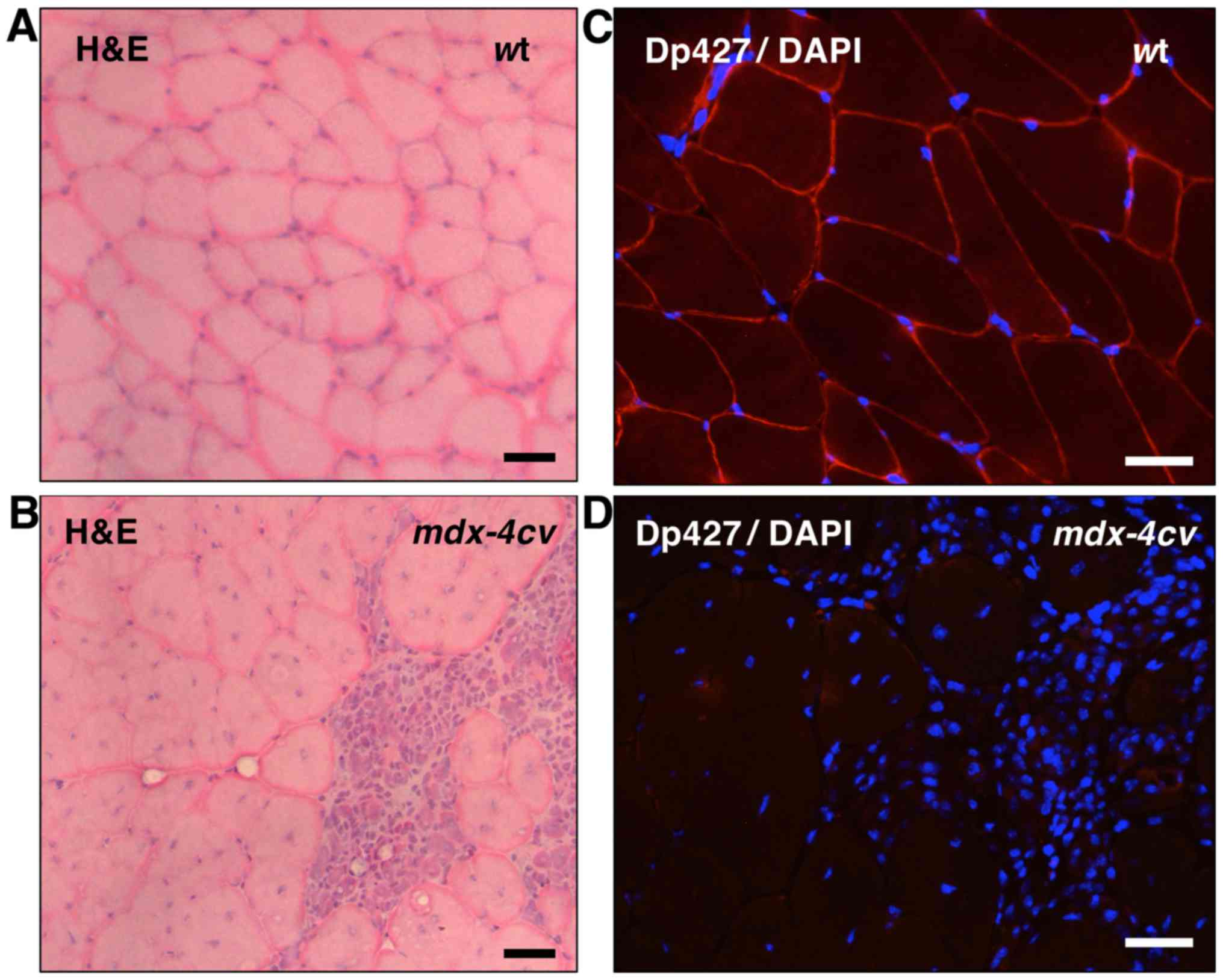
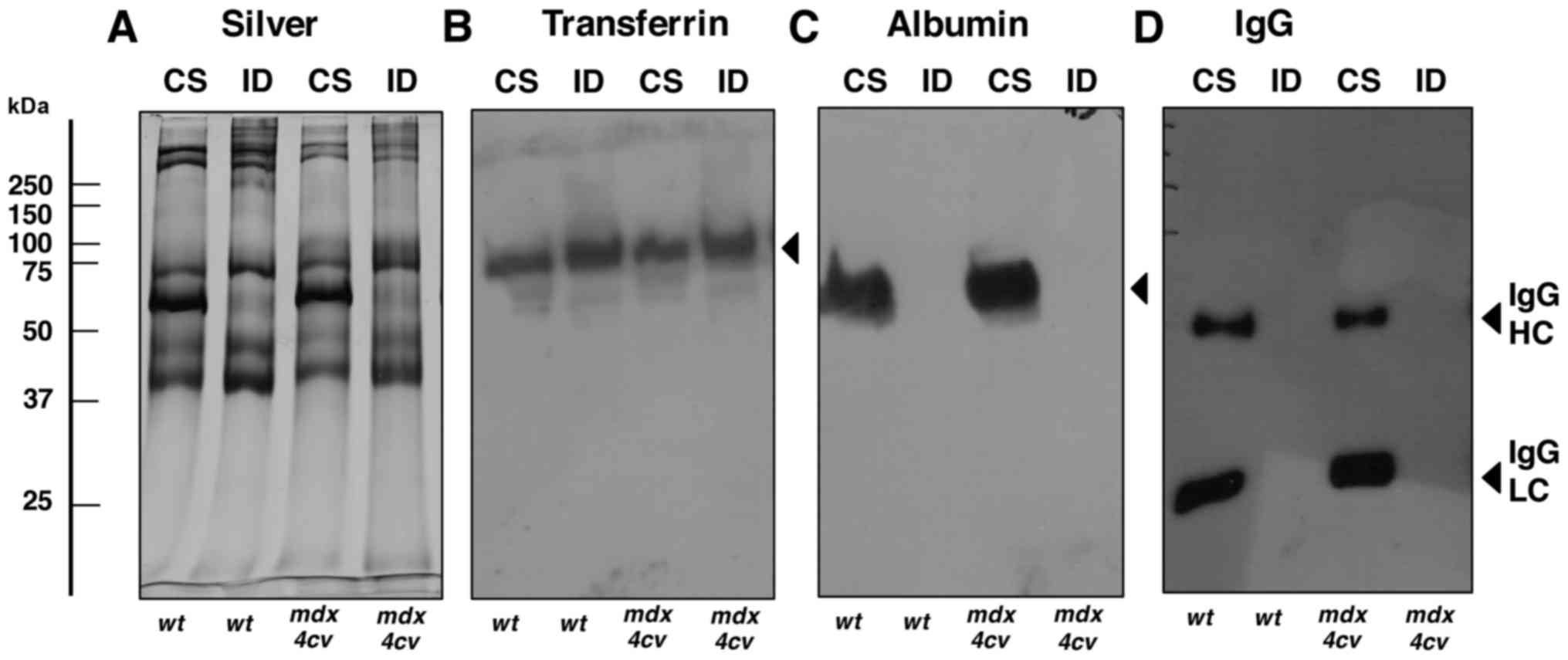
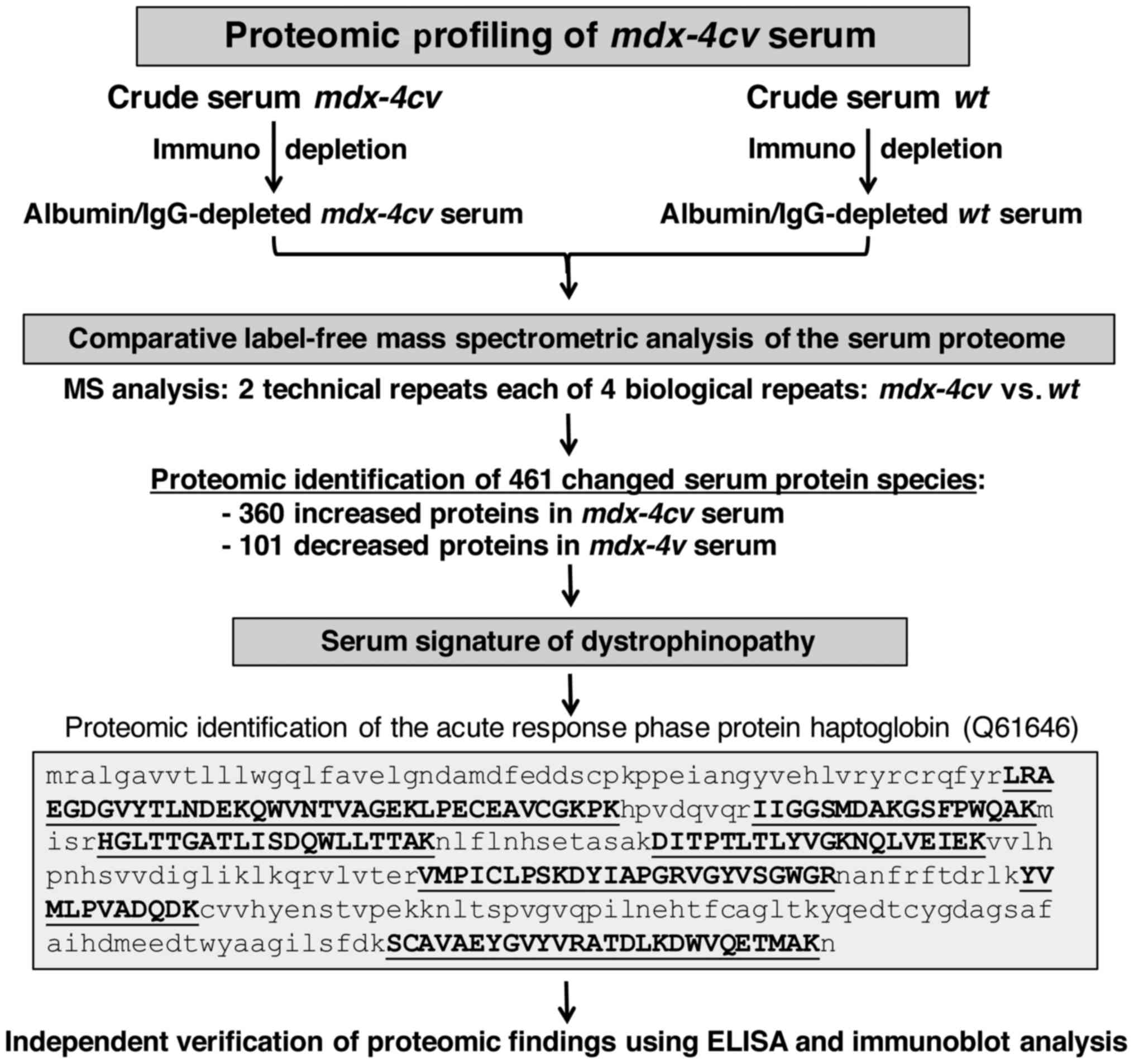
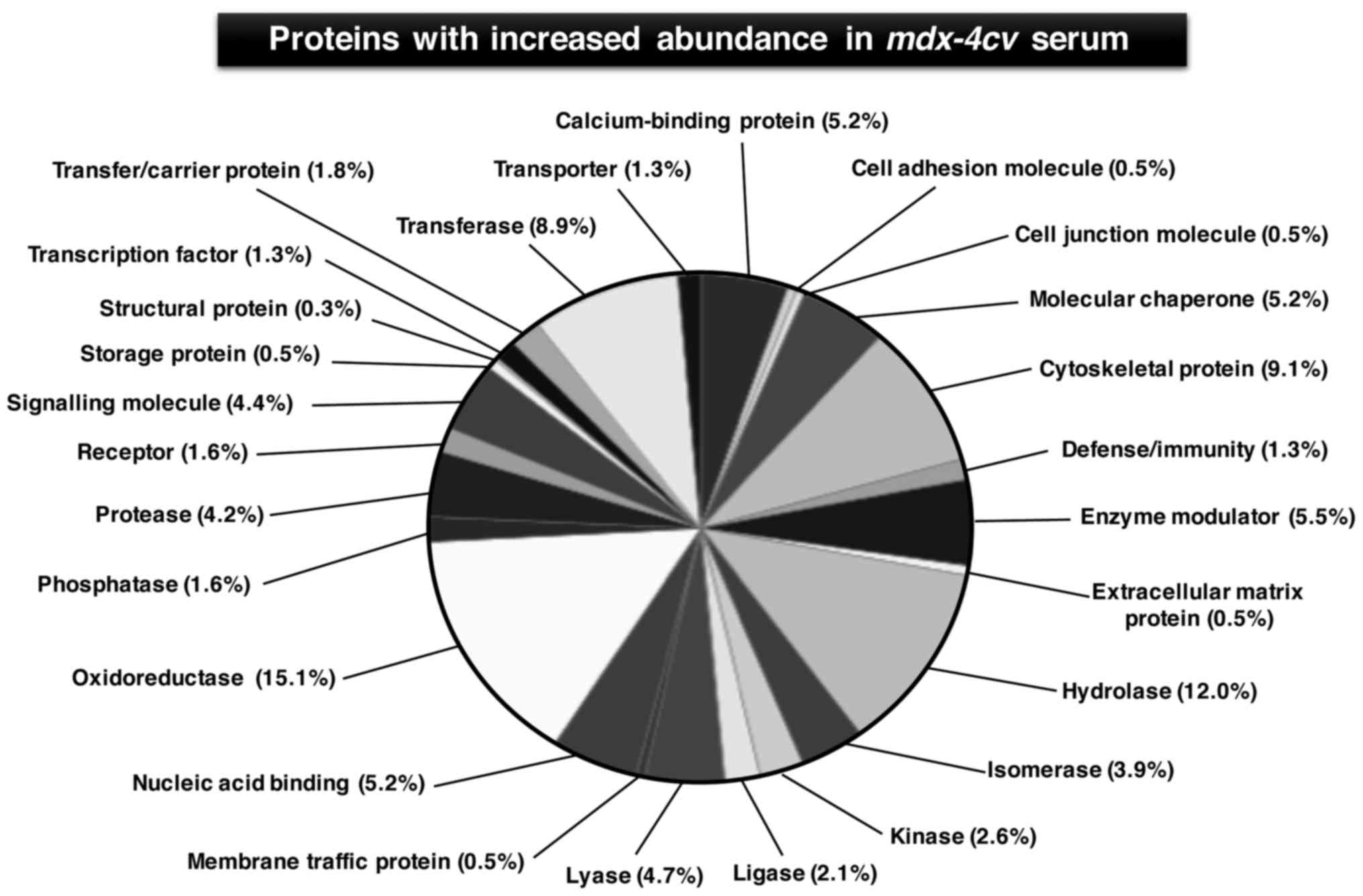
|
1
|
Flanigan KM: Duchenne and Becker muscular
dystrophies. Neurol Clin. 32:671–688. viii2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mah JK, Korngut L, Dykeman J, Day L,
Pringsheim T and Jette N: A systematic review and meta-analysis on
the epidemiology of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy.
Neuromuscul Disord. 24:482–491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guiraud S, Aartsma-Rus A, Vieira NM,
Davies KE, van Ommen GJ and Kunkel LM: The pathogenesis and therapy
of muscular dystrophies. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 16:281–308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohlendieck K: Towards an understanding of
the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex: Linkage between the
extracellular matrix and the membrane cytoskeleton in muscle
fibers. Eur J Cell Biol. 69:1–10. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Allen DG, Zhang BT and Whitehead NP:
Stretch-induced membrane damage in muscle: Comparison of wild-type
and mdx mice. Adv Exp Med Biol. 682:297–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Allen DG, Whitehead NP and Froehner SC:
Absence of dystrophin disrupts skeletal muscle signaling: Roles of
Ca2+, reactive oxygen species, and nitric oxide in the
development of muscular dystrophy. Physiol Rev. 96:253–305. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hopf FW, Turner PR and Steinhardt RA:
Calcium misregulation and the pathogenesis of muscular dystrophy.
Subcell Biochem. 45:429–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shin J, Tajrishi MM, Ogura Y and Kumar A:
Wasting mechanisms in muscular dystrophy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2266–2279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mázala DA, Grange RW and Chin ER: The role
of proteases in excitation-contraction coupling failure in muscular
dystrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C33–C40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Holland A, Murphy S, Dowling P and
Ohlendieck K: Pathoproteomic profiling of the skeletal muscle
matrisome in dystrophinopathy associated myofibrosis. Proteomics.
16:345–366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Serra F, Quarta M, Canato M, Toniolo L, De
Arcangelis V, Trotta A, Spath L, Monaco L, Reggiani C and Naro F:
Inflammation in muscular dystrophy and the beneficial effects of
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Muscle Nerve. 46:773–784.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
De Paepe B and De Bleecker JL: Cytokines
and chemokines as regulators of skeletal muscle inflammation:
Presenting the case of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Mediators
Inflamm. 540370:2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mojumdar K, Liang F, Giordano C, Lemaire
C, Danialou G, Okazaki T, Bourdon J, Rafei M, Galipeau J, Divangahi
M and Petrof BJ: Inflammatory monocytes promote progression of
Duchenne muscular dystrophy and can be therapeutically targeted via
CCR2. EMBO Mol Med. 6:1476–1492. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Villalta SA, Rosenberg AS and Bluestone
JA: The immune system in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Friend or
foe. Rare Dis. 3:e10109662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tidball JG: Mechanisms of muscle injury,
repair, and regeneration. Compr Physiol. 1:2029–2062.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rosenberg AS, Puig M, Nagaraju K, Hoffman
EP, Villalta SA, Rao VA, Wakefield LM and Woodcock J:
Immune-mediated pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Sci
Transl Med. 7:299rv42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Villalta SA, Rosenthal W, Martinez L, Kaur
A, Sparwasser T, Tidball JG, Margeta M, Spencer MJ and Bluestone
JA: Regulatory T cells suppress muscle inflammation and injury in
muscular dystrophy. Sci Transl Med. 6:258ra1422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Proud CM: 50 years ago in the Journal of
Pediatrics: The use of serum creatine phosphokinase and other serum
enzymes in the diagnosis of progressive muscular dystrophy. J
Pediatr. 163:16562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Percy ME, Andrews DF and Thompson MW:
Duchenne muscular dystrophy carrier detection using logistic
discrimination: Serum creatine kinase, hemopexin, pyruvate kinase,
and lactate dehydrogenase in combination. Am J Med Genet. 13:27–38.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carter ND, Heath R, Jeffery S, Jackson MJ,
Newham DJ and Edwards RH: Carbonic anhydrase III in Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Clin Chim Acta. 133:201–208. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fröhlich T, Reitter B, Scheffner D,
Schirmer RH and Untucht-Grau R: Muscle adenylate kinase in Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 883:598–603. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Percy ME, Chang LS, Murphy EG, Oss I,
Verellen-Dumoulin C and Thompson MW: Serum creatine kinase and
pyruvate kinase in Duchenne muscular dystrophy carrier detection.
Muscle Nerve. 2:329–339. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
D'Amore PA, Brown RH Jr, Ku PT, Hoffman
EP, Watanabe H, Arahata K, Ishihara T and Folkman J: Elevated basic
fibroblast growth factor in the serum of patients with Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 35:362–365. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bernasconi P, Torchiana E, Confalonieri P,
Brugnoni R, Barresi R, Mora M, Cornelio F, Morandi L and Mantegazza
R: Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in dystrophic
patient muscles correlates with fibrosis. Pathogenetic role of a
fibrogenic cytokine. J Clin Invest. 96:1137–1144. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun G, Haginoya K, Chiba Y, Uematsu M,
Hino-Fukuyo N, Tanaka S, Onuma A, Iinuma K and Tsuchiya S: Elevated
plasma levels of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 and their
overexpression in muscle in human and mouse muscular dystrophy. J
Neurol Sci. 297:19–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nadarajah VD, van Putten M, Chaouch A,
Garrood P, Straub V, Lochmüller H, Ginjaar HB, Aartsma-Rus AM, van
Ommen GJ, den Dunnen JT and 't Hoen PA: Serum matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a biomarker for monitoring disease
progression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Neuromuscul
Disord. 21:569–578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Holland A, Carberry S and Ohlendieck K:
Proteomics of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex and
dystrophinopathy. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 14:680–697. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fuller HR, Graham LC, Llavero Hurtado M
and Wishart TM: Understanding the molecular consequences of
inherited muscular dystrophies: Advancements through proteomic
experimentation. Expert Rev Proteomics. 13:659–671. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hathout Y, Seol H, Han MH, Zhang A, Brown
KJ and Hoffman EP: Clinical utility of serum biomarkers in Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Clin Proteomics. 13:92016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alagaratnam S, Mertens BJ, Dalebout JC,
Deelder AM, van Ommen GJ, den Dunnen JT and 't Hoen PA: Serum
protein profiling in mice: Identification of Factor XIIIa as a
potential biomarker for muscular dystrophy. Proteomics.
8:1552–1563. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duguez S, Duddy W, Johnston H, Lainé J, Le
Bihan MC, Brown KJ, Bigot A, Hathout Y, Butler-Browne G and
Partridge T: Dystrophin deficiency leads to disturbance of
LAMP1-vesicle-associated protein secretion. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:2159–2174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hathout Y, Marathi RL, Rayavarapu S, Zhang
A, Brown KJ, Seol H, Gordish-Dressman H, Cirak S, Bello L, Nagaraju
K, et al: Discovery of serum protein biomarkers in the mdx mouse
model and cross-species comparison to Duchenne muscular dystrophy
patients. Hum Mol Genet. 23:6458–6469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cynthia Martin F, Hiller M, Spitali P,
Oonk S, Dalebout H, Palmblad M, Chaouch A, Guglieri M, Straub V,
Lochmüller H, et al: Fibronectin is a serum biomarker for Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Proteomics Clin Appl. 8:269–278. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ayoglu B, Chaouch A, Lochmüller H,
Politano L, Bertini E, Spitali P, Hiller M, Niks EH, Gualandi F,
Pontén F, et al: Affinity proteomics within rare diseases: A
BIO-NMD study for blood biomarkers of muscular dystrophies. EMBO
Mol Med. 6:918–936. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rouillon J, Zocevic A, Leger T, Garcia C,
Camadro JM, Udd B, Wong B, Servais L, Voit T and Svinartchouk F:
Proteomics profiling of urine reveals specific titin fragments as
biomarkers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord.
24:563–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Coenen-Stass AM, McClorey G, Manzano R,
Betts CA, Blain A, Saleh AF, Gait MJ, Lochmüller H, Wood MJ and
Roberts TC: Identification of novel, therapy-responsive protein
biomarkers in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by
aptamer-based serum proteomics. Sci Rep. 5:170142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rouillon J, Poupiot J, Zocevic A, Amor F,
Léger T, Garcia C, Camadro JM, Wong B, Pinilla R, Cosette J, et al:
Serum proteomic profiling reveals fragments of MYOM3 as potential
biomarkers for monitoring the outcome of therapeutic interventions
in muscular dystrophies. Hum Mol Genet. 24:4916–4932. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hathout Y, Brody E, Clemens PR, Cripe L,
DeLisle RK, Furlong P, Gordish-Dressman H, Hache L, Henricson E,
Hoffman EP, et al: Large-scale serum protein biomarker discovery in
Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:7153–7158.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oonk S, Spitali P, Hiller M, Switzar L,
Dalebout H, Calissano M, Lochmüller H, Aartsma-Rus A, 't Hoen PA
and van der Burgt YE: Comparative mass spectrometric and
immunoassay-based proteome analysis in serum of Duchenne muscular
dystrophy patients. Proteomics Clin Appl. 10:290–299. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Im WB, Phelps SF, Copen EH, Adams EG,
Slightom JL and Chamberlain JS: Differential expression of
dystrophin isoforms in strains of mdx mice with different
mutations. Hum Mol Genet. 5:1149–1153. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Danko I, Chapman V and Wolff JA: The
frequency of revertants in mdx mouse genetic models for Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Pediatr Res. 32:128–131. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mitrpant C, Fletcher S, Iversen PL and
Wilton SD: By-passing the nonsense mutation in the 4 CV mouse model
of muscular dystrophy by induced exon skipping. J Gene Med.
11:46–56. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Kinzie E, Berger FG, Lim SK and
Baumann H: Haptoglobin, an inflammation-inducible plasma protein.
Redox Rep. 6:379–385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chapman VM, Miller DR, Armstrong D and
Caskey CT: Recovery of induced mutations for X chromosome-linked
muscular dystrophy in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:1292–1296.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Partridge TA: The mdx mouse model as a
surrogate for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. FEBS J. 280:4177–4186.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carberry S, Zweyer M, Swandulla D and
Ohlendieck K: Comparative proteomic analysis of the
contractile-protein-depleted fraction from normal versus dystrophic
skeletal muscle. Anal Biochem. 446:108–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hortin GL and Sviridov D: The dynamic
range problem in the analysis of the plasma proteome. J Proteomics.
73:629–636. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Anderson L and Anderson NG: The human
plasma proteome: History, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 1:845–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Holland A, Henry M, Meleady P, Winkler CK,
Krautwald M, Brinkmeier H and Ohlendieck K: Comparative label-free
mass spectrometric analysis of mildly versus severely affected mdx
mouse skeletal muscles identifies annexin, lamin, and vimentin as
universal dystrophic markers. Molecules. 20:11317–11344. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Holland A, Dowling P, Meleady P, Henry M,
Zweyer M, Mundegar RR, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Label-free
mass spectrometric analysis of the mdx-4cv diaphragm identifies the
matricellular protein periostin as a potential factor involved in
dystrophinopathy-related fibrosis. Proteomics. 15:2318–2331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Murphy S, Zweyer M, Mundegar RR, Henry M,
Meleady P, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Concurrent label-free mass
spectrometric analysis of dystrophin isoform Dp427 and the
myofibrosis marker collagen in crude extracts from mdx-4cv skeletal
muscles. Proteomes. 3:298–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Di Luca A, Henry M, Meleady P and O'Connor
R: Label-free LC-MS analysis of HER2+ breast cancer cell
line response to HER2 inhibitor treatment. Daru. 23:402015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Linge A, Maurya P, Friedrich K, Baretton
GB, Kelly S, Henry M, Clynes M, Larkin A and Meleady P:
Identification and functional validation of RAD23B as a potential
protein in human breast cancer progression. J Proteome Res.
13:3212–3222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Murphy S, Dowling P, Zweyer M, Mundegar
RR, Henry M, Meleady P, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic
analysis of dystrophin deficiency and associated changes in the
aged mdx-4cv heart model of dystrophinopathy-related
cardiomyopathy. J Proteomics. 145:24–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mi H, Muruganujan A and Thomas PD: PANTHER
in 2013: Modeling the evolution of gene function, and other gene
attributes, in the context of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids
Res. 41(D1): D377–D386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Staunton L, Zweyer M, Swandulla D and
Ohlendieck K: Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of
middle-aged vs. aged vastus lateralis reveals increased levels of
carbonic anhydrase isoform 3 in senescent human skeletal muscle.
Int J Mol Med. 30:723–733. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Holland A, Dowling P, Zweyer M, Swandulla
D, Henry M, Clynes M and Ohlendieck K: Proteomic profiling of
cardiomyopathic tissue from the aged mdx model of Duchenne muscular
dystrophy reveals a drastic decrease in laminin, nidogen and
annexin. Proteomics. 13:2312–2323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lewis C, Jockusch H and Ohlendieck K:
Proteomic profiling of the dystrophin-deficient MDX heart reveals
drastically altered levels of key metabolic and contractile
proteins. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010:6485012010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Murphy S, Henry M, Meleady P, Zweyer M,
Mundegar RR, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Simultaneous
pathoproteomic evaluation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex
and secondary changes in the mdx-4cv mouse model of Duchenne
muscular dystrophy. Biology (Basel). 4:397–423. 2015.
|
|
61
|
Murphy S, Zweyer M, Henry M, Meleady P,
Mundegar RR, Swandulla D and Ohlendieck K: Label-free mass
spectrometric analysis reveals complex changes in the brain
proteome from the mdx-4cv mouse model of Duchenne muscular
dystrophy. Clin Proteomics. 12:272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dowling P, Holland A and Ohlendieck K:
Mass spectrometry-based identification of muscle-associated and
muscle-derived proteomic biomarkers of dystrophinopathies. J
Neuromuscul Dis. 1:15–40. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gianazza E, Miller I, Palazzolo L,
Parravicini C and Eberini I: With or without you - Proteomics with
or without major plasma/serum proteins. J Proteomics. 140:62–80.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Omenn GS, States DJ, Adamski M, Blackwell
TW, Menon R, Hermjakob H, Apweiler R, Haab BB, Simpson RJ, Eddes
JS, et al: Overview of the HUPO Plasma Proteome Project: Results
from the pilot phase with 35 collaborating laboratories and
multiple analytical groups, generating a core dataset of 3020
proteins and a publicly-available database. Proteomics.
5:3226–3245. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pietrowska M, Marczak L, Polanska J,
Behrendt K, Nowicka E, Walaszczyk A, Chmura A, Deja R, Stobiecki M,
Polanski A, et al: Mass spectrometry-based serum proteome pattern
analysis in molecular diagnostics of early stage breast cancer. J
Transl Med. 7:602009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Smith MP, Wood SL, Zougman A, Ho JT, Peng
J, Jackson D, Cairns DA, Lewington AJ, Selby PJ and Banks RE: A
systematic analysis of the effects of increasing degrees of serum
immunodepletion in terms of depth of coverage and other key aspects
in top-down and bottom-up proteomic analyses. Proteomics.
11:2222–2235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dowling P, Hayes C, Ting KR, Hameed A,
Meiller J, Mitsiades C, Anderson KC, Clynes M, Clarke C, Richardson
P and O'Gorman P: Identification of proteins found to be
significantly altered when comparing the serum proteome from
Multiple Myeloma patients with varying degrees of bone disease. BMC
Genomics. 15:9042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Araújo JE, Jorge S, Teixeira E, Costa F,
Ramos A, Lodeiro C, Santos HM and Capelo JL: A cost-effective
method to get insight into the peritoneal dialysate effluent
proteome. J Proteomics. 145:207–213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gundry RL, Fu Q, Jelinek CA, Van Eyk JE
and Cotter RJ: Investigation of an albumin-enriched fraction of
human serum and its albuminome. Proteomics Clin Appl. 1:73–88.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gundry RL, White MY, Nogee J, Tchernyshyov
I and Van Eyk JE: Assessment of albumin removal from an
immunoaffinity spin column: Critical implications for proteomic
examination of the albuminome and albumin-depleted samples.
Proteomics. 9:2021–2028. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tirumalai RS, Chan KC, Prieto DA, Issaq
HJ, Conrads TP and Veenstra TD: Characterization of the low
molecular weight human serum proteome. Mol Cell Proteomics.
2:1096–1103. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rayavarapu S, Coley W, Cakir E, Jahnke V,
Takeda S, Aoki Y, Grodish-Dressman H, Jaiswal JK, Hoffman EP, Brown
KJ, et al: Identification of disease specific pathways using in
vivo SILAC proteomics in dystrophin deficient mdx mouse. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 12:1061–1073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Roberts TC, Johansson HJ, McClorey G,
Godfrey C, Blomberg KE, Coursindel T, Gait MJ, Smith CI, Lehtiö J,
El Andaloussi S and Wood MJ: Multi-level omics analysis in a murine
model of dystrophin loss and therapeutic restoration. Hum Mol
Genet. 24:6756–6768. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Turk R, Hsiao JJ, Smits MM, Ng BH,
Pospisil TC, Jones KS, Campbell KP and Wright ME: Molecular
signatures of membrane protein complexes underlying muscular
dystrophy. Mol Cell Proteomics. 15:2169–2185. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Schrödl W, Büchler R, Wendler S, Reinhold
P, Muckova P, Reindl J and Rhode H: Acute phase proteins as
promising biomarkers: Perspectives and limitations for human and
veterinary medicine. Proteomics Clin Appl. 10:1077–1092. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ohlendieck K: Proteomic identification of
biomarkers of skeletal muscle disorders. Biomarkers Med. 7:169–186.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Levy AP, Asleh R, Blum S, Levy NS,
Miller-Lotan R, Kalet-Litman S, Anbinder Y, Lache O, Nakhoul FM,
Asaf, et al: Haptoglobin: Basic and clinical aspects. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:293–304. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
John HA and Purdom IF: Elevated plasma
levels of haptoglobin in Duchenne muscular dystrophy:
Electrophoretic variants in patients with a severe form of the
disease. Electrophoresis. 10:489–493. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Górecki DC: Dystrophin: The dead calm of a
dogma. Rare Dis. 4:e11537772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kharraz Y, Guerra J, Mann CJ, Serrano AL
and Muñoz-Cánoves P: Macrophage plasticity and the role of
inflammation in skeletal muscle repair. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:4914972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sinadinos A, Young CN, Al-Khalidi R, Teti
A, Kalinski P, Mohamad S, Floriot L, Henry T, Tozzi G, Jiang T, et
al: 2R X7 purinoceptor: A therapeutic target for ameliorating the
symptoms of duchenne muscular dystrophy. PLoS Med. 12:e10018882015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Veenstra TD, Conrads TP, Hood BL, Avellino
AM, Ellenbogen RG and Morrison RS: Biomarkers: Mining the biofluid
proteome. Mol Cell Proteomics. 4:409–418. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Savino R, Paduano S, Preianò M and
Terracciano R: The proteomics big challenge for biomarkers and new
drug-targets discovery. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13926–13948. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Stastna M and Van Eyk JE: Secreted
proteins as a fundamental source for biomarker discovery.
Proteomics. 12:722–735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Drucker E and Krapfenbauer K: Pitfalls and
limitations in translation from biomarker discovery to clinical
utility in predictive and personalised medicine. EPMA J. 4:72013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sun L, Hu S, Yu L, Guo C, Sun L, Yang Z,
Qi J and Ran Y: Serum haptoglobin as a novel molecular biomarker
predicting colorectal cancer hepatic metastasis. Int J Cancer.
138:2724–2731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|