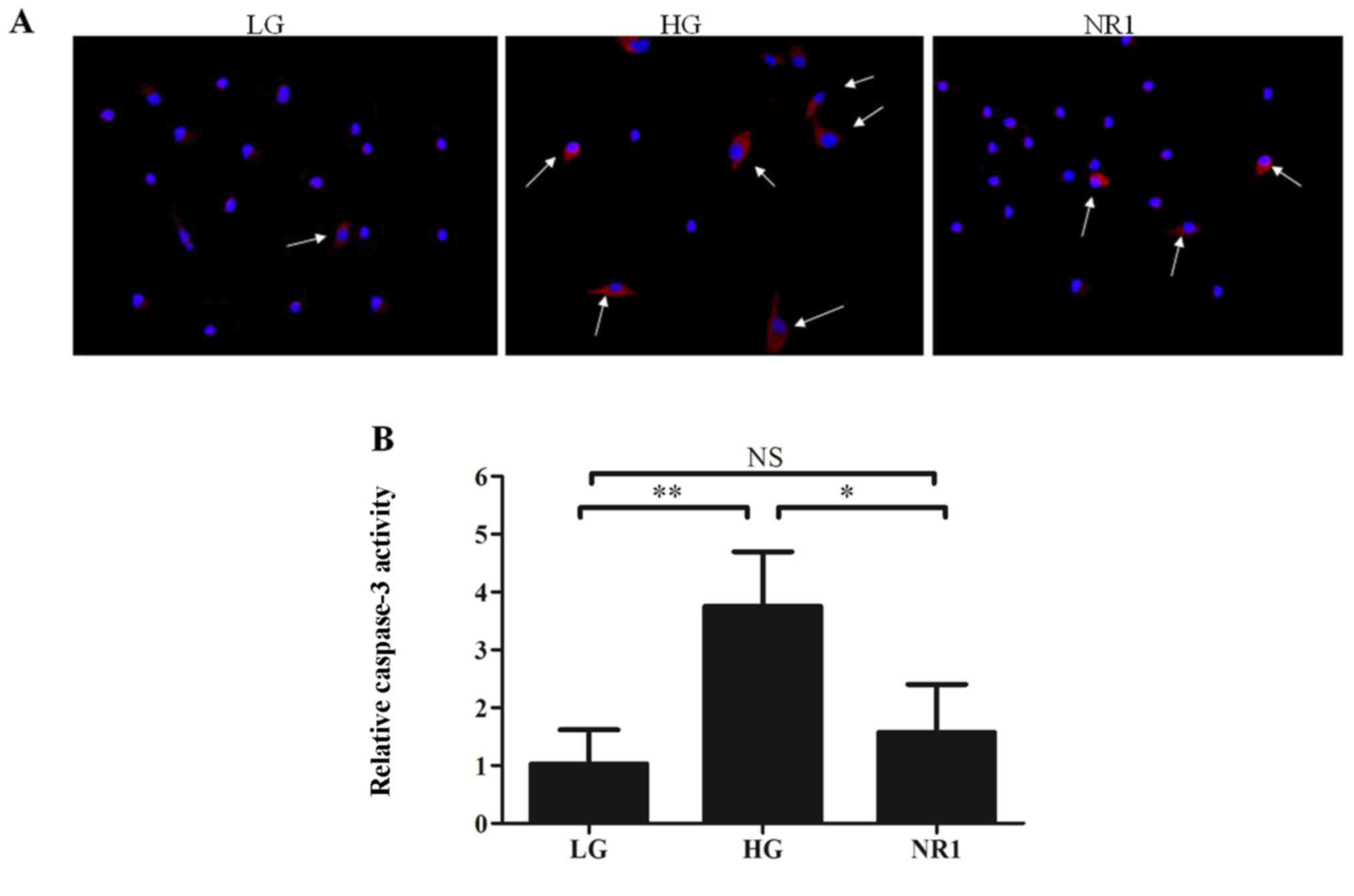
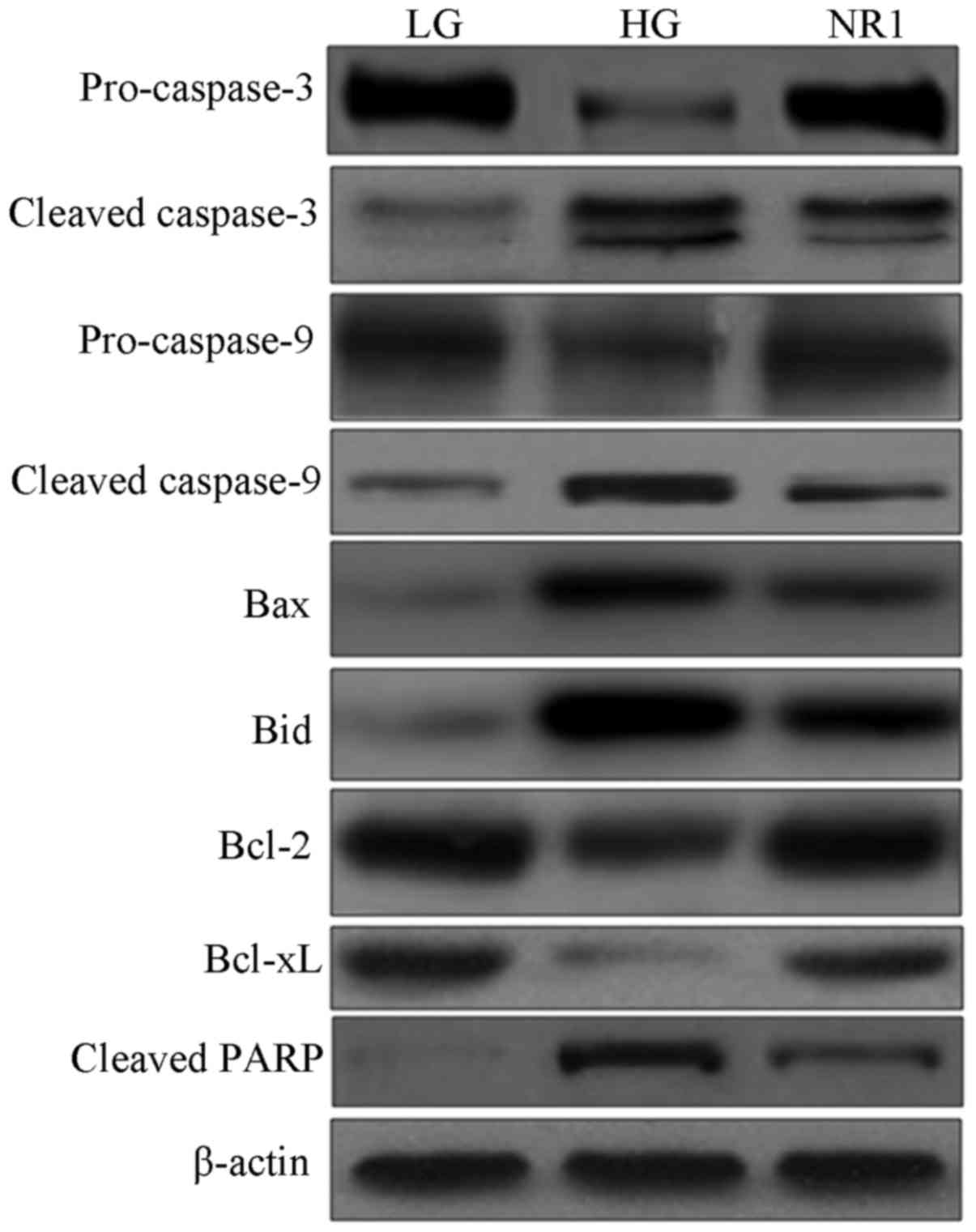
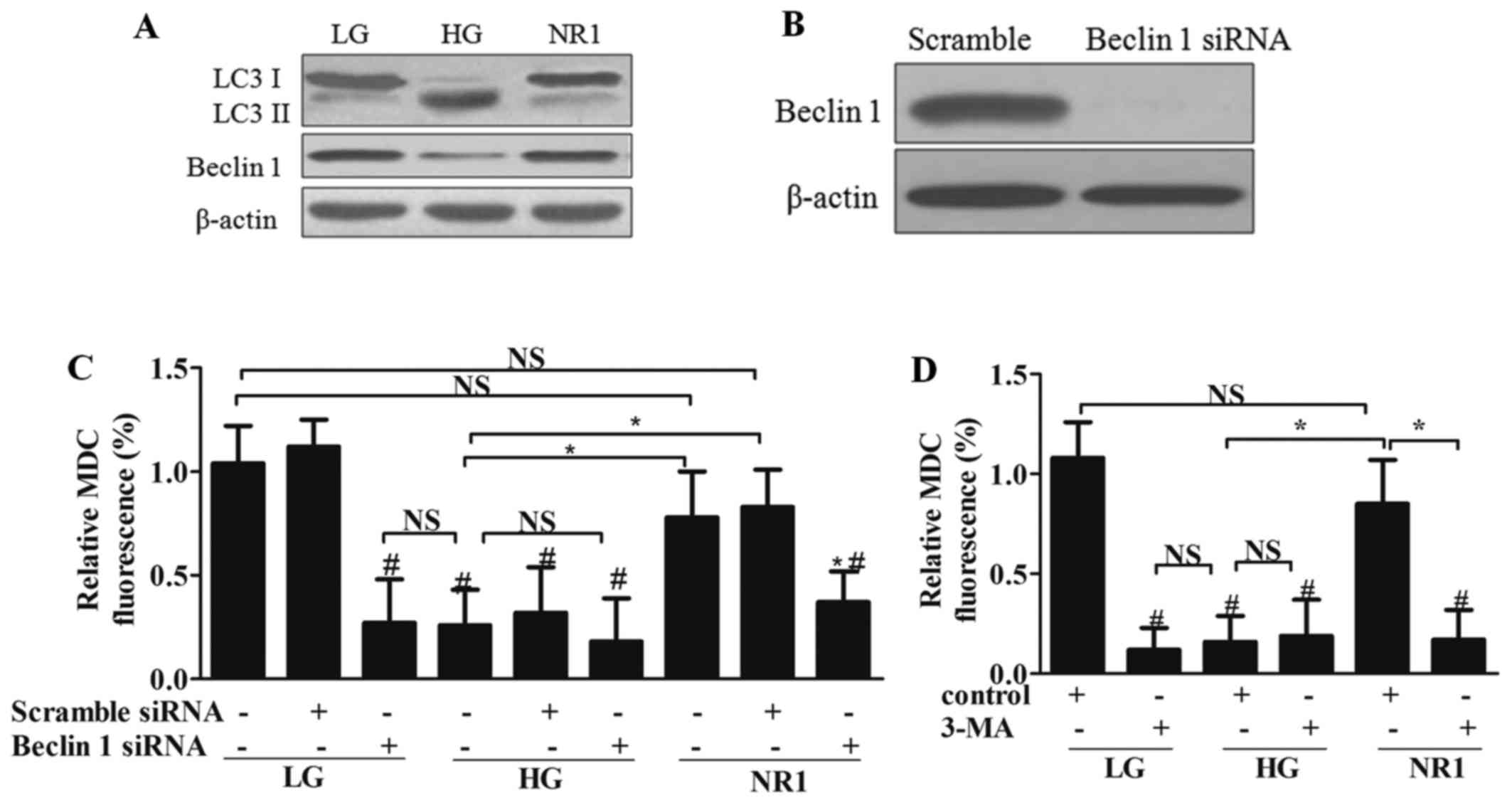
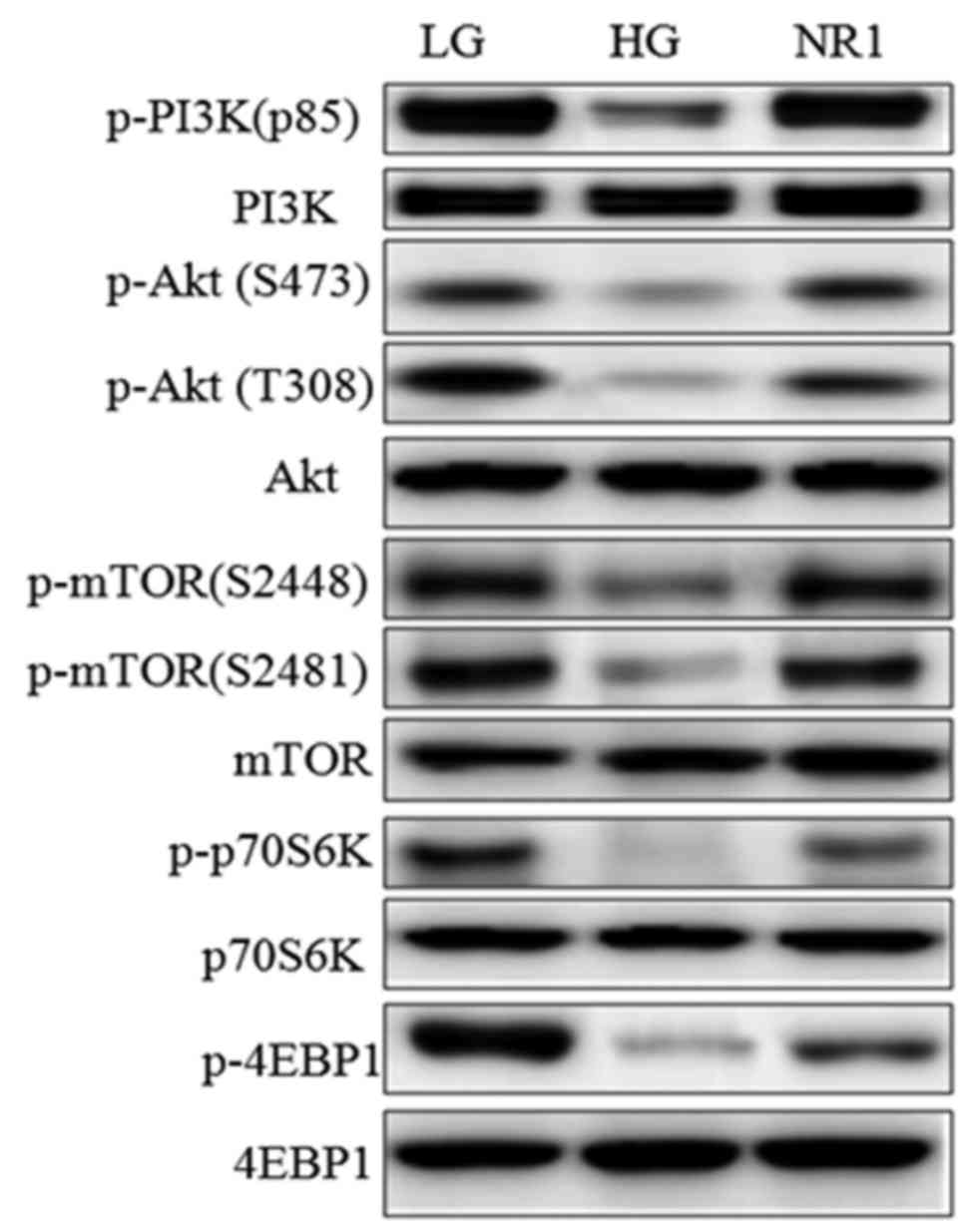
|
1
|
Mogensen CE: Microalbuminuria as a
predictor of clinical diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 31:673–689.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudberg S, Persson B and Dahlquist G:
Increased glomerular filtration rate as a predictor of diabetic
nephropathy - an 8-year prospective study. Kidney Int. 41:822–828.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White KE, Bilous RW and Diabiopsies Study
Group: Structural alterations to the podocyte are related to
proteinuria in type 2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
19:1437–1440. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kriz W, Gretz N and Lemley KV: Progression
of glomerular diseases: is the podocyte the culprit. Kidney Int.
54:687–697. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dalla Vestra M, Masiero A, Roiter AM,
Saller A, Crepaldi G and Fioretto P: Is podocyte injury relevant in
diabetic nephropathy? Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 52:1031–1035. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyer TW, Bennett PH and Nelson RG:
Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in
Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria.
Diabetologia. 42:1341–1344. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pavenstadt H, Kriz W and Kretzler M: Cell
biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev. 83:253–307. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang G, Lv J, Li T, Huai G, Li X, Xiang
S, Wang L, Qin Z, Pang J, Zou B and Wang Y: Notoginsenoside R1
ameliorates podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by
activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med.
38:1179–1189. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Quaggin SE: Transcriptional regulation of
podocyte specification and differentiation. Microsc Res Tech.
57:208–211. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
White KE, Bilous RW, Marshall SM, El Nahas
M, Remuzzi G, Piras G, De Cosmo S and Viberti G: Podocyte number in
normotensive type 1 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Diabetes.
51:3083–3089. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verzola D, Gandolfo MT, Ferrario F,
Rastaldi MP, Villaggio B, Gianiorio F, Giannoni M, Rimoldi L,
Lauria F, Miji M, et al: Apoptosis in the kidneys of patients with
type II diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 72:1262–1272. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu WJ, Tang HT, Jia YT, Ma B, Fu JF, Wang
Y, Lv KY and Xia ZF: Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Shock. 34:314–320. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gui D, Wei L, Jian G, Guo Y, Yang J and
Wang N: Notoginsenoside R1 ameliorates podocyte adhesion under
diabetic condition through α3β1 integrin upregulation in vitro and
in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1849–1862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hartleben B, Gödel M, Meyer-Schwesinger C,
Liu S, Ulrich T, Köbler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ,
Lindenmeyer MT, et al: Autophagy influences glomerular disease
susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J
Clin Invest. 120:1084–1096. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schiffer M, Bitzer M, Roberts IS, Kopp JB,
ten Dijke P, Mundel P and Böttinger EP: Apoptosis in podocytes
induced by TGF-beta and Smad7. J Clin Invest. 108:807–816. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Isermann B, Vinnikov IA, Madhusudhan T,
Herzog S, Kashif M, Blautzik J, Corat MA, Zeier M, Blessing E, Oh
J, et al: Activated protein C protects against diabetic nephropathy
by inhibiting endothelial and podocyte apoptosis. Nat Med.
13:1349–1358. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mundel P and Shankland SJ: Podocyte
biology and response to injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:3005–3015.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zeng C, Fan Y, Wu J, Shi S, Chen Z, Zhong
Y, Zhang C, Zen K and Liu Z: Podocyte autophagic activity plays a
protective role in renal injury and delays the progression of
podocytopathies. J Pathol. 234:203–213. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tejada T, Catanuto P, Ijaz A, Santos JV,
Xia X, Sanchez P, Sanabria N, Lenz O, Elliot SJ and Fornoni A:
Failure to phosphorylate AKT in podocytes from mice with early
diabetic nephropathy promotes cell death. Kidney Int. 73:1385–1393.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao H, Shi W, Liu S, Wang W, Zhang B,
Zhang Y, Xu L, Liang X and Liang Y: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
prevents puromycin aminonucleoside-induced apoptosis of glomerular
podocytes by activating the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt-signaling pathway. Am J Nephrol. 30:34–43. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feng Z, Tang L, Wu L, Cui S, Hong Q, Cai
G, Wu D, Fu B, Wei R and Chen X: Na+/H+
exchanger-1 reduces podocyte injury caused by endoplasmic reticulum
stress via autophagy activation. Lab Invest. 94:439–454. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cinà DP, Onay T, Paltoo A, Li C, Maezawa
Y, De Arteaga J, Jurisicova A and Quaggin SE: Inhibition of MTOR
disrupts autophagic flux in podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol.
23:412–420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S,
Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP,
Hartleben G, et al: Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic
nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2197–2209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saleem MA, O'Hare MJ, Reiser J, Coward RJ,
Inward CD, Farren T, Xing CY, Ni L, Mathieson PW and Mundel P: A
conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating
nephrin and podocin expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:630–638.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li C, Chen J, Lu B, Shi Z, Wang H, Zhang
B, Zhao K, Qi W, Bao J and Wang Y: Molecular switch role of Akt in
Polygonatum odoratum lectin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in
human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. PLoS One.
9:e1015262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang H, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Agaricus bisporus lectins mediates islet β-cell proliferation
through regulation of cell cycle proteins. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
237:287–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Li C, Qi P and Bao
J: Antihyperglycemic effect of ginsenoside Rh2 by inducing islet
β-cell regeneration in mice. Horm Metab Res. 44:33–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rantanen M, Palmén T, Pätäri A, Ahola H,
Lehtonen S, Aström E, Floss T, Vauti F, Wurst W and Ruiz P: Nephrin
TRAP mice lack slit diaphragms and show fibrotic glomeruli and
cystic tubular lesions. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:1586–1594. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kawachi H, Koike H, Kurihara H, Sakai T
and Shimizu F: Cloning of rat homologue of podocin: expression in
proteinuric states and in developing glomeruli. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:46–56. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wiggins JE, Goyal M, Sanden SK, Wharram
BL, Shedden KA, Misek DE, Kuick RD and Wiggins RC: Podocyte
hypertrophy, 'adaptation,' and 'decompensation' associated with
glomerular enlargement and glomerulosclerosis in the aging rat:
prevention by calorie restriction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:2953–2966.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Reiser J, Kriz W, Kretzler M and Mundel P:
The glomerular slit diaphragm is a modified adherens junction. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 11:1–8. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nielsen JS and McNagny KM: The role of
podocalyxin in health and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1669–1676.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Yamamoto T and
Kihara I: Variable expression of desmin in rat glomerular
epithelial cells. The Am J Pathol. 136:899–908. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Floege J, Alpers CE, Sage EH, Pritzl P,
Gordon K, Johnson RJ and Couser WG: Markers of complement-dependent
and complement-independent glomerular visceral epithelial cell
injury in vivo. Expression of antiadhesive proteins and
cytoskeletal changes. Lab Invest. 67:486–497. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Somlo S and Mundel P: Getting a foothold
in nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet. 24:333–335. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kerjaschki D: Caught flat-footed: podocyte
damage and the molecular bases of focal glomerulosclerosis. J Clin
Invest. 108:1583–1587. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Saleem MA, Ni L, Witherden I, Tryggvason
K, Ruotsalainen V, Mundel P and Mathieson PW: Co-localization of
nephrin, podocin, and the actin cytoskeleton: evidence for a role
in podocyte foot process formation. Am J Pathol. 161:1459–1466.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Asanuma K, Tanida I, Shirato I, Ueno T,
Takahara H, Nishitani T, Kominami E and Tomino Y: MAP-LC3, a
promising autophagosomal marker, is processed during the
differentiation and recovery of podocytes from PAN nephrosis. FASEB
J. 17:1165–1167. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nunez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y and Inohara N:
Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene.
17:3237–3245. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mohr S, McCormick TS and Lapetina EG:
Macrophages resistant to endogenously generated nitric
oxide-mediated apoptosis are hypersensitive to exogenously added
nitric oxide donors: dichotomous apoptotic response independent of
caspase 3 and reversal by the mitogen-activated protein kinase
kinase (MEK) inhibitor PD 098059. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:5045–5050. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wada T, Pippin JW, Marshall CB, Griffin SV
and Shankland SJ: Dexamethasone prevents podocyte apoptosis induced
by puromycin aminonucleoside: role of p53 and Bcl-2-related family
proteins. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:2615–2625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li X, Zhang X, Li X, Ding F and Ding J:
The role of survivin in podocyte injury induced by puromycin
aminonucleoside. Int J Mol Sci. 15:6657–6673. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen YQ, Wang XX, Yao XM, Zhang DL, Yang
XF, Tian SF and Wang NS: MicroRNA-195 promotes apoptosis in mouse
podocytes via enhanced caspase activity driven by BCL2
insufficiency. Am J Nephrol. 34:549–559. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gui D, Guo Y, Wang F, Liu W, Chen J, Chen
Y, Huang J and Wang N: Astragaloside IV, a novel antioxidant,
prevents glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
PLoS One. 7:e398242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA
and Sugimoto C: PI3K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene.
22:8983–8998. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huber TB, Hartleben B, Kim J, Schmidts M,
Schermer B, Keil A, Egger L, Lecha RL, Borner C, Pavenstädt H, et
al: Nephrin and CD2AP associate with phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase
and stimulate AKT-dependent signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 23:4917–4928.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|