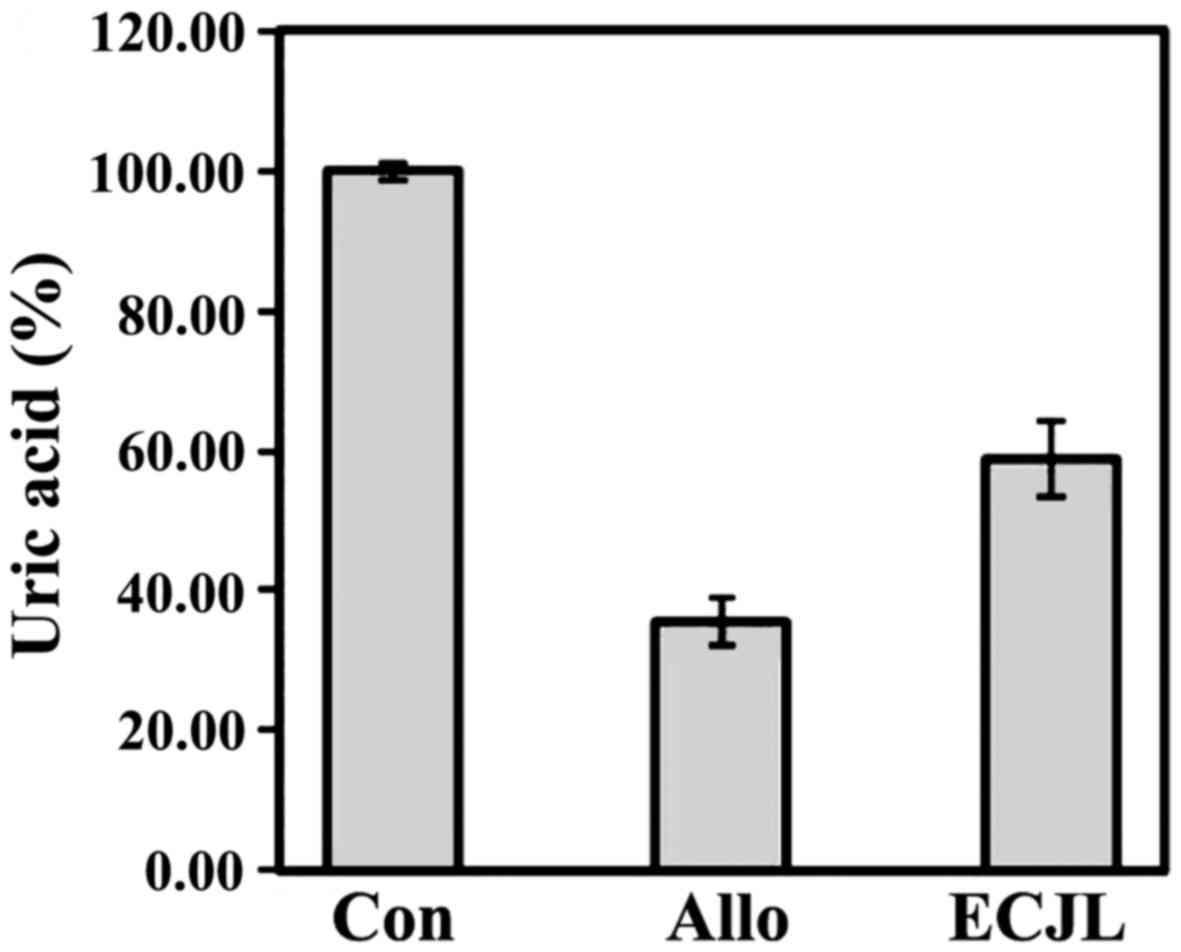
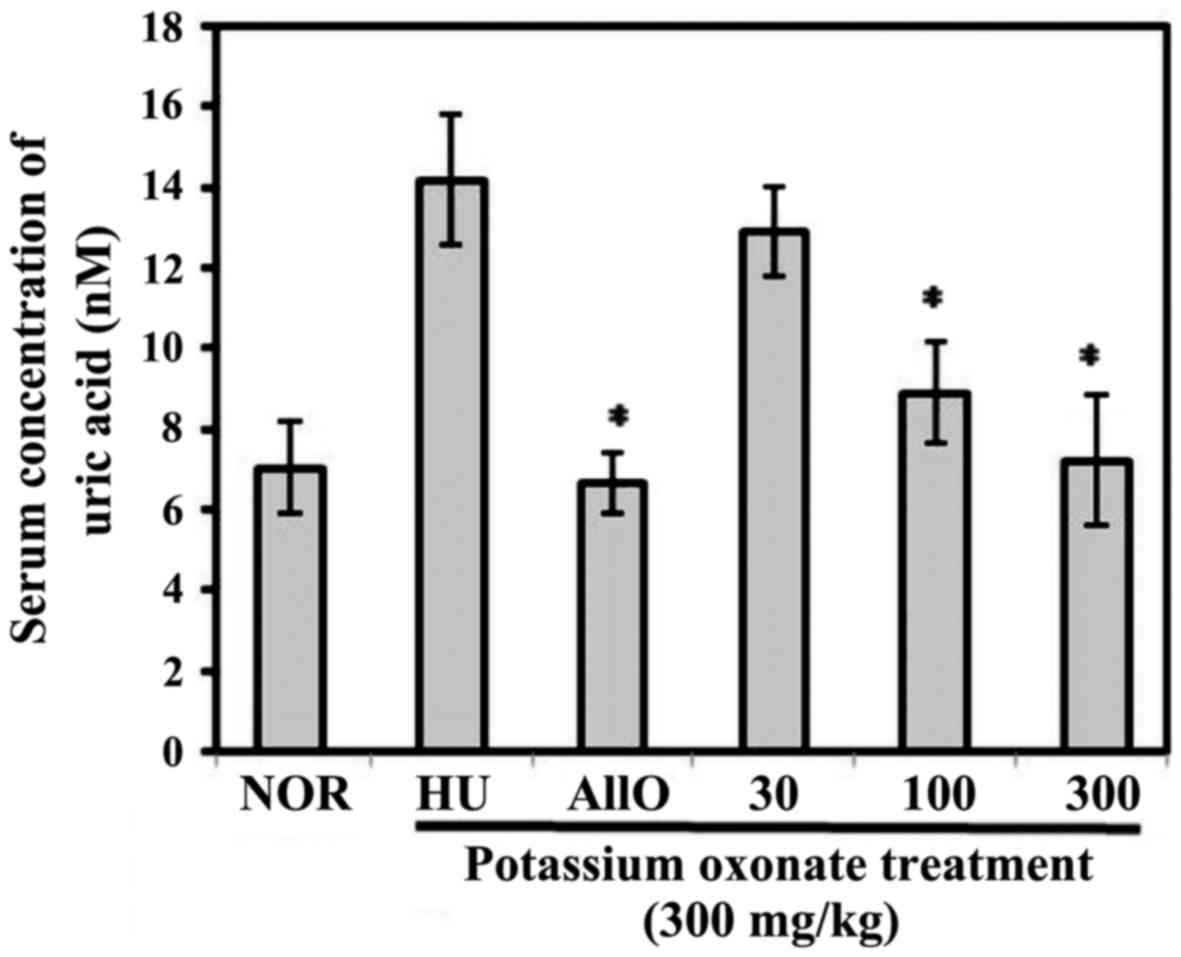
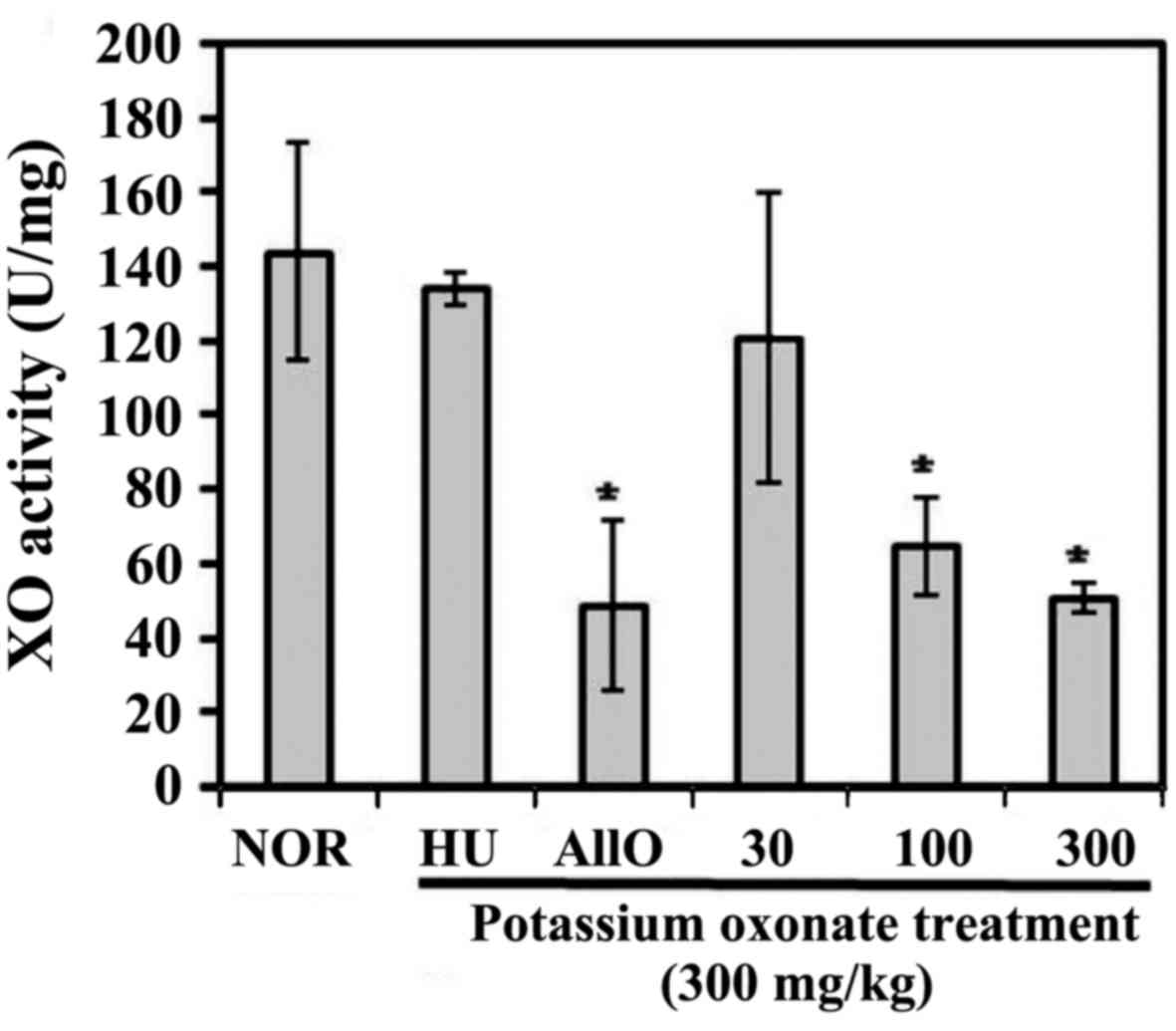
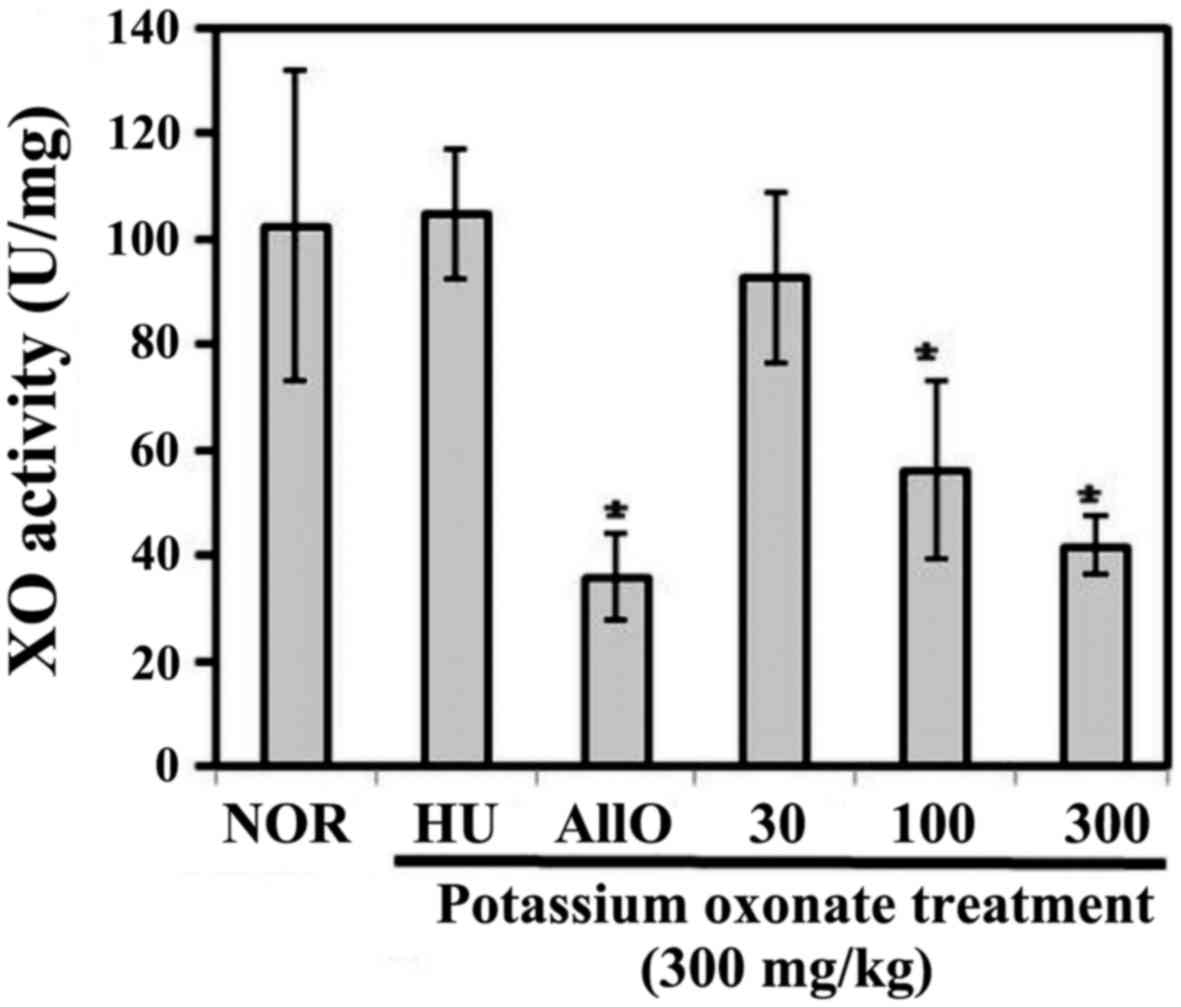
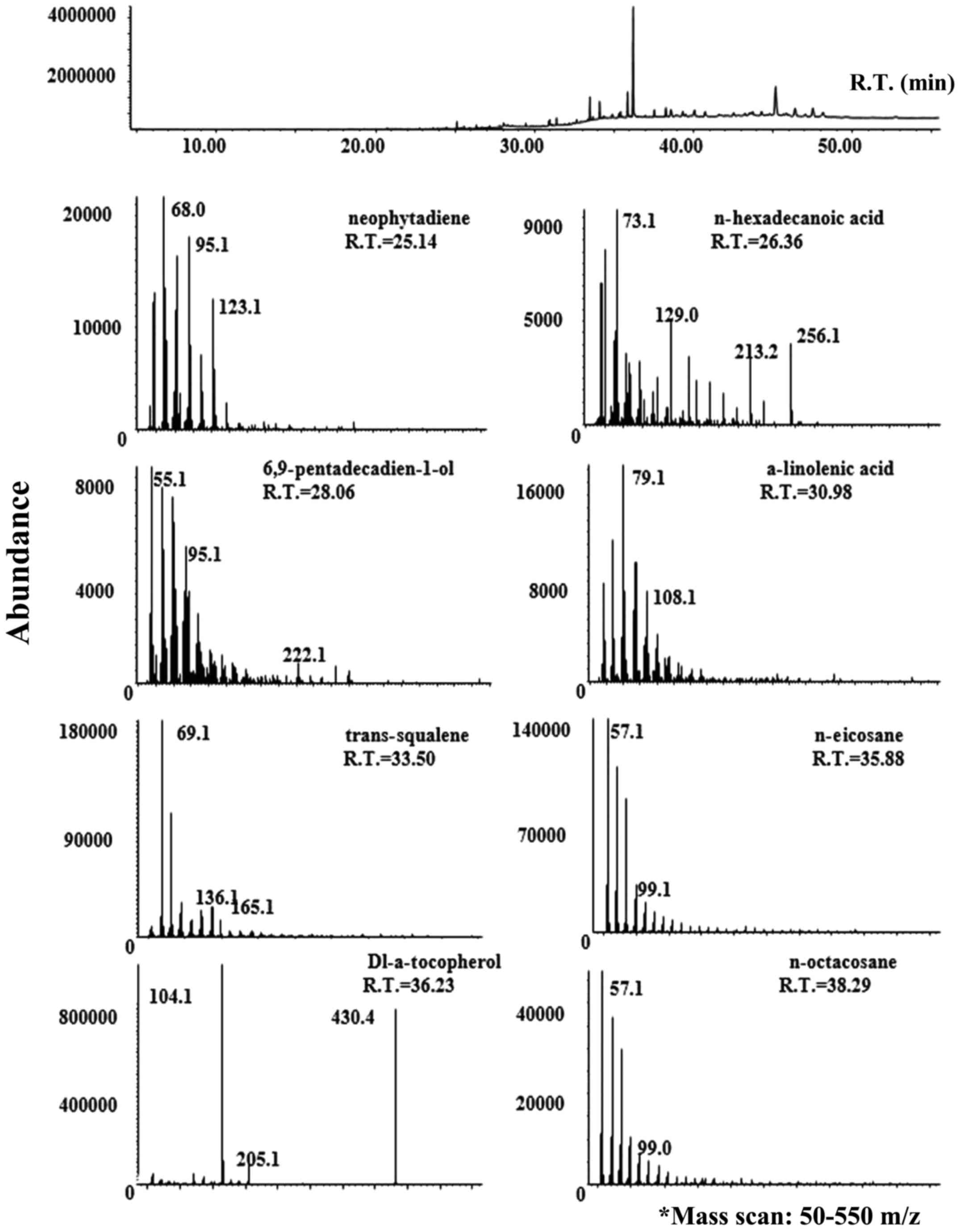
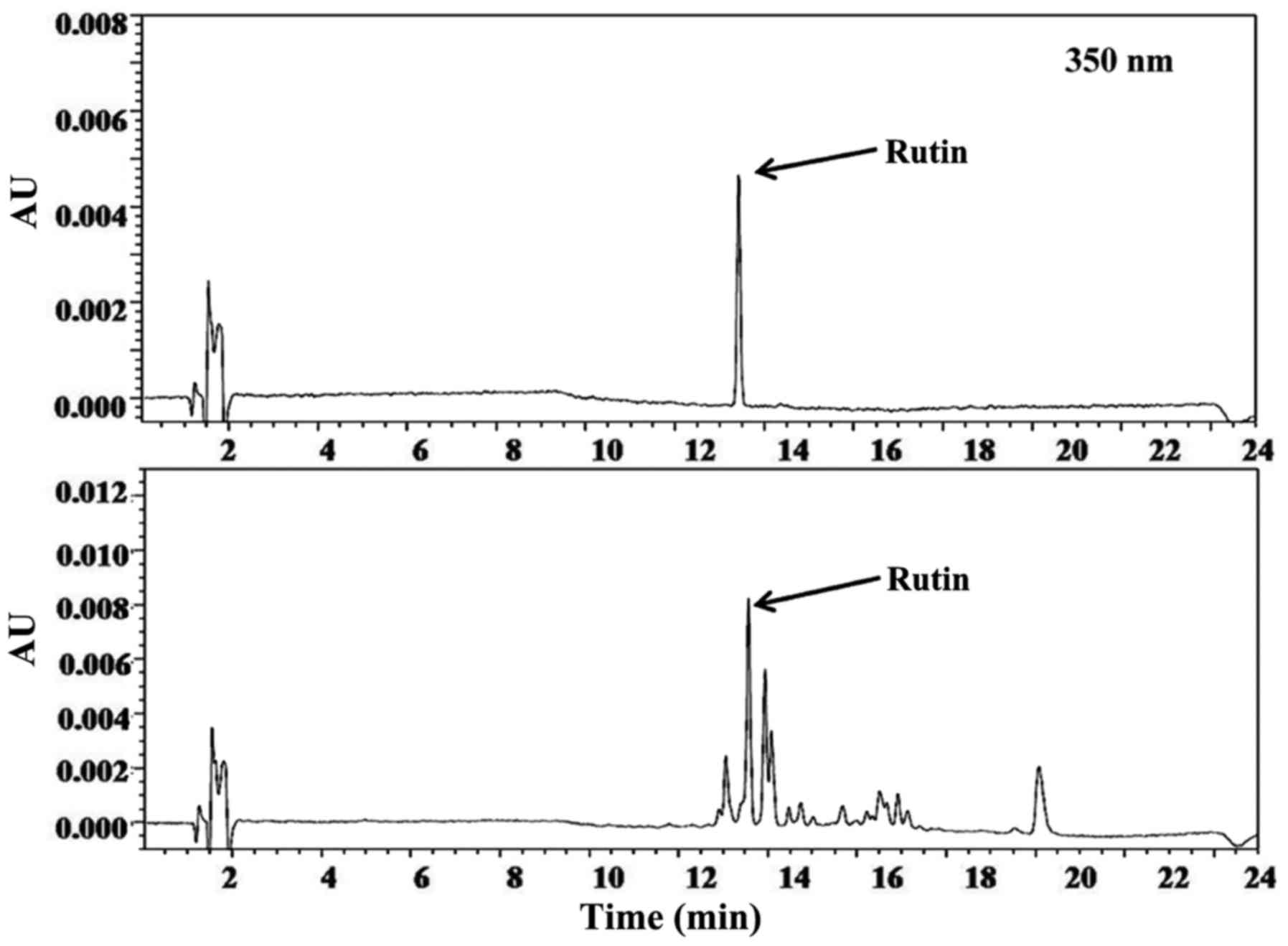
|
1
|
Yoshikawa M, Murakami T, Yoshizumi S,
Murakami N, Yamahara J and Matsuda H: Bioactive saponins and
glycosides. V. Acylated polyhydroxyolean-12-ene triterpene
oligoglycosides, camelliasaponins A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2, from
the seeds of Camellia japonica L: Structures and inhibitory
activity on alcohol absorption. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
44:1899–1907. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yoshikawa M, Morikawa T, Asao Y, Fujiwara
E, Nakamura S and Matsuda H: Medicinal flowers. XV. The structures
of noroleanane- and oleanane-type triterpene oligoglycosides with
gastroprotective and platelet aggregation activities from flower
buds of Camellia japonica. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 55:606–612.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Heo J: Dongui Bogam. Naeuiwon edition.
Bubinmunhwasa publisher; Seoul, Korea: 1613
|
|
4
|
Cha SS, Lee KE, Lee SH, Choi MJ and Shim
JK: Decomposition and nutrient dynamics of leaf litter of Camellia
japonica L. in Korea. Korean J Environ Ecol. 30:110–117. 2016.In
Korean. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hwang EJ, Cha YJ, Park MH, Lee JW and Lee
SY: Cytotoxicity and chemosensitizing effect of Camellia (Camellia
japonica) tea extracts. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 33:487–493.
2004.In Korean. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang JL, Ha TK, Dhodary B, Pyo E, Nguyen
NH, Cho H, Kim E and Oh WK: Oleanane triterpenes from the flowers
of Camellia japonica inhibit porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV)
replication. J Med Chem. 58:1268–1280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Onodera K, Hanashiro K and Yasumoto T:
Camellianoside, a novel antioxidant glycoside from the leaves of
Camellia japonica. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 70:1995–1998. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thao NT, Hung TM, Lee MK, Kim JC, Min BS
and Bae K: Triterpenoids from Camellia japonica and their cytotoxic
activity. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 58:121–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nagata T, Tsushida T, Hamaya E, Enoki N,
Manabe S and Nishino C: Camellidins, antifungal saponins isolated
from Camellia japonica. Agric Biol Chem. 49:1181–1186. 1985.
|
|
10
|
Park JC, Hur JM, Park JG, Hatano T,
Yoshida T, Miyashiro H, Min BS and Hattori M: Inhibitory effects of
Korean medicinal plants and camelliatannin H from Camellia japonica
on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. Phytother Res.
16:422–426. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao M, Zhu D, Sun-Waterhouse D, Su G, Lin
L, Wang X and Dong Y: In vitro and in vivo studies on adlay-derived
seed extracts: Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, serum
uric acid suppression, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects. J
Agric Food Chem. 62:7771–7778. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lemos Lima Rde C, Ferrari FC, de Souza MR,
de Sá Pereira BM, de Paula CA and Saúde-Guimarães DA: Effects of
extracts of leaves from Sparattosperma leucanthum on hyperuricemia
and gouty arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 161:194–199. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chu YH, Chen CJ, Wu SH and Hsieh JF:
Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by Rhodiola crenulata extracts and
their phytochemicals. J Agric Food Chem. 62:3742–3749. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kramer HM and Curhan G: The association
between gout and nephrolithiasis: The National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey III, 1988–1994. Am J Kidney Dis. 40:37–42. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi HJ, Lee CH, Lee JH, Yoon BY, Kim HA,
Suh CH, Choi ST, Song JS, Joo HY, Choi SJ, et al: Current gout
treatment and flare in South Korea: Prophylactic duration
associated with fewer gout flares. Int J Rheum Dis. Aug
27–2014.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bae MS, Shin JS, Lee KY, Lee KH and Kim
YJ: Long-range transport of biomass burning emissions based on
organic molecular markers and carbonaceous thermal distribution.
Sci Total Environ. 466–467:56–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim YH, Cho ML, Kim DB, Shin GH, Lee JH,
Lee JS, Park SO, Lee SJ, Shin HM and Lee OH: The antioxidant
activity and their major antioxidant compounds from Acanthopanax
senticosus and A. koreanum. Molecules. 20:13281–13295. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seo JH, Kim JE, Shim JH, Yoon G, Bang MA,
Bae CS, Lee KJ, Park DH and Cho SS: HPLC analysis, optimization of
extraction conditions and biological evaluation of Corylopsis
coreana Uyeki flos. Molecules. 21:942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arimboor R, Rangan M, Aravind SG and
Arumughan C: Tetrahydroamentoflavone (THA) from Semecarpus
anacardium as a potent inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. J
Ethnopharmacol. 133:1117–1120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huo LN, Wang W, Zhang CY, Shi HB, Liu Y,
Liu XH, Guo BH, Zhao DM and Gao H: Bioassay-guided isolation and
identification of xanthine oxidase inhibitory constituents from the
leaves of Perilla frutescens. Molecules. 20:17848–17859. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perron NR and Brumaghim JL: A review of
the antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenol compounds related to iron
binding. Cell Biochem Biophys. 53:75–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu LM, Cheng SF, Shieh PC, Lee JC, Chen
JJ, Ho CT, Kuo SC, Kuo DH, Huang LJ and Way TD: The methanol
extract of Euonymus laxiflorus, Rubia lanceolata and Gardenia
jasminoides inhibits xanthine oxidase and reduce serum uric acid
level in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 70:179–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu XH, Yu CH, Zhang CF, Anderson S and
Zhang YW: Smilax riparia reduces hyperuricemia in mice as a
potential treatment of gout. Am J Chin Med. 42:257–259. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gurwitz JH, Kalish SC, Bohn RL, Glynn RJ,
Monane M, Mogun H and Avorn J: Thiazide diuretics and the
initiation of anti-gout therapy. J Clin Epidemiol. 50:953–959.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ardan T, Kovaceva J and Cejková J:
Comparative histochemical and immunohistochemical study on xanthine
oxidoreductase/xanthine oxidase in mammalian corneal epithelium.
Acta Histochem. 106:69–75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grassi D, Ferri L, Desideri G, Di Giosia
P, Cheli P, Del Pinto R, Properzi G and Ferri C: Chronic
hyperuricemia, uric acid deposit and cardiovascular risk. Curr
Pharm Des. 19:2432–2438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Catignani GL, Chytil F and Darby WJ:
Vitamin E deficiency: Immunochemical evidence for increased
accumulation of liver xanthine oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
71:1966–1968. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mohd Fahami NA, Ibrahim IA, Kamisah Y and
Mohd Ismail N: Palm vitamin E reduces catecholamines, xanthine
oxidase activity and gastric lesions in rats exposed to
water-immersion restraint stress. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:542012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang ZR, Lin YK and Fang JY: Biological
and pharmacological activities of squalene and related compounds:
Potential uses in cosmetic dermatology. Molecules. 14:540–554.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park SY, Seetharaman R, Ko MJ, Kim DY, Kim
TH, Yoon MK, Kwak JH, Lee SJ, Bae YS and Choi YW: Ethyl linoleate
from garlic attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory
cytokine production by inducing heme oxygenase-1 in RAW264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 19:253–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen YS, Hu QH, Zhang X, Zhu Q and Kong
LD: Beneficial effect of rutin on oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and
renal dysfunction in mice. Pharmacology. 92:75–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Azuma CM, dos Santos FCS and Lago JHG:
Flavonoids and fatty acids of Camellia japonica leaves extract. Rev
Bras Farmacogn. 21:1159–1162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Pauff JM and Hille R: Inhibition studies
of bovine xanthine oxidase by luteolin, silibinin, quercetin, and
curcumin. J Nat Prod. 72:725–731. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu JX, Wang Y, Kong LD, Yang C and Zhang
X: Effects of Biota orientalis extract and its flavonoid
constituents, quercetin and rutin on serum uric acid levels in
oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine
oxidase activities in mouse liver. J Ethnopharmacol. 93:133–140.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shin JW, Seol IC and Son CG:
Interpretation of animal dose and human equivalent dose for drug
development. J Korean Orient Med. 31:1–7. 2010.
|