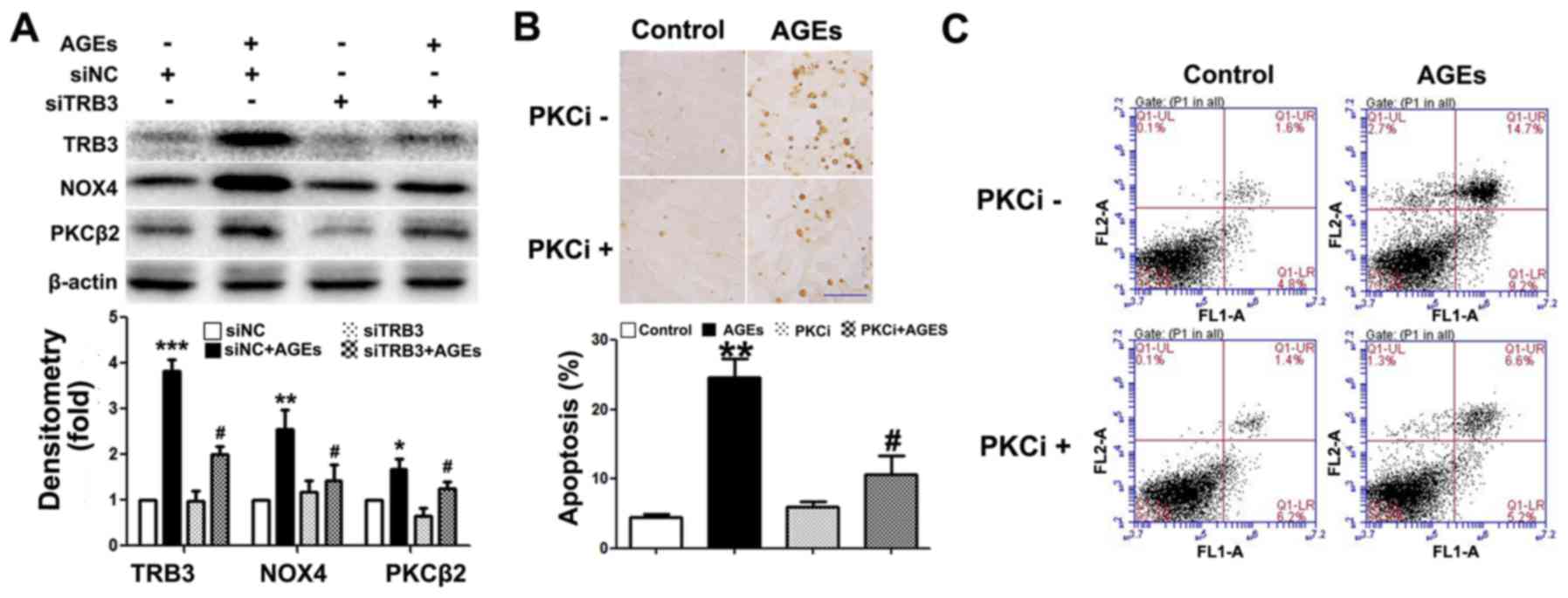
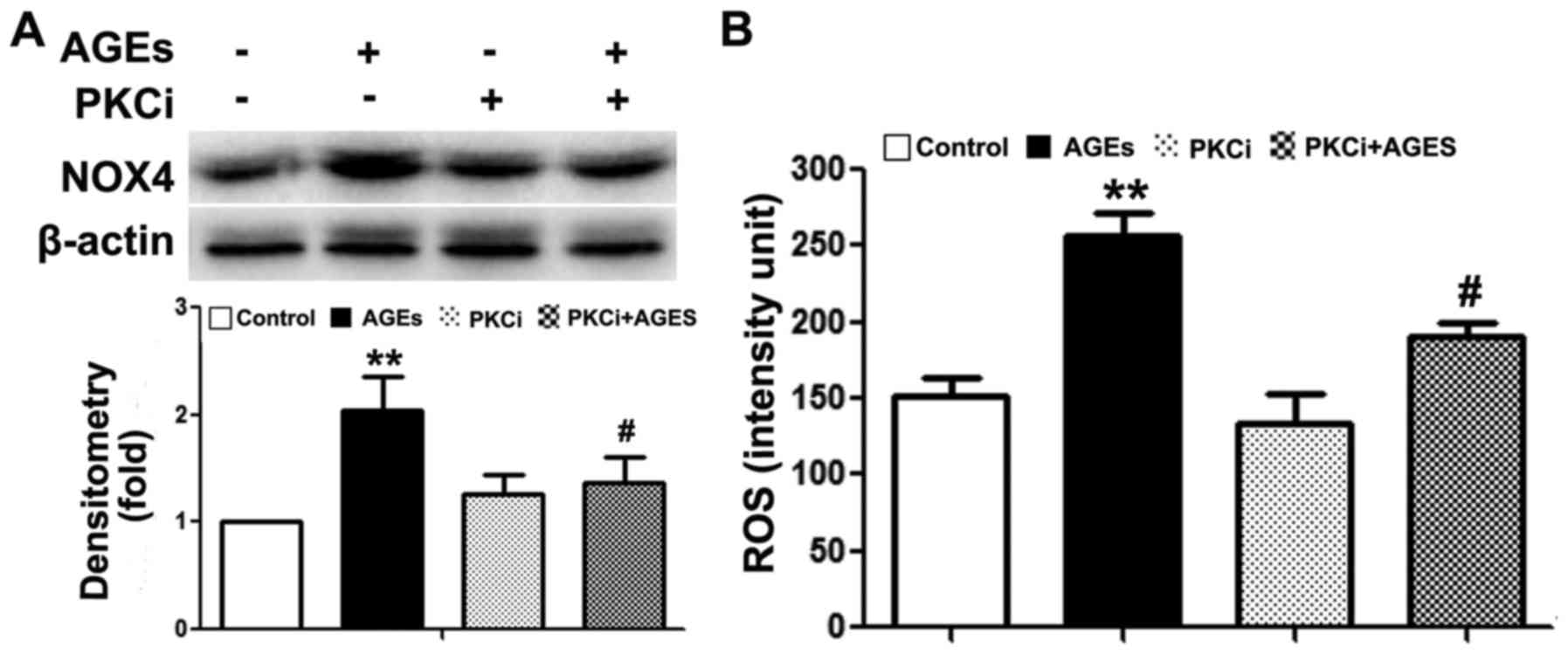
|
1
|
Nowotny K, Jung T, Höhn A, Weber D and
Grune T: Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules. 5:194–222. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Volchuk A and Ron D: The endoplasmic
reticulum stress response in the pancreatic β-cell. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 12(Suppl 2): 48–57. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lim M, Park L, Shin G, Hong H, Kang I and
Park Y: Induction of apoptosis of β cells of the pancreas by
advanced glycation end-products, important mediators of chronic
complications of diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1150:311–315.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee BW, Chae HY, Kwon SJ, Park SY, Ihm J
and Ihm SH: RAGE ligands induce apoptotic cell death of pancreatic
β-cells via oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med. 26:813–818.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jung H, Joo J, Jeon Y, Lee J, In J, Kim D,
Kang E, Kim Y, Lim Y, Kang J, et al: Advanced glycation end
products downregulate glucokinase in mice. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
27:557–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Puddu A, Storace D, Durante A, Odetti P
and Viviani GL: Glucagon-like peptide-1 counteracts the detrimental
effects of advanced glycation end-products in the pancreatic beta
cell line HIT-T 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:462–466. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jakus V and Rietbrock N: Advanced
glycation end-products and the progress of diabetic vascular
complications. Physiol Res. 53:131–142. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baumann M: Role of advanced glycation end
products in hypertension and cardiovascular risk: human studies. J
Am Soc Hypertens. 6:427–435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chilelli NC, Burlina S and Lapolla A:
AGEs, rather than hyperglycemia, are responsible for microvascular
complications in diabetes: a 'glycoxidation-centric' point of view.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 23:913–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamagishi S, Nakamura N, Suematsu M,
Kaseda K and Matsui T: Advanced glycation end products: a molecular
target for vascular complications in diabetes. Mol Med. 21(Suppl
1): S32–S40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li BY, Li XL, Gao HQ, Zhang JH, Cai Q,
Cheng M and Lu M: Grape seed procyanidin B2 inhibits advanced
glycation end product-induced endothelial cell apoptosis through
regulating GSK3β phosphorylation. Cell Biol Int. 35:663–669. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun C, Liang C, Ren Y, Zhen Y, He Z, Wang
H, Tan H, Pan X and Wu Z: Advanced glycation end products depress
function of endothelial progenitor cells via p38 and ERK 1/2
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Basic Res Cardiol.
104:42–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Adamopoulos C, Piperi C, Gargalionis AN,
Dalagiorgou G, Spilioti E, Korkolopoulou P, Diamanti-Kandarakis E
and Papavassiliou AG: Advanced glycation end products upregulate
lysyl oxidase and endothelin-1 in human aortic endothelial cells
via parallel activation of ERK1/2-NF-κB and JNK-AP-1 signaling
pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:1685–1698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Morita M, Yano S, Yamaguchi T and Sugimoto
T: Advanced glycation end products-induced reactive oxygen species
generation is partly through NF-kappa B activation in human aortic
endothelial cells. J Diabetes Complications. 27:11–15. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sang HQ, Gu JF, Yuan JR, Zhang MH, Jia XB
and Feng L: The protective effect of Smilax glabra extract on
advanced glycation end products-induced endothelial dysfunction in
HUVECs via RAGE-ERK1/2-NF-κB pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
155:785–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin N, Zhang H and Su Q: Advanced
glycation end-products induce injury to pancreatic beta cells
through oxidative stress. Diabetes Metab. 38:250–257. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu Y, Shu T, Lin Y, Wang H, Yang J, Shi Y
and Han X: Inhibition of the receptor for advanced glycation
endproducts (RAGE) protects pancreatic β-cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 404:159–165. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Coughlan MT, Yap FY, Tong DC,
Andrikopoulos S, Gasser A, Thallas-Bonke V, Webster DE, Miyazaki J,
Kay TW, Slattery RM, et al: Advanced glycation end products are
direct modulators of β-cell function. Diabetes. 60:2523–2532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng WP, Wang BW, Lo HM and Shyu KG:
Mechanical stretch induces apoptosis regulator TRB3 in cultured
cardiomyocytes and volume-overloaded heart. PLoS One.
10:e01232352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni RN and Montminy
M: TRB3: a tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by
insulin in liver. Science. 300:1574–1577. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qian B, Wang H, Men X, Zhang W, Cai H, Xu
S, Xu Y, Ye L, Wollheim CB and Lou J: TRIB3 [corrected] is
implicated in glucotoxicity- and endoplasmic
reticulum-stress-induced [corrected] beta-cell apoptosis. J
Endocrinol. 199:407–416. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin J, Fang N, Lou J, Zhang W, Xu S, Liu
H, Fang Q, Wang Z, Liu J, Men X, et al: TRB3 is involved in free
fatty acid-induced INS-1-derived cell apoptosis via the protein
kinase C δ pathway. PLoS One. 9:e960892014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fang N, Zhang W, Xu S, Lin H, Wang Z, Liu
H, Fang Q, Li C, Peng L and Lou J: TRIB3 alters endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced β-cell apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway.
Metabolism. 63:822–830. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scivittaro V, Ganz MB and Weiss MF: AGEs
induce oxidative stress and activate protein kinase C-β(II) in
neonatal mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
278:F676–F683. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li L and Renier G: Activation of
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced form) oxidase
by advanced glycation end products links oxidative stress to
altered retinal vascular endothelial growth factor expression.
Metabolism. 55:1516–1523. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang H, Jiang YW, Zhang WJ, Xu SQ, Liu HL,
Yang WY and Lou JN: Differential activations of PKC/PKA related to
microvasculopathy in diabetic GK rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 302:E173–E182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Huang D, Shen D, Zhang C, Ma Y,
Babcock SA, Chen B and Ren J: Inhibition of protein kinase C βII
isoform ameliorates methylglyoxal advanced glycation
endproduct-induced cardiomyocyte contractile dysfunction. Life Sci.
94:83–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo B, Zhang W, Xu S, Lou J, Wang S and
Men X: GSK-3β mediates dexamethasone-induced pancreatic β cell
apoptosis. Life Sci. 144:1–7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Singh VP, Bali A, Singh N and Jaggi AS:
Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. Korean
J Physiol Pharmacol. 18:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bierhaus A, Humpert PM, Morcos M, Wendt T,
Chavakis T, Arnold B, Stern DM and Nawroth PP: Understanding RAGE,
the receptor for advanced glycation end products. J Mol Med (Berl).
83:876–886. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, Yan SD,
Wang F, Pan YC, Elliston K, Stern D and Shaw A: Cloning and
expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation
end products of proteins. J Biol Chem. 267:14998–15004.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hofmann MA, Drury S, Fu C, Qu W, Taguchi
A, Lu Y, Avila C, Kambham N, Bierhaus A, Nawroth P, et al: RAGE
mediates a novel proinflammatory axis: a central cell surface
receptor for S100/calgranulin polypeptides. Cell. 97:889–901. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hori O, Brett J, Slattery T, Cao R, Zhang
J, Chen JX, Nagashima M, Lundh ER, Vijay S, Nitecki D, et al: The
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is a cellular
binding site for amphoterin. Mediation of neurite outgrowth and
co-expression of rage and amphoterin in the developing nervous
system. J Biol Chem. 270:25752–25761. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue
B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L, Lin C, Yu J, et al:
RAGE mediates amyloid-β peptide transport across the blood-brain
barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med. 9:907–913. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mackic JB, Stins M, McComb JG, Calero M,
Ghiso J, Kim KS, Yan SD, Stern D, Schmidt AM, Frangione B, et al:
Human blood-brain barrier receptors for Alzheimer's amyloid-beta
1–;40. Asymmetrical binding, endocytosis, and transcytosis at the
apical side of brain microvascular endothelial cell monolayer. J
Clin Invest. 102:734–743. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lo MC, Chen MH, Lee WS, Lu CI, Chang CR,
Kao SH and Lee HM: Nε-(carboxymethyl) lysine-induced mitochondrial
fission and mitophagy cause decreased insulin secretion from
β-cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 309:E829–E839.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hasnain SZ, Prins JB and McGuckin MA:
Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in β-cell dysfunction in
diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol. 56:R33–R54. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA and
Grodsky GM: Are oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways
mediators of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction? Diabetes.
52:1–8. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nisimoto Y, Diebold BA, Cosentino-Gomes D
and Lambeth JD: Nox4: a hydrogen peroxide-generating oxygen sensor.
Biochemistry. 53:5111–5120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Prudente S, Sesti G, Pandolfi A, Andreozzi
F, Consoli A and Trischitta V: The mammalian tribbles homolog
TRIB3, glucose homeostasis, and cardiovascular diseases. Endocr
Rev. 33:526–546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Humphrey RK, Newcomb CJ, Yu SM, Hao E, Yu
D, Krajewski S, Du K and Jhala US: Mixed lineage kinase-3
stabilizes and functionally cooperates with TRIBBLES-3 to
compromise mitochondrial integrity in cytokine-induced death of
pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 285:22426–22436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ohoka N, Yoshii S, Hattori T, Onozaki K
and Hayashi H: TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced
via ATF4-CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J.
24:1243–1255. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zou CG, Cao XZ, Zhao YS, Gao SY, Li SD,
Liu XY, Zhang Y and Zhang KQ: The molecular mechanism of
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in PC-12 neuronal
cells: the protective effect of insulin-like growth factor I.
Endocrinology. 150:277–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Schwarzer R, Dames S, Tondera D, Klippel A
and Kaufmann J: TRB3 is a PI 3-kinase dependent indicator for
nutrient starvation. Cell Signal. 18:899–909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ord D, Meerits K and Ord T: TRB3 protects
cells against the growth inhibitory and cytotoxic effect of ATF4.
Exp Cell Res. 313:3556–3567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gorasia DG, Dudek L, Veith PD, Shankar R,
Safavi-Hemami H, Williamson NA, Reynolds EC, Hubbard MJ and Purcell
AW: Pancreatic beta cells are highly susceptible to oxidative and
ER stresses during the development of diabetes. J Proteome Res.
14:688–699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhang K: Integration of ER stress,
oxidative stress and the inflammatory response in health and
disease. Int J Clin Exp Med. 3:33–40. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pérez LM, Milkiewicz P, Ahmed-Choudhury J,
Elias E, Ochoa JE, Sánchez Pozzi EJ, Coleman R and Roma MG:
Oxidative stress induces actin-cytoskeletal and tight-junctional
alterations in hepatocytes by a Ca2+-dependent,
PKC-mediated mechanism: protective effect of PKA. Free Radic Biol
Med. 40:2005–2017. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Pérez LM, Milkiewicz P, Elias E, Coleman
R, Sánchez Pozzi EJ and Roma MG: Oxidative stress induces
internalization of the bile salt export pump, Bsep, and bile salt
secretory failure in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets: a role for
protein kinase C and prevention by protein kinase A. Toxicol Sci.
91:150–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|