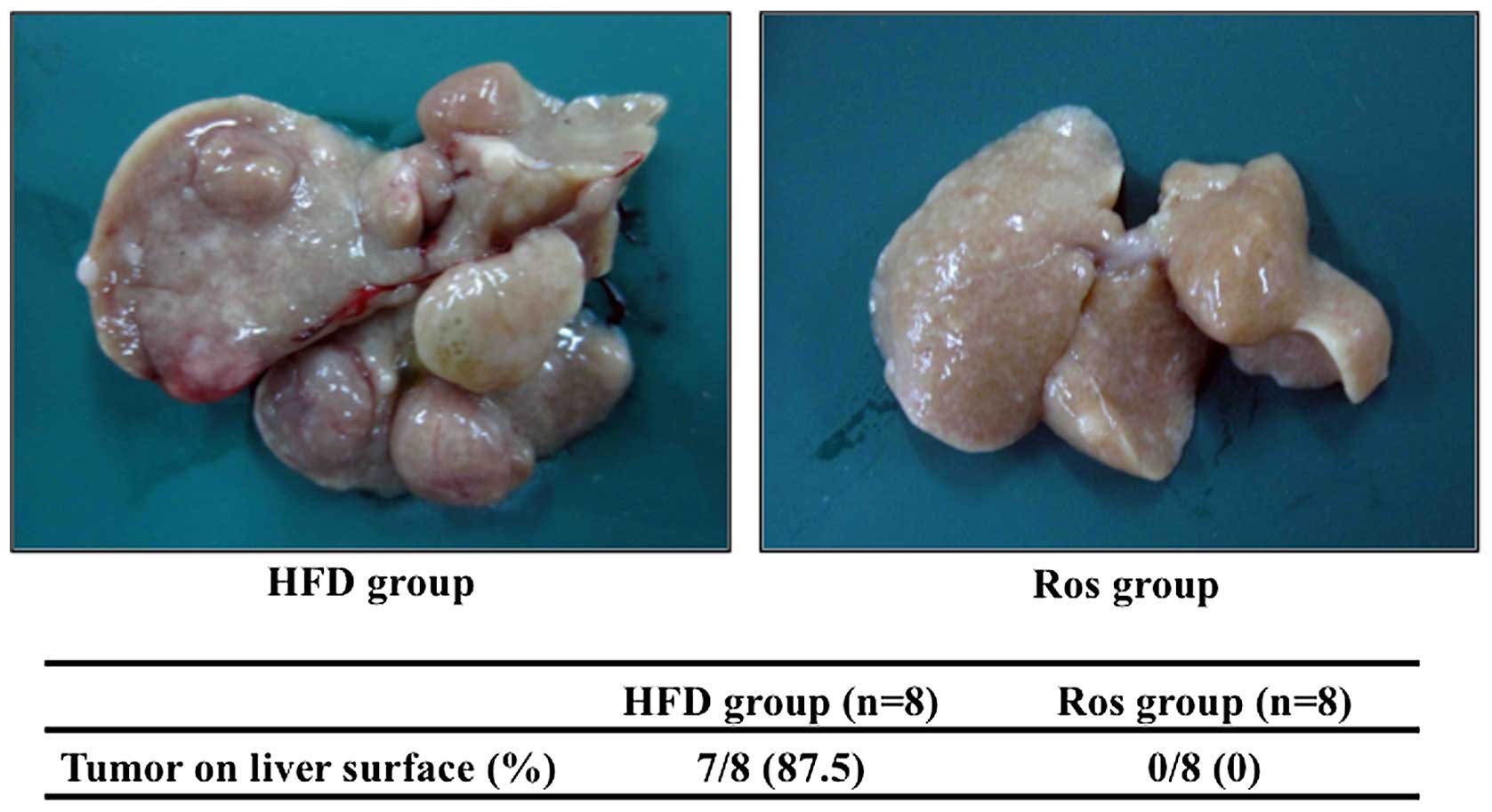
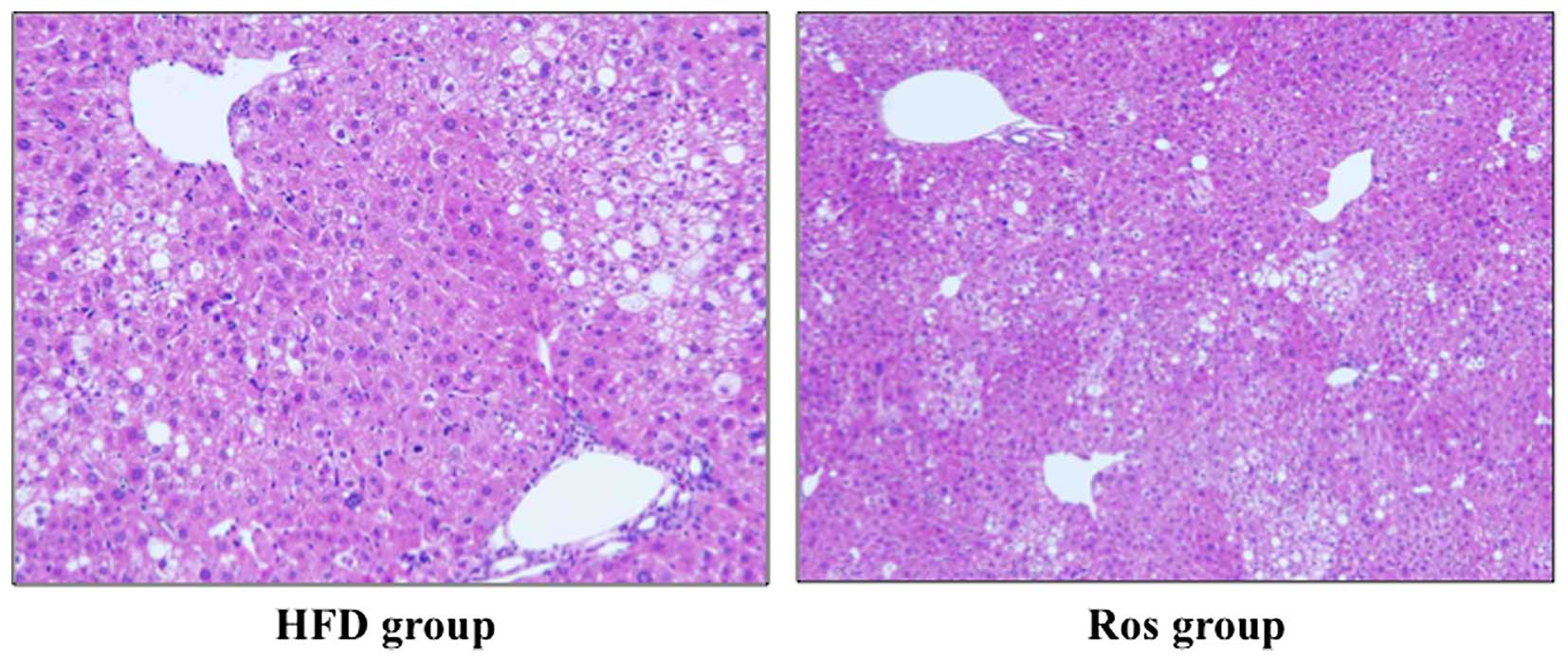
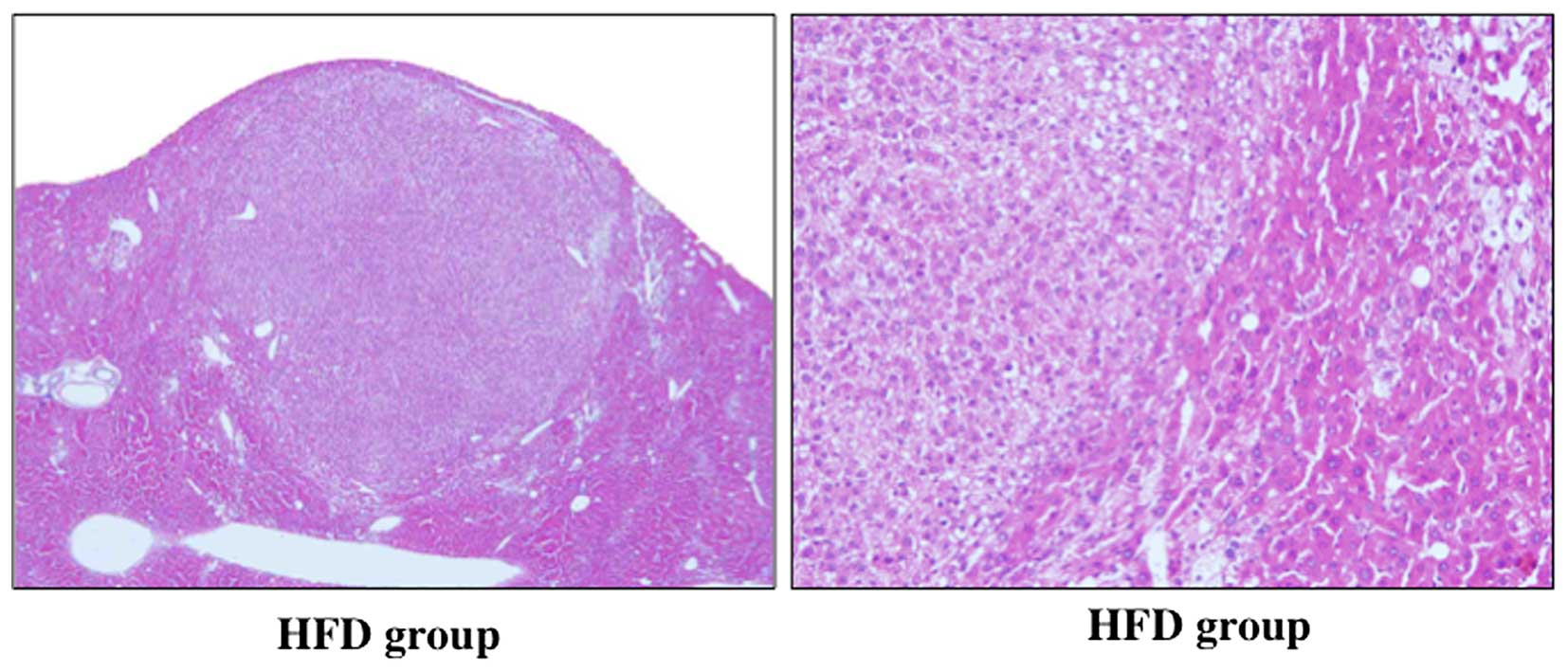
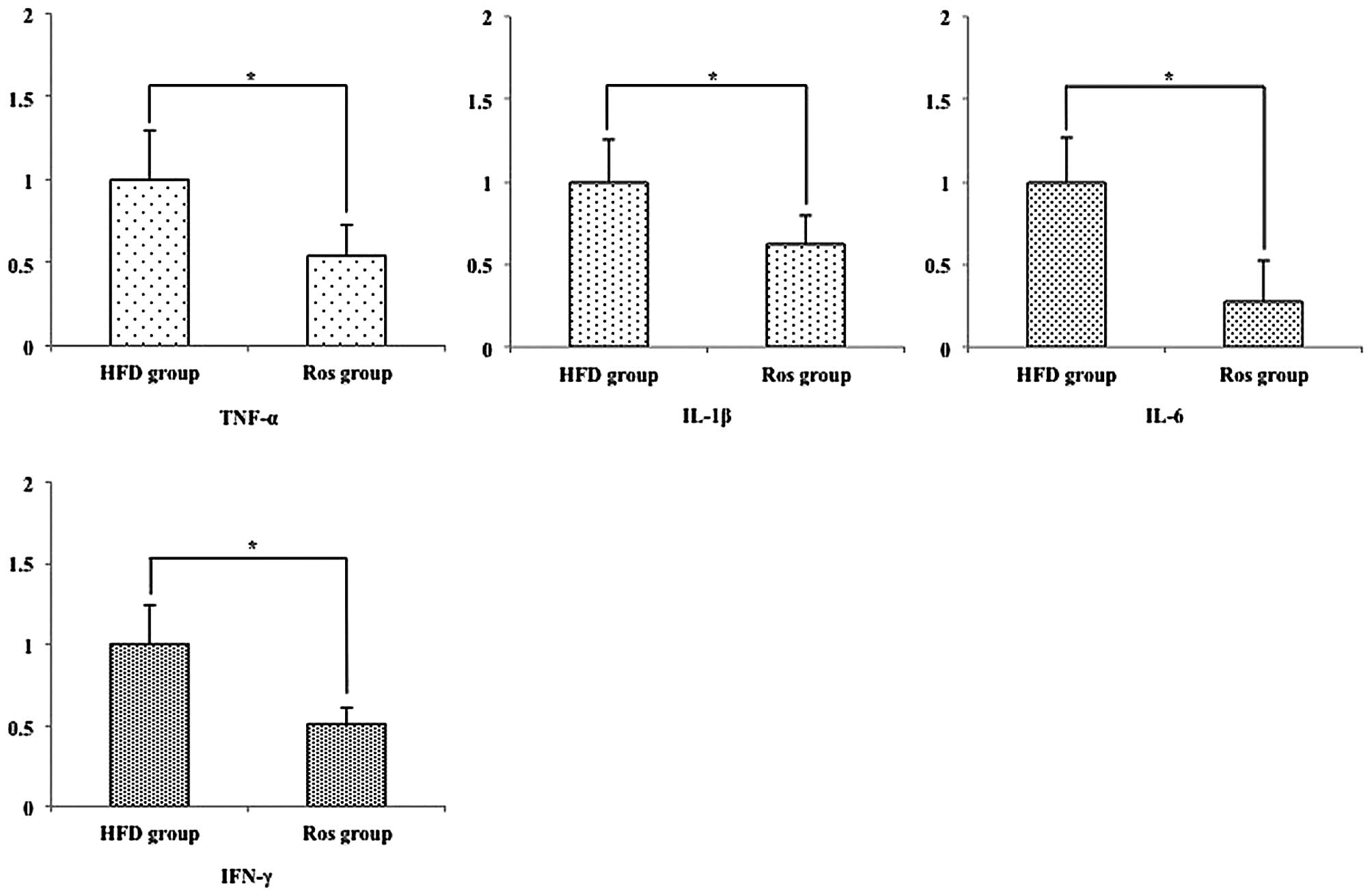
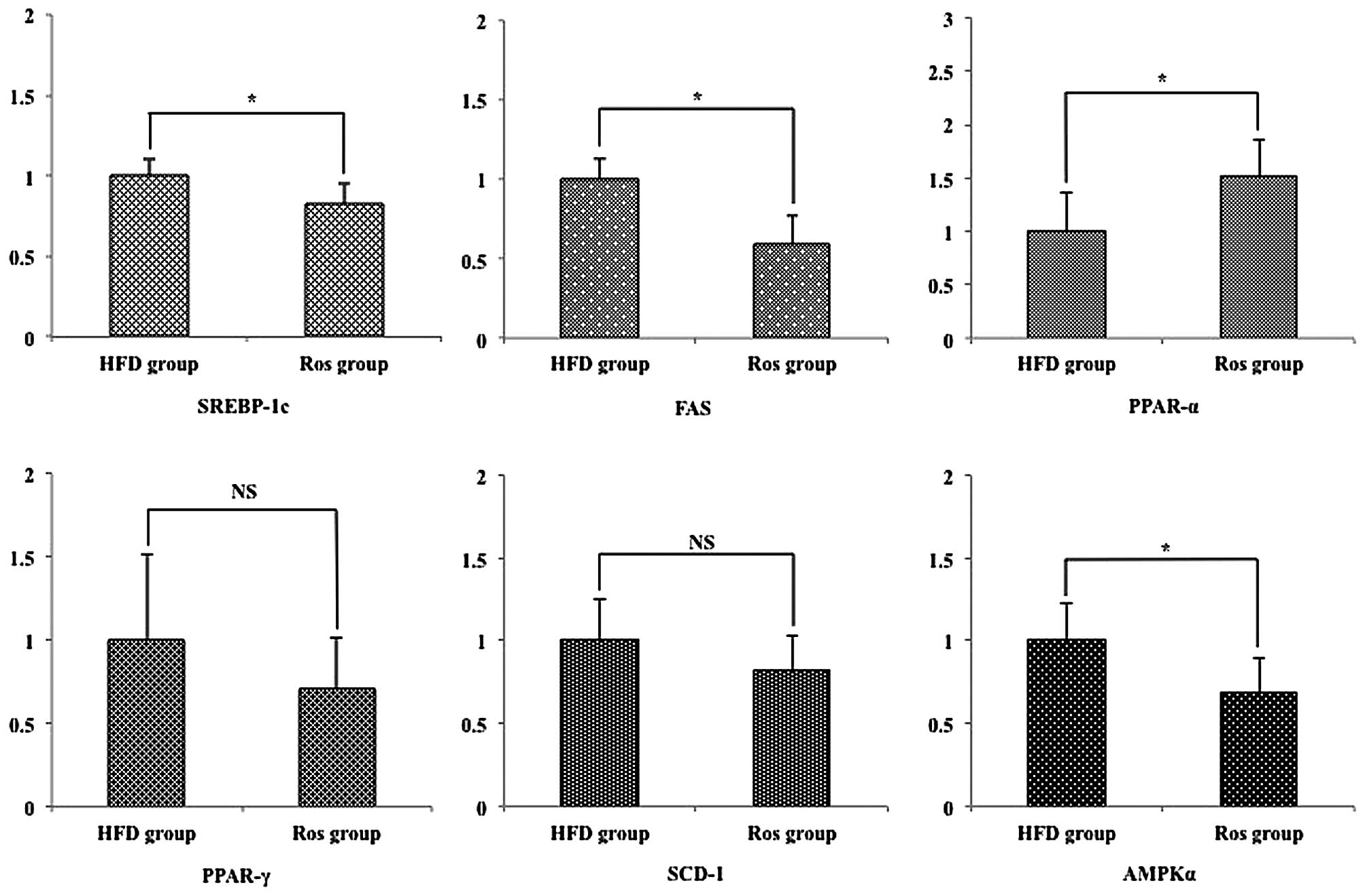
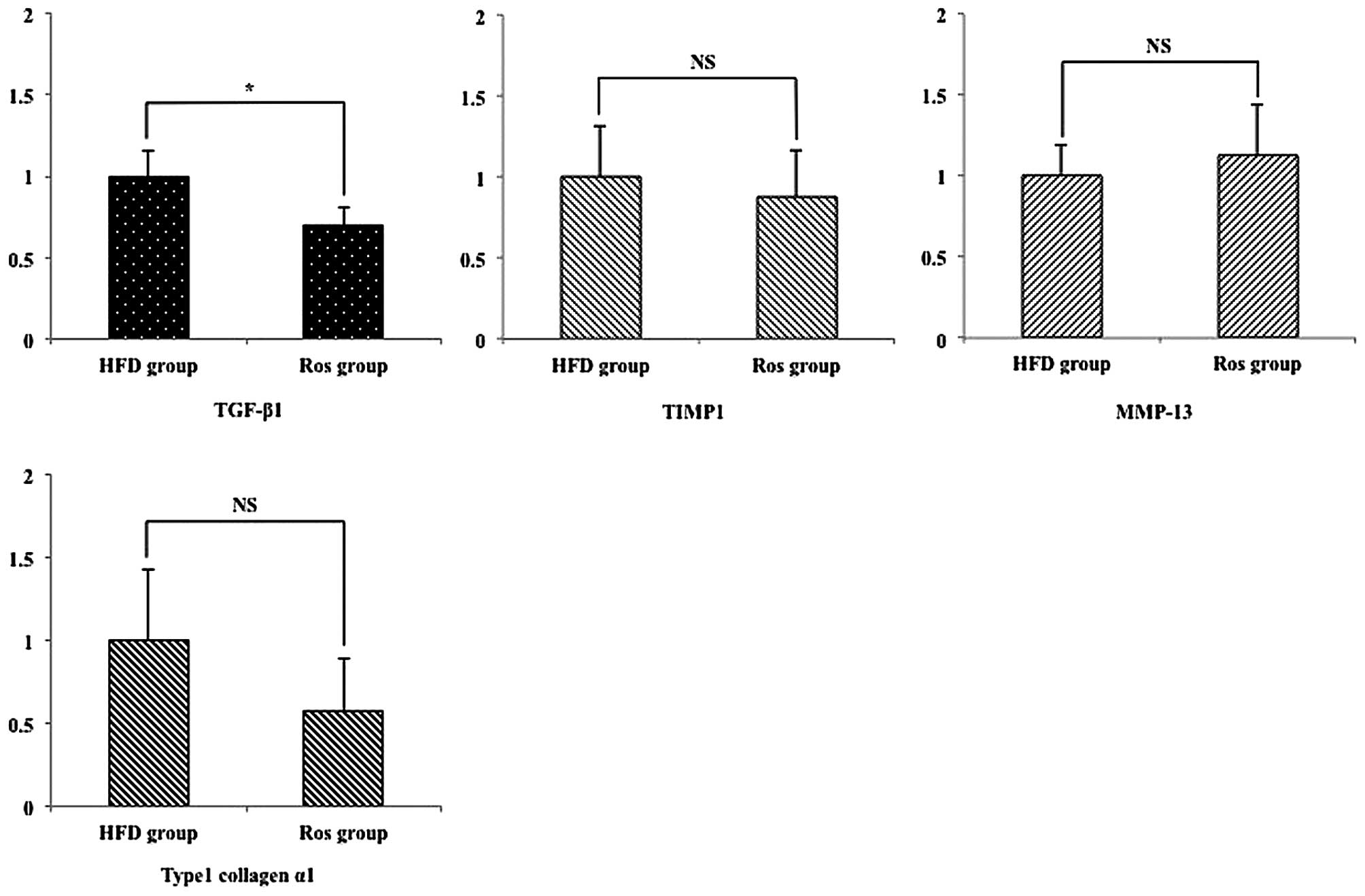
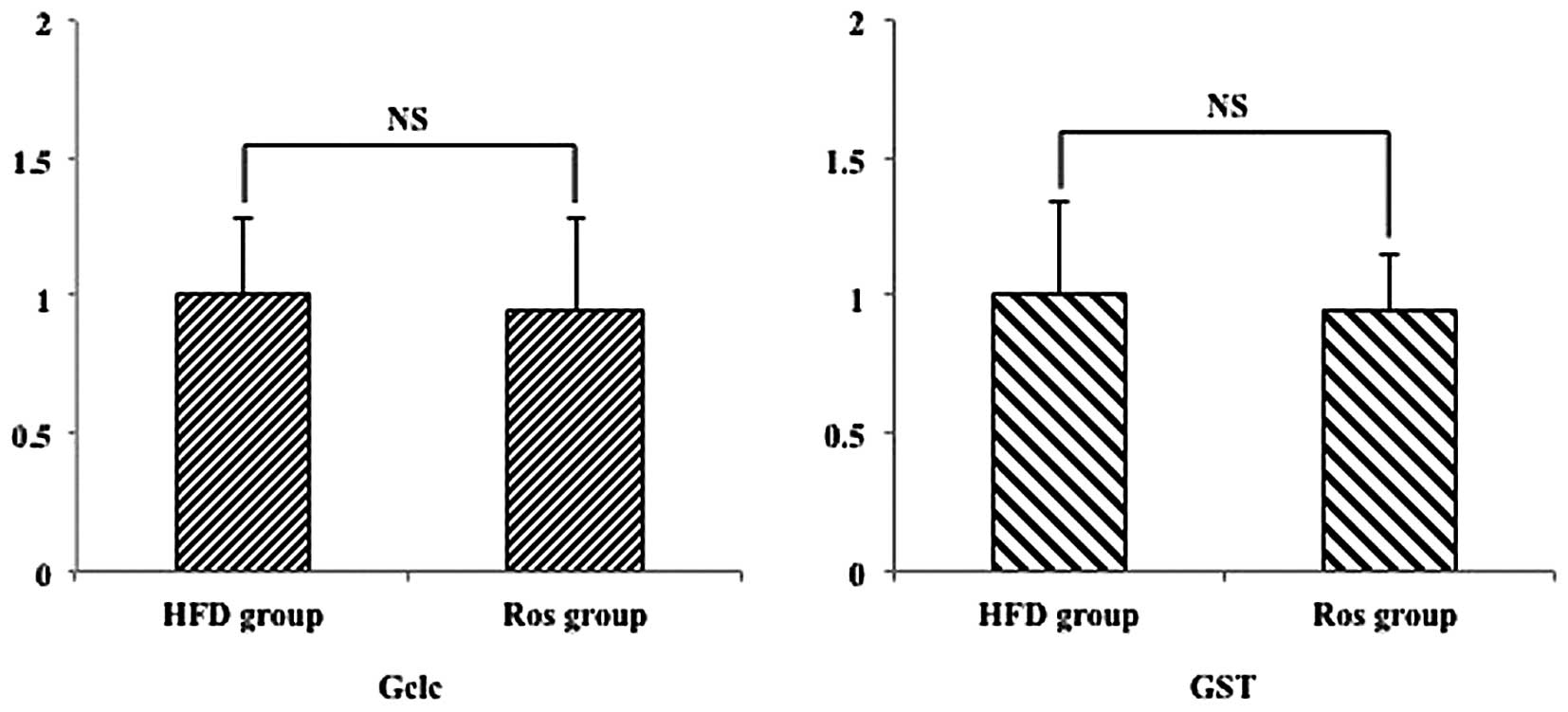
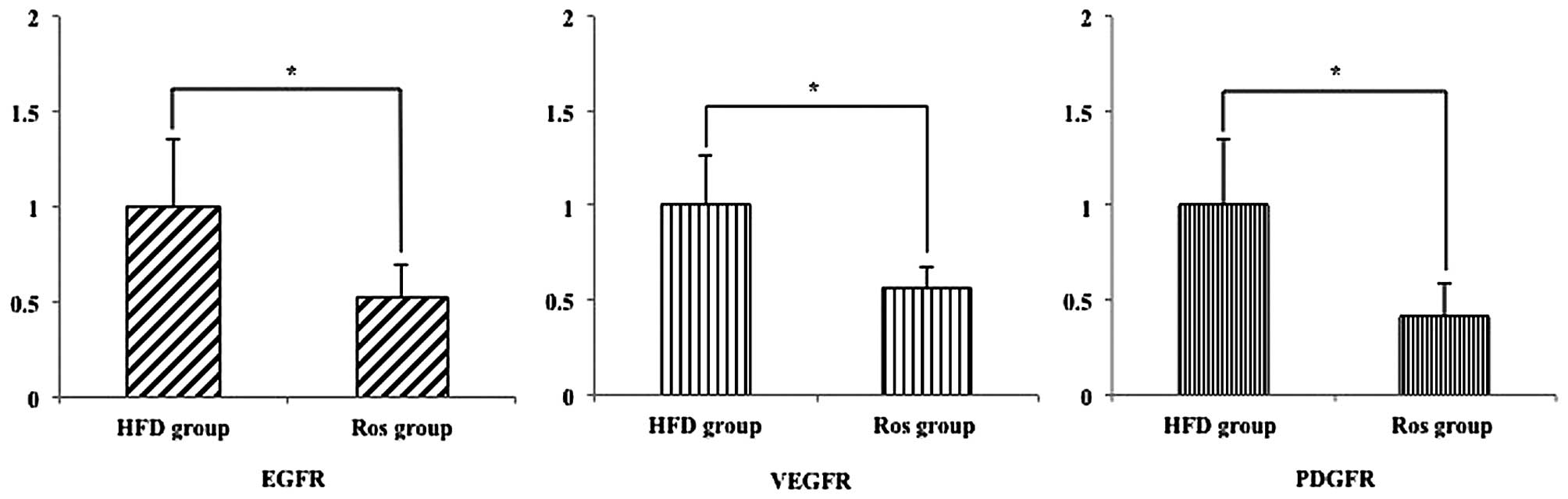
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB and Oh
BJ: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a
hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 55:434–438.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aviram M, Rosenblat M, Bisgaier CL and
Newton RS: Atrovastatin and gemfibrozil metabolities, but not the
parent drugs are potent antioxidants against lipoprotein oxidation.
Antherosclerosis. 138:272–280. 1998.
|
|
5
|
Ridker PM, Cannon CP, Morrow D, Rifai N,
Rose LM, McCabe CH, Pfeffer MA and Braunwald E; Pravastatin or
Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy-Thrombolysis in
Myocardial Infarction 22 (PROVE IT-TIMI 22) Investigators:
C-reactive protein levels and outcomes after statin therapy. N Engl
J Med. 352:20–28. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laufs U, La Fata V, Plutzky J and Liao JK:
Upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by HMG CoA
reductase inhibitors. Circulation. 97:1129–1135. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nezasa K, Higaki K, Matsumura T, Inazawa
K, Hasegawa H, Nakano M and Koike M: Liver-specific distribution of
rosuvastatin in rats: Comparison with pravastatin and simvastatin.
Drug Metab Dispos. 30:1158–1163. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ikeda Y, Young LH and Lefer AM:
Rosuvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, protects ischemic
reperfused myocardium in normocholesterolemic rats. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 41:649–656. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bulhak A, Sjoquist PO and Pernow J:
Rosuvastatin protects the myocardium against ischaemia-reperfusion
injury via inhibition of GGPP synthesis. Cardiovasc J S Afr.
15:S112004.
|
|
10
|
Weinberg EO, Scherrer-Crosbie M, Picard
MH, Nasseri BA, MacGillivray C, Gannon J, Lian Q, Bloch KD and Lee
RT: Rosuvastatin reduces experimental left ventricular infarct size
after ischemia-reperfusion injury but not total coronary occlusion.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 288:H1802–H1809. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bulhak AA, Gourine AV, Gonon AT, Sjöquist
PO, Valen G and Pernow J: Oral pre-treatment with rosuvastatin
protects porcine myocardium from ischaemia/reperfusion injury via a
mechanism related to nitric oxide but not to serum cholesterol
level. Acta Physiol Scand. 183:151–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takakura K, Koido S, Fujii M, Hashiguchi
T, Shibazaki Y, Yoneyama H, Katagi H, Kajihara M, Misawa T, Homma
S, et al: Characterization of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-derived
hepatocellular carcinoma as a human stratification model in mice.
Anticancer Res. 34:4849–4855. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao B: Innate immunity and
steatohepatitis: A critical role of another toll (TLR-9).
Gastroenterology. 139:27–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Horton JD, Shah NA, Warrington JA,
Anderson NN, Park SW, Brown MS and Goldstein JL: Combined analysis
of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout
mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:12027–12032. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Foretz M, Ancellin N, Andreelli F,
Saintillan Y, Grondin P, Kahn A, Thorens B, Vaulont S and Viollet
B: Short-term overexpression of a constitutively active form of
AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver leads to mild
hypoglycemia and fatty liver. Diabetes. 54:1331–1339. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cohen P and Friedman JM: Leptin and the
control of metabolism: Role for stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1).
J Nutr. 134:2455S–2463S. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu S, Rao S and Reddy JK: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors, fatty acid oxidation,
steatohepatitis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Curr Mol Med. 3:561–572.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI
and Spiegelman BM: mPPAR gamma 2: Tissue-specific regulator of an
adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev. 8:1224–1234. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Friedman SL: The cellular basis of hepatic
fibrosis. Mechanism and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med.
328:1828–1835. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gorrini C, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 12:931–947. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chaparro M, González Moreno L,
Trapero-Marugán M, Medina J and Moreno-Otero R: Review article:
Pharmacological therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with sorafenib
and other oral agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 28:1269–1277. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Siegelin MD, Raskett CM, Gilbert CA, Ross
AH and Altieri DC: Sorafenib exerts anti-glioma activity in vitro
and in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 478:165–170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tontonoz P, Kim JB, Graves RA and
Spiegelman BM: ADD1: A novel helix-loop-helix transcription factor
associated with adipocyte determination and differentiation. Mol
Cell Biol. 13:4753–4759. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hardie DG and Carling D: The AMP-activated
protein kinase–fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem.
246:259–273. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Winder WW and Hardie DG: AMP-activated
protein kinase, a metabolic master switch: Possible roles in type 2
diabetes. Am J Physiol. 277:E1–E10. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishii H, Horie Y, Ohshima S, Anezaki Y,
Kinoshita N, Dohmen T, Kataoka E, Sato W, Goto T, Sasaki J, et al:
Eicosapentaenoic acid ameliorates steatohepatitis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatocyte-specific Pten-deficient
mice. J Hepatol. 50:562–571. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|