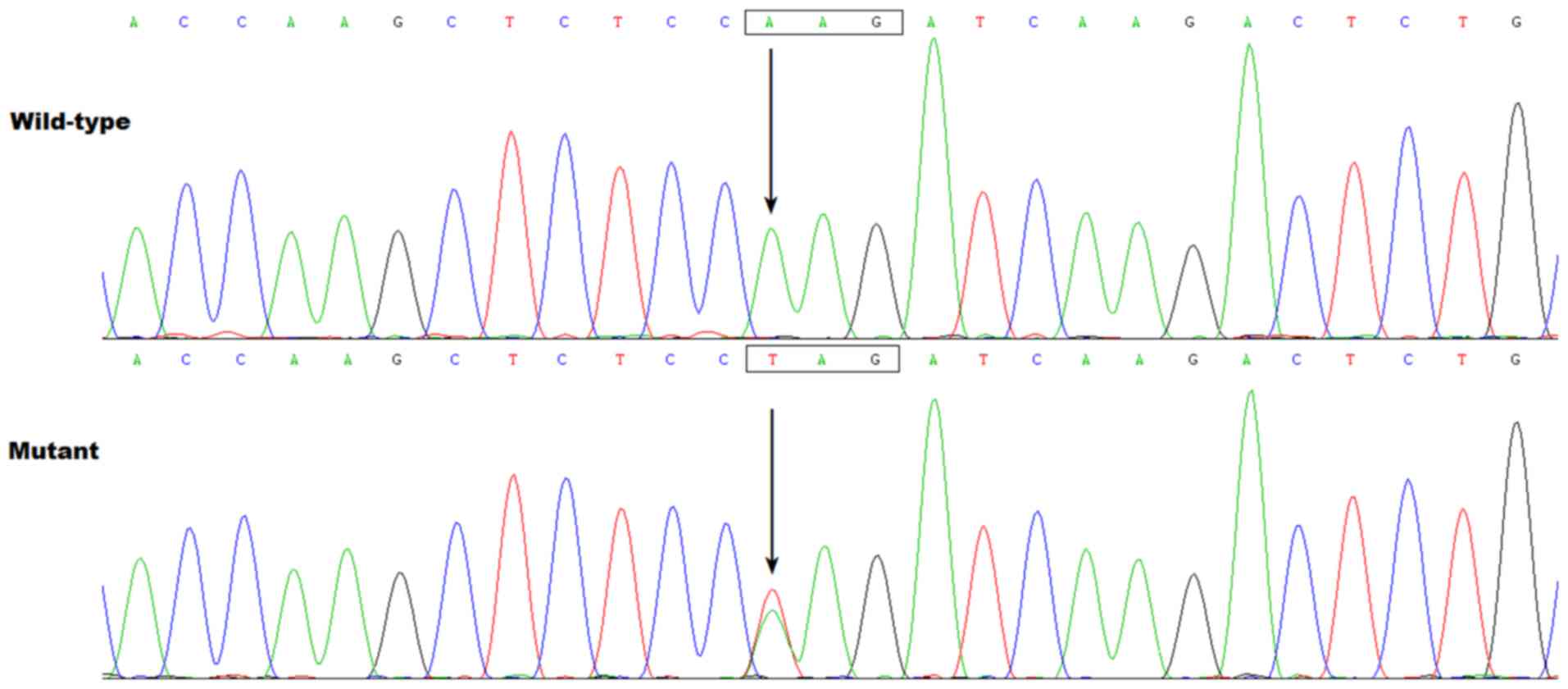
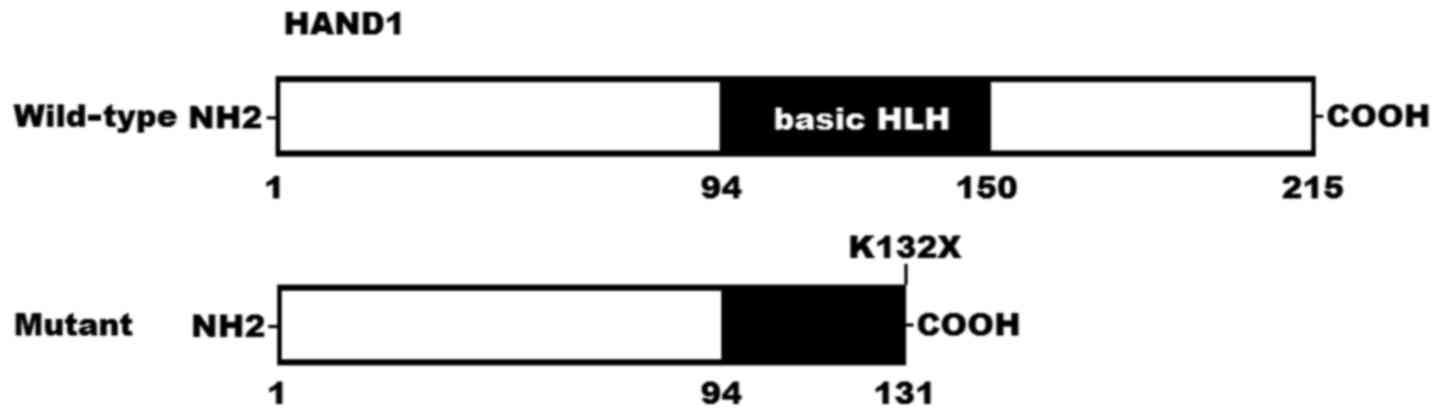
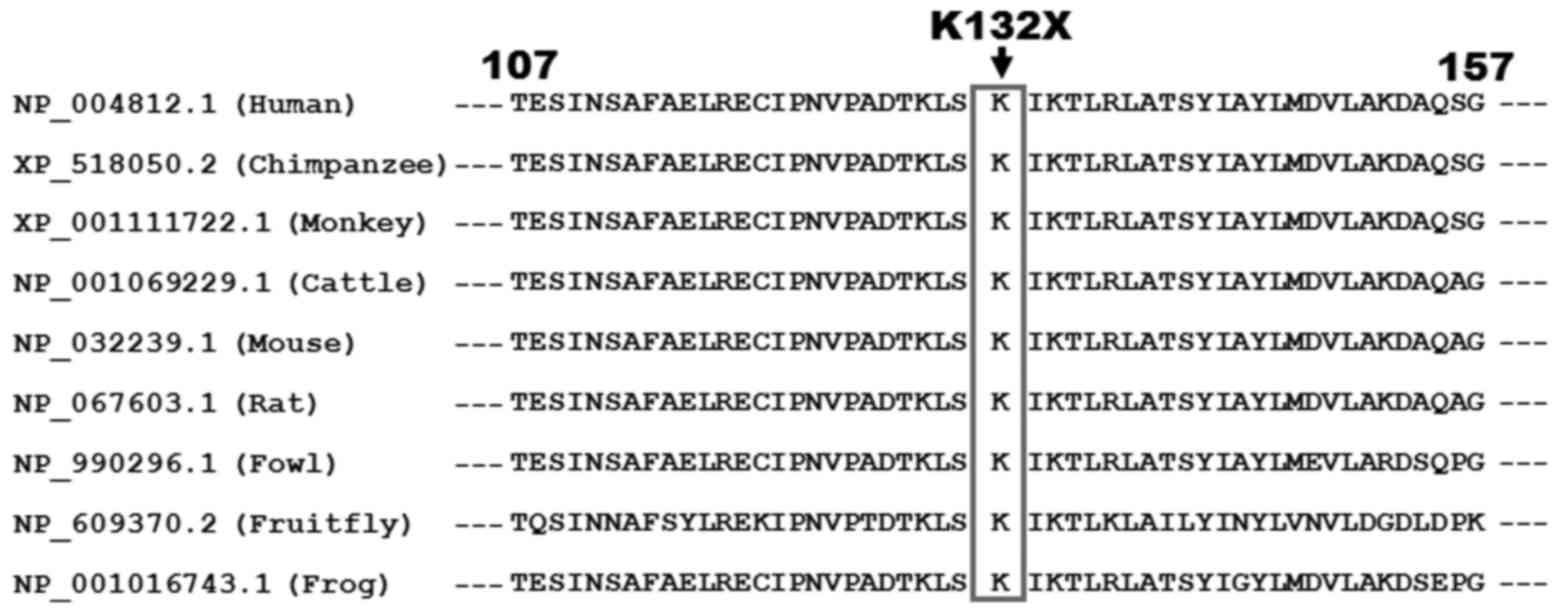
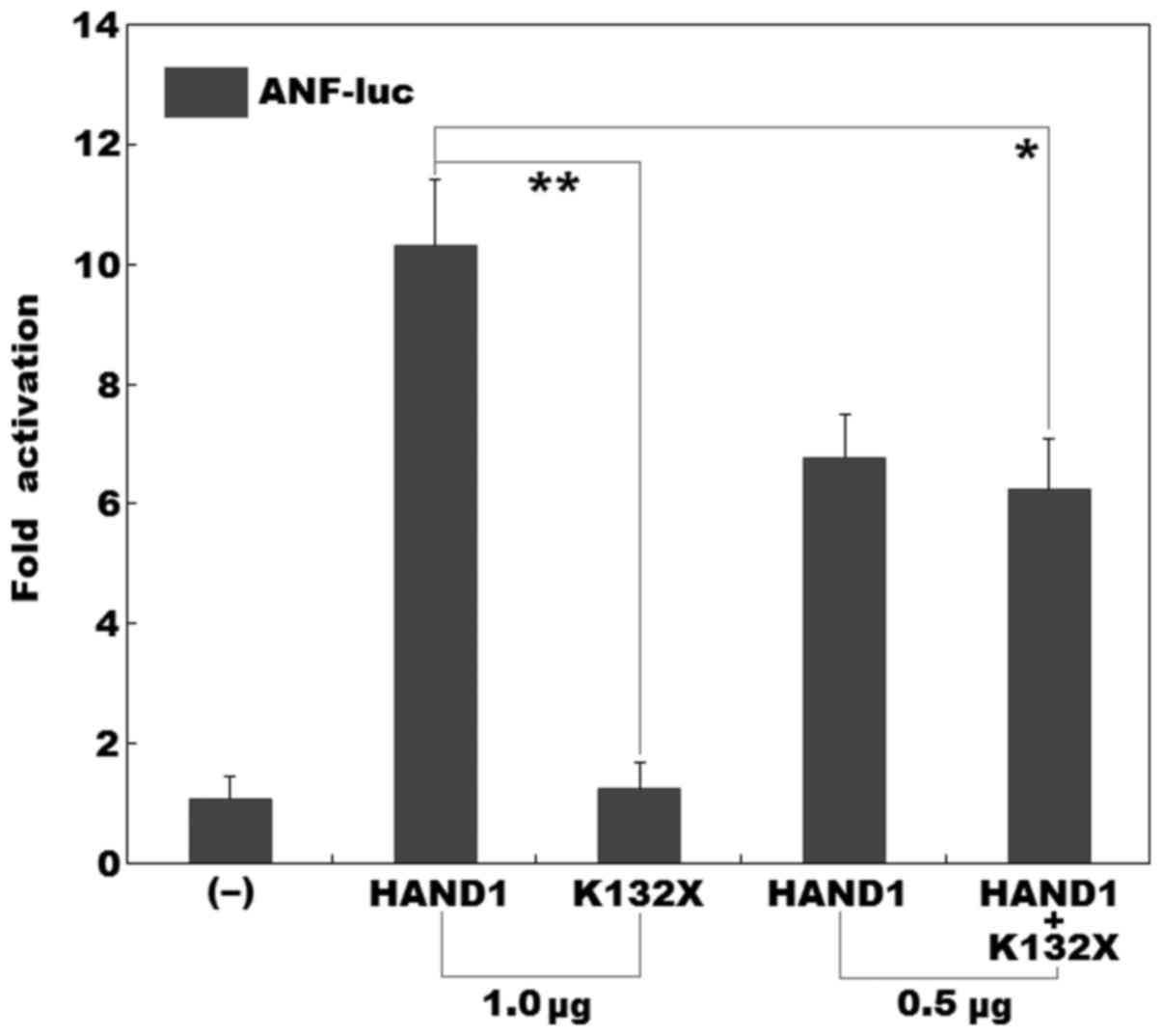
|
1
|
Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett
DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ,
Howard VJ, et al American Heart Association Statistics Committee
and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke
statistics - 2015 update: A report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 131:e29–e322. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Global Burden of Disease Study 2013
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and
chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013. A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.
Lancet. 386:743–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Feltez G, Coronel CC, Pellanda LC and
Lukrafka JL: Exercise capacity in children and adolescents with
corrected congenital heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 36:1075–1082.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rosenblum O, Katz U, Reuveny R, Williams
CA and Dubnov-Raz G: Exercise performance in children and young
adults after complete and incomplete repair of congenital heart
disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 36:1573–1581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kahr PC, Radke RM, Orwat S, Baumgartner H
and Diller GP: Analysis of associations between congenital heart
defect complexity and health-related quality of life using a
meta-analytic strategy. Int J Cardiol. 199:197–203. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Diller GP, Bräutigam A, Kempny A, Uebing
A, Alonso-Gonzalez R, Swan L, Babu-Narayan SV, Baumgartner H,
Dimopoulos K and Gatzoulis MA: Depression requiring anti-depressant
drug therapy in adult congenital heart disease: Prevalence, risk
factors, and prognostic value. Eur Heart J. 37:771–782. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun L, Macgowan CK, Sled JG, Yoo SJ,
Manlhiot C, Porayette P, Grosse-Wortmann L, Jaeggi E, McCrindle BW,
Kingdom J, et al: Reduced fetal cerebral oxygen consumption is
associated with smaller brain size in fetuses with congenital heart
disease. Circulation. 131:1313–1323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marelli A, Miller SP, Marino BS, Jefferson
AL and Newburger JW: Brain in congenital heart disease across the
lifespan: The cumulative burden of injury. Circulation.
133:1951–1962. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S,
Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A,
Beghetti M, et al: 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the
Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European
Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society
(ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and
Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and
Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 37:67–119. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Stout KK, Broberg CS, Book WM, Cecchin F,
Chen JM, Dimopoulos K, Everitt MD, Gatzoulis M, Harris L, Hsu DT,
et al American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology,
Council on Functional Genomics and Translational Biology, and
Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Imaging: Chronic Heart
Failure in Congenital Heart Disease: A Scientific Statement From
the American Heart Association. Circulation. 133:770–801.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wald RM, Valente AM and Marelli A: Heart
failure in adult congenital heart disease: Emerging concepts with a
focus on tetralogy of Fallot. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 25:422–432.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McLeod CJ and Warnes C: Recognition and
management of arrhythmias in adult congenital heart disease. Curr
Opin Cardiol. 31:117–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti
A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, Elliott PM, Fitzsimons D, Hatala R,
Hindricks G, et al: 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of
patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden
cardiac death: The Task Force for the Management of Patients with
Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death
of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by:
Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology
(AEPC). Eur Heart J. 36:2793–2867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Diller GP and Baumgartner H: Sudden
cardiac death during exercise in patients with congenital heart
disease: The exercise paradox and the challenge of appropriate
counselling. Eur Heart J. 37:627–629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van der Bom T, Zomer AC, Zwinderman AH,
Meijboom FJ, Bouma BJ and Mulder BJ: The changing epidemiology of
congenital heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 8:50–60. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tutarel O, Kempny A, Alonso-Gonzalez R,
Jabbour R, Li W, Uebing A, Dimopoulos K, Swan L, Gatzoulis MA and
Diller GP: Congenital heart disease beyond the age of 60: Emergence
of a new population with high resource utilization, high morbidity,
and high mortality. Eur Heart J. 35:725–732. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Niwa K: Adults with congenital heart
disease transition. Curr Opin Pediatr. 27:576–580. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jenkins KJ, Correa A, Feinstein JA, Botto
L, Britt AE, Daniels SR, Elixson M, Warnes CA and Webb CL; American
Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young:
Noninherited risk factors and congenital cardiovascular defects:
current knowledge: a scientific statement from the American Heart
Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young:
endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation.
115:2995–3014. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andersen TA, Troelsen KL and Larsen LA: Of
mice and men: Molecular genetics of congenital heart disease. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 71:1327–1352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Homsy J, Zaidi S, Shen Y, Ware JS, Samocha
KE, Karczewski KJ, DePalma SR, McKean D, Wakimoto H, Gorham J, et
al: De novo mutations in congenital heart disease with
neurodevelopmental and other congenital anomalies. Science.
350:1262–1266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Klena NT, Gabriel GC, Liu X, Kim AJ,
Lemke K, Chen Y, Chatterjee B, Devine W, Damerla RR, et al: Global
genetic analysis in mice unveils central role for cilia in
congenital heart disease. Nature. 521:520–524. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guimier A, Gabriel GC, Bajolle F, Tsang M,
Liu H, Noll A, Schwartz M, El Malti R, Smith LD, Klena NT, et al:
MMP21 is mutated in human heterotaxy and is required for normal
left-right asymmetry in vertebrates. Nat Genet. 47:1260–1263. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Racedo SE, McDonald-McGinn DM, Chung JH,
Goldmuntz E, Zackai E, Emanuel BS, Zhou B, Funke B and Morrow BE:
Mouse and human CRKL is dosage sensitive for cardiac outflow tract
formation. Am J Hum Genet. 96:235–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mlynarski EE, Sheridan MB, Xie M, Guo T,
Racedo SE, McDonald-McGinn DM, Gai X, Chow EW, Vorstman J, Swillen
A, et al International Chromosome 22q11.2 Consortium: International
Chromosome 22q11.2 Consortium: Copy-number variation of the glucose
transporter gene SLC2A3 and congenital heart defects in the 22q11.2
deletion syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 96:753–764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo T, Chung JH, Wang T, McDonald-McGinn
DM, Kates WR, Hawuła W, Coleman K, Zackai E, Emanuel BS and Morrow
BE: Histone modifier genes alter conotruncal heart phenotypes in
22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 97:869–877. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Quintero-Rivera F, Xi QJ, Keppler-Noreuil
KM, Lee JH, Higgins AW, Anchan RM, Roberts AE, Seong IS, Fan X,
Lage K, et al: MATR3 disruption in human and mouse associated with
bicuspid aortic valve, aortic coarctation and patent ductus
arteriosus. Hum Mol Genet. 24:2375–2389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sanchez-Castro M, Pichon O, Briand A,
Poulain D, Gournay V, David A and Le Caignec C: Disruption of the
SEMA3D gene in a patient with congenital heart defects. Hum Mutat.
36:30–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Theis JL, Zimmermann MT, Evans JM, Eckloff
BW, Wieben ED, Qureshi MY, O'Leary PW and Olson TM: Recessive MYH6
mutations in hypoplastic left heart with reduced ejection fraction.
Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 8:564–571. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kassab K, Hariri H, Gharibeh L, Fahed AC,
Zein M, El-Rassy I, Nemer M, El-Rassi I, Bitar F and Nemer G: GATA5
mutation homozygosity linked to a double outlet right ventricle
phenotype in a Lebanese patient. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 4:160–171.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Perrot A, Schmitt KR, Roth EM, Stiller B,
Posch MG, Browne EN, Timmann C, Horstmann RD, Berger F and Özcelik
C: CCN1 mutation is associated with atrial septal defect. Pediatr
Cardiol. 36:295–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Mao JH, Ding KK, Xu WJ, Liu XY,
Qiu XB, Li RG, Qu XK, Xu YJ, Huang RT, et al: A novel NKX2.6
mutation associated with congenital ventricular septal defect.
Pediatr Cardiol. 36:646–656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zheng J, Li F, Liu J, Xu Z, Zhang H, Fu Q,
Wang J and Sun K: Investigation of somatic NKX2-5 mutations in
Chinese children with congenital heart disease. Int J Med Sci.
12:538–543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pan Y, Wang ZG, Liu XY, Zhao H, Zhou N,
Zheng GF, Qiu XB, Li RG, Yuan F, Shi HY, et al: A novel TBX1
loss-of-function mutation associated with congenital heart disease.
Pediatr Cardiol. 36:1400–1410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao CM, Peng LY, Li L, Liu XY, Wang J,
Zhang XL, Yuan F, Li RG, Qiu XB and Yang YQ: PITX2 loss-of-function
mutation contributes to congenital endocardial cushion defect and
Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome. PLoS One. 10:e01244092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deng X, Pan H, Wang J, Wang B, Cheng Z,
Cheng L, Zhao L, Li H and Ma X: Functional analysis of two novel
mutations in TWIST1 protein motifs found in ventricular septal
defect patients. Pediatr Cardiol. 36:1602–1609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pan Y, Geng R, Zhou N, Zheng GF, Zhao H,
Wang J, Zhao CM, Qiu XB, Yang YQ and Liu XY: TBX20 loss-of-function
mutation contributes to double outlet right ventricle. Int J Mol
Med. 35:1058–1066. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang J, Zhu M, Wang Y, Hou X, Wu H, Wang
D, Shen H, Hu Z and Zou J: Whole-exome sequencing identify a new
mutation of MYH7 in a Chinese family with left ventricular
noncompaction. Gene. 558:138–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sifrim A, Hitz MP, Wilsdon A, Breckpot J,
Turki SH, Thienpont B, McRae J, Fitzgerald TW, Singh T, Swaminathan
GJ, et al INTERVAL Study; UK10K Consortium; Deciphering
Developmental Disorders Study: Distinct genetic architectures for
syndromic and nonsyndromic congenital heart defects identified by
exome sequencing. Nat Genet. 48:1060–1065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boyle L, Wamelink MM, Salomons GS, Roos B,
Pop A, Dauber A, Hwa V, Andrew M, Douglas J, Feingold M, et al:
Mutations in TKT are the cause of a syndrome including short
stature, developmental delay, and congenital heart defects. Am J
Hum Genet. 98:1235–1242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li N, Subrahmanyan L, Smith E, Yu X, Zaidi
S, Choi M, Mane S, Nelson-Williams C, Bahjati M, Kazemi M, et al:
Mutations in the histone modifier PRDM6 are associated with
isolated nonsyndromic patent ductus arteriosus. Am J Hum Genet.
98:1082–1091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fregeau B, Kim BJ, Hernández-García A,
Jordan VK, Cho MT, Schnur RE, Monaghan KG, Juusola J, Rosenfeld JA,
Bhoj E, et al: De novo mutations of RERE cause a genetic syndrome
with features that overlap those associated with proximal 1p36
deletions. Am J Hum Genet. 98:963–970. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Priest JR, Osoegawa K, Mohammed N, Nanda
V, Kundu R, Schultz K, Lammer EJ, Girirajan S, Scheetz T, Waggott
D, et al: De novo and rare variants at multiple loci support the
oligogenic origins of atrioventricular septal heart defects. PLoS
Genet. 12:e10059632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Werner P, Latney B, Deardorff MA and
Goldmuntz E: MESP1 mutations in patients with congenital heart
defects. Hum Mutat. 37:308–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
LaHaye S, Corsmeier D, Basu M, Bowman JL,
Fitzgerald-Butt S, Zender G, Bosse K, McBride KL, White P and Garg
V: Utilization of whole exome sequencing to identify causative
mutations in familial congenital heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc
Genet. 9:320–329. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu D, Liu QQ, Guan LH, Jiang X, Zhou DX,
Beghetti M, Qu JM and Jing ZC: BMPR2 mutation is a potential
predisposing genetic risk factor for congenital heart disease
associated pulmonary vascular disease. Int J Cardiol. 211:132–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun YM, Wang J, Qiu XB, Yuan F, Li RG, Xu
YJ, Qu XK, Shi HY, Hou XM, Huang RT, et al: A HAND2
loss-of-function mutation causes familial ventricular septal defect
and pulmonary stenosis. G3 (Bethesda). 6:987–992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yoshida A, Morisaki H, Nakaji M, Kitano M,
Kim KS, Sagawa K, Ishikawa S, Satokata I, Mitani Y, Kato H, et al:
Genetic mutation analysis in Japanese patients with non-syndromic
congenital heart disease. J Hum Genet. 61:157–162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lu CX, Gong HR, Liu XY, Wang J, Zhao CM,
Huang RT, Xue S and Yang YQ: A novel HAND2 loss-of-function
mutation responsible for tetralogy of Fallot. Int J Mol Med.
37:445–451. 2016.
|
|
50
|
Cao Y, Wang J, Wei C, Hou Z, Li Y, Zou H,
Meng M, Wang W and Jiang L: Genetic variations of NKX2-5 in
sporadic atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect in
Chinese Yunnan population. Gene. 575:29–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Chen J, Qi B, Zhao J, Liu W, Duan R and
Zhang M: A novel mutation of GATA4 (K300T) associated with familial
atrial septal defect. Gene. 575:473–477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tong YF: Mutations of NKX2.5 and GATA4
genes in the development of congenital heart disease. Gene.
588:86–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Wang B, Chen S, Fu Q and
Sun K: A novel missense mutation of GATA4 in a Chinese family with
congenital heart disease. PLoS One. 11:e01589042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun YM, Wang J, Qiu XB, Yuan F, Xu YJ, Li
RG, Qu XK, Huang RT, Xue S and Yang YQ: ITX2 loss-of-function
mutation contributes to tetralogy of Fallot. Gene. 577:258–264.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhou YM, Dai XY, Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ,
Qiu XB and Yang YQ: A novel TBX20 loss of function mutation
contributes to adult onset dilated cardiomyopathy or congenital
atrial septal defect. Mol Med Rep. 14:3307–3314. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li FF, Deng X, Zhou J, Yan P, Zhao EY and
Liu SL: Characterization of human bone morphogenetic protein gene
variants for possible roles in congenital heart disease. Mol Med
Rep. 14:1459–1464. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kelle AM, Bentley SJ, Rohena LO, Cabalka
AK and Olson TM: Ebstein anomaly, left ventricular non-compaction,
and early onset heart failure associated with a de novo
α-tropomyosin gene mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 170:2186–2190. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Thattaliyath BD, Livi CB, Steinhelper ME,
Toney GM and Firulli AB: HAND1 and HAND2 are expressed in the
adult-rodent heart and are modulated during cardiac hypertrophy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 297:870–875. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Reamon-Buettner SM, Ciribilli Y, Inga A
and Borlak J: A loss-of-function mutation in the binding domain of
HAND1 predicts hypoplasia of the human hearts. Hum Mol Genet.
17:1397–1405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Morin S, Pozzulo G, Robitaille L, Cross J
and Nemer M: MEF2-dependent recruitment of the HAND1 transcription
factor results in synergistic activation of target promoters. J
Biol Chem. 280:32272–32278. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Srivastava D, Cserjesi P and Olson EN: A
subclass of bHLH proteins required for cardiac morphogenesis.
Science. 270:1995–1999. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Risebro CA, Smart N, Dupays L,
Breckenridge R, Mohun TJ and Riley PR: Hand1 regulates
cardiomyocyte proliferation versus differentiation in the
developing heart. Development. 133:4595–4606. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Firulli AB, McFadden DG, Lin Q, Srivastava
D and Olson EN: Heart and extra-embryonic mesodermal defects in
mouse embryos lacking the bHLH transcription factor Hand1. Nat
Genet. 18:266–270. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Riley P, Anson-Cartwright L and Cross JC:
The Hand1 bHLH transcription factor is essential for placentation
and cardiac morphogenesis. Nat Genet. 18:271–275. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
McFadden DG, Barbosa AC, Richardson JA,
Schneider MD, Srivastava D and Olson EN: The Hand1 and Hand2
transcription factors regulate expansion of the embryonic cardiac
ventricles in a gene dosage-dependent manner. Development.
132:189–201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Natarajan A, Yamagishi H, Ahmad F, Li D,
Roberts R, Matsuoka R, Hill S and Srivastava D: Human eHAND, but
not dHAND, is down-regulated in cardiomyopathies. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 33:1607–1614. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Reamon-Buettner SM, Ciribilli Y, Traverso
I, Kuhls B, Inga A and Borlak J: A functional genetic study
identifies HAND1 mutations in septation defects of the human heart.
Hum Mol Genet. 18:3567–3578. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cheng Z, Lib L, Li Z, Liu M, Yan J, Wang B
and Ma X: Two novel HAND1 mutations in Chinese patients with
ventricular septal defect. Clin Chim Acta. 413:675–677. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhou YM, Dai XY, Qiu XB, Yuan F, Li RG, Xu
YJ, Qu XK, Huang RT, Xue S and Yang YQ: HAND1 loss-of-function
mutation associated with familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 54:1161–1167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
McCulley DJ and Black BL: Transcription
factor pathways and congenital heart disease. Curr Top Dev Biol.
100:253–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|