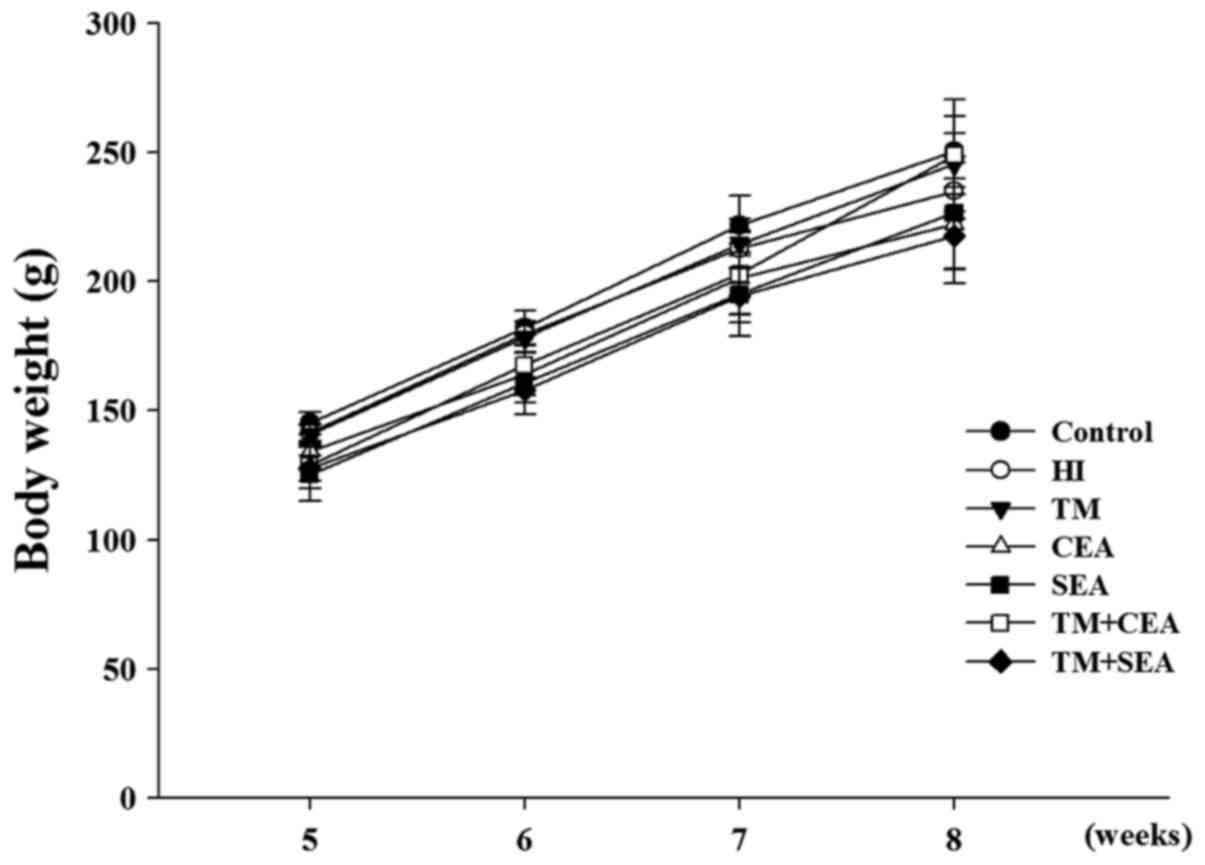
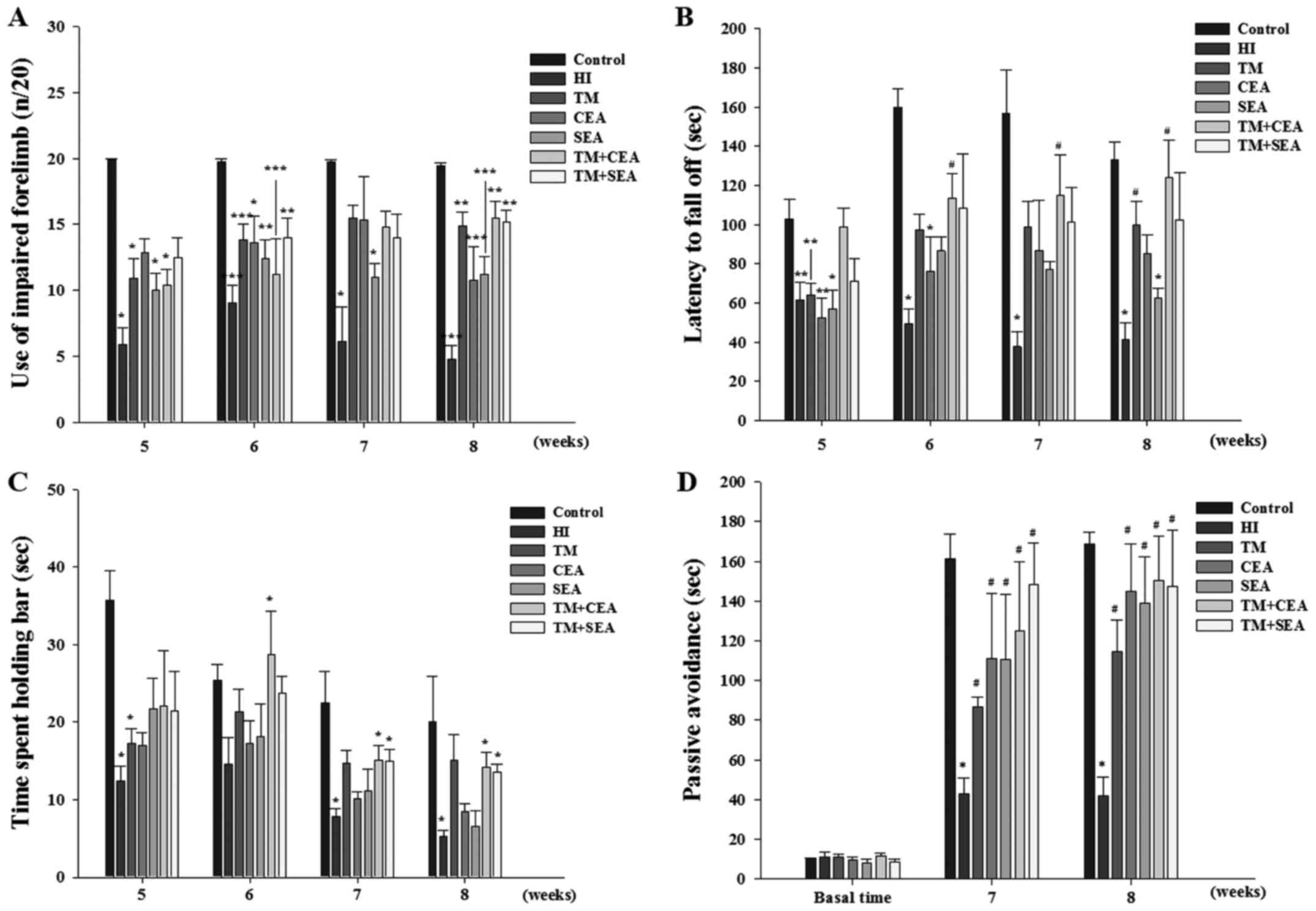
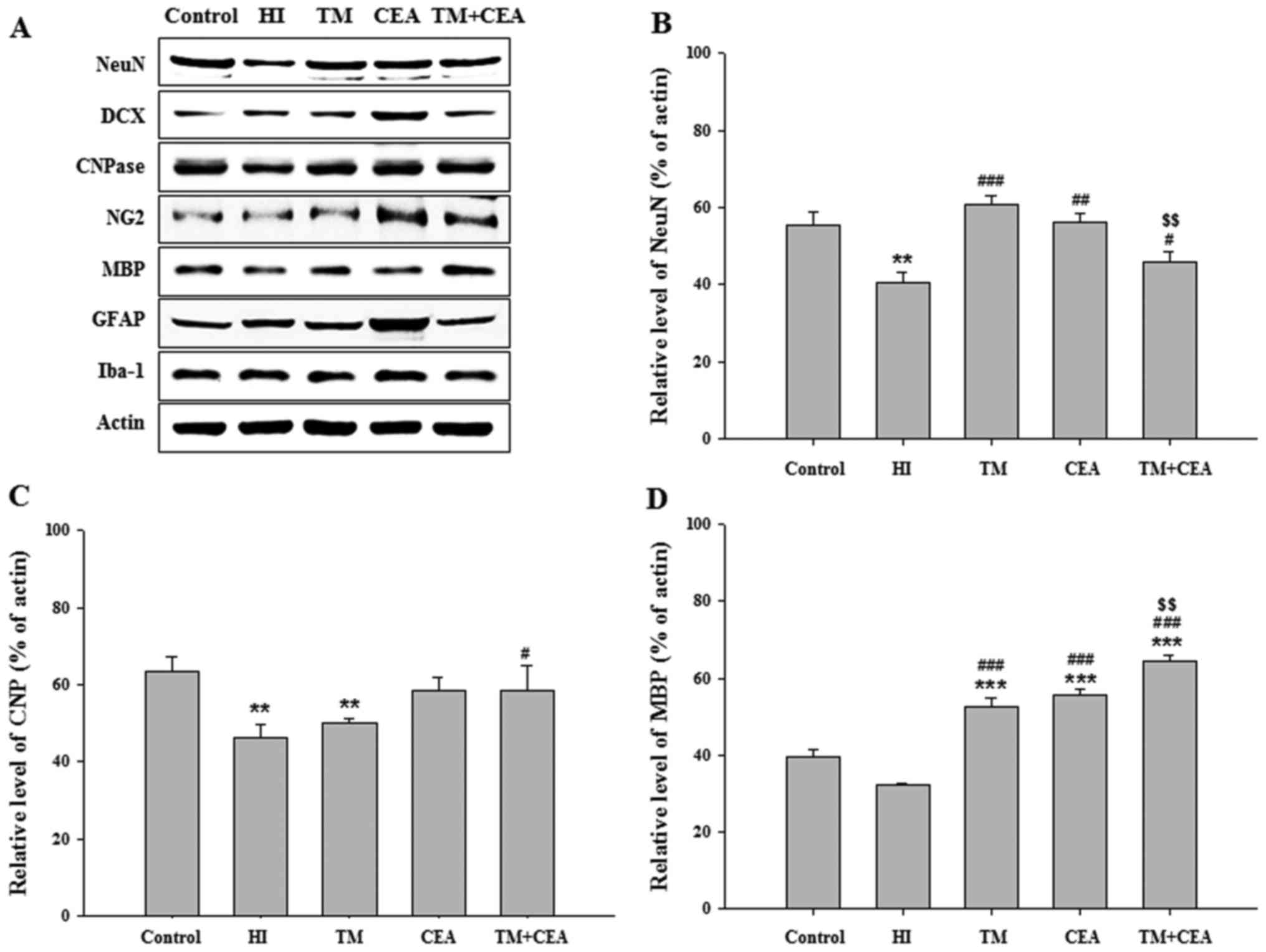
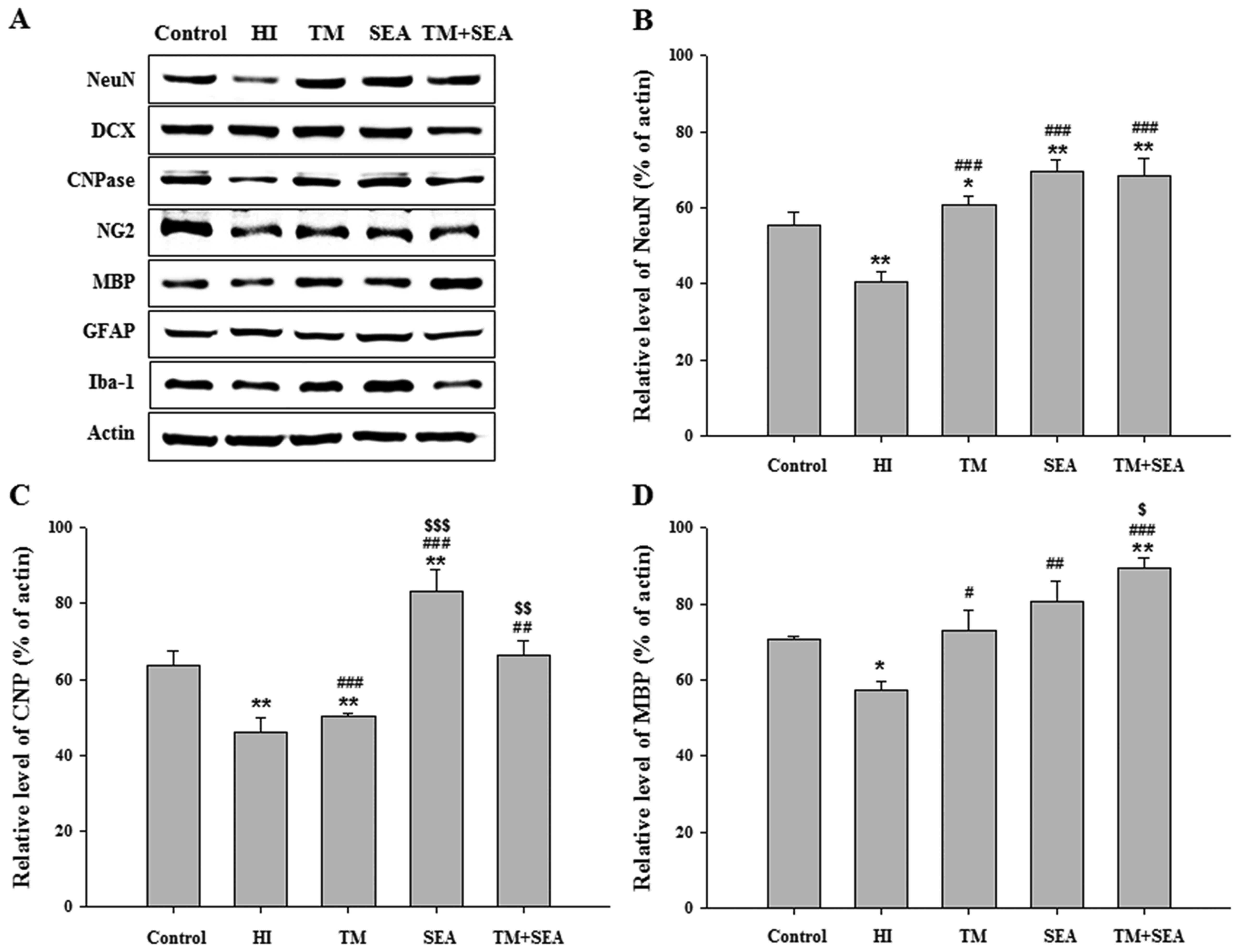
|
1
|
Eikenes L, Løhaugen GC, Brubakk AM,
Skranes J and Håberg AK: Young adults born preterm with very low
birth weight demonstrate widespread white matter alterations on
brain DTI. Neuroimage. 54:1774–1785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Salmaso N, Jablonska B, Scafidi J,
Vaccarino FM and Gallo V: Neurobiology of premature brain injury.
Nat Neurosci. 17:341–346. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Strata F, Coq JO, Byl N and Merzenich MM:
Effects of sensorimotor restriction and anoxia on gait and motor
cortex organization: implications for a rodent model of cerebral
palsy. Neuroscience. 129:141–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bennet L, Tan S, Van den Heuij L, Derrick
M, Groenendaal F, van Bel F, Juul S, Back SA, Northington F,
Robertson NJ, et al: Cell therapy for neonatal hypoxia-ischemia and
cerebral palsy. Ann Neurol. 71:589–600. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van Handel M, Swaab H, de Vries LS and
Jongmans MJ: Long-term cognitive and behavioral consequences of
neonatal encephalopathy following perinatal asphyxia: a review. Eur
J Pediatr. 166:645–654. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aarnoudse-Moens CS, Weisglas-Kuperus N,
van Goudoever JB and Oosterlaan J: Meta-analysis of neurobehavioral
outcomes in very preterm and/or very low birth weight children.
Pediatrics. 124:717–728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Damiano DL: Activity, activity, activity:
rethinking our physical therapy approach to cerebral palsy. Phys
Ther. 86:1534–1540. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Richards CLMF, Dumas F, Marcoux S, Lepage
C and Menier C: Early and intensive treadmill locomotor training
for young children with cerebral palsy: a feasibility study.
Pediatr Phys Ther. 9:158–165. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cherng RJ, Liu CF, Lau TW and Hong RB:
Effect of treadmill training with body weight support on gait and
gross motor function in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Am J
Phys Med Rehabil. 86:548–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsai SW, Chen HL, Chang YC and Chen CM:
Molecular mechanisms of treadmill therapy on neuromuscular atrophy
induced via botulinum toxin A. Neural Plast. 2013:5932712013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Willoughby KL, Dodd KJ and Shields N: A
systematic review of the effectiveness of treadmill training for
children with cerebral palsy. Disabil Rehabil. 31:1971–1979. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mutlu A, Krosschell K and Spira DG:
Treadmill training with partial body-weight support in children
with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol.
51:268–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chrysagis N, Skordilis EK, Stavrou N,
Grammatopoulou E and Koutsouki D: The effect of treadmill training
on gross motor function and walking speed in ambulatory adolescents
with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med
Rehabil. 91:747–760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jones MW, Morgan E, Shelton JE and
Thorogood C: Cerebral palsy: introduction and diagnosis (part I). J
Pediatr Health Care. 21:146–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wessels M, Lucas C, Eriks I and de Groot
S: Body weight-supported gait training for restoration of walking
in people with an incomplete spinal cord injury: a systematic
review. J Rehabil Med. 42:513–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu P, Mills E, Moher D and Seely D:
Acupuncture in post-stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized trials. Stroke. 41:e171–e179. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Duncan B, Shen K, Zou LP, Han TL, Lu ZL,
Zheng H, Walsh M, Venker C, Su Y, Schnyer R, et al: Evaluating
intense rehabilitative therapies with and without acupuncture for
children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial. Arch
Phys Med Rehabil. 93:808–815. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu ZH, Qi YC, Pan PG, Ma MM, Qian XG and
Fu WJ: Clinical observation on treatment of clearing the governor
vessel and refreshing the mind needling in neural development and
remediation of children with cerebral palsy. Chin J Integr Med.
19:505–509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang K, Zhang R, He F, Lin LB, Xiang XH,
Ping XJ, Han JS, Zhao GP, Zhang QH and Cui CL: Electroacupuncture
frequency-related transcriptional response in rat arcuate nucleus
revealed region-distinctive changes in response to low- and
high-frequency electroacupuncture. J Neurosci Res. 90:1464–1473.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim YR, Kim HN, Ahn SM, Choi YH, Shin HK
and Choi BT: Electroacupuncture promotes post-stroke functional
recovery via enhancing endogenous neurogenesis in mouse focal
cerebral ischemia. PLoS One. 9:e900002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sharma A, Sane H, Kulkarni P, D'sa M,
Gokulchandran N and Badhe P: Improved quality of life in a case of
cerebral palsy after bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation.
Cell J. 17:389–394. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Porambo M, Phillips AW, Marx J, Ternes K,
Arauz E, Pletnikov M, Wilson MA, Rothstein JD, Johnston MV and
Fatemi A: Trans planted glial restricted precursor cells improve
neurobehavioral and neuropathological outcomes in a mouse model of
neonatal white matter injury despite limited cell survival. Glia.
63:452–465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fernández-López D, Natarajan N, Ashwal S
and Vexler ZS: Mechanisms of perinatal arterial ischemic stroke. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 34:921–932. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Back SA, Han BH, Luo L, Chricton CA,
Xanthoudakis S, Tam J, Arvin KL and Holtzman DM: Selective
vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to
hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci. 22:455–463. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Follett PL, Deng W, Dai W, Talos DM,
Massillon LJ, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ and Jensen FE: Glutamate
receptor-mediated oligodendrocyte toxicity in periventricular
leukomalacia: a protective role for topiramate. J Neurosci.
24:4412–4420. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Volpe JJ: Brain injury in premature
infants: a complex amalgam of destructive and developmental
disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 8:110–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Ploughman M: Exercise is brain food: the
effects of physical activity on cognitive function. Dev
Neurorehabil. 11:236–240. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cengiz P, Uluc K, Kendigelen P, Akture E,
Hutchinson E, Song C, Zhang L, Lee J, Budoff GE, Meyerand E, et al:
Chronic neurological deficits in mice after perinatal hypoxia and
ischemia correlate with hemispheric tissue loss and white matter
injury detected by MRI. Dev Neurosci. 33:270–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan LW, Lin S, Pang Y, Lei M, Zhang F,
Rhodes PG and Cai Z: Hypoxia-ischemia induced neurological
dysfunction and brain injury in the neonatal rat. Behav Brain Res.
165:80–90. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang ZG and Chopp M: Neurorestorative
therapies for stroke: underlying mechanisms and translation to the
clinic. Lancet Neurol. 8:491–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abe K, Yamashita T, Takizawa S, Kuroda S,
Kinouchi H and Kawahara N: Stem cell therapy for cerebral ischemia:
from basic science to clinical applications. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 32:1317–1331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shinoyama M, Ideguchi M, Kida H, Kajiwara
K, Kagawa Y, Maeda Y, Nomura S and Suzuki M: Cortical
region-specific engraftment of embryonic stem cell-derived neural
progenitor cells restores axonal sprouting to a subcortical target
and achieves motor functional recovery in a mouse model of neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 7:1282013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rice JE III, Vannucci RC and Brierley JB:
The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the
rat. Ann Neurol. 9:131–141. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duarte NA, Grecco LA, Galli M, Fregni F
and Oliveira CS: Effect of transcranial direct-current stimulation
combined with treadmill training on balance and functional
performance in children with cerebral palsy: a double-blind
randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 9:e1057772014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Yager JY: Animal models of
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the newborn. Semin Pediatr Neurol.
11:31–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Towfighi J, Zec N, Yager J, Housman C and
Vannucci RC: Temporal evolution of neuropathologic changes in an
immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia: a light microscopic study.
Acta Neuropathol. 90:375–386. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McPherson RJ, Mascher-Denen M and Juul SE:
Postnatal stress produces hyperglycemia in adult rats exposed to
hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr Res. 66:278–282. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jablonska B, Scafidi J, Aguirre A,
Vaccarino F, Nguyen V, Borok E, Horvath TL, Rowitch DH and Gallo V:
Oligodendrocyte regeneration after neonatal hypoxia requires
FoxO1-mediated 27Kip1 expression. J Neurosci.
32:14775–14793. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck
S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, Kuhn HG
and Aigner L: Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect
neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 21:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schinder AF and Poo M: The neurotrophin
hypothesis for synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 23:639–645.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ding Y, Li J, Luan X, Ding YH, Lai Q,
Rafols JA, Phillis JW, Clark JC and Diaz FG: Exercise
pre-conditioning reduces brain damage in ischemic rats that may be
associated with regional angiogenesis and cellular overexpression
of neurotrophin. Neuroscience. 124:583–591. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hwang DH, Shin HY, Kwon MJ, Choi JY, Ryu
BY and Kim BG: Survival of neural stem cell grafts in the lesioned
spinal cord is enhanced by a combination of treadmill locomotor
training via insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling. J Neurosci.
34:12788–12800. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Skup M, Dwornik A, Macias M, Sulejczak D,
Wiater M and Czarkowska-Bauch J: Long-term locomotor training
up-regulates TrkB(FL) receptor-like proteins, brain-derived
neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin 4 with different topographies
of expression in oligodendroglia and neurons in the spinal cord.
Exp Neurol. 176:289–307. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ying Z, Roy RR, Zhong H, Zdunowski S,
Edgerton VR and Gomez-Pinilla F: BDNF-exercise interactions in the
recovery of symmetrical stepping after a cervical hemisection in
rats. Neuroscience. 155:1070–1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Manni L, Albanesi M, Guaragna M, Barbaro
Paparo S and Aloe L: Neurotrophins and acupuncture. Auton Neurosci.
157:9–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Childs JT, Xie L, Mao XO and
Greenberg DA: Vascular endothelial growth factor-B (VEGFB)
stimulates neurogenesis: evidence from knockout mice and growth
factor administration. Dev Biol. 289:329–335. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ding Y, Zhang RY, He B, Liu Z, Zhang K,
Ruan JW, Ling EA, Wu JL and Zeng YS: Combination of
electroacupuncture and grafted mesenchymal stem cells
overexpressing TrkC improves remyelination and function in
demyelinated spinal cord of rats. Sci Rep. 5:91332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Strube W, Nitsche MA, Wobrock T, Bunse T,
Rein B, Herrmann M, Schmitt A, Nieratschker V, Witt SH, Rietschel
M, et al: BDNF-Val66Met-polymorphism impact on cortical plasticity
in schizophrenia patients: a proof-of-concept study. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 18:182014.
|
|
49
|
Ohira K, Furuta T, Hioki H, Nakamura KC,
Kuramoto E, Tanaka Y, Funatsu N, Shimizu K, Oishi T, Hayashi M, et
al: Ischemia-induced neurogenesis of neocortical layer 1 progenitor
cells. Nat Neurosci. 13:173–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Johnston MV: Plasticity in the developing
brain: implications for rehabilitation. Dev Disabil Res Rev.
15:94–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang SF, Ding Y, Ruan JW, Zhang W, Wu JL,
He B, Zhang YJ, Li Y and Zeng YS: An experimental
electro-acupuncture study in treatment of the rat demyelinated
spinal cord injury induced by ethidium bromide. Neurosci Res.
70:294–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Elfving B, Christensen T, Ratner C,
Wienecke J and Klein AB: Transient activation of mTOR following
forced treadmill exercise in rats. Synapse. 67:620–625. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim JY, Kim JM and Ko EY: The effect of
the action observation physical training on the upper extremity
function in children with cerebral palsy. J Exerc Rehabil.
10:176–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kwon SJ, Song KS, Kim H, Kim YS, Choi WS
and Kwon SO: Low-intensity treadmill exercise and bright light
upregulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and
intracellular signaling pathway in rat hippocampus and cerebral
cortex. Anim Cells Syst. 18:135–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|