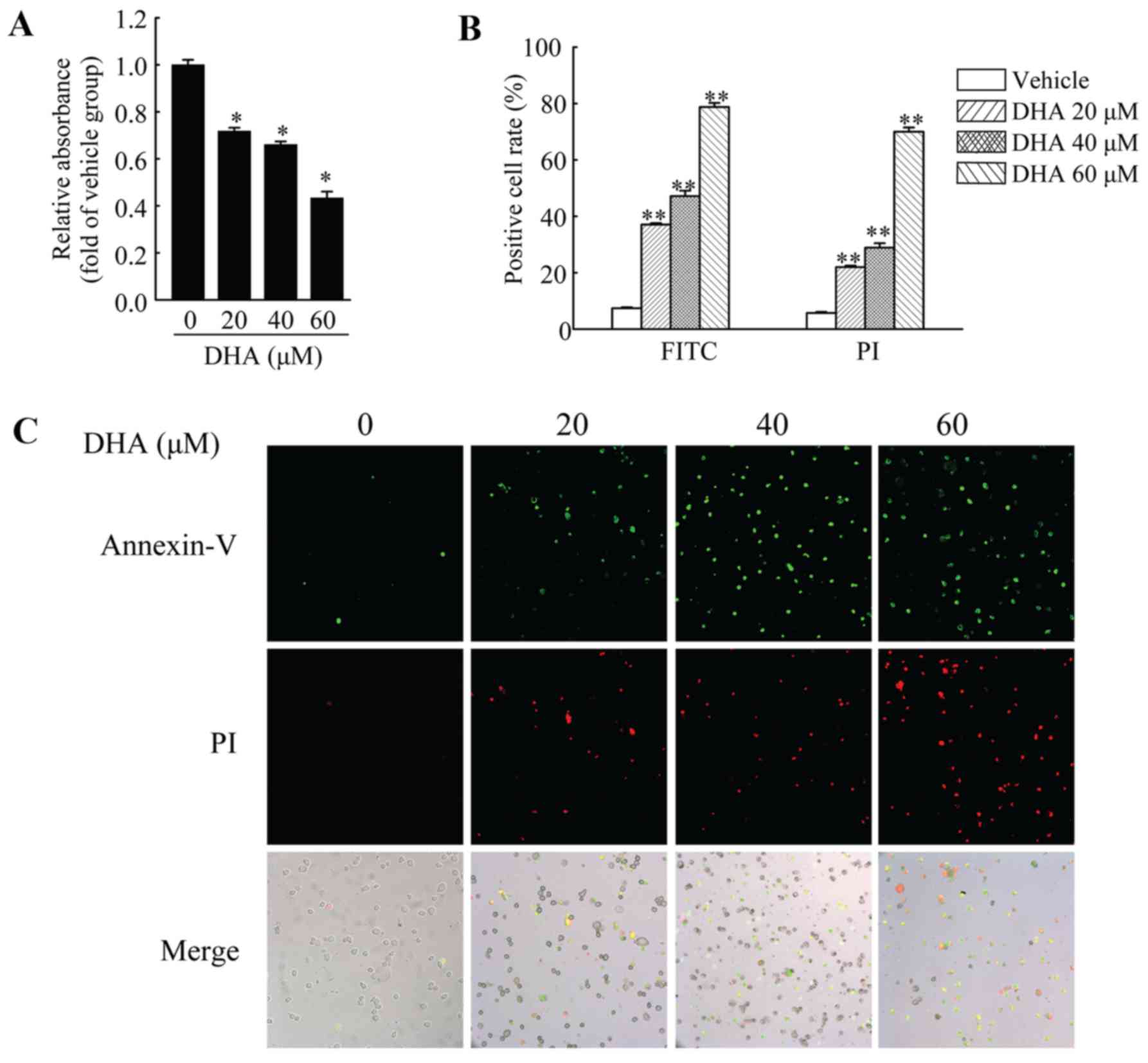
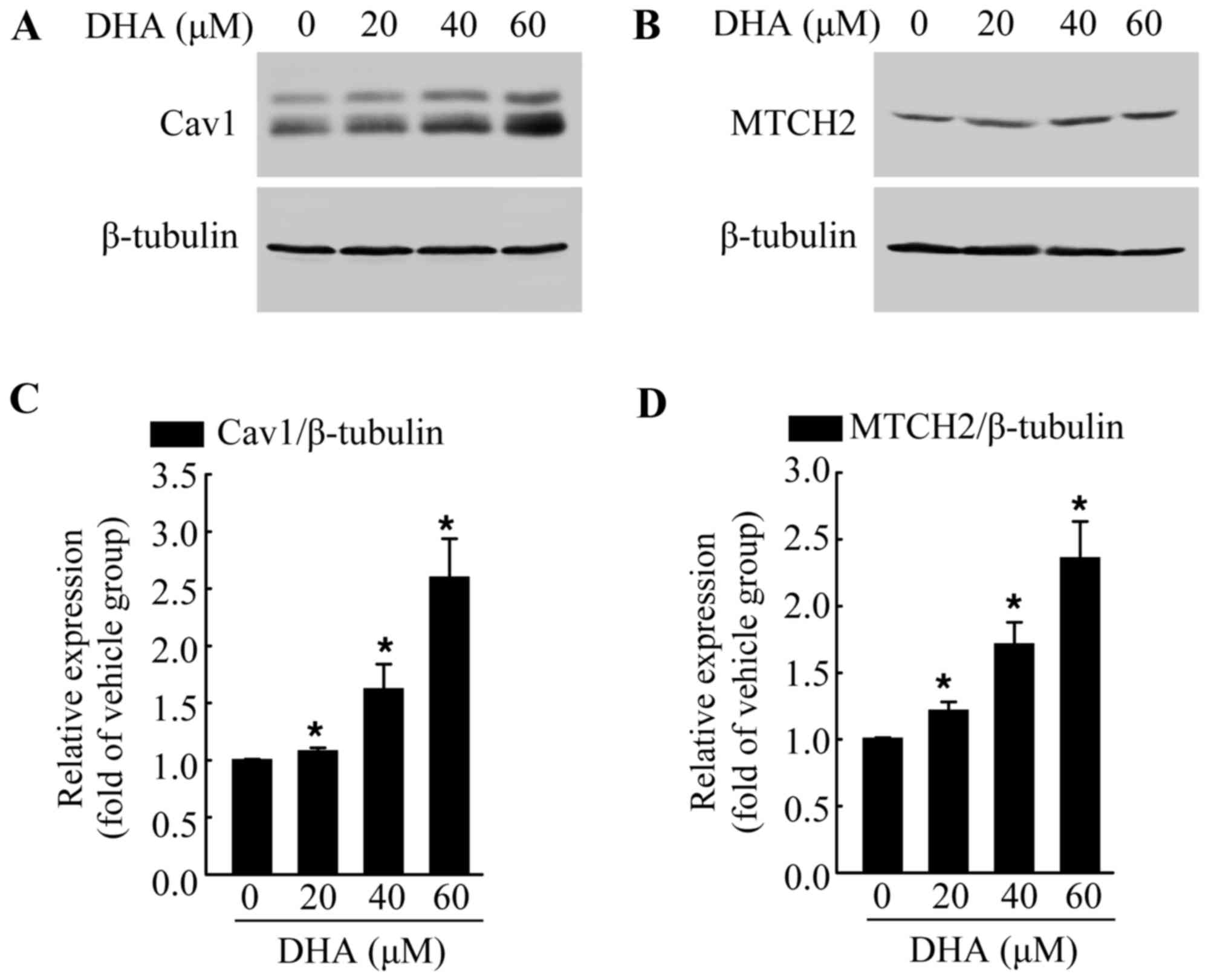
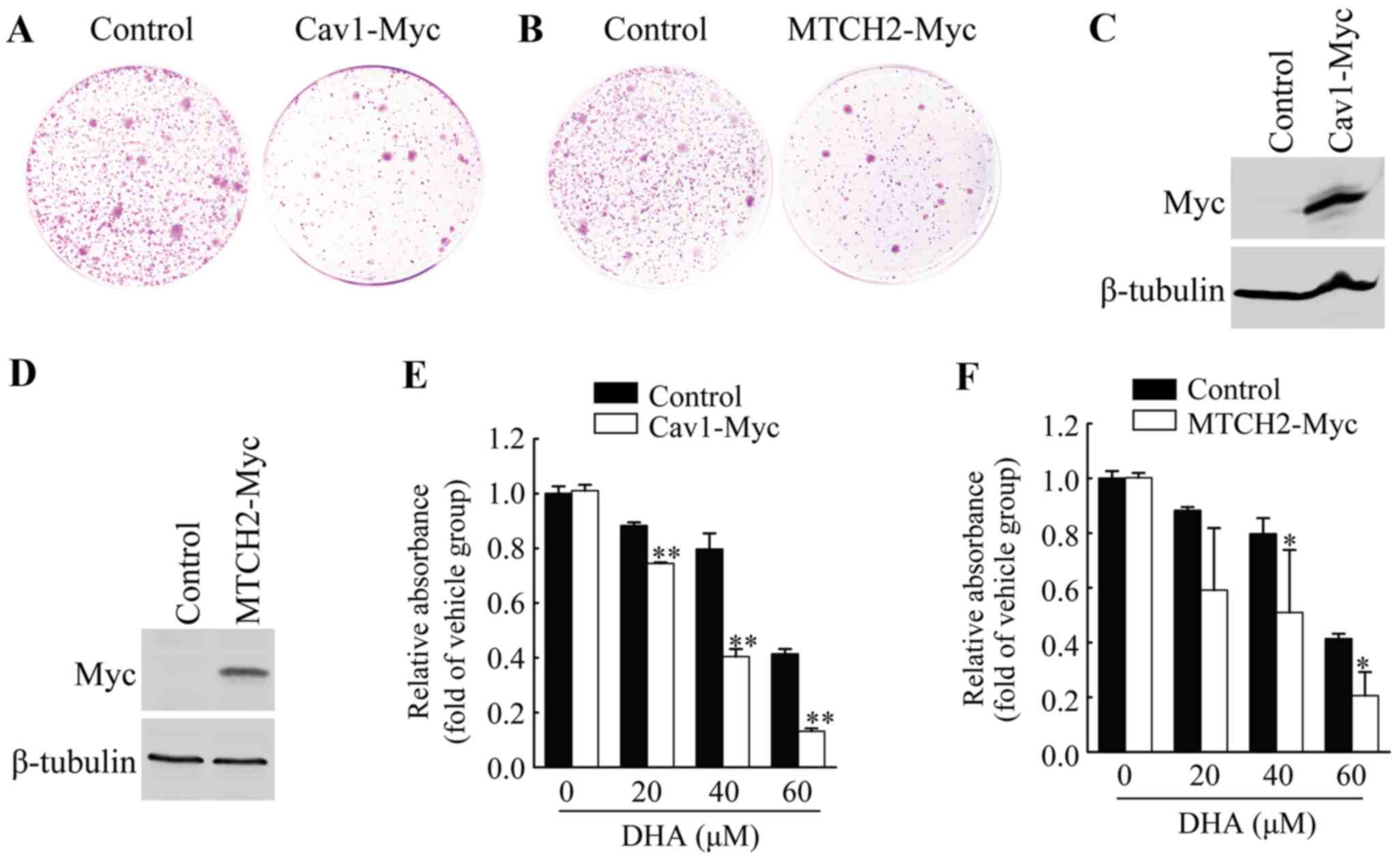
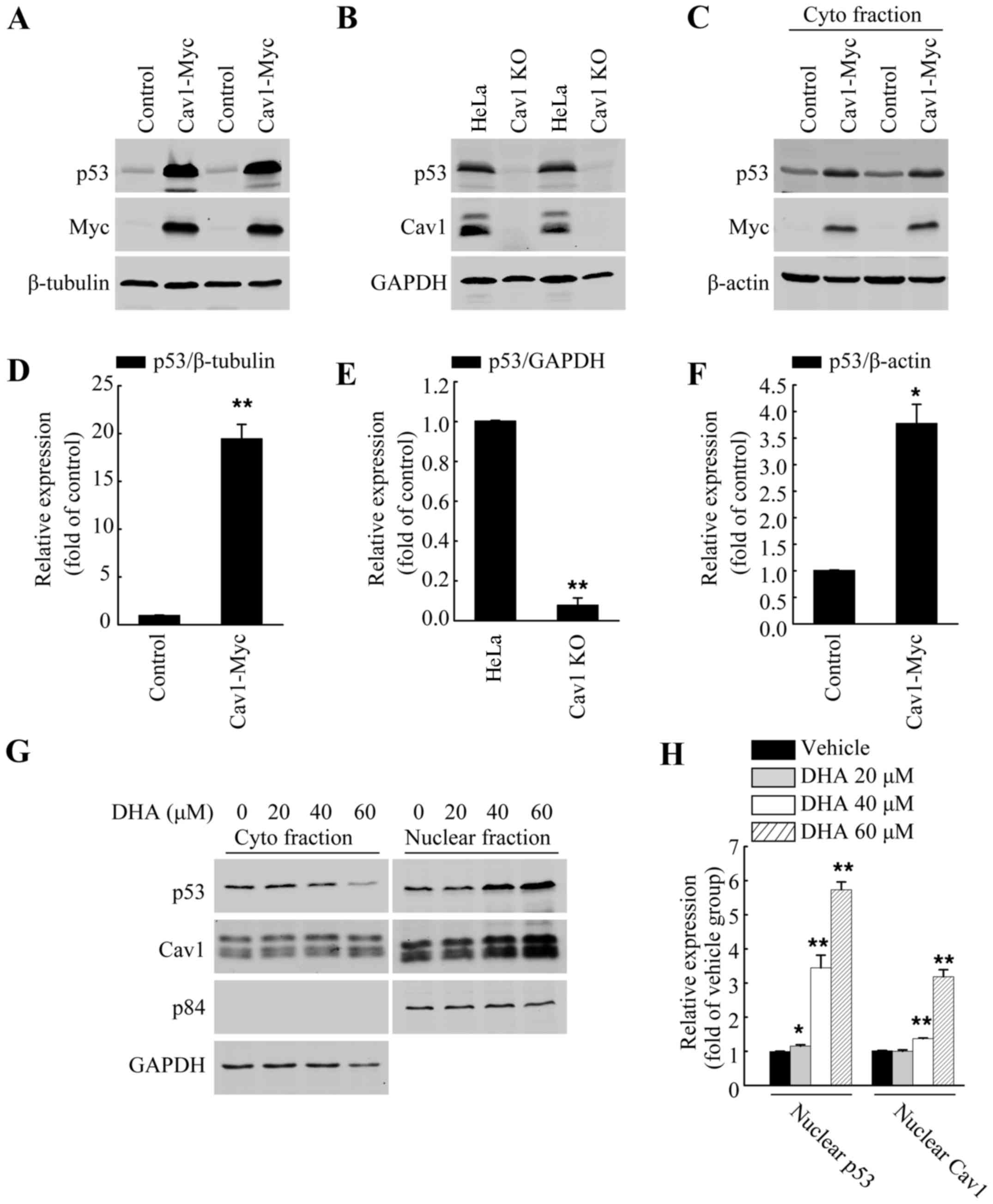
|
1
|
Cao L, Duanmu W, Yin Y, Zhou Z, Ge H, Chen
T, Tan L, Yu A, Hu R, Fei L, et al: Dihydroartemisinin exhibits
anti-glioma stem cell activity through inhibiting p-AKT and
activating caspase-3. Pharmazie. 69:752–758. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Lucibello M, Adanti S, Antelmi E, Dezi D,
Ciafrè S, Carcangiu ML, Zonfrillo M, Nicotera G, Sica L, De Braud
F, et al: Phospho-TCTP as a therapeutic target of
Dihydroartemisinin for aggressive breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
6:5275–5291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu M, Sun L, Zhou J, Zhao Y and Deng X:
Dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis is associated with inhibition
of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium atpase activity in
colorectal cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:137–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao K, Li J and Wang Z:
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits cell proliferation via
AKT/GSK3β/cyclinD1 pathway and induces apoptosis in A549 lung
cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8684–8691. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Zhang CZ, Zhang H, Yun J, Chen GG and Lai
PBS: Dihydroartemisinin exhibits antitumor activity toward
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:1278–1289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao X, Zhong H, Wang R, Liu D, Waxman S,
Zhao L and Jing Y: Dihydroartemisinin and its derivative induce
apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia through Noxa-mediated pathway
requiring iron and endoperoxide moiety. Oncotarget. 6:5582–5596.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu YY, Chen TS, Wang XP and Li L:
Single-cell analysis of dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species-mediated caspase-8 activation and
mitochondrial pathway in ASTC-a-1 cells using fluorescence imaging
techniques. J Biomed Opt. 15:0460282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cabello CM, Lamore SD, Bair WB III, Qiao
S, Azimian S, Lesson JL and Wondrak GT: The redox antimalarial
dihydroartemisinin targets human metastatic melanoma cells but not
primary melanocytes with induction of NOXA-dependent apoptosis.
Invest New Drugs. 30:1289–1301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ji Y, Zhang YC, Pei LB, Shi LL, Yan JL and
Ma XH: Anti-tumor effects of dihydroartemisinin on human
osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 351:99–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang CZ, Pan Y, Cao Y, Lai PB, Liu L,
Chen GG and Yun J: Histone deacetylase inhibitors facilitate
dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis in liver cancer in vitro and
in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e398702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simmons GE Jr, Taylor HE and Hildreth JE:
Caveolin-1 suppresses human immunodeficiency virus-1 replication by
inhibiting acetylation of NF-κB. Virology. 432:110–119. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garrean S, Gao XP, Brovkovych V, Shimizu
J, Zhao YY, Vogel SM and Malik AB: Caveolin-1 regulates NF-kappaB
activation and lung inflammatory response to sepsis induced by
lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 177:4853–4860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang XM, Kim HP, Song R and Choi AM:
Caveolin-1 confers anti-inflammatory effects in murine macrophages
via the MKK3/p38 MAPK pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
34:434–442. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huertas-Martínez J, Rello-Varona S,
Herrero-Martín D, Barrau I, García-Monclús S, Sáinz-Jaspeado M,
Lagares-Tena L, Núñez-Álvarez Y, Mateo-Lozano S, Mora J, et al:
Caveolin-1 is down-regulated in alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas and
negatively regulates tumor growth. Oncotarget. 5:9744–9755. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bender FC, Reymond MA, Bron C and Quest
AF: Caveolin-1 levels are down-regulated in human colon tumors, and
ectopic expression of caveolin-1 in colon carcinoma cell lines
reduces cell tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 60:5870–5878.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bélanger MM, Roussel E and Couet J:
Caveolin-1 is down-regulated in human lung carcinoma and acts as a
candidate tumor suppressor gene. Chest. 125(Suppl): 106S2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang X, Pan L, Pu H, Wang Y, Zhang X, Li
C and Yang Z: Loss of caveolin-1 promotes endothelial-mesenchymal
transition during sepsis: a membrane proteomic study. Int J Mol
Med. 32:585–592. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang R, He W, Li Z, Chang W, Xin Y and
Huang T: Caveolin-1 functions as a key regulator of
17β-estradiol-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in BT474 breast
cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 34:822–827. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trimmer C, Sotgia F, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Balliet RM, Eaton G, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides S, Howell A,
Iozzo RV, Pestell RG, et al: Caveolin-1 and mitochondrial SOD2
(MnSOD) function as tumor suppressors in the stromal
microenvironment: a new genetically tractable model for human
cancer associated fibroblasts. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:383–394. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Benhar M, Engelberg D and Levitzki A: ROS,
stress-activated kinases and stress signaling in cancer. EMBO Rep.
3:420–425. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao H, Gu H, Qu X, Sun J, Song B, Gao W,
Liu J and Shao Q: Involvement of the mitochondrial pathway and
Bim/Bcl-2 balance in dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis in human
breast cancer in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 31:213–218. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Volonte D, Liu Z, Musille PM, Stoppani E,
Wakabayashi N, Di YP, Lisanti MP, Kensler TW and Galbiati F:
Inhibition of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) by
caveolin-1 promotes stress-induced premature senescence. Mol Biol
Cell. 24:1852–1862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li W, Liu H, Zhou JS, Cao JF, Zhou XB,
Choi AM, Chen ZH and Shen HH: Caveolin-1 inhibits expression of
antioxidant enzymes through direct interaction with nuclear
erythroid 2 p45-related factor-2 (Nrf2). J Biol Chem.
287:20922–20930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katz C, Zaltsman-Amir Y, Mostizky Y,
Kollet N, Gross A and Friedler A: Molecular basis of the
interaction between proapoptotic truncated BID (tBID) protein and
mitochondrial carrier homologue 2 (MTCH2) protein: key players in
mitochondrial death pathway. J Biol Chem. 287:15016–15023. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zaltsman Y, Shachnai L, Yivgi-Ohana N,
Schwarz M, Maryanovich M, Houtkooper RH, Vaz FM, De Leonardis F,
Fiermonte G, Palmieri F, et al: MTCH2/MIMP is a major facilitator
of tBID recruitment to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol. 12:553–562.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leibowitz-Amit R, Tsarfaty G, Abargil Y,
Yerushalmi GM, Horev J and Tsarfaty I: Mimp, a mitochondrial
carrier homologue, inhibits Met-HGF/SF-induced scattering and
tumorigenicity by altering Met-HGF/SF signaling pathways. Cancer
Res. 66:8687–8697. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu K, Ganesan K, Tan LK, Laban M, Wu J,
Zhao XD, Li H, Leung CH, Zhu Y, Wei CL, et al: A precisely
regulated gene expression cassette potently modulates metastasis
and survival in multiple solid cancers. PLoS Genet. 4:e10001292008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arigoni M, Barutello G, Riccardo F, Ercole
E, Cantarella D, Orso F, Conti L, Lanzardo S, Taverna D, Merighi I,
et al: miR-135b coordinates progression of ErbB2-driven mammary
carcinomas through suppression of MID1 and MTCH2. Am J Pathol.
182:2058–2070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han F, Gu D, Chen Q and Zhu H: Caveolin-1
acts as a tumor suppressor by down-regulating epidermal growth
factor receptor-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Pancreas. 38:766–774. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartholomew JN, Volonte D and Galbiati F:
Caveolin-1 regulates the antagonistic pleiotropic properties of
cellular senescence through a novel Mdm2/p53-mediated pathway.
Cancer Res. 69:2878–2886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Volonte D, Zou H, Bartholomew JN, Liu Z,
Morel PA and Galbiati F: Oxidative stress-induced inhibition of
Sirt1 by caveolin-1 promotes p53-dependent premature senescence and
stimulates the secretion of interleukin 6 (IL-6). J Biol Chem.
290:4202–4214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Chrétien A, Piront N, Delaive E, Demazy C,
Ninane N and Toussaint O: Increased abundance of cytoplasmic and
nuclear caveolin 1 in human diploid fibroblasts in H(2)O(2)-induced
premature senescence and interplay with p38alpha(MAPK). FEBS Lett.
582:1685–1692. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hosoya K, Murahari S, Laio A, London CA,
Couto CG and Kisseberth WC: Biological activity of
dihydroartemisinin in canine osteosarcoma cell lines. Am J Vet Res.
69:519–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Hu W, Zhang JL, Wu XH and Zhou HJ:
Dihydroartemisinin induces autophagy and inhibits the growth of
iron-loaded human myeloid leukemia K562 cells via ROS toxicity.
FEBS Open Bio. 2:103–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim J, Kim SK, Kim HK, Mattson MP and Hyun
DH: Mitochondrial function in human neuroblastoma cells is
up-regulated and protected by NQO1, a plasma membrane redox enzyme.
PLoS One. 8:e690302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sax JK, Fei P, Murphy ME, Bernhard E,
Korsmeyer SJ and El-Deiry WS: BID regulation by p53 contributes to
chemosensitivity. Nat Cell Biol. 4:842–849. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koivusalo R, Mialon A, Pitkänen H,
Westermarck J and Hietanen S: Activation of p53 in cervical cancer
cells by human papillomavirus E6 RNA interference is transient, but
can be sustained by inhibiting endogenous nuclear export-dependent
p53 antagonists. Cancer Res. 66:11817–11824. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hietanen S, Lain S, Krausz E, Blattner C
and Lane DP: Activation of p53 in cervical carcinoma cells by small
molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:8501–8506. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|