, Hong
MC, Shin MK and Bae H: Survey and mechanism of skin depigmenting
and lightening agents. Phytother Res. 20:921–934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shimizu K, Yasutake S and Kondo R: A new
stilbene with tyrosinase inhibitory activity from Chlorophora
excelsa. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 51:318–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Park SH, Kim DS, Kim WG, Ryoo IJ, Lee DH,
Huh CH, Youn SW, Yoo ID and Park KC: Terrein: A new melanogenesis
inhibitor and its mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:2878–2885. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim DS, Jeong YM, Park IK, Hahn HG, Lee
HK, Kwon SB, Jeong JH, Yang SJ, Sohn UD and Park KC: A new
2-imino-1,3-thiazoline derivative, KHG22394, inhibits melanin
synthesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:180–183.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee do H, Kim DH, Oh IY, Kim SY, Lim YY,
Kim HM, Kim YH, Choi YM, Kim SE, Kim BJ and Kim MN: Inhibitory
effects of Saururi chinensis extracts on melanin biosynthesis in
B16F10 melanoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:772–779. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Poma A, Bianchini S and Miranda M:
Inhibition of L-tyrosine-induced micronuclei production by
phenylthiourea in human melanoma cells. Mutat Res. 446:143–148.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Casanola-Martin GM, Le-Thi-Thu H,
Marrero-Ponce Y, Castillo-Garit JA, Torrens F, Rescigno A, Abad C
and Khan MT: Tyrosinase enzyme: 1. An overview on a pharmacological
target. Curr Top Med Chem. 14:1494–1501. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smit N, Vicanova J and Pavel S: The hunt
for natural skin whitening agents. Int J Mol Sci. 10:5326–5349.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
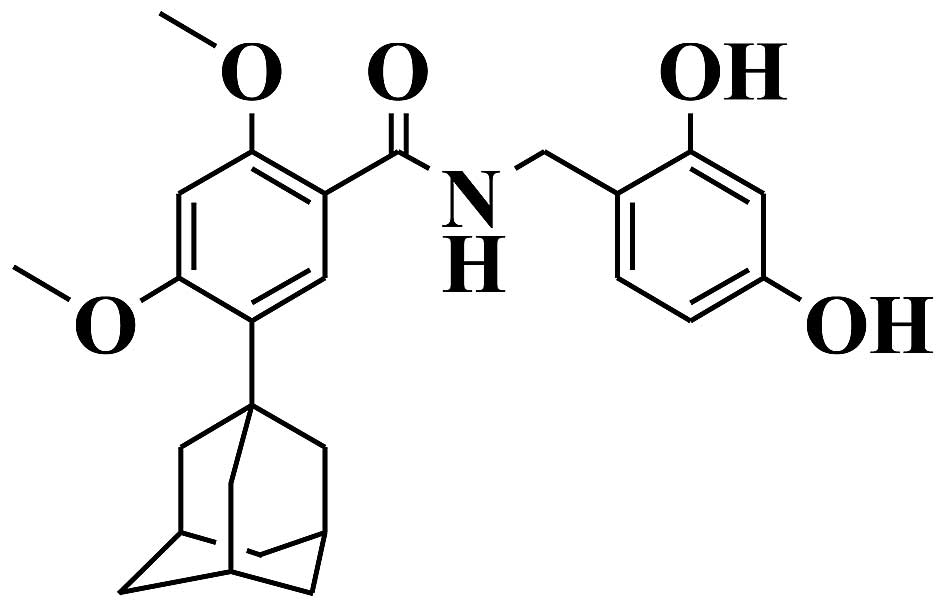
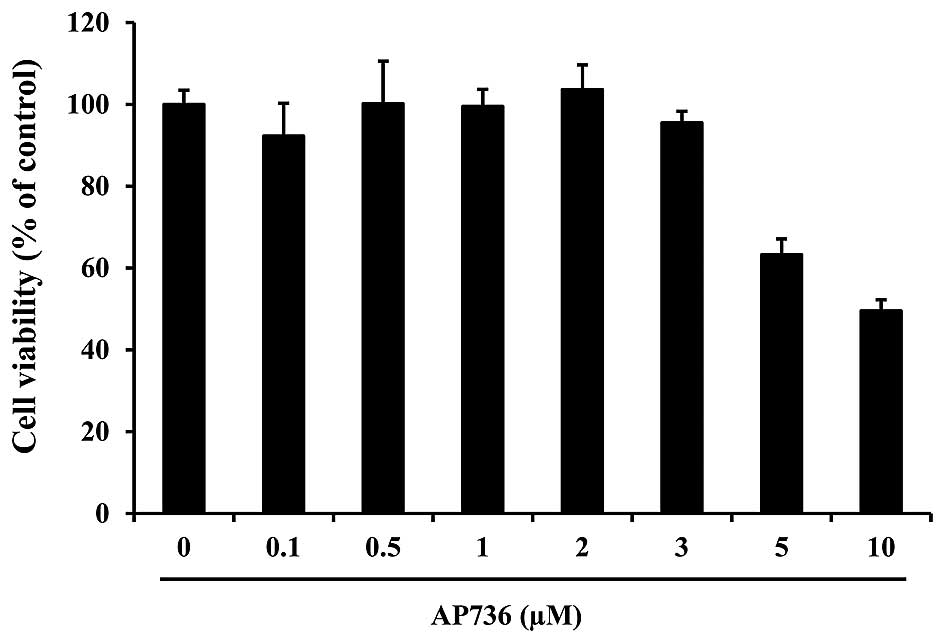
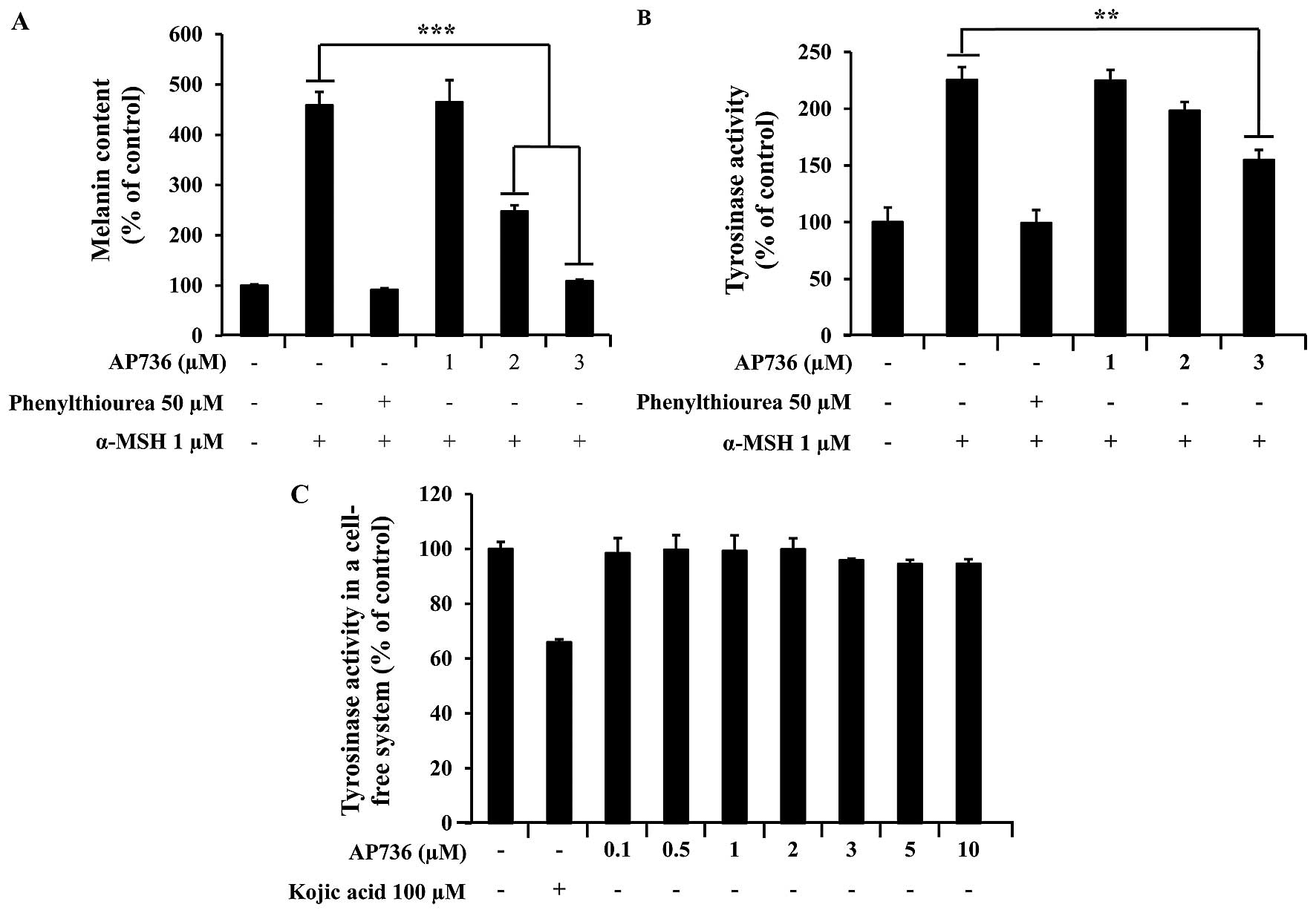
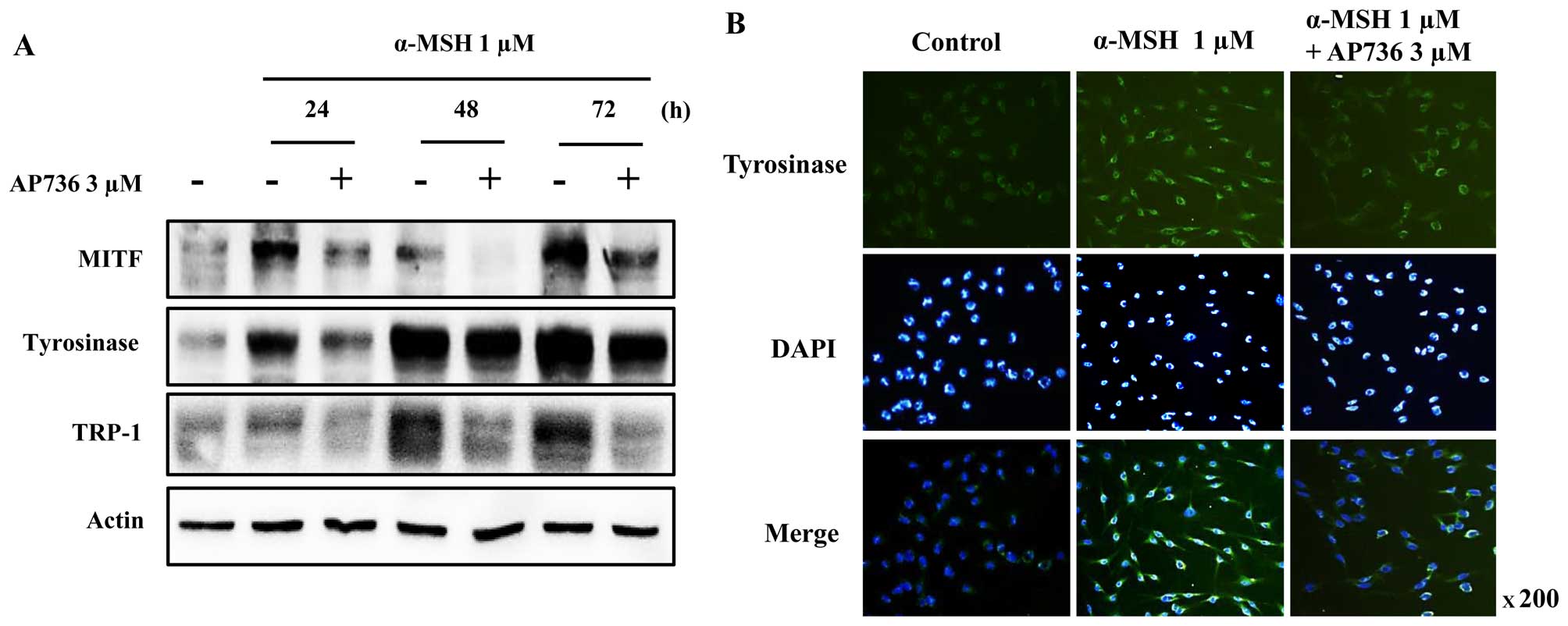
Lee CS, Jang WH, Park M, Jung K, Baek HS,
Joo YH, Park YH and Lim KM: A novel adamantyl benzylbenzamide
derivative, AP736, suppresses melanogenesis through the inhibition
of cAMP-PKA-CREB-activated microphthalmia-associated transcription
factor and tyrosinase expression. Exp Dermatol. 22:762–764. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lin YS, Chuang MT, Chen CH, Chien MY and
Hou WC: Nicotinic acid hydroxamate downregulated the melanin
synthesis and tyrosinase activity through activating the MEK/ERK
and AKT/GSK3β signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 60:4859–4864.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gillbro JM and Olsson MJ: The
melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents - existing
and new approaches. Int J Cosmet Sci. 33:210–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Son KH and Heo MY: The evaluation of
depigmenting efficacy in the skin for the development of new
whitening agents in Korea. Int J Cosmet Sci. 35:9–18. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Land EJ, Ramsden CA, Riley PA and
Stratford MR: Evidence consistent with the requirement of cresolase
activity for suicide inactivation of tyrosinase. Tohoku J Exp Med.
216:231–238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Grabacka M, Placha W, Urbanska K, Laidler
P, Płonka PM and Reiss K: PPAR gamma regulates MITF and
beta-catenin expression and promotes a differentiated phenotype in
mouse melanoma S91. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21:388–396. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Grabacka M, Plonka PM, Urbanska K and
Reiss K: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
activation decreases metastatic potential of melanoma cells in
vitro via down-regulation of Akt. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3028–3036.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Takeda K, Takemoto C, Kobayashi I,
Watanabe A, Nobukuni Y, Fisher DE and Tachibana M: Ser298 of MITF,
a mutation site in Waardenburg syndrome type 2, is a
phosphorylation site with functional significance. Hum Mol Genet.
9:125–132. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hart MJ, de los Santos R, Albert IN,
Rubinfeld B and Polakis P: Downregulation of beta-catenin by human
Axin and its association with the APC tumor suppressor,
beta-catenin and GSK3 beta. Curr Biol. 8:573–581. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A
and Kemler R: beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. EMBO J. 16:3797–3804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gwak J, Cho M, Gong SJ, Won J, Kim DE, Kim
EY, Lee SS, Kim M, Kim TK, Shin JG and Oh S:
Protein-kinase-C-mediated beta-catenin phosphorylation negatively
regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J Cell Sci. 119:4702–4709.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu J, Stevens J, Rote CA, Yost HJ, Hu Y,
Neufeld KL, White RL and Matsunami N: Siah-1 mediates a novel
beta-catenin degradation pathway linking p53 to the adenomatous
polyposis coli protein. Mol Cell. 7:927–936. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|