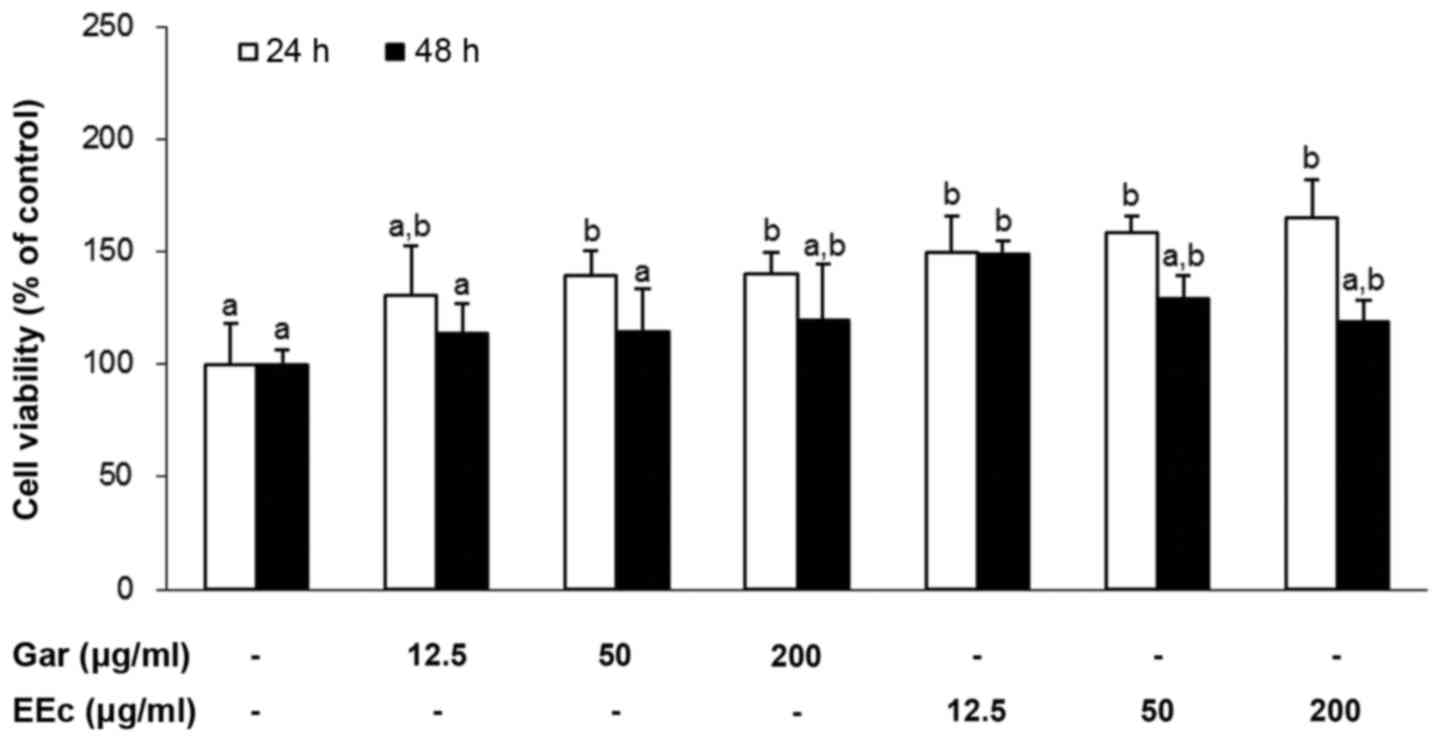
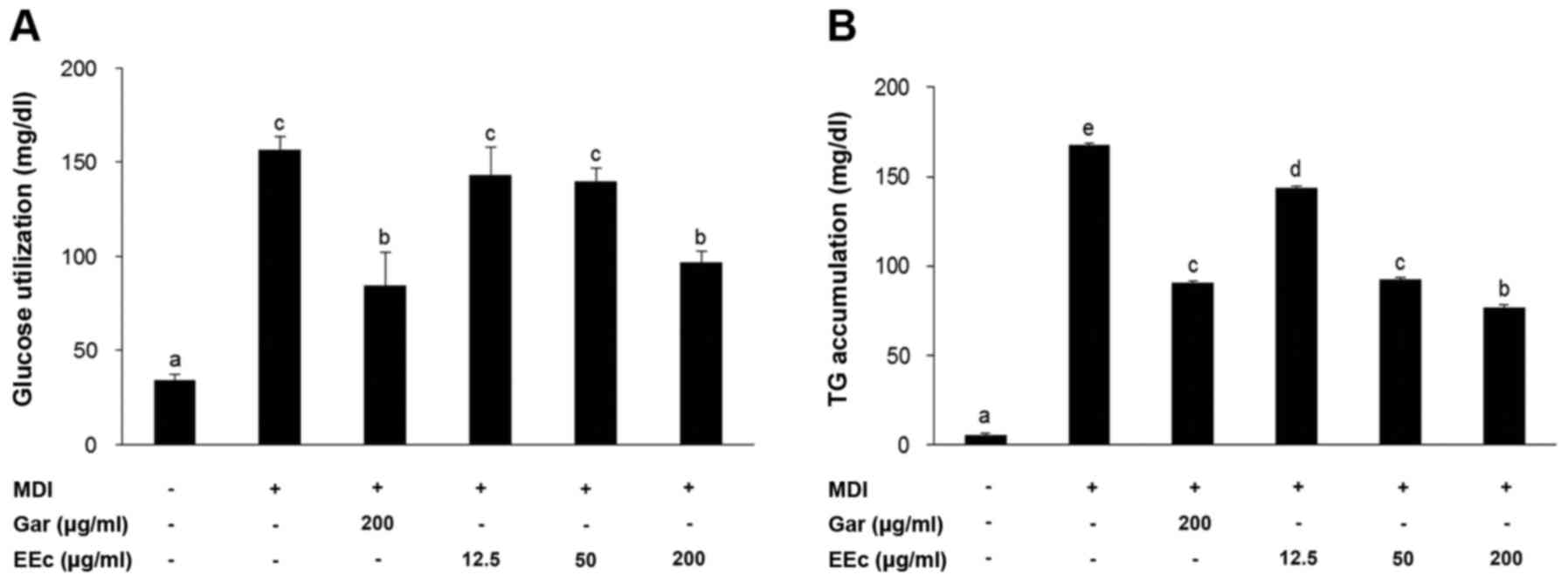
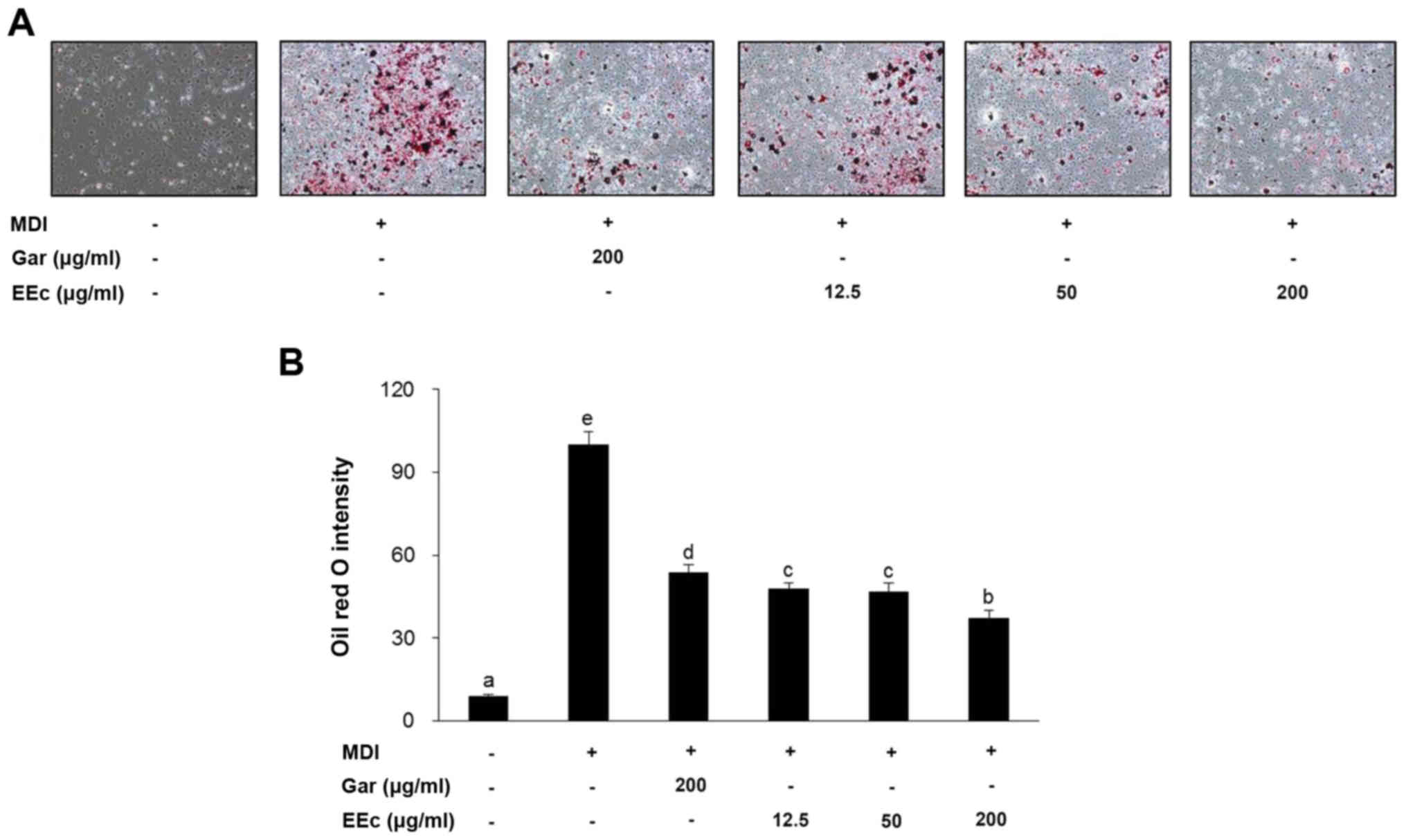
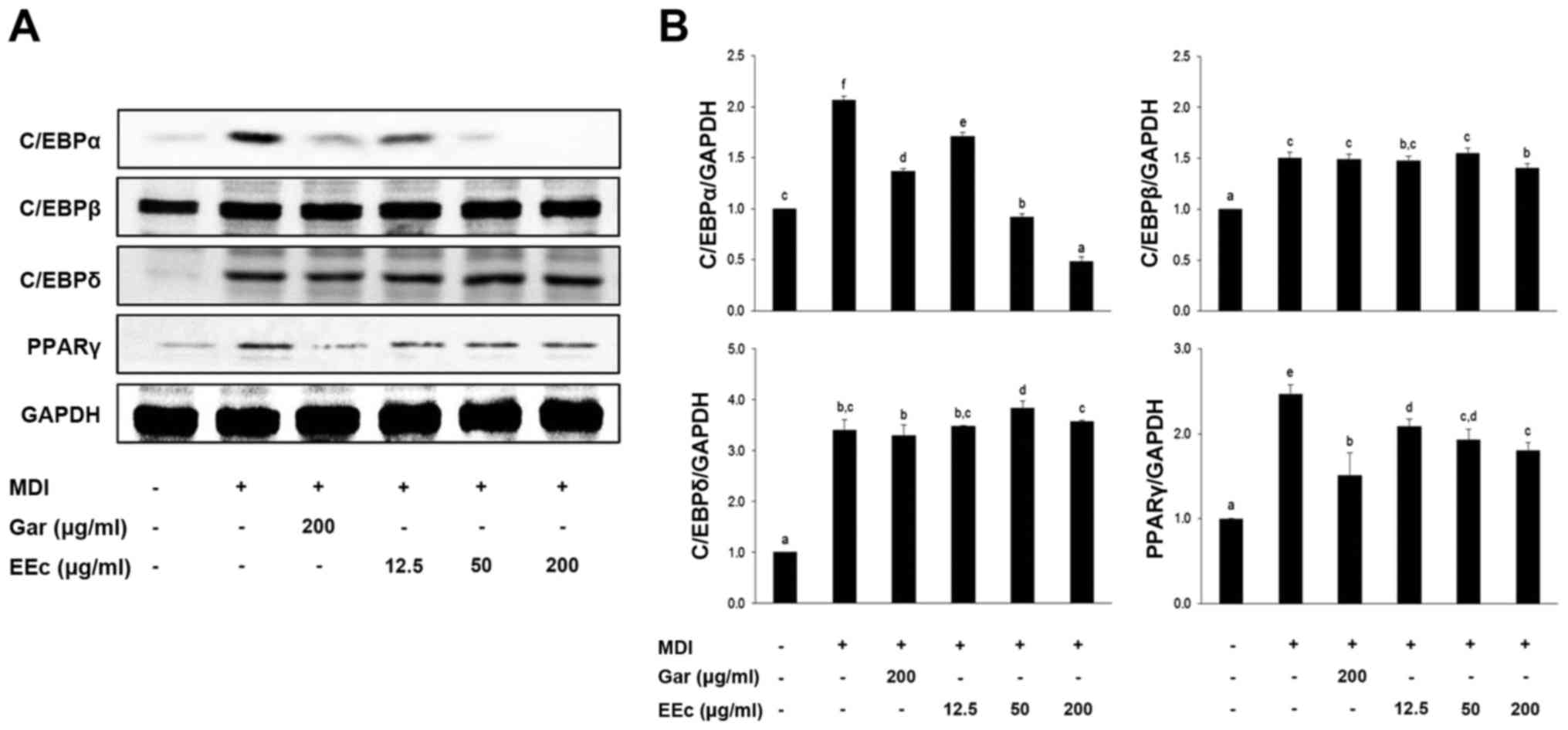
|
1
|
Formiguera X and Cantón A: Obesity:
Epidemiology and clinical aspects. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 18:1125–1146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Albu J, Allison D, Boozer CN, Heymsfield
S, Kissileff H, Kretser A, Krumhar K, Leibel R, Nonas C, Pi-Sunyer
X, et al: Obesity solutions: Report of a meeting. Nutr Rev.
55:150–156. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hossain P, Kawar B and El Nahas M: Obesity
and diabetes in the developing world - a growing challenge. N Engl
J Med. 356:213–215. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caro JF, Dohm LG, Pories WJ and Sinha MK:
Cellular alterations in liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue
responsible for insulin resistance in obesity and type II diabetes.
Diabetes Metab Rev. 5:665–689. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aggoun Y: Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and
cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Res. 61:653–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujioka K: Management of obesity as a
chronic disease: Nonpharmacologic, pharmacologic, and surgical
options. Obes Res. 10(Suppl 2): 116S–123S. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Després JP and Lemieux I: Abdominal
obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 444:881–887. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rosen ED and Spiegelman BM: Adipocytes as
regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature.
444:847–853. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang J, Eliasson B, Smith U, Cushman SW
and Sherman AS: The size of large adipose cells is a predictor of
insulin resistance in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic
patients. Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:932–938. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Balkau B, Valensi P, Eschwège E and Slama
G: A review of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 33:405–413.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kopelman PG: Obesity as a medical problem.
Nature. 404:635–643. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abate N: Obesity and cardiovascular
disease. Pathogenetic role of the metabolic syndrome and
therapeutic implications. J Diabetes Complications. 14:154–174.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang JW, Tang QQ, Vinson C and Lane MD:
Dominant-negative C/EBP disrupts mitotic clonal expansion and
differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:43–47. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Kwon JY, Seo SG, Heo YS, Yue S, Cheng JX,
Lee KW and Kim KH: Piceatannol, natural polyphenolic stilbene,
inhibits adipogenesis via modulation of mitotic clonal expansion
and insulin receptor-dependent insulin signaling in early phase of
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 287:11566–11578. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang QQ, Otto TC and Lane MD:
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is required for mitotic clonal
expansion during adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:850–855.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Christy RJ, Kaestner KH, Geiman DE and
Lane MD: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene promoter: Binding of
nuclear factors during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:2593–2597. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Farmer SR: Regulation of PPARgamma
activity during adipogenesis. Int J Obes. 29(Suppl 1): S13–S16.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Farmer SR: Transcriptional control of
adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 4:263–273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lowe CE, O'Rahilly S and Rochford JJ:
Adipogenesis at a glance. J Cell Sci. 124:2681–2686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu A, Wang Y, Xu JY, Stejskal D, Tam S,
Zhang J, Wat NM, Wong WK and Lam KS: Adipocyte fatty acid-binding
protein is a plasma biomarker closely associated with obesity and
metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem. 52:405–413. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hassan M, El Yazidi C, Landrier JF, Lairon
D, Margotat A and Amiot MJ: Phloretin enhances adipocyte
differentiation and adiponectin expression in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 361:208–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rosen ED and MacDougald OA: Adipocyte
differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
7:885–896. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nicholson AC, Hajjar DP, Zhou X, He W,
Gotto AM Jr and Han J: Anti-adipogenic action of pitavastatin
occurs through the coordinate regulation of PPARgamma and Pref-1
expression. Br J Pharmacol. 151:807–815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yeh WC, Cao Z, Classon M and McKnight SL:
Cascade regulation of adipocyte terminal differentiation by three
members of the C/EBP family of leucine zipper proteins. Genes Dev.
15:168–181. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bray GA and Tartaglia LA: Medicinal
strategies in the treatment of obesity. Nature. 404:672–677.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alemany M, Remesar X and Fernández-López
JA: Drug strategies for the treatment of obesity. IDrugs.
6:566–572. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elangbam CS: Review paper: Current
strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs and their
safety concerns. Vet Pathol. 46:10–24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rodgers RJ, Tschöp MH and Wilding JP:
Anti-obesity drugs: Past, present and future. Dis Model Mech.
5:621–626. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Buyukhatipoglu H: A possibly overlooked
side effect of Orlistat: Gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Natl
Med Assoc. 100:12072008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
van der Zwaal EM, Janhunen SK, Luijendijk
MC, Baclesanu R, Vanderschuren LJ, Adan RA and La Fleur SE:
Olanzapine and sibutramine have opposing effects on the motivation
for palatable food. Behav Pharmacol. 23:198–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Apfelbaum M, Vague P, Ziegler O, Hanotin
C, Thomas F and Leutenegger E: Long-term maintenance of weight loss
after a very-low-calorie diet: A randomized blinded trial of the
efficacy and tolerability of sibutramine. Am J Med. 106:179–184.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cunha L and Grenha A: Sulfated seaweed
polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery
applications. Mar Drugs. 14:1–41. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Grasa-López A, Miliar-García Á,
Quevedo-Corona L, Paniagua-Castro N, Escalona-Cardoso G,
Reyes-Maldonado E and Jaramillo-Flores ME: Undaria pinnatifida and
fucoxanthin ameliorate lipogenesis and markers of both inflammation
and cardiovascular dysfunction in an animal model of diet-induced
obesity. Mar Drugs. 14:1482016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Geisen U, Zenthoefer M, Peipp M, Kerber J,
Plenge J, Managò A, Fuhrmann M, Geyer R, Hennig S, Adam D, et al:
Molecular mechanisms by which a Fucus vesiculosus extract mediates
cell cycle inhibition and cell death in pancreatic cancer cells.
Mar Drugs. 13:4470–4491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gomes DL, Telles CB, Costa MS,
Almeida-Lima J, Costa LS, Keesen TS and Rocha HA: Methanolic
extracts from brown seaweeds Dictyota cilliolata and Dictyota
menstrualis induce apoptosis in human cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa
cells. Molecules. 20:6573–6591. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pereira DM, Cheel J, Areche C, San-Martin
A, Rovirosa J, Silva LR, Valentao P and Andrade PB:
Anti-proliferative activity of meroditerpenoids isolated from the
brown alga Stypopodium flabelliforme against several cancer cell
lines. Mar Drugs. 9:852–862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Patra S, Muthuraman MS, Prabhu AR,
Priyadharshini RR and Parthiban S: Evaluation of antitumor and
antioxidant activity of Sargassum tenerrimum against Ehrlich
ascites carcinoma in mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:915–921.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moussavou G, Kwak DH, Obiang-Obonou BW,
Maranguy CA, Dinzouna-Boutamba SD, Lee DH, Pissibanganga OG, Ko K,
Seo JI and Choo YK: Anticancer effects of different seaweeds on
human colon and breast cancers. Mar Drugs. 12:4898–4911. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang FW: Bioactive metabolites from
Guignardia sp., an endophytic fungus residing in Undaria
pinnatifida. Chin J Nat Med. 10:72–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Fu Z and Han C: The potential
applications of marine bioactives against diabetes and obesity. Am
J Mar Sci. 2:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wijesinghe WA and Jeon YJ: Exploiting
biological activities of brown seaweed Ecklonia cava for potential
industrial applications: A review. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 63:225–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Athukorala Y, Kim KN and Jeon YJ:
Antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of an enzymatic
hydrolysate from brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:1065–1074. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park MH, Heo SJ, Park PJ, Moon SH, Sung
SH, Jeon BT and Lee SH: 6,6′-bieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava
protects oxidative stress through inhibiting expression of ROS and
proinflammatory enzymes in high-glucose-induced human umbilical
vein endothelial cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 174:632–643. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee SH, Park MH, Kang SM, Ko SC, Kang MC,
Cho S, Park PJ, Jeon BT, Kim SK, Han JS, et al: Dieckol isolated
from Ecklonia cava protects against high-glucose induced damage to
rat insulinoma cells by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 76:1445–1451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kang SM, Lee SH, Heo SJ, Kim KN and Jeon
YJ: Evaluation of antioxidant properties of a new compound,
pyrogallol-phloro-glucinol-6,6′-bieckol isolated from brown algae,
Ecklonia cava. Nutr Res Pract. 5:495–502. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li Y, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Lee SH, Kim MM and
Kim SK: Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in
vitro: An edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorg Med Chem.
17:1963–1973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang YI, Jung SH, Lee KT and Choi JH:
8,8′-Bieckol, isolated from edible brown algae, exerts its
anti-inflammatory effects through inhibition of NF-κB signaling and
ROS production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
23:460–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee SH, Ko CI, Jee Y, Jeong Y, Kim M, Kim
JS and Jeon YJ: Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from
Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr Polym. 92:84–89. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Lee SH, Ko CI, Ahn G, You S, Kim JS, Heu
MS, Kim J, Jee Y and Jeon YJ: Molecular characteristics and
anti-inflammatory activity of the fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia
cava. Carbohydr Polym. 89:599–606. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shin HC, Hwang HJ, Kang KJ and Lee BH: An
antioxidative and antiinflammatory agent for potential treatment of
osteoarthritis from Ecklonia cava. Arch Pharm Res. 29:165–171.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ahn G, Lee W, Kim KN, Lee JH, Heo SJ, Kang
N, Lee SH, Ahn CB and Jeon YJ: A sulfated polysaccharide of
Ecklonia cava inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells by inducing
apoptosis. EXCLI J. 14:294–306. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ahn JH, Yang YI, Lee KT and Choi JH:
Dieckol, isolated from the edible brown algae Ecklonia cava,
induces apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells and inhibits tumor
xenograft growth. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:255–268. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lee W, Oh JY, Kim EA, Kang N, Kim KN, Ahn
G and Jeon YJ: A prebiotic role of Ecklonia cava improves the
mortality of Edwardsiella tarda-infected zebrafish models via
regulating the growth of lactic acid bacteria and pathogen
bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 54:620–628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee W, Ahn G, Oh JY, Kim SM, Kang N, Kim
EA, Kim KN, Jeong JB and Jeon YJ: A prebiotic effect of Ecklonia
cava on the growth and mortality of olive flounder infected with
pathogenic bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 51:313–320. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang YI, Woo JH, Seo YJ, Lee KT, Lim Y and
Choi JH: Protective effect of brown alga phlorotannins against
hyper-inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis
models. J Agric Food Chem. 64:570–578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Choi YH: The cytoprotective effects of
ethanol extract of Ecklonia cava against oxidative stress are
associated with upregulation of Nrf2-mediated HO-1 and NQO-1
expression through activation of the MAPK pathway. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 35:45–53. 2016.
|
|
57
|
Shin H, Cho AR, Kim DY, Munkhbayer S, Choi
SJ, Jang S, Kim SH, Shin HC and Kwon O: Enhancement of human hair
growth using Ecklonia cava polyphenols. Ann Dermatol. 28:15–21.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chang MY, Han SY, Shin HC, Byun JY, Rah YC
and Park MK: Protective effect of a purified polyphenolic extract
from Ecklonia cava against noise-induced hearing loss: Prevention
of temporary threshold shift. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
87:178–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Park SJ and Jeon YJ: Dieckol from Ecklonia
cava suppresses the migration and invasion of HT1080 cells by
inhibiting the focal adhesion kinase pathway downstream of Rac1-ROS
signaling. Mol Cells. 33:141–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bae MJ, Karadeniz F, Ahn BN and Kong CS:
Evaluation of effective MMP inhibitors from eight different brown
algae in human fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. Prev Nutr Food Sci.
20:153–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim EK, Tang Y, Kim YS, Hwang JW, Choi EJ,
Lee JH, Lee SH, Jeon YJ and Park PJ: First evidence that Ecklonia
cava-derived dieckol attenuates MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell
migration. Mar Drugs. 13:1785–1797. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Choi BW, Lee HS, Shin HC and Lee BH:
Multifunctional activity of polyphenolic compounds associated with
a potential for Alzheimer's disease therapy from Ecklonia cava.
Phytother Res. 29:549–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Douglas TE, Dokupil A, Reczyńska K,
Brackman G, Krok-Borkowicz M, Keppler JK, Božič M, Van Der Voort P,
Pietryga K, Samal SK, et al: Enrichment of enzymatically
mineralized gellan gum hydrogels with phlorotannin-rich Ecklonia
cava extract Seanol® to endow antibacterial properties
and promote mineralization. Biomed Mater. 11:0450152016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Choi HS, Jeon HJ, Lee OH and Lee BY:
Dieckol, a major phlorotannin in Ecklonia cava, suppresses lipid
accumulation in the adipocytes of high-fat diet-fed zebrafish and
mice: Inhibition of early adipogenesis via cell-cycle arrest and
AMPKα activation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 59:1458–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
You HN, Lee HA, Park MH, Lee JH and Han
JS: Phlorofucofuroeckol A isolated from Ecklonia cava alleviates
postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
752:92–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jeon HJ, Choi HS, Lee YJ, Hwang JH, Lee
OH, Seo MJ, Kim KJ and Lee BY: Seapolynol extracted from Ecklonia
cava inhibits adipocyte differentiation in vitro and decreases fat
accumulation in vivo. Molecules. 20:21715–21731. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Park EY, Choi H, Yoon JY, Lee IY, Seo Y,
Moon HS, Hwang JH and Jun HS: Polyphenol-rich fraction of Ecklonia
cava improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high fat diet-fed
mice. Mar Drugs. 13:6866–6883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lee SH and Jeon YJ: Efficacy and safety of
a dieckol-rich extract (AG-dieckol) of brown algae, Ecklonia cava,
in pre-diabetic individuals: A double-blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled clinical trial. Food Funct. 6:853–858. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ko SC, Lee M, Lee JH, Lee SH, Lim Y and
Jeon YJ: Dieckol, a phlorotannin isolated from a brown seaweed,
Ecklonia cava, inhibits adipogenesis through AMP-activated protein
kinase (AMPK) activation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:1253–1260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kim H, Kong CS, Lee JI, Kim H, Baek S and
Seo Y: Evaluation of inhibitory effect of phlorotannins from
Ecklonia cava on triglyceride accumulation in adipocyte. J Agric
Food Chem. 61:8541–8547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hong SY, Park JY, Sohn JS, Kim JH and Kim
MK: Effects of garcinia cambogia extract feeding on body weight and
lipid profiles in rats fed a high-carbohydrate or high-fat diet.
Food Sci Biotechnol. 18:649–654. 2009.
|
|
72
|
Chuah LO, Yeap SK, Ho WY, Beh BK and
Alitheen NB: In vitro and in vivo toxicity of garcinia or
hydroxycitric Acid: A review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:1979202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Krishnamoorthy V, Nagappan P, Sereen AK
and Rajendran R: Preliminary phytochemical screening of the fruit
rind of Garcinia cambogia and leaves of Bauhinia variegate-A
comparative study. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 3:479–486.
2014.
|
|
74
|
Ahn GN, Kim KN, Cha SH, Song CB, Lee JH,
Heo MS, Yeo IK, Lee NH, Jee YH, Kim JS, et al: Antioxidant
activities of phlorotannins purified from Ecklonia cava on free
radical scavenging using ESR and
H2O2-mediated DNA damage. Eur Food Res
Technol. 226:71–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Ahn MJ, Yoon KD, Min SY, Lee JS, Kim JH,
Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim NG, Huh H and Kim J: Inhibition of HIV-1
reverse transcriptase and protease by phlorotannins from the brown
alga Ecklonia cava. Biol Pharm Bull. 27:544–547. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Le QT, Li Y, Qian ZJ, Kim MM and Kim SK:
Inhibitory effects of polyphenols isolated from marine alga
Ecklonia cava on histamine release. Process Biochem. 44:168–176.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|