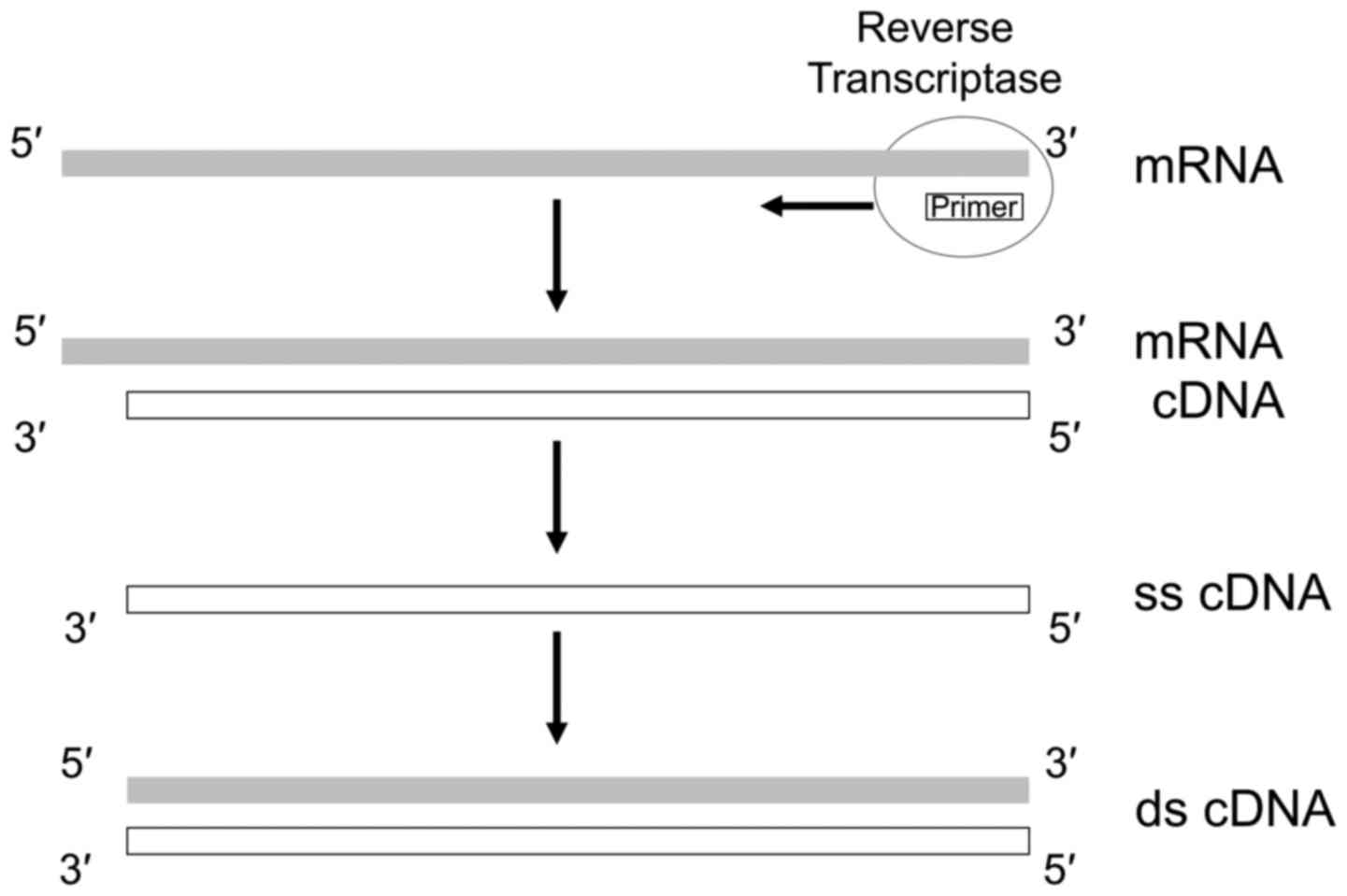
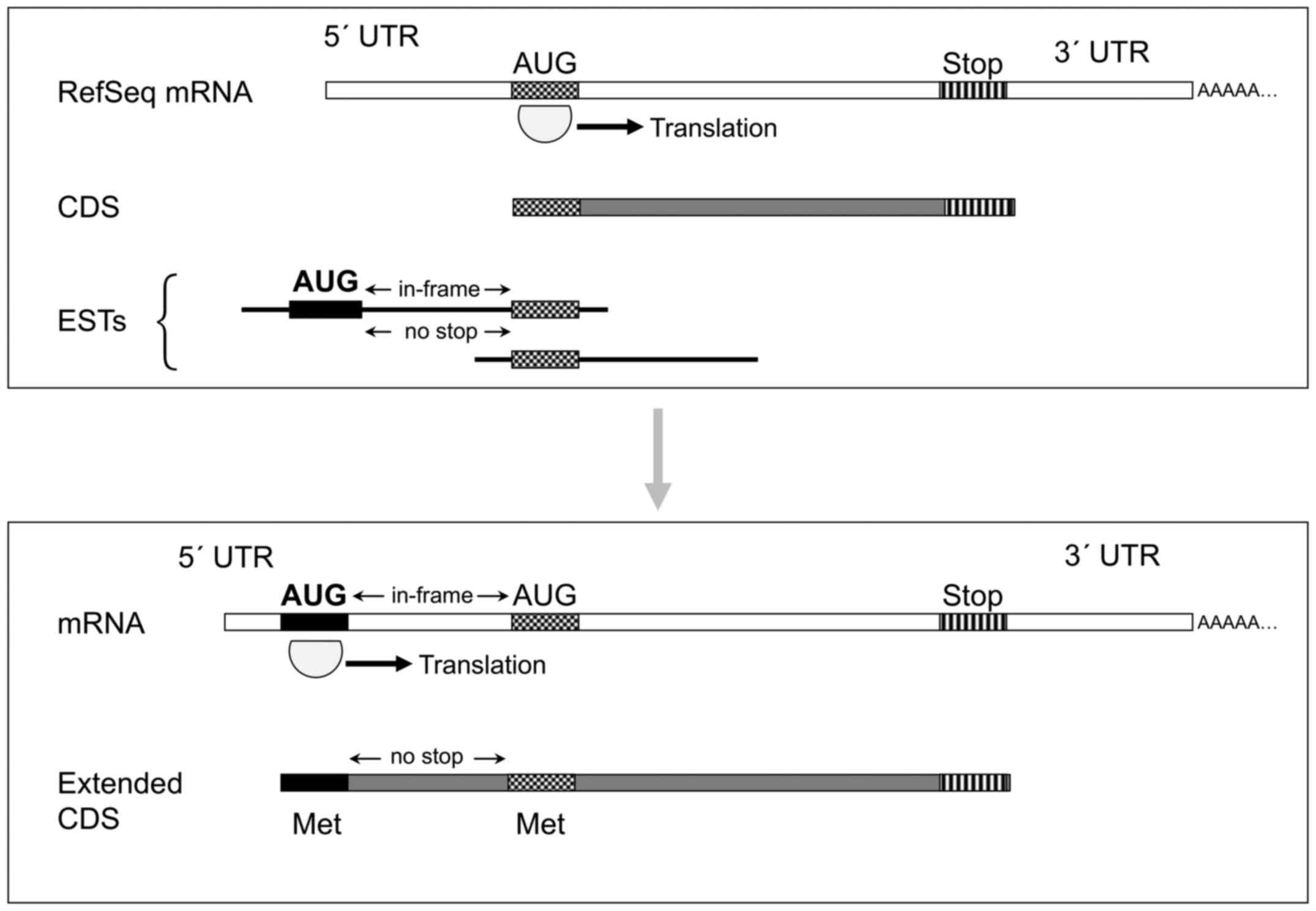
|
1
|
Borsani G, Ballabio A and Banfi S: A
practical guide to orient yourself in the labyrinth of genome
databases. Hum Mol Genet. 7:1641–1648. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pandey A and Lewitter F: Nucleotide
sequence databases: A gold mine for biologists. Trends Biochem Sci.
24:276–280. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baxevanis AD and Bateman A: The importance
of biological databases in biological discovery. Curr Protoc
Bioinformatics. 50:1.1.1–1.1.8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tropp BE: Molecular Biology: Genes to
Proteins. 3rd edition. Jones & Bartlett; Publishers, Sudbury,
MA: 2008
|
|
5
|
Sambrook J and Russel DW: Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor
Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor; NY: 2001
|
|
6
|
Vitale L, Casadei R, Canaider S, Lenzi L,
Strippoli P, D'Addabbo P, Giannone S, Carinci P and Zannotti M:
Cysteine and tyrosine-rich 1 (CYYR1), a novel unpredicted gene on
human chromosome 21 (21q21.2), encodes a cysteine and tyrosine-rich
protein and defines a new family of highly conserved
vertebrate-specific genes. Gene. 290:141–151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Lou X, Shen H, Zellmer L, Sun Y,
Liu S, Xu N and Liao DJ: Isoforms of wild type proteins often
appear as low molecular weight bands on SDS-PAGE. Biotechnol J.
9:1044–1054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick
M, Polymeropoulos MH, Xiao H, Merril CR, Wu A, Olde B, Moreno RF,
et al: Complementary DNA sequencing: Expressed sequence tags and
human genome project. Science. 252:1651–1656. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boguski MS, Lowe TM and Tolstoshev CM:
dbEST - database for 'expressed sequence tags'. Nat Genet.
4:332–333. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagaraj SH, Gasser RB and Ranganathan S: A
hitchhiker's guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Brief
Bioinform. 8:6–21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Parkinson J and Blaxter M: Expressed
sequence tags: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 533:1–12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gill RW and Sanseau P: Rapid in silico
cloning of genes using expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Biotechnol
Annu Rev. 5:25–44. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carulli JP, Artinger M, Swain PM, Root CD,
Chee L, Tulig C, Guerin J, Osborne M, Stein G, Lian J, et al: High
throughput analysis of differential gene expression. J Cell Biochem
Suppl. 30–31:286–296. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sorek R, Shamir R and Ast G: How prevalent
is functional alternative splicing in the human genome? Trends
Genet. 20:68–71. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bonizzoni P, Rizzi R and Pesole G:
Computational methods for alternative splicing prediction. Brief
Funct Genomics Proteomics. 5:46–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Brent MR: Genome annotation past, present,
and future: How to define an ORF at each locus. Genome Res.
15:1777–1786. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanger F: La structure de l'insuline. Bull
Soc Chim Biol (Paris). 37:23–35. 1955.In French.
|
|
18
|
Yanofsky C, Carlton BC, Guest JR, Helinski
DR and Henning U: On the colinearity of gene structure and protein
structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 51:266–272. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sanger F, Nicklen S and Coulson AR: DNA
sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 74:5463–5467. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ruddle FH: The William Allan Memorial
Award address: Reverse genetics and beyond. Am J Hum Genet.
36:944–953. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kozak M: Pushing the limits of the
scanning mechanism for initiation of translation. Gene. 299:1–34.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sambrook J and Russel DW: Rapid
amplification of 5′ cDNA ends. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory
Manual. 3. 3rd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold
Spring Harbor; NY: pp. 8.54–8.60. 2001
|
|
23
|
Okayama H and Berg P: High-efficiency
cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 2:161–170. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baralle F: Complete nucleotide sequence of
the 5′ noncoding region of human alpha-and beta-globin mRNA. Cell.
12:1085–1095. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Proudfoot NJ: Complete 3′ noncoding region
sequences of rabbit and human beta-globin messenger RNAs. Cell.
10:559–570. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marotta CA, Wilson JT, Forget BG and
Weissman SM: Human beta-globin messenger RNA. III Nucleotide
sequences derived from complementary DNA. J Biol Chem.
252:5040–5053. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Efstratiadis A, Kafatos FC and Maniatis T:
The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from
cloned DNA. Cell. 10:571–585. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ullrich A, Shine J, Chirgwin J, Pictet R,
Tischer E, Rutter WJ and Goodman HM: Rat insulin genes:
Construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science.
196:1313–1319. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Casadei R, Strippoli P, D'Addabbo P,
Canaider S, Lenzi L, Vitale L, Giannone S, Frabetti F, Facchin F,
Carinci P, et al: mRNA 5′ region sequence incompleteness: A
potential source of systematic errors in translation initiation
codon assignment in human mRNAs. Gene. 321:185–193. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Harbers M: The current status of cDNA
cloning. Genomics. 91:232–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carninci P, Kvam C, Kitamura A, Ohsumi T,
Okazaki Y, Itoh M, Kamiya M, Shibata K, Sasaki N, Izawa M, et al:
High-efficiency full-length cDNA cloning by biotinylated CAP
trapper. Genomics. 37:327–336. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kodzius R, Kojima M, Nishiyori H, Nakamura
M, Fukuda S, Tagami M, Sasaki D, Imamura K, Kai C, Harbers M, et
al: CAGE: Cap analysis of gene expression. Nat Methods. 3:211–222.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Frohman MA, Dush MK and Martin GR: Rapid
production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts:
Amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:8998–9002. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Denoeud F, Kapranov P, Ucla C, Frankish A,
Castelo R, Drenkow J, Lagarde J, Alioto T, Manzano C, Chrast J, et
al: Prominent use of distal 5′ transcription start sites and
discovery of a large number of additional exons in ENCODE regions.
Genome Res. 17:746–759. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suzuki Y, Ishihara D, Sasaki M, Nakagawa
H, Hata H, Tsunoda T, Watanabe M, Komatsu T, Ota T, Isogai T, et
al: Statistical analysis of the 5′ untranslated region of human
mRNA using 'Oligo-Capped' cDNA libraries. Genomics. 64:286–297.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Porcel BM, Delfour O, Castelli V, De
Berardinis V, Friedlander L, Cruaud C, Ureta-Vidal A, Scarpelli C,
Wincker P, Schächter V, et al: Numerous novel annotations of the
human genome sequence supported by a 5′-end-enriched cDNA
collection. Genome Res. 14:463–471. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Metzker ML: Sequencing technologies - the
next generation. Nat Rev Genet. 11:31–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ingolia NT, Ghaemmaghami S, Newman JR and
Weissman JS: Genome-wide analysis in vivo of translation with
nucleotide resolution using ribosome profiling. Science.
324:218–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ingolia NT, Lareau LF and Weissman JS:
Ribosome profiling of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals the
complexity and dynamics of mammalian proteomes. Cell. 147:789–802.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fritsch C, Herrmann A, Nothnagel M,
Szafranski K, Huse K, Schumann F, Schreiber S, Platzer M, Krawczak
M, Hampe J, et al: Genome-wide search for novel human uORFs and
N-terminal protein extensions using ribosomal footprinting. Genome
Res. 22:2208–2218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Van Damme P, Gawron D, Van Criekinge W and
Menschaert G: N-terminal proteomics and ribosome profiling provide
a comprehensive view of the alternative translation initiation
landscape in mice and men. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:1245–1261. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Iacono M, Mignone F and Pesole G: uAUG and
uORFs in human and rodent 5′ untranslated mRNAs. Gene. 349:97–105.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Barbosa C, Peixeiro I and Romão L: Gene
expression regulation by upstream open reading frames and human
disease. PLoS Genet. 9:e10035292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nishitani H, Hirose E, Uchimura Y,
Nakamura M, Umeda M, Nishii K, Mori N and Nishimoto T: Full-sized
RanBPM cDNA encodes a protein possessing a long stretch of proline
and glutamine within the N-terminal region, comprising a large
protein complex. Gene. 272:25–33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kobayashi A, Ito E, Toki T, Kogame K,
Takahashi S, Igarashi K, Hayashi N and Yamamoto M: Molecular
cloning and functional characterization of a new Cap'n' collar
family transcription factor Nrf3. J Biol Chem. 274:6443–6452. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nomura N, Nagase T, Miyajima N, Sazuka T,
Tanaka A, Sato S, Seki N, Kawarabayasi Y, Ishikawa K and Tabata S:
Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. II
The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0041-KIAA0080) deduced by
analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1. DNA Res.
1:223–229. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kingsley C and Winoto A: Cloning of GT
box-binding proteins: A novel Sp1 multigene family regulating
T-cell receptor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 12:4251–4261. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Strippoli P, Pelleri MC, Caracausi M,
Vitale L, Piovesan A, Locatelli C, Mimmi MC, Berardi AC, Ricotta D,
Radeghieri A, et al: An integrated route to identifying new
pathogenesis-based therapeutic approaches for trisomy 21 (Down
Syndrome) following the thought of Jérôme Lejeune. Sci Postprint.
1:e000102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Pelleri MC, Cicchini E, Locatelli C,
Vitale L, Caracausi M, Piovesan A, Rocca A, Poletti G, Seri M,
Strippoli P, et al: Systematic reanalysis of partial trisomy 21
cases with or without Down syndrome suggests a small region on
21q22.13 as critical to the phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 25:2525–2538.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hattori M, Fujiyama A, Taylor TD, Watanabe
H, Yada T, Park HS, Toyoda A, Ishii K, Totoki Y, Choi DK, et al
Chromosome 21 mapping and sequencing consortium: The DNA sequence
of human chromosome 21. Nature. 405:311–319. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Reymond A, Camargo AA, Deutsch S,
Stevenson BJ, Parmigiani RB, Ucla C, Bettoni F, Rossier C, Lyle R,
Guipponi M, et al: Nineteen additional unpredicted transcripts from
human chromosome 21. Genomics. 79:824–832. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Pesole G, Gissi C, Grillo G, Licciulli F,
Liuni S and Saccone C: Analysis of oligonucleotide AUG start codon
context in eukariotic mRNAs. Gene. 261:85–91. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Frabetti F, Casadei R, Lenzi L, Canaider
S, Vitale L, Facchin F, Carinci P, Zannotti M and Strippoli P:
Systematic analysis of mRNA 5′ coding sequence incompleteness in
Danio rerio: An automated EST-based approach. Biol Direct.
2:342007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Casadei R, Piovesan A, Vitale L, Facchin
F, Pelleri MC, Canaider S, Bianconi E, Frabetti F and Strippoli P:
Genome-scale analysis of human mRNA 5′ coding sequences based on
expressed sequence tag (EST) database. Genomics. 100:125–130. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Piovesan A, Caracausi M, Pelleri MC,
Vitale L, Martini S, Bassani C, Gurioli A, Casadei R, Soldà G and
Strippoli P: Improving mRNA 5′ coding sequence determination in the
mouse genome. Mamm Genome. 25:149–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kochetov AV, Sarai A, Rogozin IB, Shumny
VK and Kolchanov NA: The role of alternative translation start
sites in the generation of human protein diversity. Mol Genet
Genomics. 273:491–496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bazykin GA and Kochetov AV: Alternative
translation start sites are conserved in eukaryotic genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:567–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Ivanov IP, Firth AE, Michel AM, Atkins JF
and Baranov PV: Identification of evolutionarily conserved
non-AUG-initiated N-terminal extensions in human coding sequences.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:4220–4234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Arakaki TL, Pezza JA, Cronin MA, Hopkins
CE, Zimmer DB, Tolan DR and Allen KN: Structure of human brain
fructose 1,6-(bis)phosphate aldolase: Linking isozyme structure
with function. Protein Sci. 13:3077–3084. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lamour V, Quevillon S, Diriong S, N'Guyen
VC, Lipinski M and Mirande M: Evolution of the Glx-tRNA synthetase
family: The glutaminyl enzyme as a case of horizontal gene
transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:8670–8674. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hermann E, Darcissac E, Idziorek T, Capron
A and Bahr GM: Recombinant interleukin-16 selectively modulates
surface receptor expression and cytokine release in macrophages and
dendritic cells. Immunology. 97:241–248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schatz G and Dobberstein B: Common
principles of protein translocation across membranes. Science.
271:1519–1526. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nakamura M, Masuda H, Horii J, Kuma K,
Yokoyama N, Ohba T, Nishitani H, Miyata T, Tanaka M and Nishimoto
T: When overexpressed, a novel centrosomal protein, RanBPM, causes
ectopic microtubule nucleation similar to gamma-tubulin. J Cell
Biol. 143:1041–1052. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Varshavsky A: The N-end rule: Functions,
mysteries, uses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:12142–12149. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rothermel B, Vega RB, Yang J, Wu H,
Bassel-Duby R and Williams RS: A protein encoded within the Down
syndrome critical region is enriched in striated muscles and
inhibits calcineurin signaling. J Biol Chem. 275:8719–8725. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Strippoli P, Petrini M, Lenzi L, Carinci P
and Zannotti M: The murine DSCR1-like (Down syndrome candidate
region 1) gene family: Conserved synteny with the human orthologous
genes. Gene. 257:223–232. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vitale L, Frabetti F, Huntsman SA,
Canaider S, Casadei R, Lenzi L, Facchin F, Carinci P, Zannotti M,
Coppola D, et al: Sequence, 'subtle' alternative splicing and
expression of the CYYR1 (cysteine/tyrosine-rich 1) mRNA in human
neuroendocrine tumors. BMC Cancer. 7:662007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Facchin F, Canaider S, Vitale L, Frabetti
F, Griffoni C, Lenzi L, Casadei R and Strippoli P: Identification
and analysis of human RCAN3 (DSCR1L2) mRNA and protein isoforms.
Gene. 407:159–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Facchin F, Vitale L, Bianconi E, Piva F,
Frabetti F, Strippoli P, Casadei R, Pelleri MC, Piovesan A and
Canaider S: Complexity of bidirectional transcription and
alternative splicing at human RCAN3 locus. PLoS One. 6:e245082011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Casadei R, Pelleri MC, Vitale L, Facchin
F, Canaider S, Strippoli P, Vian M, Piovesan A, Bianconi E, Mariani
E, et al: Characterization of human gene locus CYYR1: A complex
multi-transcript system. Mol Biol Rep. 41:6025–6038. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Tanaka A and
Nomura N: Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human
genes. V The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0161-KIAA0200)
deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1. DNA
Res. 3:17–24. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ribieras S, Lefèbvre O, Tomasetto C and
Rio MC: Mouse Trefoil factor genes: Genomic organization, sequences
and methylation analyses. Gene. 266:67–75. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Doglio L, Goode DK, Pelleri MC, Pauls S,
Frabetti F, Shimeld SM, Vavouri T and Elgar G: Parallel evolution
of chordate cis-regulatory code for development. PLoS Genet.
9:e10039042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hinnebusch AG, Ivanov IP and Sonenberg N:
Translational control by 5′-untranslated regions of eukaryotic
mRNAs. Science. 352:1413–1416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Caracausi M, Vitale L, Pelleri MC,
Piovesan A, Bruno S and Strippoli P: A quantitative transcriptome
reference map of the normal human brain. Neurogenetics. 15:267–287.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Pelleri MC, Piovesan A, Caracausi M,
Berardi AC, Vitale L and Strippoli P: Integrated differential
transcriptome maps of Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (AMKL) in
children with or without Down Syndrome (DS). BMC Med Genomics.
7:632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Manning AG, Crawford BD, Waskiewicz AJ and
Pilgrim DB: unc-119 homolog required for normal development of the
zebrafish nervous system. Genesis. 40:223–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Piovesan A, Vitale L, Pelleri MC and
Strippoli P: Universal tight correlation of codon bias and pool of
RNA codons (codonome): The genome is optimized to allow any
distribution of gene expression values in the transcriptome from
bacteria to humans. Genomics. 101:282–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Komar AA: The Yin and Yang of codon usage.
Hum Mol Genet. 25(R2): R77–R85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Piovesan A, Caracausi M, Antonaros F,
Pelleri MC and Vitale L: GeneBase 11: A tool to summarise data from
NCBI gene datasets and its application to an update of human gene
statistics. Database (Oxford). 2016. pii: baw153. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ahsan B, Saito TL, Hashimoto S, Muramatsu
K, Tsuda M, Sasaki A, Matsushima K, Aigaki T and Morishita S:
MachiBase: A Drosophila melanogaster 5′-end mRNA transcription
database. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database): D49–D53. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Machida RJ and Lin YY: Four methods of
preparing mRNA 5′ end libraries using the Illumina sequencing
platform. PLoS One. 9:e1018122014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Helbig AO, Gauci S, Raijmakers R, van
Breukelen B, Slijper M, Mohammed S and Heck AJ: Profiling of
N-acetylated protein termini provides in-depth insights into the
N-terminal nature of the proteome. Mol Cell Proteomics. 9:928–939.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Doucet A and Overall CM: Amino-Terminal
Oriented Mass Spectrometry of Substrates (ATOMS) N-terminal
sequencing of proteins and proteolytic cleavage sites by
quantitative mass spectrometry. Methods Enzymol. 501:275–293. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|