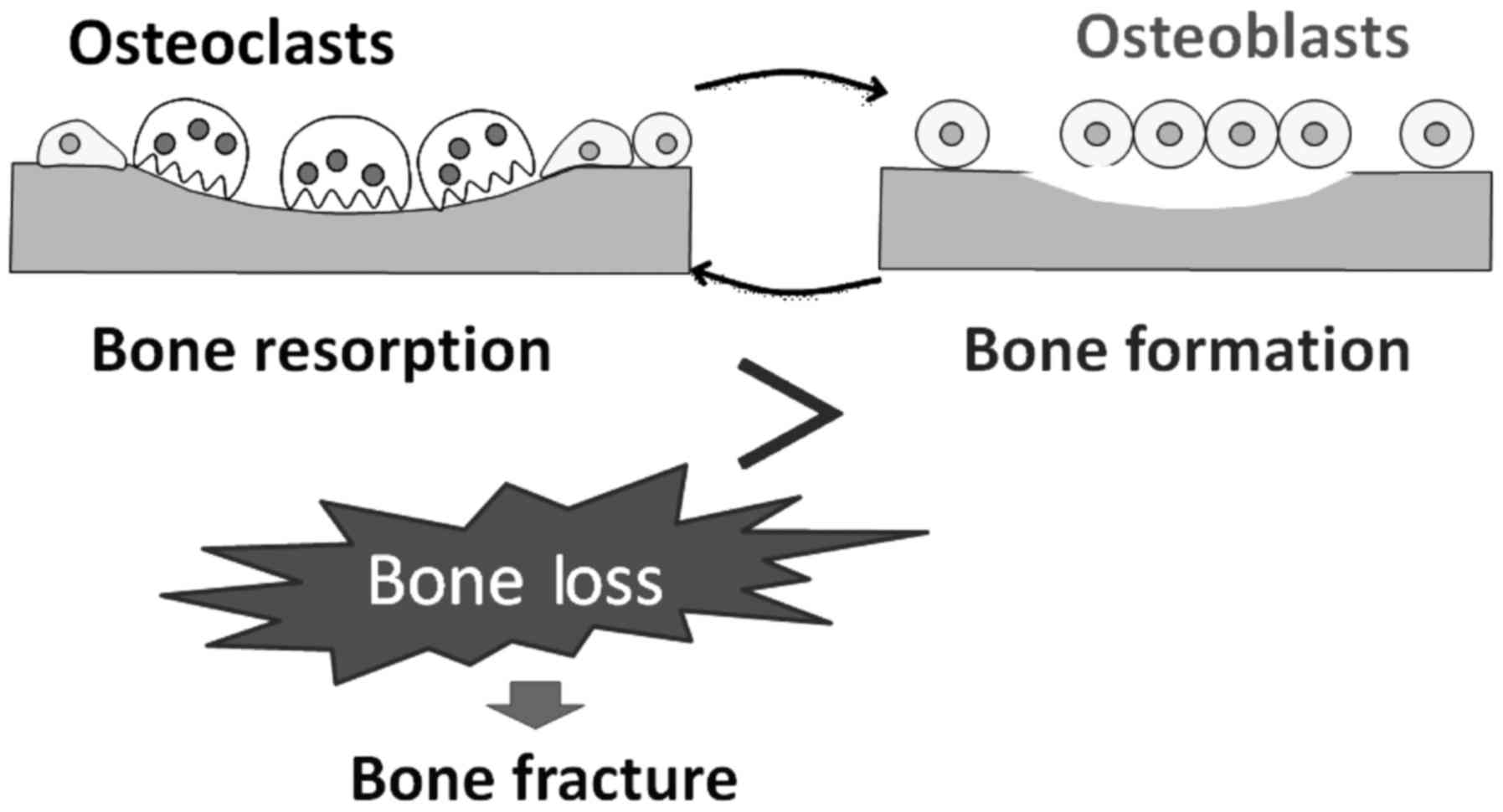
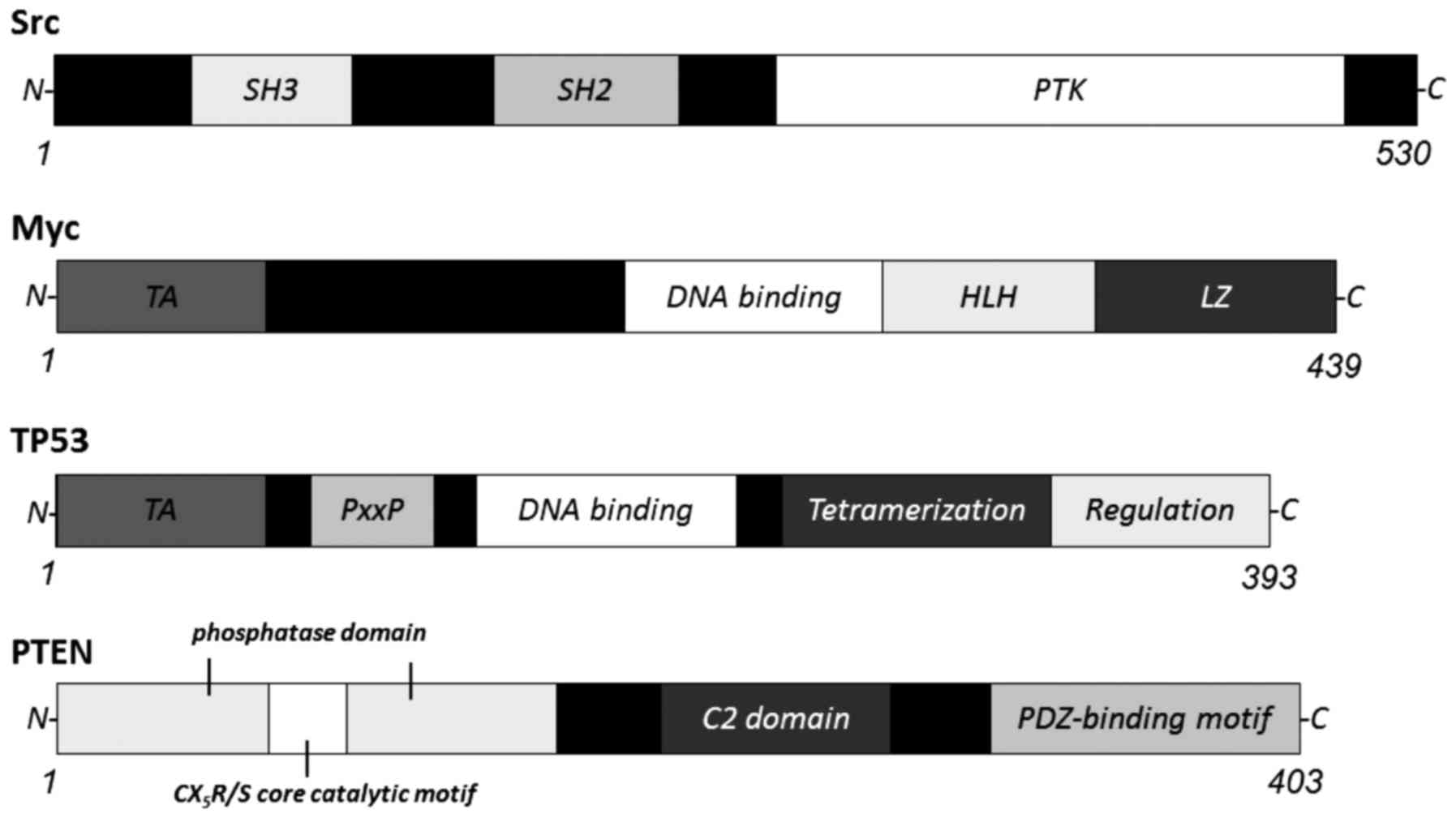
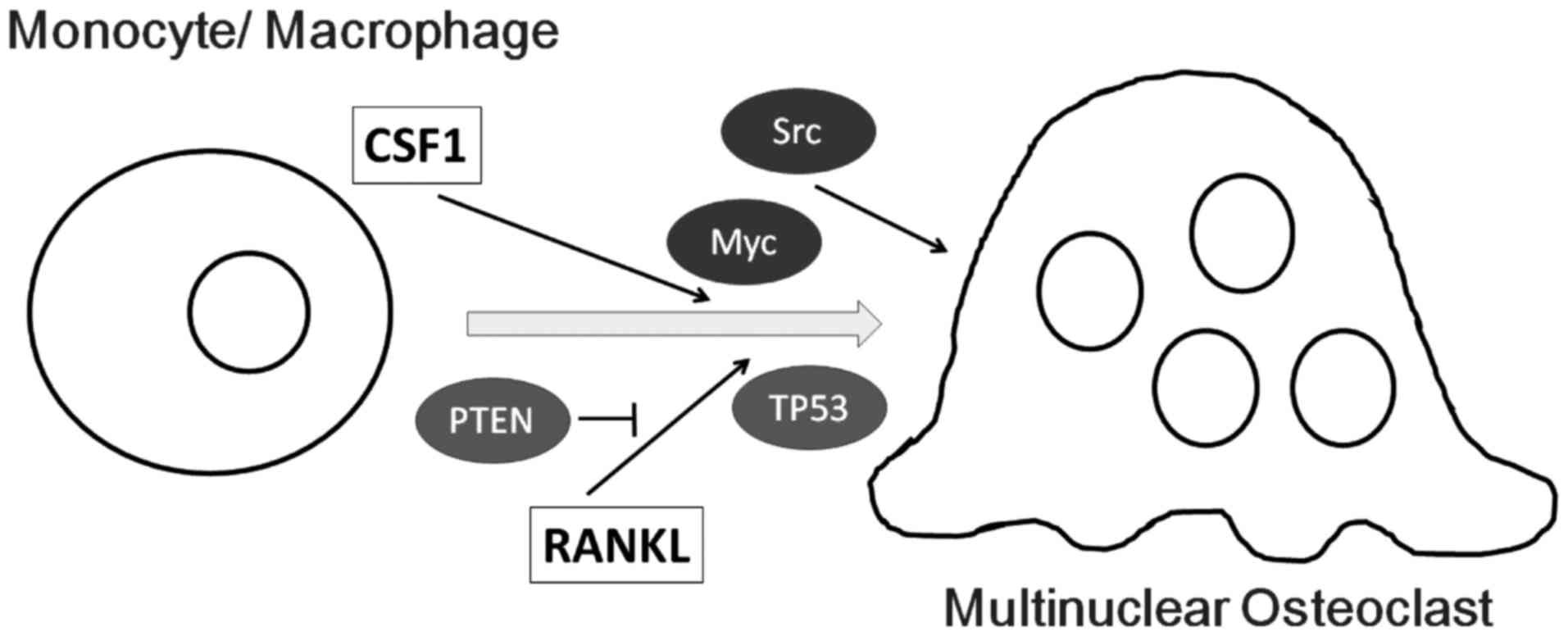
|
1
|
Ward LM, Konji VN and Ma J: The management
of osteoporosis in children. Osteoporos Int. 27:2147–2179. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pi C, Li YP, Zhou X and Gao B: The
expression and function of microRNAs in bone homeostasis. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 20:119–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Horwood NJ: Macrophage polarization and
bone formation: a review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 51:79–86. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sartori R and Sandri M: BMPs and the
muscle-bone connection. Bone. 80:37–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paul S, Lee JC and Yeh LC: A comparative
study on BMP-induced osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis in
primary cultures of adult rat bone marrow cells. Growth Factors.
27:121–131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Riggs BL, Khosla S and Melton LJ III: Sex
steroids and the construction and conservation of the adult
skeleton. Endocr Rev. 23:279–302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murphy CM, Schindeler A, Gleeson JP, Yu
NY, Cantrill LC, Mikulec K, Peacock L, O'Brien FJ and Little DG: A
collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold allows for binding and co-delivery
of recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins and bisphosphonates.
Acta Biomater. 10:2250–2258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Papapetrou PD: Bisphosphonate-associated
adverse events. Hormones (Athens). 8:96–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mandal CC, Ghosh-Choudhury G and
Ghosh-Choudhury N: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt signal relay
cooperates with Smad in bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced colony
stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) expression and osteoclast
differentiation. Endocrinology. 150:4989–4998. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lampiasi N, Russo R and Zito F: The
alternative faces of macrophage generate osteoclasts. BioMed Res
Int. 2016:90896102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mandal CC, Das F, Ganapathy S, Harris SE,
Choudhury GG and Ghosh-Choudhury N: Bone morphogenetic protein-2
(BMP-2) activates NFATc1 transcription factor via an autoregulatory
loop involving Smad/Akt/Ca2+ signaling. J Biol Chem.
291:1148–1161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li W, Liu Z, Zhao C and Zhai L: Binding of
MMP-9-degraded fibronectin to β6 integrin promotes invasion via the
FAK-Src-related Erk1/2 and PI3K/Akt/Smad-1/5/8 pathways in breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 34:1345–1352. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aguirre E, Renner O, Narlik-Grassow M and
Blanco-Aparicio C: Genetic modeling of PIM proteins in cancer:
proviral tagging and cooperation with oncogenes, tumor suppressor
genes, and carcinogens. Front Oncol. 4:1092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu XM and Salter MW: Src, a molecular
switch governing gain control of synaptic transmission mediated by
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:7697–7704. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ingraham CA, Cox ME, Ward DC, Fults DW and
Maness PF: c-Src and other proto-oncogenes implicated in neuronal
differentiation. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 10:1–14. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reichmann E: Oncogenes and epithelial cell
transformation. Semin Cancer Biol. 5:157–165. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kramer JL, Baltathakis I, Alcantara OS and
Boldt DH: Differentiation of functional dendritic cells and
macrophages from human peripheral blood monocyte precursors is
dependent on expression of p21 (WAF1/CIP1) and requires iron. Br J
Haematol. 117:727–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grabliauskaite K, Hehl AB, Seleznik GM,
Saponara E, Schlesinger K, Zuellig RA, Dittmann A, Bain M, Reding
T, Sonda S, et al: p21WAF1/Cip1 limits senescence and
acinar-to-ductal metaplasia formation during pancreatitis. J
Pathol. 235:502–514. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nakanishi A, Wada Y, Kitagishi Y and
Matsuda S: Link between PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway and NOX proteinin
diseases. Aging Dis. 5:203–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsuda S, Nakanishi A, Minami A, Wada Y
and Kitagishi Y: Functions and characteristics of PINK1 and Parkin
in cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 20:491–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Günzl P and Schabbauer G: Recent advances
in the genetic analysis of PTEN and PI3K innate immune properties.
Immunobiology. 213:759–765. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Appelman-Dijkstra NM and Papapoulos SE:
Modulating bone resorption and bone formation in opposite
directions in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Drugs.
75:1049–1058. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
An J, Yang H, Zhang Q, Liu C, Zhao J,
Zhang L and Chen B: Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis:
the effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone
formation. Life Sci. 147:46–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wagner EF and Eferl R: Fos/AP-1 proteins
in bone and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 208:126–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Asagiri M and Takayanagi H: The molecular
understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 40:251–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee MS, Kim HS, Yeon JT, Choi SW, Chun CH,
Kwak HB and Oh J: GM-CSF regulates fusion of mononuclear
osteoclasts into bone-resorbing osteoclasts by activating the
Ras/ERK pathway. J Immunol. 183:3390–3399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takayanagi H: The role of NFAT in
osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1116:227–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Macián F, López-Rodríguez C and Rao A:
Partners in transcription: NFAT and AP-1. Oncogene. 20:2476–2489.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng XZ, He LG, Wang S, Wang K, Zhang YY,
Tao L, Li XJ and Liu SW: Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1
activation and DC-STAMP expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 37:255–263.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee EJ, Kim JL, Gong JH, Park SH and Kang
YH: Inhibition of osteoclast activation by phloretin through
disturbing αvβ3 integrin-c-Src pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2015:6801452015.
|
|
31
|
Fukunaga T, Zou W, Warren JT and
Teitelbaum SL: Vinculin regulates osteoclast function. J Biol Chem.
289:13554–13564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shakespeare W, Yang M, Bohacek R, Cerasoli
F, Stebbins K, Sundaramoorthi R, Azimioara M, Vu C, Pradeepan S,
Metcalf C III, et al: Structure-based design of an
osteoclast-selective, nonpeptide src homology 2 inhibitor with in
vivo antiresorptive activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:9373–9378.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rucci N, Ricevuto E, Ficorella C, Longo M,
Perez M, Di Giacinto C, Funari A, Teti A and Migliaccio S: In vivo
bone metastases, osteoclastogenic ability, and phenotypic
characterization of human breast cancer cells. Bone. 34:697–709.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Recchia I, Rucci N, Funari A, Migliaccio
S, Taranta A, Longo M, Kneissel M, Susa M, Fabbro D and Teti A:
Reduction of c-Src activity by substituted
5,7-diphenyl-pyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidines induces osteoclast
apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Involvement of ERK1/2 pathway Bone.
34:65–79. 2004.
|
|
35
|
Battaglino R, Kim D, Fu J, Vaage B, Fu XY
and Stashenko P: c-Myc is required for osteoclast differentiation.
J Bone Miner Res. 17:763–773. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Daumer KM, Taparowsky EJ, Hall DJ and
Steinbeck MJ: Transcription from the tartrate-resistant acid
phosphatase promoter is negatively regulated by the Myc
oncoprotein. J Bone Miner Res. 17:1701–1709. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wilhelm K, Happel K, Eelen G, Schoors S,
Oellerich MF, Lim R, Zimmermann B, Aspalter IM, Franco CA, Boettger
T, et al: FOXO1 couples metabolic activity and growth state in the
vascular endothelium. Nature. 529:216–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adapala NS, Barbe MF, Tsygankov AY,
Lorenzo JA and Sanjay A: Loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction enhances
osteoclast survival due to p21-Ras mediated PI3K activation
independent of Cbl-b. J Cell Biochem. 115:1277–1289. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rubin J, Murphy TC, Rahnert J, Song H,
Nanes MS, Greenfield EM, Jo H and Fan X: Mechanical inhibition of
RANKL expression is regulated by H-Ras-GTPase. J Biol Chem.
281:1412–1418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sharma R, Wu X, Rhodes SD, Chen S, He Y,
Yuan J, Li J, Yang X, Li X, Jiang L, et al: Hyperactive Ras/MAPK
signaling is critical for tibial nonunion fracture in
neurofibromin-deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 22:4818–4828. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zauli G, Rimondi E, Corallini F, Fadda R,
Capitani S and Secchiero P: MDM2 antagonist Nutlin-3 suppresses the
proliferation and differentiation of human pre-osteoclasts through
a p53-dependent pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 22:1621–1630. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Kua HY, Hu Y, Guo K, Zeng Q, Wu Q,
Ng HH, Karsenty G, de Crombrugghe B, Yeh J, et al: p53 functions as
a negative regulator of osteoblastogenesis, osteoblast-dependent
osteoclastogenesis, and bone remodeling. J Cell Biol. 172:115–125.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zambetti GP, Horwitz EM and Schipani E:
Skeletons in the p53 tumor suppressor closet: genetic evidence that
p53 blocks bone differentiation and development. J Cell Biol.
172:795–797. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang J, Lazarenko OP, Blackburn ML,
Badger TM, Ronis MJ and Chen JR: Blueberry consumption prevents
loss of collagen in bone matrix and inhibits senescence pathways in
osteoblastic cells. Age (Dordr). 35:807–820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li Y and Tollefsbol TO: p16(INK4a)
suppression by glucose restriction contributes to human cellular
lifespan extension through SIRT1-mediated epigenetic and genetic
mechanisms. PLoS One. 6:e174212011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Campisi J and d'Adda di Fagagna F:
Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 8:729–740. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Huang H and Young KH: The PTEN
tumor suppressor gene and its role in lymphoma pathogenesis. Aging
(Albany NY). 7:1032–1049. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang LY, Ho-Fun Lee V, Wong AM, Kwong DL,
Zhu YH, Dong SS, Kong KL, Chen J, Tsao SW, Guan XY, et al:
Micro-RNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN.
Carcinogenesis. 34:454–463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Blüml S, Friedrich M, Lohmeyer T, Sahin E,
Saferding V, Brunner J, Puchner A, Mandl P, Niederreiter B, Smolen
JS, et al: Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in myeloid
cells controls inflammatory bone destruction by regulating the
osteoclastogenic potential of myeloid cells. Ann Rheum Dis.
74:227–233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jang HD, Noh JY, Shin JH, Lin JJ and Lee
SY: PTEN regulation by the Akt/GSK-3β axis during RANKL signaling.
Bone. 55:126–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sugatani T, Alvarez U and Hruska KA: PTEN
regulates RANKL- and osteopontin-stimulated signal transduction
during osteoclast differentiation and cell motility. J Biol Chem.
278:5001–5008. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hu G, Han C and Chen J: Inhibition of
oncogene expression by green tea and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate
in mice. Nutr Cancer. 24:203–209. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Prasad KN, Kumar A, Kochupillai V and Cole
WC: High doses of multiple antioxidant vitamins: essential
ingredients in improving the efficacy of standard cancer therapy. J
Am Coll Nutr. 18:13–25. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xie L, Jiang Y, Ouyang P, Chen J, Doan H,
Herndon B, Sylvester JE, Zhang K, Molteni A, Reichle M, et al:
Effects of dietary calorie restriction or exercise on the PI3K and
Ras signaling pathways in the skin of mice. J Biol Chem.
282:28025–28035. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang L, Bi HC, Liu YH, Wang YT, Xue XP
and Huang M: CAR-mediated up-regulation of CYP3A4 expression in
LS174T cells by Chinese herbal compounds. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.
26:331–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yeon JT, Kim KJ, Choi SW, Moon SH, Park
YS, Ryu BJ, Oh J, Kim MS, Erkhembaatar M, Son YJ, et al:
Anti-osteoclastogenic activity of praeruptorin A via inhibition of
p38/Akt-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling and PLCγ-independent Ca2+
oscillation. PLoS One. 9:e889742014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hasegawa S, Yonezawa T, Ahn JY, Cha BY,
Teruya T, Takami M, Yagasaki K, Nagai K and Woo JT: Honokiol
inhibits osteoclast differentiation and function in vitro. Biol
Pharm Bull. 33:487–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li J, Shao X, Wu L, Feng T, Jin C, Fang M,
Wu N and Yao H: Honokiol: an effective inhibitor of tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced up-regulation of inflammatory cytokine and
chemokine production in human synovial fibroblasts. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:380–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hahm ER, Singh KB and Singh SV: c-Myc is a
novel target of cell cycle arrest by honokiol in prostate cancer
cells. Cell Cycle. 15:2309–2320. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu H, Zang C, Emde A, Planas-Silva MD,
Rosche M, Kühnl A, Schulz CO, Elstner E, Possinger K and Eucker J:
Anti-tumor effect of honokiol alone and in combination with other
anti-cancer agents in breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:43–51.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang J, Lazarenko OP, Blackburn ML,
Shankar K, Badger TM, Ronis MJ and Chen JR: Feeding blueberry diets
in early life prevent senescence of osteoblasts and bone loss in
ovariectomized adult female rats. PLoS One. 6:e244862011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu W, Lu X, He G, Gao X, Li M, Wu J, Li
Z, Wu J, Wang J and Luo C: Cytosolic protection against ultraviolet
induced DNA damage by blueberry anthocyanins and anthocyanidins in
hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Biotechnol Lett. 35:491–498. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Vetterli L, Brun T, Giovannoni L, Bosco D
and Maechler P: Resveratrol potentiates glucose-stimulated insulin
secretion in INS-1E beta-cells and human islets through a
SIRT1-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 286:6049–6060. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Martí-Centelles R, Falomir E, Murga J,
Carda M and Marco JA: Inhibitory effect of cytotoxic stilbenes
related to resveratrol on the expression of the VEGF, hTERT and
c-Myc genes. Eur J Med Chem. 103:488–496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wang X, Wang D and Zhao Y: Effect and
mechanism of resveratrol on the apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma
cell line A549. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:527–531. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Lee SJ, Park K, Ha SD, Kim WJ and Moon SK:
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract inhibits human colon cancer cells:
the role of ERK1/2, G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest and p53
expression. Phytother Res. 24:1870–1876. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lee SJ, Ryu DH, Jang LC, Cho SC, Kim WJ
and Moon SK: Suppressive effects of an ethanol extract of Gleditsia
sinensis thorns on human SNU-5 gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
29:1609–1616. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lu Y, Li CS and Dong Q: Chinese herb
related molecules of cancer-cell-apoptosis: a minireview of
progress between Kanglaite injection and related genes. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 27:312008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li B, Zhao J, Wang CZ, Searle J, He TC,
Yuan CS and Du W: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis and
paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal cancer cells through
activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 301:185–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gali-Muhtasib H, Kuester D, Mawrin C,
Bajbouj K, Diestel A, Ocker M, Habold C, Foltzer-Jourdainne C,
Schoenfeld P, Peters B, et al: Thymoquinone triggers inactivation
of the stress response pathway sensor CHEK1 and contributes to
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:5609–5618.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ichwan SJ, Al-Ani IM, Bilal HG, Suriyah
WH, Taher M and Ikeda MA: Apoptotic activities of thymoquinone, an
active ingredient of black seed (Nigella sativa), in cervical
cancer cell lines. Chin J Physiol. 57:249–255. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lee SJ, Kim HM, Cho YH, Park K, Kim EJ,
Jung KH, Kim CH, Kim WJ and Moon SK: Aqueous extract of Magnolia
officinalis mediates proliferative capacity, p21WAF1 expression and
TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activity in human urinary bladder
cancer 5637 cells; involvement of p38 MAP kinase. Oncol Rep.
18:729–736. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dong LH, Wen JK, Miao SB, Jia Z, Hu HJ,
Sun RH, Wu Y and Han M: Baicalin inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through suppressing
PDGFRβ-ERK signaling and increase in p27 accumulation and prevents
injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia. Cell Res. 20:1252–1262.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang L, Pu Z and Wang J, Zhang Z, Hu D
and Wang J: Baicalin inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cell proliferation via the AKT/HIF-1α/p27-associated
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 15:8153–8168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Byambaragchaa M, Dela Cruz J, Kh A and
Hwang SG: Anticancer potential of an ethanol extract of Saussurea
involucrata against hepatic cancer cells in vitro. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:7527–7532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu J, Shen M, Yue Z, Yang Z, Wang M, Li
C, Xin C, Wang Y, Mei Q and Wang Z: Triptolide inhibits
colon-rectal cancer cells proliferation by induction of G1 phase
arrest through upregulation of p21. Phytomedicine. 19:756–762.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu TE, Zhang L, Wang S, Chen C and Zheng
J: Tripterygium glycosides induce premature ovarian failure in rats
by promoting p53 phosphorylation and activating the
serine/threonine kinase 11-p53-p21 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
10:12–18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Wong TF, Takeda T, Li B, Tsuiji K,
Kitamura M, Kondo A and Yaegashi N: Curcumin disrupts uterine
leiomyosarcoma cells through AKT-mTOR pathway inhibition. Gynecol
Oncol. 122:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yoshida H, Okumura N, Kitagishi Y,
Nishimura Y and Matsuda S: Ethanol extract of Rosemary repressed
PTEN expression in K562 culture cells. Int J Appl Biol Pharm
Technol. 2:316–322. 2011.
|
|
80
|
Wang X, He H, Lu Y, Ren W, Teng KY, Chiang
CL, Yang Z, Yu B, Hsu S, Jacob ST, et al: Indole-3-carbinol
inhibits tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
suppression of microRNA-21 and upregulation of phosphatase and
tensin homolog. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:244–253. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
Royston KJ and Tollefsbol TO: The
epigenetic impact of cruciferous vegetables on cancer prevention.
Curr Pharmacol Rep. 1:46–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Eason RR, Velarde MC, Chatman L Jr, Till
SR, Geng Y, Ferguson M, Badger TM and Simmen RC: Dietary exposure
to whey proteins alters rat mammary gland proliferation, apoptosis,
and gene expression during postnatal development. J Nutr.
134:3370–3377. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ghosh-Choudhury T, Mandal CC, Woodruff K,
St Clair P, Fernandes G, Choudhury GG and Ghosh-Choudhury N: Fish
oil targets PTEN to regulate NFkappaB for downregulation of
anti-apoptotic genes in breast tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 118:213–228. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Ishii H, Horie Y, Ohshima S, Anezaki Y,
Kinoshita N, Dohmen T, Kataoka E, Sato W, Goto T, Sasaki J, et al:
Eicosapentaenoic acid ameliorates steatohepatitis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatocyte-specific Pten-deficient
mice. J Hepatol. 50:562–571. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Rovito D, Giordano C, Vizza D, Plastina P,
Barone I, Casaburi I, Lanzino M, De Amicis F, Sisci D, Mauro L, et
al: Omega-3 PUFA ethanolamides DHEA and EPEA induce autophagy
through PPARγ activation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell
Physiol. 228:1314–1322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Kitagishi Y and Matsuda S: Diets involved
in PPAR and PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway may contribute to neuroprotection
in a traumatic brain injury. Alzheimers Res Ther. 5:422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Burdick AD, Bility MT, Girroir EE, Billin
AN, Willson TM, Gonzalez FJ and Peters JM: Ligand activation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-beta/delta(PPARbeta/delta) inhibits cell growth of human
N/TERT-1 keratinocytes. Cell Signal. 19:1163–1171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR, Siddharth S,
Das D, Nayak A and Kundu CN: Resveratrol and curcumin
synergistically induces apoptosis in cigarette smoke condensate
transformed breast epithelial cells through a p21(Waf1/Cip1)
mediated inhibition of Hh-Gli signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
66:75–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|