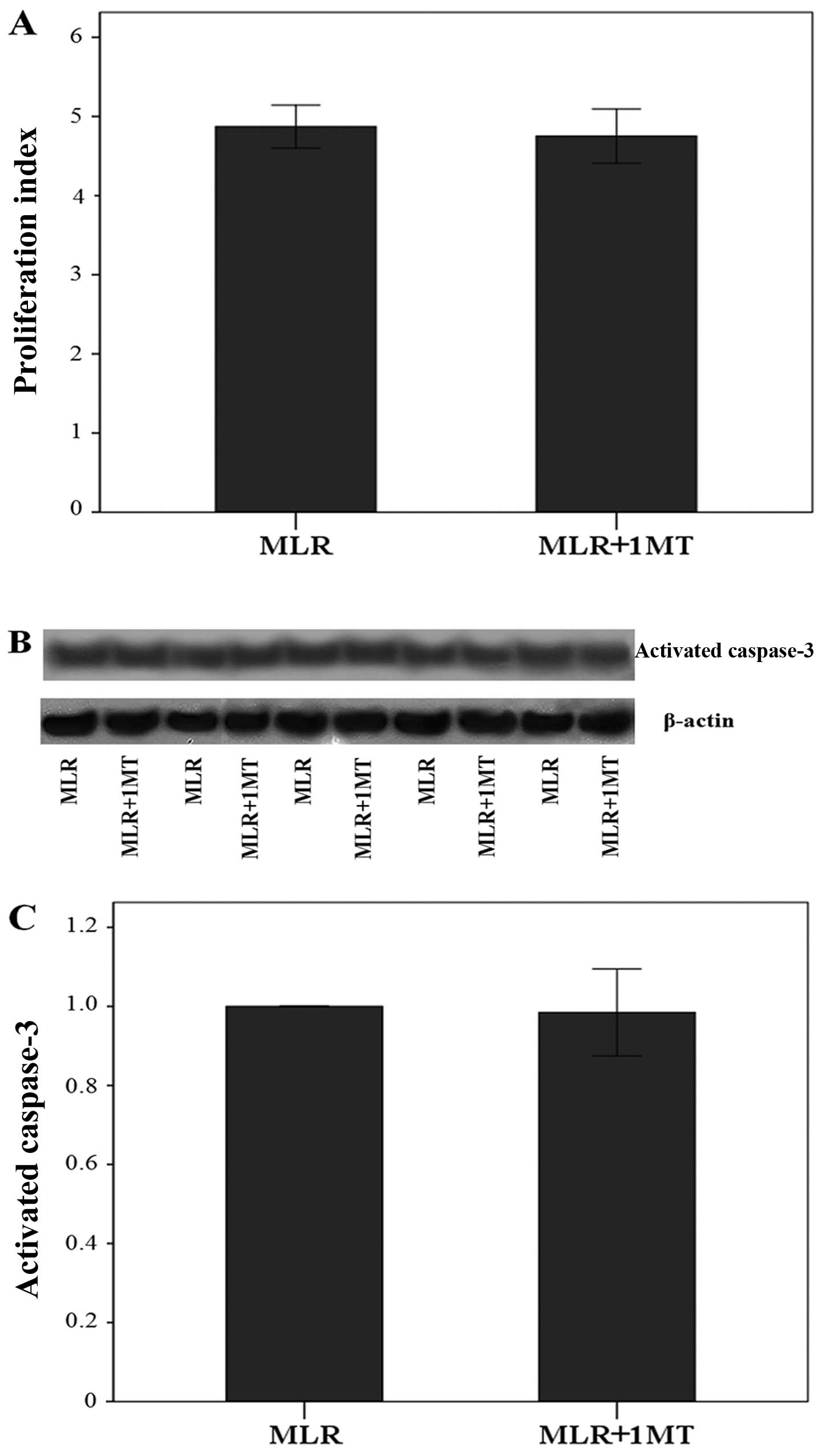
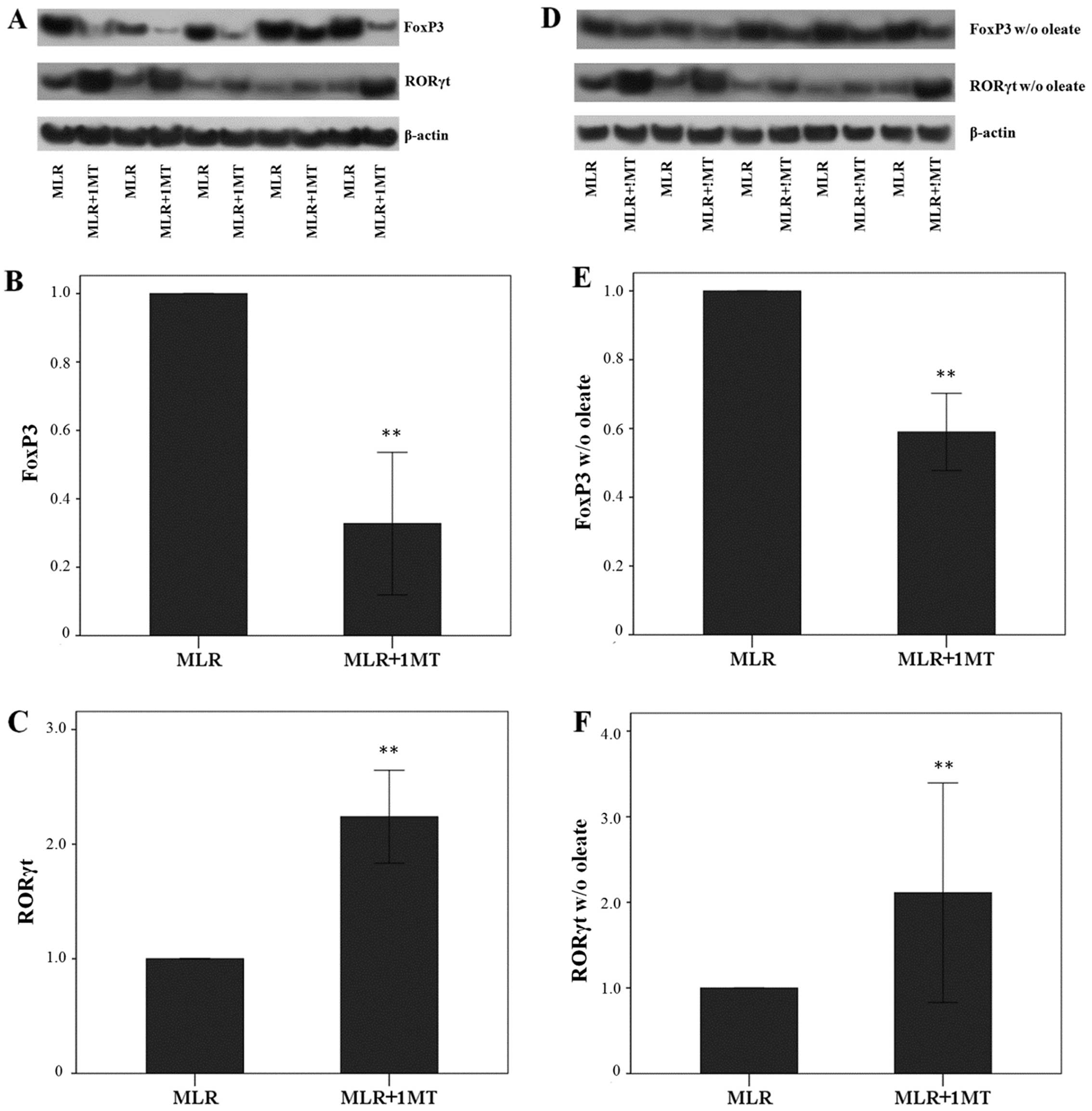
|
1
|
Seo SK, Choi JH, Kim YH, Kang WJ, Park HY,
Suh JH, Choi BK, Vinay DS and Kwon BS: 4-1BB-mediated immunotherapy
of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 10:1088–1094. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gurtner GJ, Newberry RD, Schloemann SR,
McDonald KG and Stenson WF: Inhibition of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase augments trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis in
mice. Gastroenterology. 125:1762–1773. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kwidzinski E, Bunse J, Aktas O, Richter D,
Mutlu L, Zipp F, Nitsch R and Bechmann I: Indolamine
2,3-dioxygenase is expressed in the CNS and down-regulates
autoimmune inflammation. FASEB J. 19:1347–1349. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alexander AM, Crawford M, Bertera S,
Rudert WA, Takikawa O, Robbins PD and Trucco M: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase expression in transplanted NOD Islets prolongs
graft survival after adoptive transfer of diabetogenic splenocytes.
Diabetes. 51:356–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beutelspacher SC, Pillai R, Watson MP, Tan
PH, Tsang J, McClure MO, George AJ and Larkin DF: Function of
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in corneal allograft rejection and
prolongation of allograft survival by over-expression. Eur J
Immunol. 36:690–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Tredget EE, Ghaffari A, Lin X,
Kilani RT and Ghahary A: Local expression of indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase protects engraftment of xenogeneic skin substitute.
J Invest Dermatol. 126:128–136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I,
Conway SJ, Marshall B, Brown C and Mellor AL: Prevention of
allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science.
281:1191–1193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mellor AL, Sivakumar J, Chandler P, Smith
K, Molina H, Mao D and Munn DH: Prevention of T cell-driven
complement activation and inflammation by tryptophan catabolism
during pregnancy. Nat Immunol. 2:64–68. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Munn DH and Mellor AL: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase and tumor-induced tolerance. J Clin Invest.
117:1147–1154. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eleftheriadis T, Yiannaki E, Antoniadi G,
Liakopoulos V, Pissas G, Galaktidou G and Stefanidis I: Plasma
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and arginase type I may contribute to
decreased blood T-cell count in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail.
34:1118–1122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eleftheriadis T, Liakopoulos V, Antoniadi
G, Stefanidis I and Galaktidou G: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is
increased in hemodialysis patients and affects immune response to
hepatitis B vaccination. Vaccine. 29:2242–2247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munn DH, Sharma MD, Baban B, Harding HP,
Zhang Y, Ron D and Mellor AL: GCN2 kinase in T cells mediates
proliferative arrest and anergy induction in response to
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunity. 22:633–642. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
depletes tryptophan, activates general control non-derepressible 2
kinase and down-regulates key enzymes involved in fatty acid
synthesis in primary human CD4+ T cells. Immunology.
146:292–300. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Spanoulis A, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase increases p53 levels in alloreactive human T cells,
and both indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and p53 suppress glucose
uptake, glycolysis and proliferation. Int Immunol. 26:673–684.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Yiannaki E,
Markala D, Arampatzis S, Antoniadi G, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis
I: Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in mixed lymphocyte
reaction affects glucose influx and enzymes involved in aerobic
glycolysis and glutaminolysis in alloreactive T-cells. Hum Immunol.
74:1501–1509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Antoniadi G,
Tsogka K, Sounidaki M, Liakopoulos V and Stefanidis I: Indoleamine
2,3 dioxygenase downregulates T cell receptor complex ζ chain and c
Myc, and reduces proliferation, lactate dehydrogenase levels and
mitochondrial glutaminase in human T cells. Mol Med Rep.
13:925–932. 2016.
|
|
17
|
Cobbold SP, Adams E, Farquhar CA, Nolan
KF, Howie D, Lui KO, Fairchild PJ, Mellor AL, Ron D and Waldmann H:
Infectious tolerance via the consumption of essential amino acids
and mTOR signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12055–12060. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mezrich JD, Fechner JH, Zhang X, Johnson
BP, Burlingham WJ and Bradfield CA: An interaction between
kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate
regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 185:3190–3198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M,
Tritschler I, Trump S, Schumacher T, Jestaedt L, Schrenk D, Weller
M, et al: An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl
hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 478:197–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
King NJ and Thomas SR: Molecules in focus:
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:2167–2172.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Curti A, Trabanelli S, Salvestrini V,
Baccarani M and Lemoli RM: The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
in the induction of immune tolerance: Focus on hematology. Blood.
113:2394–2401. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maciver NJ, Jacobs SR, Wieman HL, Wofford
JA, Coloff JL and Rathmell JC: Glucose metabolism in lymphocytes is
a regulated process with significant effects on immune cell
function and survival. J Leukoc Biol. 84:949–957. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fox CJ, Hammerman PS and Thompson CB: Fuel
feeds function: Energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nat Rev
Immunol. 5:844–852. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, Milasta S,
Carter R, Finkelstein D, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Chi H, Munger
J, et al: The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic
reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 35:871–882.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Berod L, Friedrich C, Nandan A, Freitag J,
Hagemann S, Harmrolfs K, Sandouk A, Hesse C, Castro CN, Bähre H, et
al: De novo fatty acid synthesis controls the fate between
regulatory T and T helper 17 cells. Nat Med. 20:1327–1333. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR,
Macintyre AN, MacIver NJ, Mason EF, Sullivan SA, Nichols AG and
Rathmell JC: Cutting edge: Distinct glycolytic and lipid oxidative
metabolic programs are essential for effector and regulatory
CD4+ T cell subsets. J Immunol. 186:3299–3303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sato T, Deiwick A, Raddatz G, Koyama K and
Schlitt HJ: Interactions of allogeneic human mononuclear cells in
the two-way mixed leucocyte culture (MLC): Influence of cell
numbers, subpopulations and cyclosporin. Clin Exp Immunol.
115:301–308. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lopaschuk GD, Ussher JR, Folmes CD, Jaswal
JS and Stanley WC: Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and
disease. Physiol Rev. 90:207–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schreurs M, Kuipers F and van der Leij FR:
Regulatory enzymes of mitochondrial beta-oxidation as targets for
treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev. 11:380–388. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bieber LL and Fiol C: Purification and
assay of carnitine acyltransferases. Methods Enzymol. 123:276–284.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gallinetti J, Harputlugil E and Mitchell
JR: Amino acid sensing in dietary-restriction-mediated longevity:
Roles of signal-transducing kinases GCN2 and TOR. Biochem J.
449:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Raphael I, Nalawade S, Eagar TN and
Forsthuber TG: T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in
autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 74:5–17. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Fallarino F, Grohmann U, You S, McGrath
BC, Cavener DR, Vacca C, Orabona C, Bianchi R, Belladonna ML, Volpi
C, et al: The combined effects of tryptophan starvation and
tryptophan catabolites down-regulate T cell receptor zeta-chain and
induce a regulatory phenotype in naive T cells. J Immunol.
176:6752–6761. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sharma MD, Baban B, Chandler P, Hou DY,
Singh N, Yagita H, Azuma M, Blazar BR, Mellor AL and Munn DH:
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells from mouse tumor-draining lymph nodes
directly activate mature Tregs via indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J
Clin Invest. 117:2570–2582. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sharma MD, Hou DY, Liu Y, Koni PA, Metz R,
Chandler P, Mellor AL, He Y and Munn DH: Indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase controls conversion of Foxp3+ Tregs to
TH17-like cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Blood.
113:6102–6111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lochner M, Berod L and Sparwasser T: Fatty
acid metabolism in the regulation of T cell function. Trends
Immunol. 36:81–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|