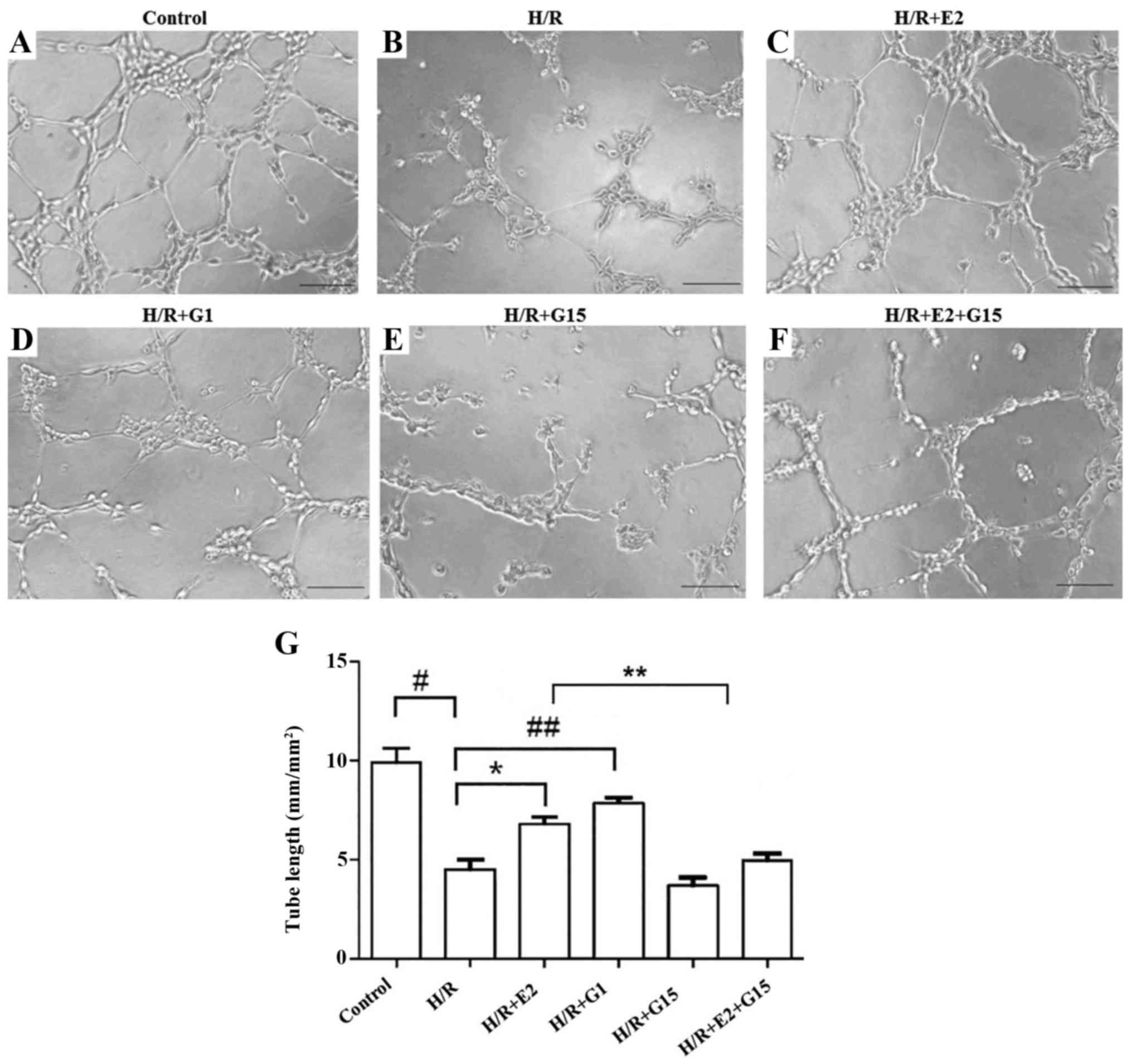
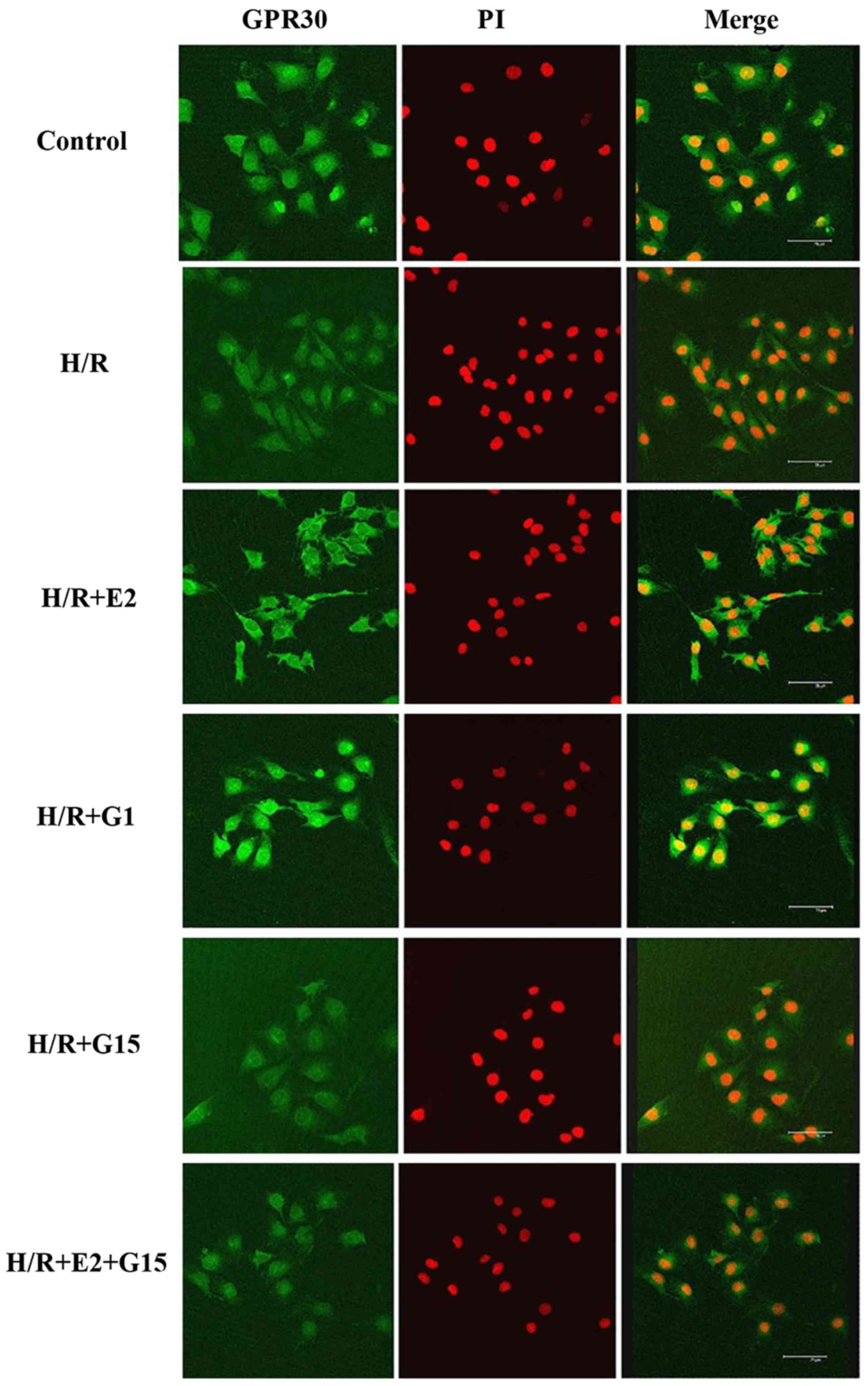
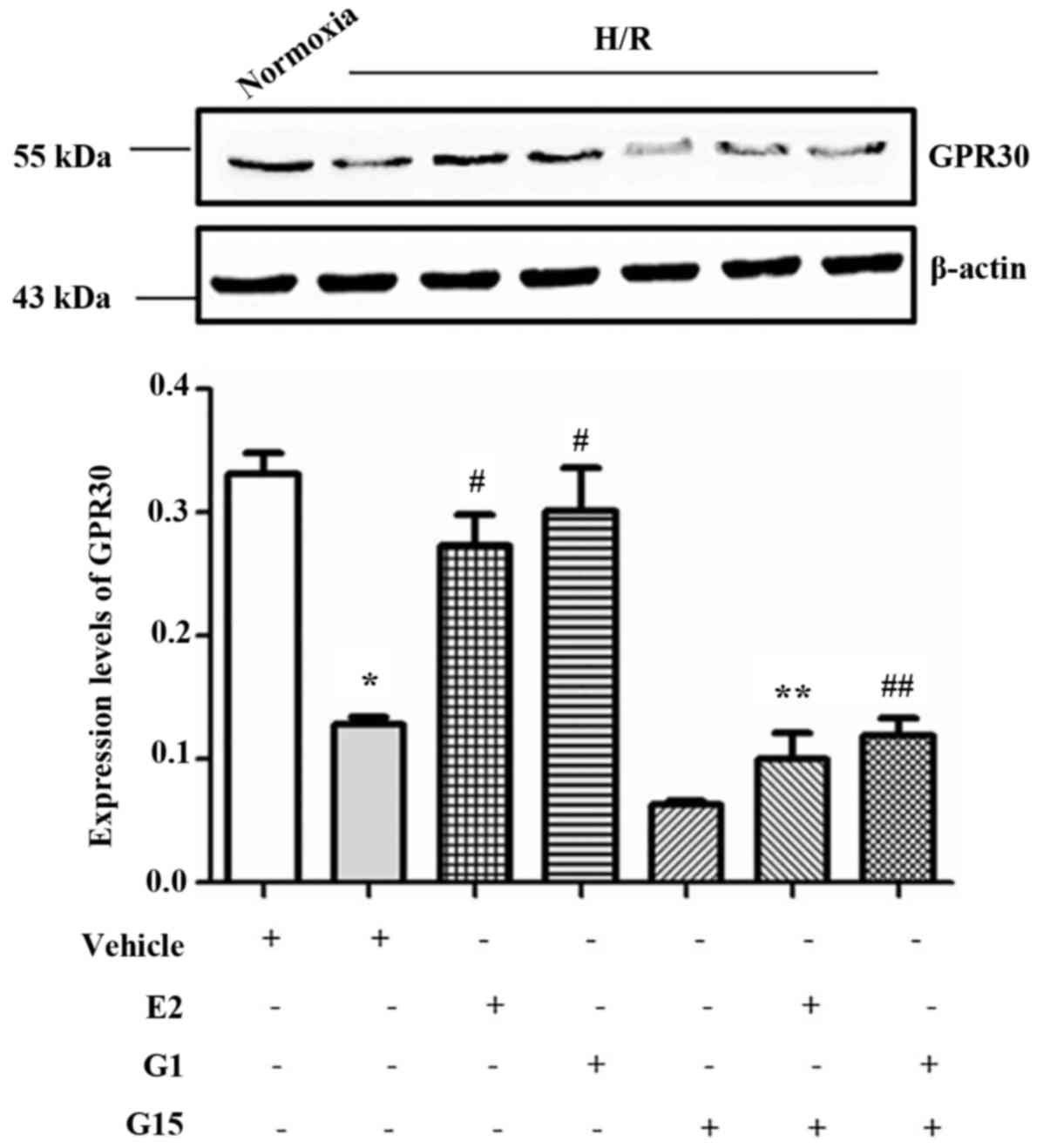
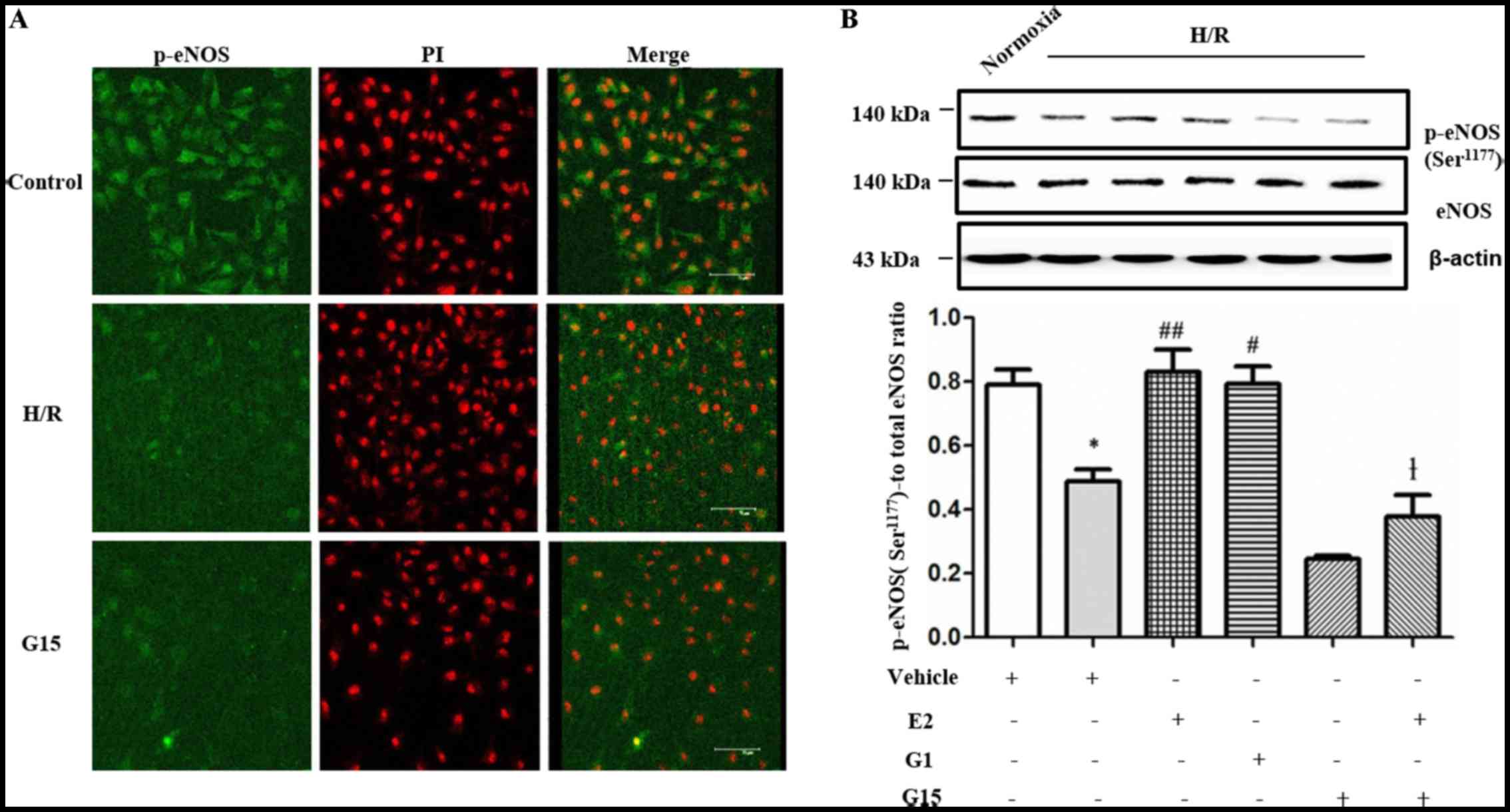
|
1
|
Khong Y and Brosens I: Defective deep
placentation. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 25:301–311.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sibai B, Dekker G and Kupferminc M:
Preeclampsia. Lancet. 365:785–799. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roberts JM and Hubel CA: Is oxidative
stress the link in the two-stage model of preeclampsia? Lancet.
354:788–789. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hubel CA: Oxidative stress in the
pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 222:222–235.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chakrabarti S and Davidge ST: G-protein
coupled receptor 30 (GPR30): A novel regulator of endothelial
inflammation. PLoS One. 7:e523572012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rubanyi GM, Johns A and Kauser K: Effect
of estrogen on endothelial function and angiogenesis. Vascul
Pharmacol. 38:89–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeisler H, Jirecek S, Hohlagschwandtner M,
Knöfler M, Tempfer C and Livingston JC: Concentrations of estrogens
in patients with preeclampsia. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 114:458–461.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tamimi R, Lagiou P, Vatten LJ, Mucci L,
Trichopoulos D, Hellerstein S, Ekbom A, Adami HO and Hsieh CC:
Pregnancy hormones, preeclampsia, and implications for breast
cancer risk in the offspring. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
12:647–650. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jobe SO, Tyler CT and Magness RR: Aberrant
synthesis, metabolism, and plasma accumulation of circulating
estrogens and estrogen metabolites in preeclampsia implications for
vascular dysfunction. Hypertension. 61:480–487. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Molvarec A, Vér A, Fekete A, Rosta K,
Derzbach L, Derzsy Z, Karádi I and Rigó J Jr: Association between
estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) gene polymorphisms and severe
preeclampsia. Hypertens Res. 30:205–211. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maruyama A, Nakayama T, Sato N, Mizutani
Y, Furuya K and Yamamoto T: Association study using single
nucleotide polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor beta (ESR2) gene
for preeclampsia. Hypertens Res. 27:903–909. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Thomas P, Pang Y, Filardo EJ and Dong J:
Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in
human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 146:624–632. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Revankar CM, Cimino DF, Sklar LA,
Arterburn JB and Prossnitz ER: A transmembrane intracellular
estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science.
307:1625–1630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tong C, Feng X, Chen J, Qi X, Zhou L, Shi
S, Kc K, Stanley JL, Baker PN and Zhang H: G protein-coupled
receptor 30 regulates trophoblast invasion and its deficiency is
associated with preeclampsia. J Hypertens. 34:710–718. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Chen Z, Zhou X, Shi S, Qi H, Baker
PN and Zhang H: Imbalance between proliferation and
apoptosis-related impaired GPR30 expression is involved in
preeclampsia. Cell Tissue Res. 366:499–508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB and Sklar LA:
GPR30: A G protein-coupled receptor for estrogen. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 265–266:138–142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hung TH, Skepper JN, Charnock-Jones DS and
Burton GJ: Hypoxia-reoxygenation: A potent inducer of apoptotic
changes in the human placenta and possible etiological factor in
preeclampsia. Circ Res. 90:1274–1281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo X, Yao ZW, Qi HB, Liu DD, Chen GQ,
Huang S and Li QS: Gadd45α as an upstream signaling molecule of p38
MAPK triggers oxidative stress-induced sFlt-1 and sEng upregulation
in preeclampsia. Cell Tissue Res. 344:551–565. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dhar-Mascareño M, Cárcamo JM and Golde DW:
Hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in
human endothelial cells are inhibited by vitamin C. Free Radic Biol
Med. 38:1311–1322. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SR and Lo EH: Interactions between p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase and caspase-3 in cerebral
endothelial cell death after hypoxia-reoxygenation. Stroke.
34:2704–2709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee SR and Lo EH: Induction of
caspase-mediated cell death by matrix metalloproteinases in
cerebral endothelial cells after hypoxia-reoxygenation. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 24:720–727. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tian R, Wang Z, Shi Z, Li D, Wang Y, Zhu
Y, Lin W, Gui Y and Zheng XL: Differential expression of
G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor-30 in human myometrial and
uterine leiomyoma smooth muscle. Fertil Steril. 99:256–263. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Otto C, Rohde-Schulz B, Schwarz G, Fuchs
I, Klewer M, Brittain D, Langer G, Bader B, Prelle K, Nubbemeyer R,
et al: G protein-coupled receptor 30 localizes to the endoplasmic
reticulum and is not activated by estradiol. Endocrinology.
149:4846–4856. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Bai B, Luo X, Xiao X, Liu X, Ding
Y, Zhang H, Gao L, Li J and Qi H: Downregulated Krüppel-like factor
8 is involved in decreased trophoblast invasion under
hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions. Reprod Sci. 21:72–81. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Marconcini L, Marchiò S, Morbidelli L,
Cartocci E, Albini A, Ziche M, Bussolino F and Oliviero S:
c-fos-induced growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor D
induces angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:9671–9676. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim KM, Kim NS, Kim J, Park JS, Yi JM, Lee
J and Bang OS: Magnolol suppresses vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting Ras-dependent
mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. Nutr Cancer. 65:1245–1253. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Batenburg WW, Jansen PM, van den Bogaerdt
AJ and J Danser AH: Angiotensin II-aldosterone interaction in human
coronary microarteries involves GPR30, EGFR, and endothelial NO
synthase. Cardiovasc Res. 94:136–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li ZL, Liu JC, Liu SB, Li XQ, Yi DH and
Zhao MG: Improvement of vascular function by acute and chronic
treatment with the GPR30 agonist G1 in experimental diabetes
mellitus. PLoS One. 7:e387872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Placental
debris, oxidative stress and preeclampsia. Placenta. 21:597–602.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Allaire AD, Ballenger KA, Wells SR,
McMahon MJ and Lessey BA: Placental apoptosis in preeclampsia.
Obstet Gynecol. 96:271–276. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Burton GJ, Charnock-Jones DS and Jauniaux
E: Regulation of vascular growth and function in the human
placenta. Reproduction. 138:895–902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cong B, Xu Y, Sheng H, Zhu X, Wang L, Zhao
W, Tang Z, Lu J and Ni X: Cardioprotection of 17β-estradiol against
hypoxia/reoxygenation in cardiomyocytes is partly through
up-regulation of CRH receptor type 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:17–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Murata T, Dietrich HH, Xiang C and Dacey
RG Jr: G protein-coupled estrogen receptor agonist improves
cerebral microvascular function after hypoxia/reoxygenation injury
in male and female rats. Stroke. 44:779–785. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Granger DN, Kvietys PR and Perry MA:
Leukocyte - endothelial cell adhesion induced by ischemia and
reperfusion. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 71:67–75. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zulueta JJ, Sawhney R, Yu FS, Cote CC and
Hassoun PM: Intracellular generation of reactive oxygen species in
endothelial cells exposed to anoxia-reoxygenation. Am J Physiol.
272:L897–L902. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song Y, Zhao XP, Song K and Shang ZJ:
Ephrin-A1 is up-regulated by hypoxia in cancer cells and promotes
angiogenesis of HUVECs through a coordinated cross-talk with eNOS.
PLoS One. 8:e744642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rowlands DJ, Chapple S, Siow RC and Mann
GE: Equol-stimulated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species activate
endothelial nitric oxide synthase and redox signaling in
endothelial cells: Roles for F-actin and GPR30. Hypertension.
57:833–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kolkova Z, Casslén V, Henic E, Ahmadi S,
Ehinger A, Jirström K and Casslén B: The G protein-coupled estrogen
receptor 1 (GPER/GPR30) does not predict survival in patients with
ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 5:92012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|