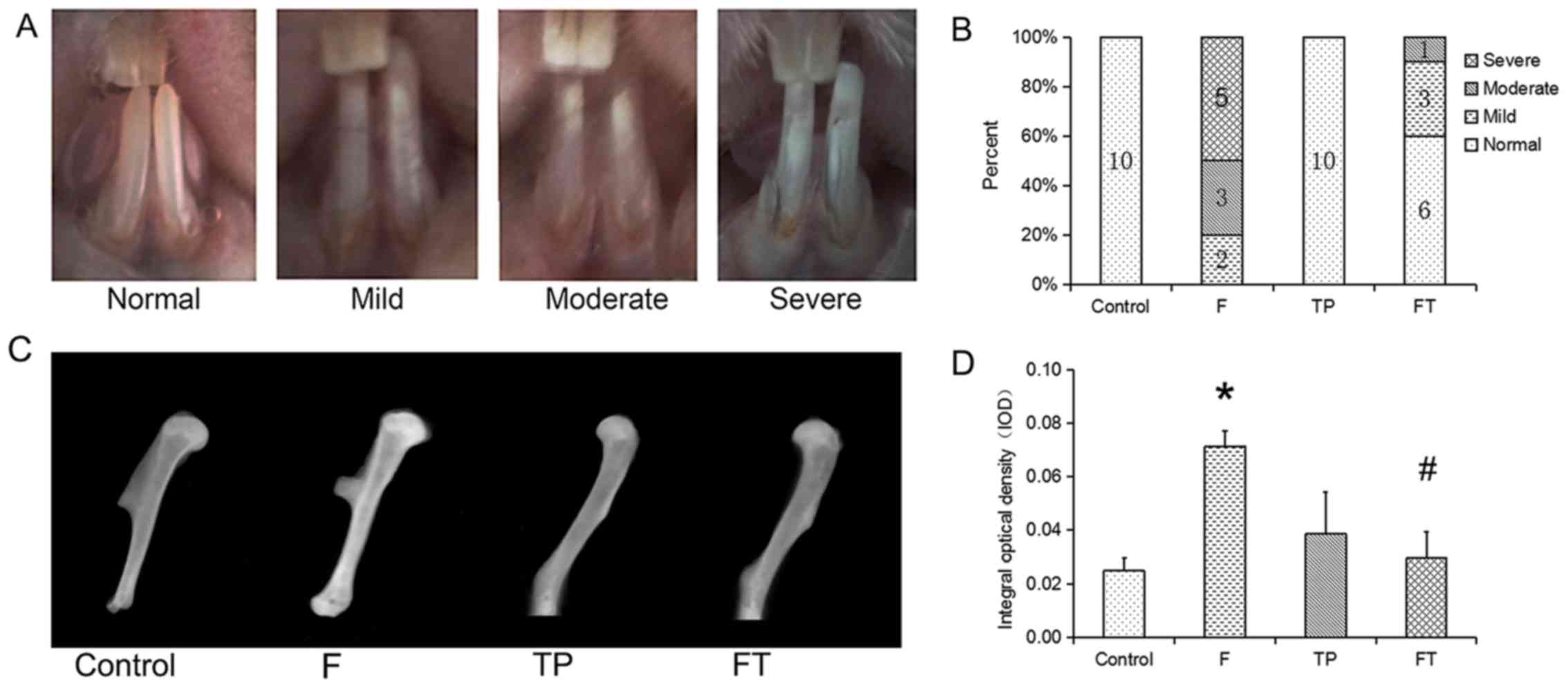
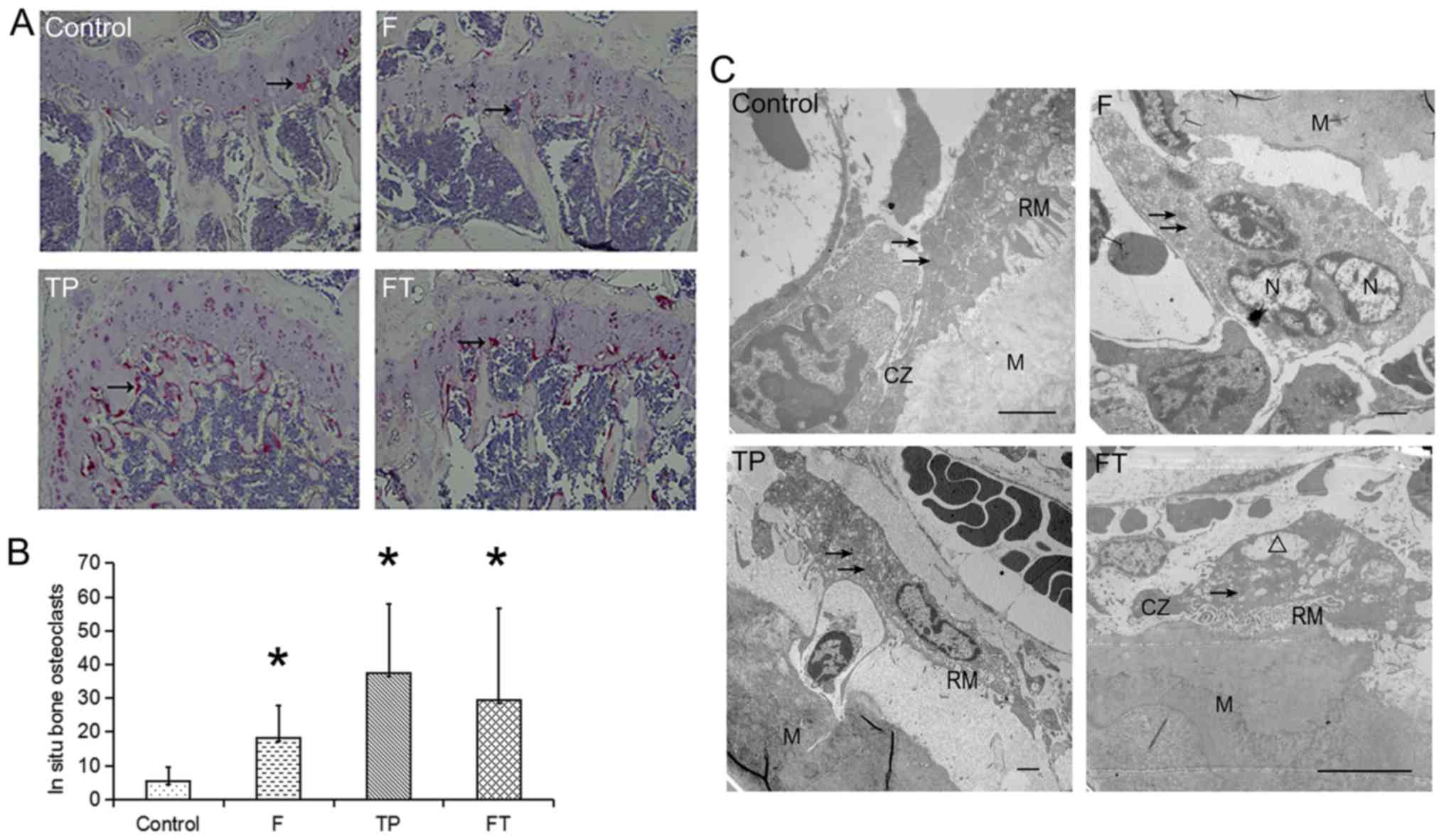
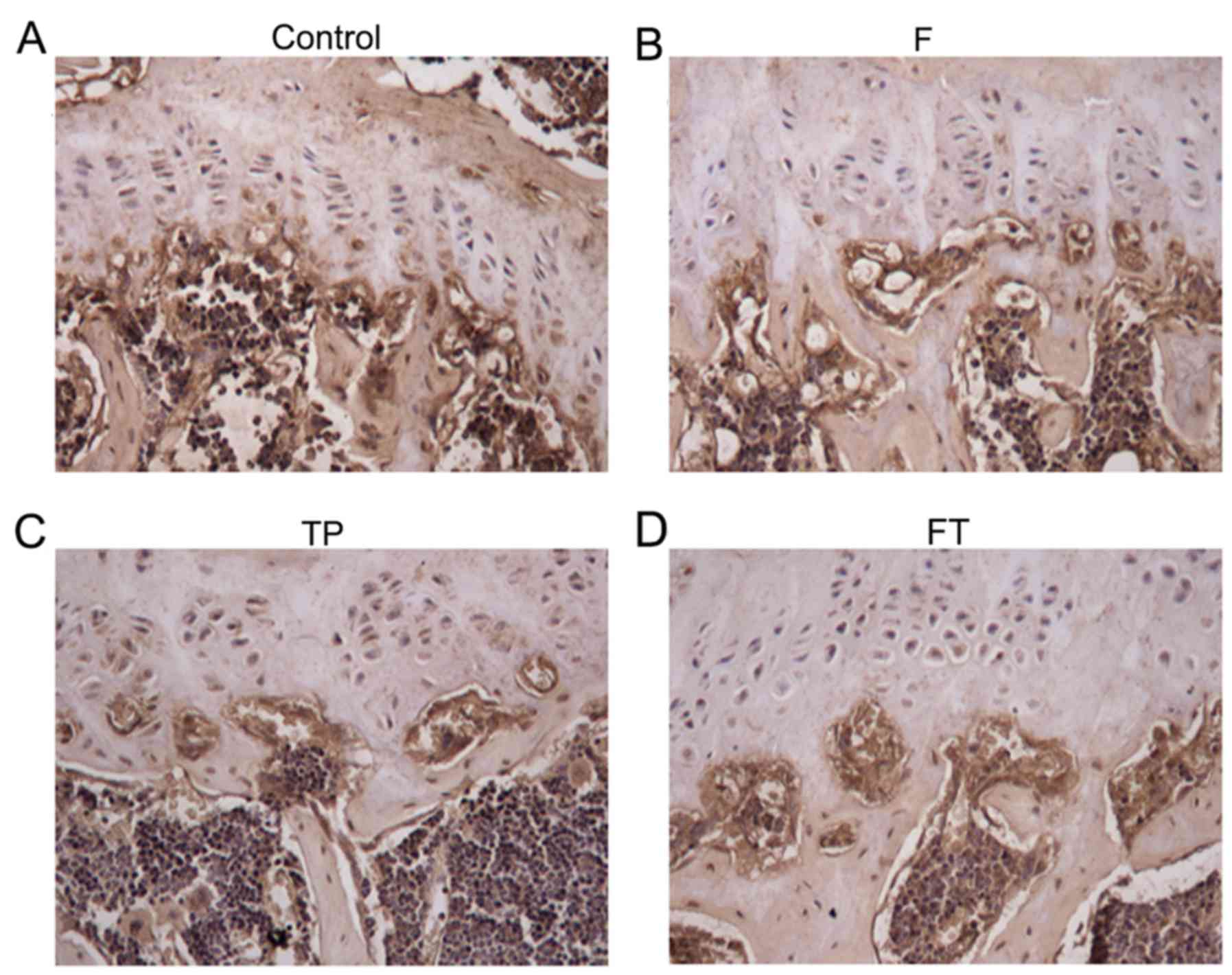
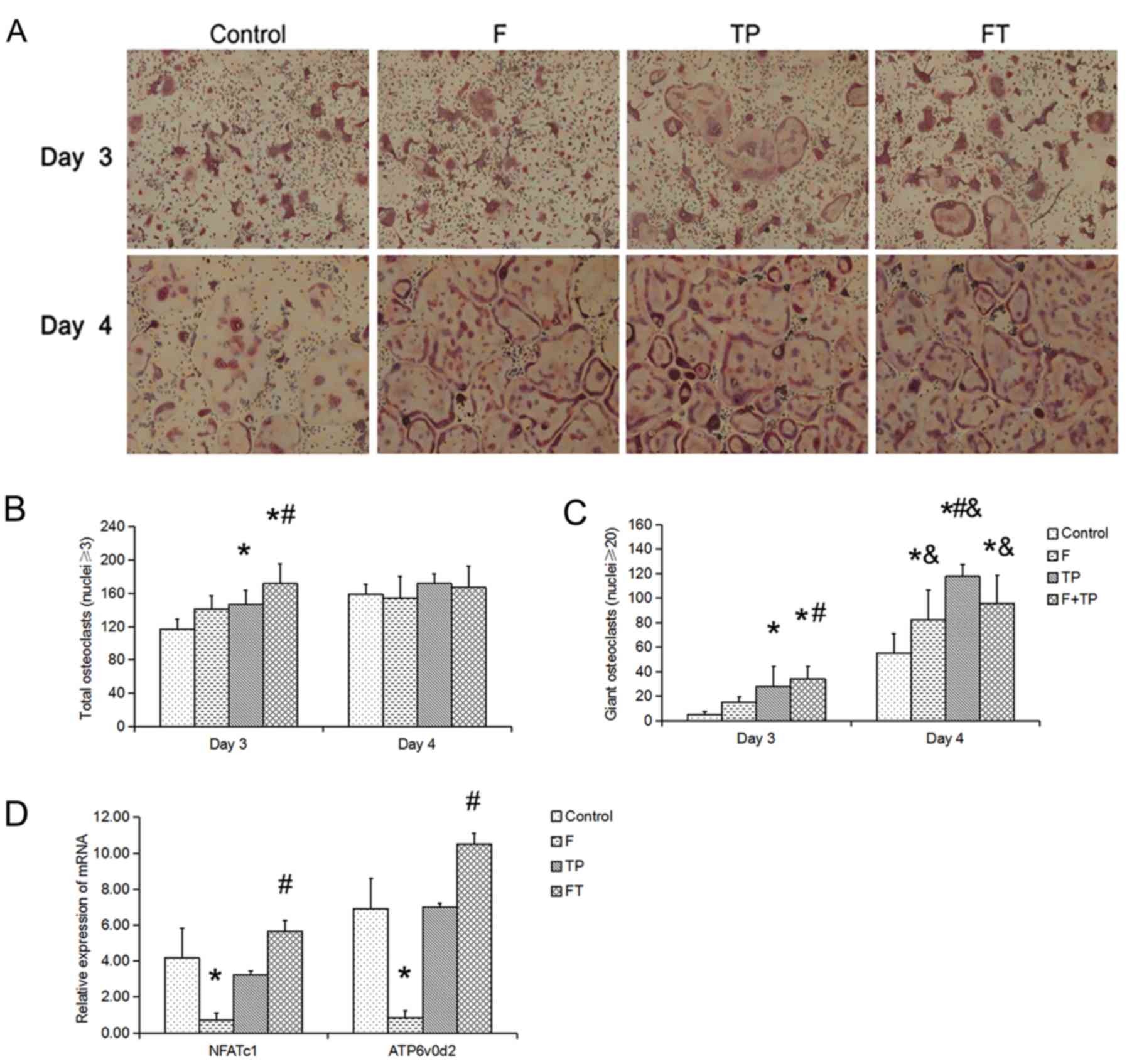
|
1
|
WHO: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/fluoride-in-drinking-water/en/.
Accessed Nov 10, 2011.
|
|
2
|
Wang C, Gao Y, Wang W, Zhao L, Zhang W,
Han H, Shi Y, Yu G and Sun D: A national cross-sectional study on
effects of fluoride-safe water supply on the prevalence of
fluorosis in China. BMJ Open. 2:e0015642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun D and Gao Y: Molecular mechanism of
pathogenesis of osteofluorosis: a discussion in the view of bone
turnover. Chin J Endemiol. 27:239–241. 2008.
|
|
4
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Väänänen HK, Zhao H, Mulari M and Halleen
JM: The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci.
113:377–381. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Väänänen HK, Karhukorpi EK, Sundquist K,
Wallmark B, Roininen I, Hentunen T, Tuukkanen J and Lakkakorpi P:
Evidence for the presence of a proton pump of the vacuolar
H(+)-ATPase type in the ruffled borders of osteoclasts. J Cell
Biol. 111:1305–1311. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim K, Lee SH, Ha Kim J, Choi Y and Kim N:
NFATc1 induces osteoclast fusion via up-regulation of Atp6v0d2 and
the dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). Mol
Endocrinol. 22:176–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Baron R, Neff L, Louvard D and Courtoy PJ:
Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption:
Evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a
100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border.
J Cell Biol. 101:2210–2222. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Blair HC, Teitelbaum SL, Ghiselli R and
Gluck S: Osteoclastic bone resorption by a polarized vacuolar
proton pump. Science. 245:855–857. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kornak U, Kasper D, Bösl MR, Kaiser E,
Schweizer M, Schulz A, Friedrich W, Delling G and Jentsch TJ: Loss
of the ClC-7 chloride channel leads to osteopetrosis in mice and
man. Cell. 104:205–215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jentsch TJ, Stein V, Weinreich F and
Zdebik AA: Molecular structure and physiological function of
chloride channels. Physiol Rev. 82:503–568. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Q, Wei Q, He A, Jia R and Xiao Y:
CLC-7: A potential therapeutic target for the treatment of
osteoporosis and neurodegeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
384:277–279. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leisle L, Ludwig CF, Wagner FA, Jentsch TJ
and Stauber T: ClC-7 is a slowly voltage-gated
2Cl(−)/1H(+)-exchanger and requires Ostm1 for transport activity.
EMBO J. 30:2140–2152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lange PF, Wartosch L, Jentsch TJ and
Fuhrmann JC: ClC-7 requires Ostm1 as a beta-subunit to support bone
resorption and lysosomal function. Nature. 440:220–223. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun D, Gao Y, Zhao L, Yu G, Wu L and Li Q:
A cross-sectional survey on drinking brick-tea type fluorosis in
China. Chin J Endemiol. 27:513–517. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Sun D, Gao Y, Yu G, Liu Y, Zhao X, Wu L,
Li Q and Sun Y: Prevalence characteristics of drink-tea type
fluorosis. Chin J Endemiol. 27:121–123. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Varol E, Icli A, Aksoy F, Bas HA, Sutcu R,
Ersoy IH, Varol S and Ozaydin M: Evaluation of total oxidative
status and total antioxidant capacity in patients with endemic
fluorosis. Toxicol Ind Health. 29:175–180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Cui KP, Xu YY, Gao YL, Zhao J, Li
DS, Li XL and Huang HJ: Coal-burning endemic fluorosis is
associated with reduced activity in antioxidative enzymes and
Cu/Zn-SOD gene expression. Environ Geochem Health. 36:107–115.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cabrera C, Artacho R and Giménez R:
Beneficial effects of green tea - a review. J Am Coll Nutr.
25:79–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Cao JJ and Wang JS: Green
tea and bone metabolism. Nutr Res. 29:437–456. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen CL, Yeh JK, Stoecker BJ, Chyu MC and
Wang JS: Green tea polyphenols mitigate deterioration of bone
microarchitecture in middle-aged female rats. Bone. 44:684–690.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Junrui P, Bingyun L, Yanhui G, Xu J, Darko
GM and Dianjun S: Relationship between fluoride exposure and
osteoclast markers during RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 46:241–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu XL, Song J, Liu KJ, Wang WP, Xu C,
Zhang YZ and Liu Y: Role of inhibition of osteogenesis function by
Sema4D/Plexin-B1 signaling pathway in skeletal fluorosis in vitro.
J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 35:712–715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dean HT: Fluorine in the control of dental
caries. J Am Dent Assoc. 52:1–8. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dean HT: Endemic fluorosis and its
relation to dental caries. 1938. Public Health Rep. 121(Suppl 1):
213–219; discussion 212. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Drozdzowska B, Pluskiewicz W and Tarnawska
B: Panoramic-based mandibular indices in relation to mandibular
bone mineral density and skeletal status assessed by dual energy
X-ray absorptiometry and quantitative ultrasound. Dentomaxillofac
Radiol. 31:361–367. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nordahl J, Andersson G and Reinholt FP:
Chondroclasts and osteoclasts in bones of young rats: Comparison of
ultrastructural and functional features. Calcif Tissue Int.
63:401–408. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nordahl J, Hollberg K, Mengarelli-Widholm
S, Andersson G and Reinholt FP: Morphological and functional
features of clasts in low phosphate, vitamin D-deficiency rickets.
Calcif Tissue Int. 67:400–407. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chambers TJ: Regulation of the
differentiation and function of osteoclasts. J Pathol. 192:4–13.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen JQ, Heldman MR, Herrmann MA, Kedei N,
Woo W, Blumberg PM and Goldsmith PK: Absolute quantitation of
endogenous proteins with precision and accuracy using a capillary
western system. Anal Biochem. 442:97–103. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dragomir A and Roomans GM: Increased
chloride efflux in colchicine-resistant airway epithelial cell
lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:253–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen S, Wan XL and Sears M: pICln can
regulate swelling-induced Cl− currents in either layer of rabbit
ciliary epithelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 246:59–63. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan D, Gurumurthy A, Wright M, Pfeiler TW,
Loboa EG and Everett ET: Genetic background influences fluoride's
effects on osteoclastogenesis. Bone. 41:1036–1044. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Linkhart TA, Linkhart SG, Kodama Y, Farley
JR, Dimai HP, Wright KR, Wergedal JE, Sheng M, Beamer WG, Donahue
LR, et al: Osteoclast formation in bone marrow cultures from two
inbred strains of mice with different bone densities. J Bone Miner
Res. 14:39–46. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Judex S, Garman R, Squire M, Donahue LR
and Rubin C: Genetically based influences on the site-specific
regulation of trabecular and cortical bone morphology. J Bone Miner
Res. 19:600–606. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Turner CH, Hsieh YF, Müller R, Bouxsein
ML, Baylink DJ, Rosen CJ, Grynpas MD, Donahue LR and Beamer WG:
Genetic regulation of cortical and trabecular bone strength and
microstructure in inbred strains of mice. J Bone Miner Res.
15:1126–1131. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Turner CH, Hsieh YF, Müller R, Bouxsein
ML, Rosen CJ, McCrann ME, Donahue LR and Beamer WG: Variation in
bone biomechanical properties, microstructure, and density in BXH
recombinant inbred mice. J Bone Miner Res. 16:206–213. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szewczyk KA, Fuller K and Chambers TJ:
Distinctive subdomains in the resorbing surface of osteoclasts.
PLoS One. 8:e602852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu H1, Xu G and Li YP: Atp6v0d2 is an
essential component of the osteoclast-specific proton pump that
mediates extracellular acidification in bone resorption. J Bone
Miner Res. 24:871–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Väänänen K: Mechanism of osteoclast
mediated bone resorption - rationale for the design of new
therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 57:959–971. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Taranta A, Migliaccio S, Recchia I,
Caniglia M, Luciani M, De Rossi G, Dionisi-Vici C, Pinto RM,
Francalanci P, Boldrini R, et al: Genotype-phenotype relationship
in human ATP6i-dependent autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Am J
Pathol. 162:57–68. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
de Vernejoul MC and Bénichou O: Human
osteopetrosis and other sclerosing disorders: Recent genetic
developments. Calcif Tissue Int. 69:1–6. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pei J, Li B, Gao Y, Wei Y, Zhou L, Yao H,
Wang J and Sun D: Fluoride decreased osteoclastic bone resorption
through the inhibition of NFATc1 gene expression. Environ Toxicol.
29:588–595. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Teitelbaum SL and Ross FP: Genetic
regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet.
4:638–649. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Neutzsky-Wulff AV, Sims NA, Supanchart C,
Kornak U, Felsenberg D, Poulton IJ, Martin TJ, Karsdal MA and
Henriksen K: Severe developmental bone phenotype in ClC-7 deficient
mice. Dev Biol. 344:1001–1010. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Plans V, Rickheit G and Jentsch TJ:
Physiological roles of CLC Cl(−)/H (+) exchangers in renal proximal
tubules. Pflugers Arch. 458:23–37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|