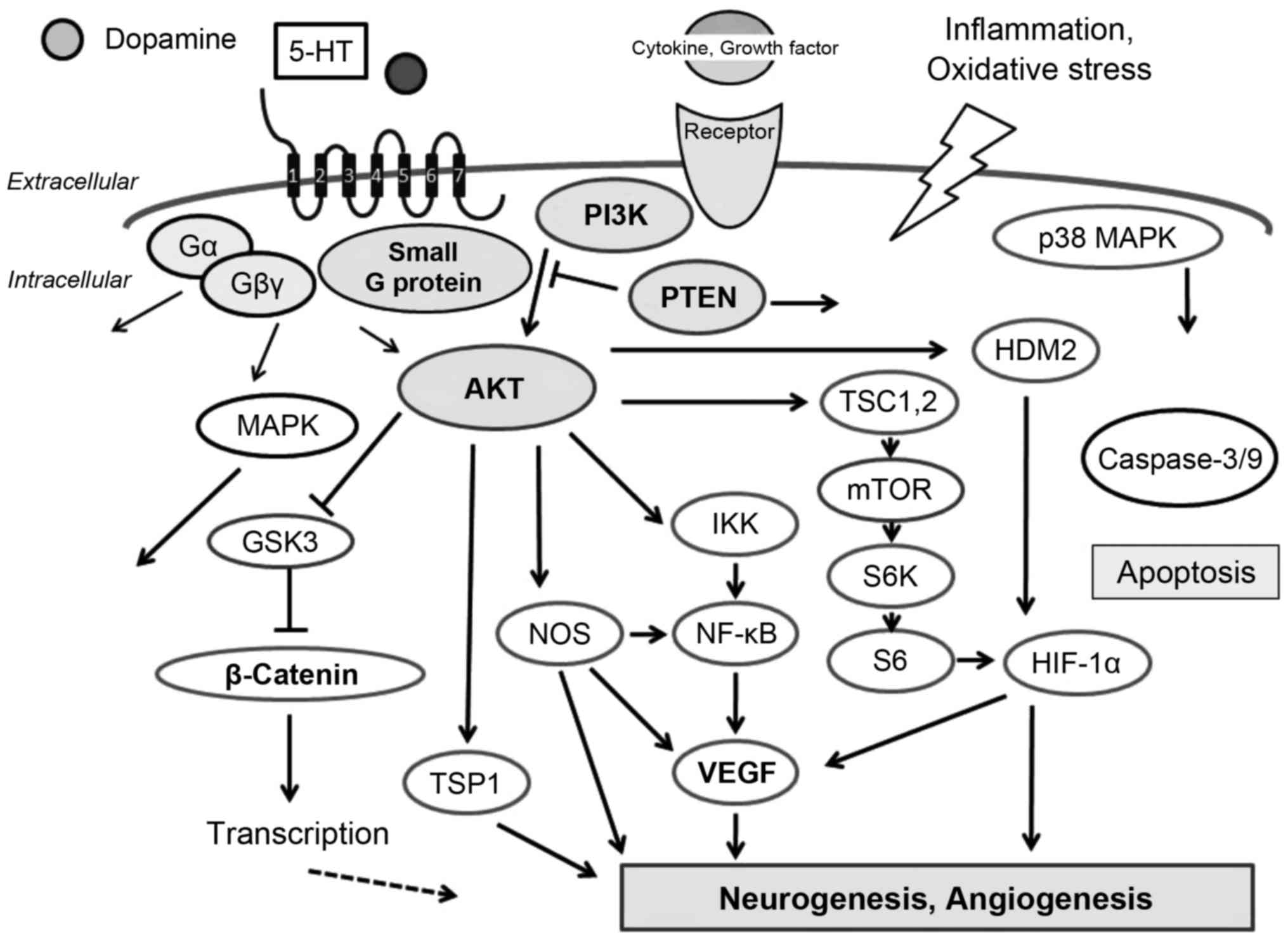
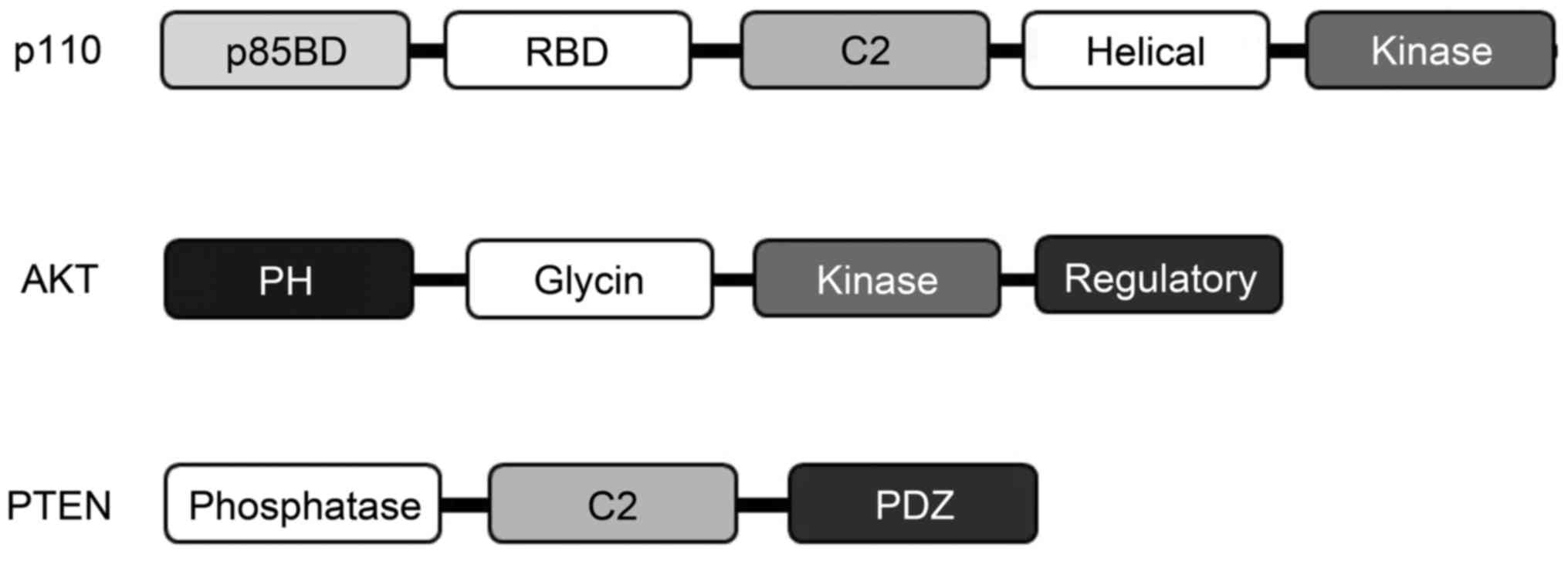
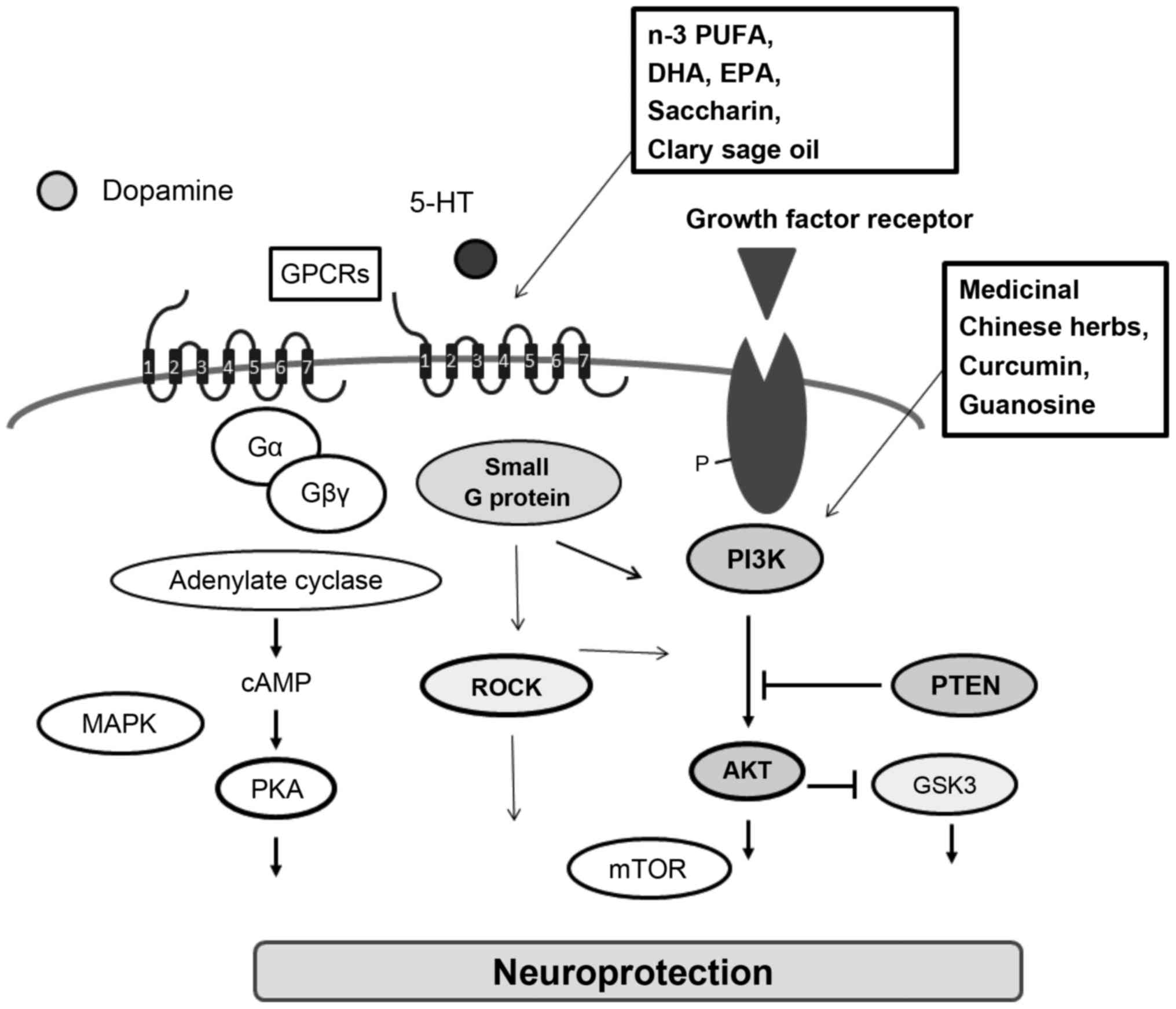
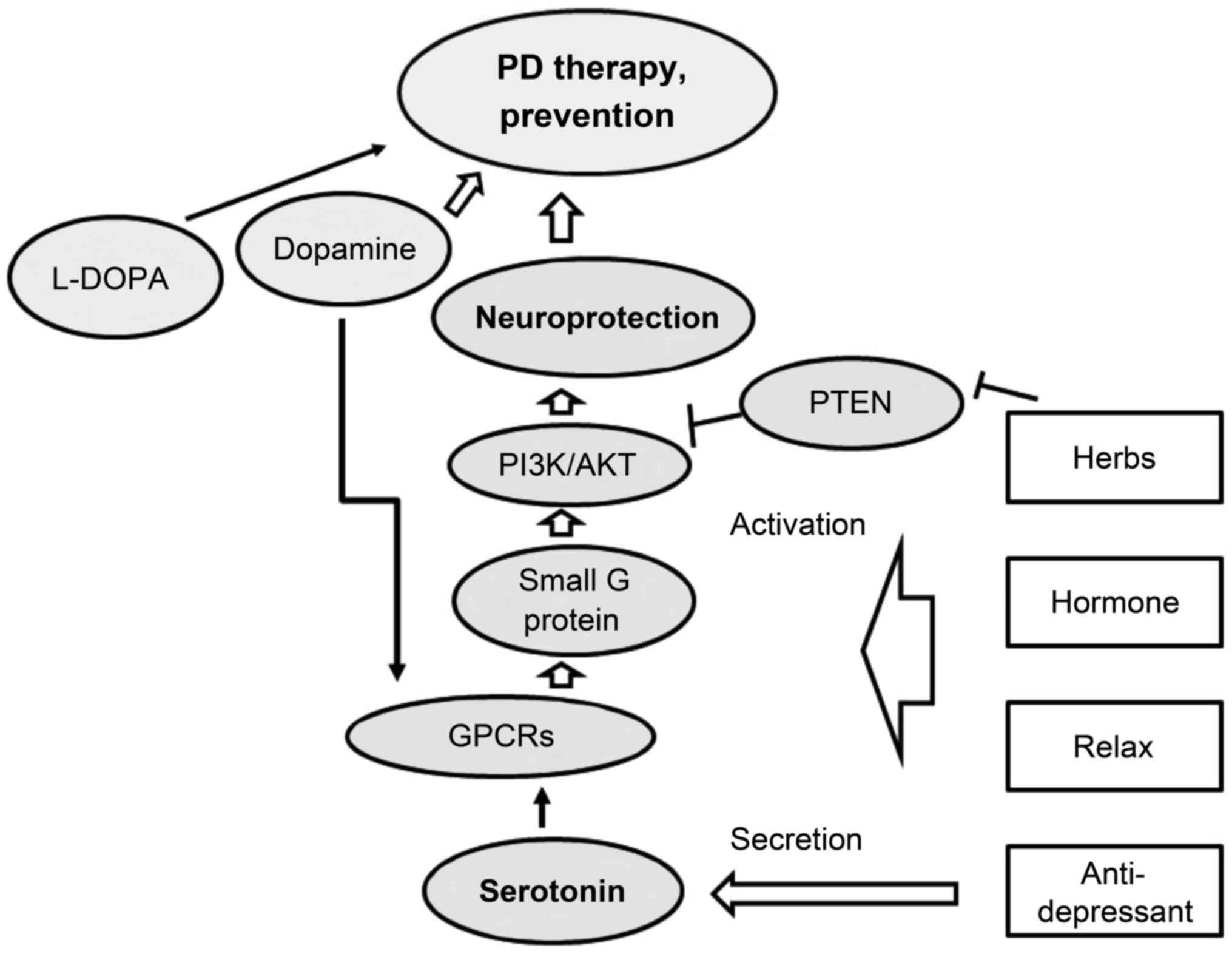
|
1
|
Armento ME, Stanley MA, Marsh L, Kunik ME,
York MK, Bush AL and Calleo JS: Cognitive behavioral therapy for
depression and anxiety in Parkinson's disease: A clinical review. J
Parkinsons Dis. 2:135–151. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jagmag SA, Tripathi N, Shukla SD, Maiti S
and Khurana S: Evaluation of models of Parkinson's disease. Front
Neurosci. 9:5032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Luo Y, Hoffer A, Hoffer B and Qi X:
Mitochondria: A therapeutic target for Parkinson's disease? Int J
Mol Sci. 16:20704–20730. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giráldez-Pérez R, Antolín-Vallespín M,
Muñoz M and Sánchez-Capelo A: Models of α-synuclein aggregation in
Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2:1762014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim WS, Kågedal K and Halliday GM:
Alpha-synuclein biology in Lewy body diseases. Alzheimers Res Ther.
6:732014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tokuhira N, Kitagishi Y, Suzuki M, Minami
A, Nakanishi A, Ono Y, Kobayashi K, Matsuda S and Ogura Y:
PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway as a target for Crohn's disease therapy
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 35:10–16. 2015.
|
|
7
|
Nakanishi A, Wada Y, Kitagishi Y and
Matsuda S: Link between PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway and NOX protein in
diseases. Aging Dis. 5:203–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang JS, Cho CY, Hong CC, Yan MD, Hsieh
MC, Lay JD, Lai GM, Cheng AL and Chuang SE: Oxidative stress
enhances Axl-mediated cell migration through an Akt1/Rac1-dependent
mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:1246–1256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo H, Yang Y, Duan J, Wu P, Jiang Q and
Xu C: PTEN-regulated AKT/FoxO3a/Bim signaling contributes to
reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in selenite-treated
colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e4812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Wang S and Shang YC:
Oxidant stress and signal transduction in the nervous system with
the PI3-K, Akt, and mTOR cascade. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13830–13866.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma Y, Zhao P, Zhu J, Yan C, Li L, Zhang H,
Zhang M, Gao X and Fan X: Naoxintong protects primary neurons from
oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation induced injury through
PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016:58159462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Flor PJ and Acher FC: Orthosteric versus
allosteric GPCR activation: The great challenge of group-III
mGluRs. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:414–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bohn LM, Gainetdinov RR and Caron MG: G
protein-coupled receptor kinase/beta-arrestin systems and drugs of
abuse: Psychostimulant and opiate studies in knockout mice.
Neuromolecular Med. 5:41–50. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bhattacharya M, Babwah AV and Ferguson SS:
Small GTP-binding protein-coupled receptors. Biochem Soc Trans.
32:1040–1044. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu CY, Yang YC, Li CC, Liu KL, Lii CK and
Chen HW: Andrographolide inhibits TNFα-induced ICAM-1 expression
via suppression of NADPH oxidase activation and induction of HO-1
and GCLM expression through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt/AP-1
pathways in human endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 91:40–50.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song S, Zhou F and Chen WR: Low-level
laser therapy regulates microglial function through Src-mediated
signaling pathways: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:2192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akagi T, Murata K, Shishido T and Hanafusa
H: v-Crk activates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway by
utilizing focal adhesion kinase and H-Ras. Mol Cell Biol.
22:7015–7023. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ballou LM, Chattopadhyay M, Li Y, Scarlata
S and Lin RZ: Galphaq binds to p110alpha/p85alpha phosphoinositide
3-kinase and displaces Ras. Biochem J. 394:557–562. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Fritsch R, de Krijger I, Fritsch K, George
R, Reason B, Kumar MS, Diefenbacher M, Stamp G and Downward J: Ras
and Rho families of GTPases directly regulate distinct
phosphoinositide 3-kinase isoforms. Cell. 153:1050–1063. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dale LB, Bhattacharya M, Anborgh PH,
Murdoch B, Bhatia M, Nakanishi S and Ferguson SS: G protein-coupled
receptor kinase-mediated desensitization of metabotropic glutamate
receptor 1A protects against cell death. J Biol Chem.
275:38213–38220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suire S, Lécureuil C, Anderson KE,
Damoulakis G, Niewczas I, Davidson K, Guillou H, Pan D, Clark J,
Stephens L and Hawkins PT: GPCR activation of Ras and PI3Kc in
neutrophils depends on PLCβ2/β3 and the RasGEF RasGRP4. EMBO J.
31:3118–3129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu CL, Wang JZ, Xia XP, Pan CW, Shao XX,
Xia SL, Yang SX and Zheng B: Rab11-FIP2 promotes colorectal cancer
migration and invasion by regulating PI3K/AKT/MMP7 signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 470:397–404. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi GX, Cai W and Andres DA: Rit subfamily
small GTPases: Regulators in neuronal differentiation and survival.
Cell Signal. 25:2060–2068. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Uehara R, Hosoya H and Mabuchi I: In vivo
phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II in sea
urchin eggs and its role in controlling myosin localization and
function during cytokinesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 65:100–115.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Koyanagi M, Takahashi J, Arakawa Y, Doi D,
Fukuda H, Hayashi H, Narumiya S and Hashimoto N: Inhibition of the
Rho/ROCK pathway reduces apoptosis during transplantation of
embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors. J Neurosci Res.
86:270–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li G, Liu L, Shan C, Cheng Q, Budhraja A,
Zhou T, Cui H and Gao N: RhoA/ROCK/PTEN signaling is involved in
AT-101-mediated apoptosis in human leukemia cells in vitro and in
vivo. Cell Death Dis. 5:e9982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang S and Kim HM: The RhoA-ROCK-PTEN
pathway as a molecular switch for anchorage dependent cell
behavior. Biomaterials. 33:2902–2915. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song H and Gao D: Fasudil, a
Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, attenuates retinal
ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Mol Med. 28:193–198.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Man JH, Liang B, Gu YX, Zhou T, Li AL, Li
T, Jin BF, Bai B, Zhang HY, Zhang WN, et al: Gankyrin plays an
essential role in Ras-induced tumorigenesis through regulation of
the RhoA/ROCK pathway in mammalian cells. J Clin Invest.
120:2829–2841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Dhand R,
Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry MJ, Waterfield MD and Downward J:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature.
370:527–532. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chu JM, Chen LW, Chan YS and Yung KK:
Neuroprotective effects of neurokinin receptor one in dopaminergic
neurons are mediated through Akt/PKB cell signaling pathway.
Neuropharmacology. 61:1389–1398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saunders C, Siuta M, Robertson SD, Davis
AR, Sauer J, Matthies HJ, Gresch PJ, Airey DC, Lindsley CW, Schetz
JA, et al: Neuronal ablation of p-Akt at Ser473 leads to altered
5-HT1A/2A receptor function. Neurochem Int. 73:113–121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Dizeyi N, Hedlund P, Bjartell A, Tinzl M,
Austild-Taskén K and Abrahamsson PA: Serotonin activates MAP kinase
and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in prostate cancer cell lines. Urol
Oncol. 29:436–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gil S, Park C, Lee J and Koh H: The roles
of striatal serotonin and L-amino-acid decarboxylase on
L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in a hemiparkinsonian rat model. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 30:817–825. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mazzucchi S, Frosini D, Ripoli A,
Nicoletti V, Linsalata G, Bonuccelli U and Ceravolo R: Serotonergic
antidepressant drugs and L-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's
disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 131:191–195. 2015.
|
|
37
|
Chan RJ, McBride AW and Crabb DW: Seven
transmembrane domain receptor subtypes identified in NG108-15 cells
by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 205:1311–1317. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
González-Maeso J and Sealfon SC:
Agonist-trafficking and hallucinogens. Curr Med Chem. 16:1017–1027.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Polter AM, Yang S, Jope RS and Li X:
Functional significance of glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulation by
serotonin. Cell Signal. 24:265–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zamani A and Qu Z: Serotonin activates
angiogenic phosphorylation signaling in human endothelial cells.
FEBS Lett. 586:2360–2365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yin JA, Liu XJ, Yuan J, Jiang J and Cai
SQ: Longevity manipulations differentially affect
serotonin/dopamine level and behavioral deterioration in aging
Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci. 34:3947–3958. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ivachtchenko AV and Ivanenkov YA: 5-HT(6)
receptor antagonists: A patent update. Part 1. Sulfonyl
derivatives. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 22:917–964. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ponimaskin E, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T,
Richter DW, Schachner M and Dityatev A: Morphogenic signaling in
neurons via neurotransmitter receptors and small GTPases. Mol
Neurobiol. 35:278–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang G and Stackman RW Jr: The role of
serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in memory and cognition. Front
Pharmacol. 6:2252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miguelez C, Morera-Herreras T, Torrecilla
M, Ruiz-Ortega JA and Ugedo L: Interaction between the 5-HT system
and the basal ganglia: Functional implication and therapeutic
perspective in Parkinson's disease. Front Neural Circuits.
8:212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cummings JL: Lewy body diseases with
dementia: Pathophysiology and treatment. Brain Cogn. 28:266–280.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Monti JM: The role of dorsal raphe nucleus
serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons, and of their receptors,
in regulating waking and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Sleep Med
Rev. 14:319–327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Monti JM and Jantos H: The roles of
dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep
and waking. Prog Brain Res. 172:625–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Soiza-Reilly M and Commons KG:
Quantitative analysis of glutamatergic innervation of the mouse
dorsal raphe nucleus using array tomography. J Comp Neurol.
519:3802–3814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Di Giovanni G, Esposito E and Di Matteo V:
Role of serotonin in central dopamine dysfunction. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 16:179–194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Roussakis AA, Politis M, Towey D and
Piccini P: Serotonin-to-dopamine transporter ratios in Parkinson
disease: Relevance for dyskinesias. Neurology. 86:1152–1158. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sekigawa A, Takamatsu Y, Sekiyama K and
Hashimoto M: Role of α-and β-synucleins in the axonal pathology of
Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies. Biomolecules.
5:1000–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Buddhala C, Loftin SK, Kuley BM, Cairns
NJ, Campbell MC, Perlmutter JS and Kotzbauer PT: Dopaminergic,
serotonergic, and noradrenergic deficits in Parkinson disease. Ann
Clin Transl Neurol. 2:949–959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mace JL, Porter RJ, Dalrymple-Alford JC,
Collins C and Anderson TJ: Acute tryptophan depletion and Lewy body
dementias. Int Psychogeriatr. 28:1487–1491. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Peña E, Mata M, López-Manzanares L, Kurtis
M, Eimil M, Martínez-Castrillo JC, Navas I, Posada IJ, Prieto C,
Ruíz-Huete C, et al: Antidepressants in Parkinson's disease.
Recommendations by the movement disorder study group of the
Neurological Association of Madrid. Neurologia. Mar 19–2016.Epub
ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kim SR, Chen X, Oo TF, Kareva T, Yarygina
O, Wang C, During M, Kholodilov N and Burke RE: Dopaminergic
pathway reconstruction by Akt/Rheb-induced axon regeneration. Ann
Neurol. 70:110–120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lin CH, Lin HI, Chen ML, Lai TT, Cao LP,
Farrer MJ, Wu RM and Chien CT: Lovastatin protects neurite
degeneration in LRRK2-G2019S parkinsonism through activating the
Akt/Nrf pathway and inhibiting GSK3β activity. Hum Mol Genet.
25:1965–1978. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cui Q, Li X and Zhu H: Curcumin
ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal oxidative damage via activation
of the Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:1381–1388. 2016.
|
|
59
|
Li X, Xie W, Xie C, Huang C, Zhu J, Liang
Z, Deng F, Zhu M, Zhu W, Wu R, et al: Curcumin modulates
miR-19/PTEN/AKT/p53 axis to suppress bisphenol A-induced MCF-7
breast cancer cell proliferation. Phytother Res. 28:1553–1560.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yu W, Zha W, Ke Z, Min Q, Li C, Sun H and
Liu C: Curcumin protects neonatal rat cardiomyocytes against high
glucose-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:41585912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chong CM, Zhou ZY, Razmovski-Naumovski V,
Cui GZ, Zhang LQ, Sa F, Hoi PM, Chan K and Lee SM: Danshensu
protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced damage of PC12 cells in
vitro and dopaminergic neurons in zebrafish. Neurosci Lett.
543:121–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S, Li X and Li Q:
Neuroprotective effects of puerarin on
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson's
disease model in mice. Phytother Res. 28:179–186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Bao XQ, Kong XC, Kong LB, Wu LY, Sun H and
Zhang D: Squamosamide derivative FLZ protected dopaminergic neuron
by activating Akt signaling pathway in 6-OHDA-induced in vivo and
in vitro Parkinson's disease models. Brain Res. 1547:49–57. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kwon SH, Ma SX, Hong SI, Kim SY, Lee SY
and Jang CG: Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. bark attenuates
6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death through inhibition of
oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 152:173–182.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dewapriya P, Himaya SW, Li YX and Kim SK:
Tyrosol exerts a protective effect against dopaminergic neuronal
cell death in in vitro model of Parkinson's disease. Food Chem.
141:1147–1157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tasaki Y, Yamamoto J, Omura T, Sakaguchi
T, Kimura N, Ohtaki K, Ono T, Suno M, Asari M, Ohkubo T, et al:
Meloxicam ameliorates motor dysfunction and dopaminergic
neurodegeneration by maintaining Akt-signaling in a mouse
Parkinson's disease model. Neurosci Lett. 521:15–19. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jin MC, Yoo JM, Sok DE and Kim MR:
Neuroprotective effect of N-acetyl-5-hydroxytryptamines on
glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in HT-22 cells. Neurochem Res.
39:2440–2451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ma J, Wang Z, Liu C, Shen H, Chen Z, Yin
J, Zuo G, Duan X, Li H and Chen G: Pramipexole-induced hypothermia
reduces early brain injury via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway in
subarachnoid hemorrhage rats. Sci Rep. 6:238172016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kuo HC, Chang HC, Lan WC, Tsai FH, Liao JC
and Wu CR: Protective effects of Drynaria fortunei against
6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage in B35 cells via the
PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct. 5:1956–1965. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Giuliani P, Ballerini P, Buccella S,
Ciccarelli R, Rathbone MP, Romano S, D'Alimonte I, Caciagli F, Di
Iorio P and Pokorski M: Guanosine protects glial cells against
6-hydroxydopamine toxicity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 837:23–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
He Z, Chen AY, Rojanasakul Y, Rankin GO
and Chen YC: Gallic acid, a phenolic compound, exerts
anti-angiogenic effects via the PTEN/AKT/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling
pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 35:291–297. 2016.
|
|
72
|
Caruso V, Le Grevés M, Shirazi Fard S,
Haitina T, Olszewski PK, Alsiö J, Schiöth HB and Fredriksson R: The
orphan G protein-coupled receptor gene GPR178 is evolutionary
conserved and altered in response to acute changes in food intake.
PLoS One. 10:e01220612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Guixà-González R, Javanainen M,
Gómez-Soler M, Cordobilla B, Domingo JC, Sanz F, Pastor M, Ciruela
F, Martinez-Seara H and Selent J: Membrane omega-3 fatty acids
modulate the oligomerisation kinetics of adenosine A2A and dopamine
D2 receptors. Sci Rep. 6:198392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Young G and Conquer J: Omega-3 fatty acids
and neuropsychiatric disorders. Reprod Nutr Dev. 45:1–28. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Young GS, Conquer JA and Thomas R: Effect
of randomized supplementation with high dose olive, flax or fish
oil on serum phospholipid fatty acid levels in adults with
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Reprod Nutr Dev.
45:549–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yang RH, Lin J, Hou XH, Cao R, Yu F, Liu
HQ, Ji AL, Xu XN, Zhang L and Wang F: Effect of docosahexaenoic
acid on hippocampal neurons in high-glucose condition: Involvement
of PI3K/AKT/nuclear factor-κB-mediated inflammatory pathways.
Neuroscience. 274:218–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Simon BR, Parlee SD, Learman BS, Mori H,
Scheller EL, Cawthorn WP, Ning X, Gallagher K, Tyrberg B,
Assadi-Porter FM, et al: Artificial sweeteners stimulate
adipogenesis and suppress lipolysis independently of sweet taste
receptors. J Biol Chem. 288:32475–32489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Huang W, Zhao Y, Zhu X, Cai Z, Wang S, Yao
S, Qi Z and Xie P: Fluoxetine upregulates phosphorylated-AKT and
phosphorylated-ERK1/2 proteins in neural stem cells: Evidence for a
crosstalk between AKT and ERK1/2 pathways. J Mol Neurosci.
49:244–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Morandini L, Ramallo MR, Moreira RG, Höcht
C, Somoza GM, Silva A and Pandolfi M: Serotonergic outcome, stress
and sexual steroid hormones, and growth in a South American cichlid
fish fed with an L-tryptophan enriched diet. Gen Comp Endocrinol.
223:27–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Seol GH, Shim HS, Kim PJ, Moon HK, Lee KH,
Shim I, Suh SH and Min SS: Antidepressant-like effect of Salvia
sclarea is explained by modulation of dopamine activities in rats.
J Ethnopharmacol. 130:187–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Lee KB, Cho E and Kang YS: Changes in
5-hydroxytryptamine and cortisol plasma levels in menopausal women
after inhalation of clary sage oil. Phytother Res. 28:1599–1605.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Qiu Y, Huang X, Huang L, Tang L, Jiang J,
Chen L and Li S: 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist improves behavior
performance of delirium rats through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR
activation-induced NLRP3 activity. IUBMB Life. 68:311–319. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Benmansour S, Privratsky AA, Adeniji OS
and Frazer A: Signaling mechanisms involved in the acute effects of
estradiol on 5-HT clearance. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
17:765–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cui J, Shen Y and Li R: Estrogen synthesis
and signaling pathways during aging: From periphery to brain.
Trends Mol Med. 19:197–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Nakaso K, Tajima N, Horikoshi Y, Nakasone
M, Hanaki T, Kamizaki K and Matsura T: The estrogen receptor
β-PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the cytoprotective effects of
tocotrienol in a cellular Parkinson's disease model. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1842:1303–1312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Marwarha G, Rhen T, Schommer T and Ghribi
O: The oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol regulates α-synuclein and
tyrosine hydroxylase expression levels in human neuroblastoma cells
through modulation of liver X receptors and estrogen receptors -
relevance to Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 119:1119–1136. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Deusser J, Schmidt S, Ettle B, Plötz S,
Huber S, Müller CP, Masliah E, Winkler J and Kohl Z: Serotonergic
dysfunction in the A53T alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson's
disease. J Neurochem. 135:589–597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fazili NA and Naeem A: Anti-fibrillation
potency of caffeic acid against an antidepressant induced
fibrillogenesis of human α-synuclein: Implications for Parkinson's
disease. Biochimie. 108:178–185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|