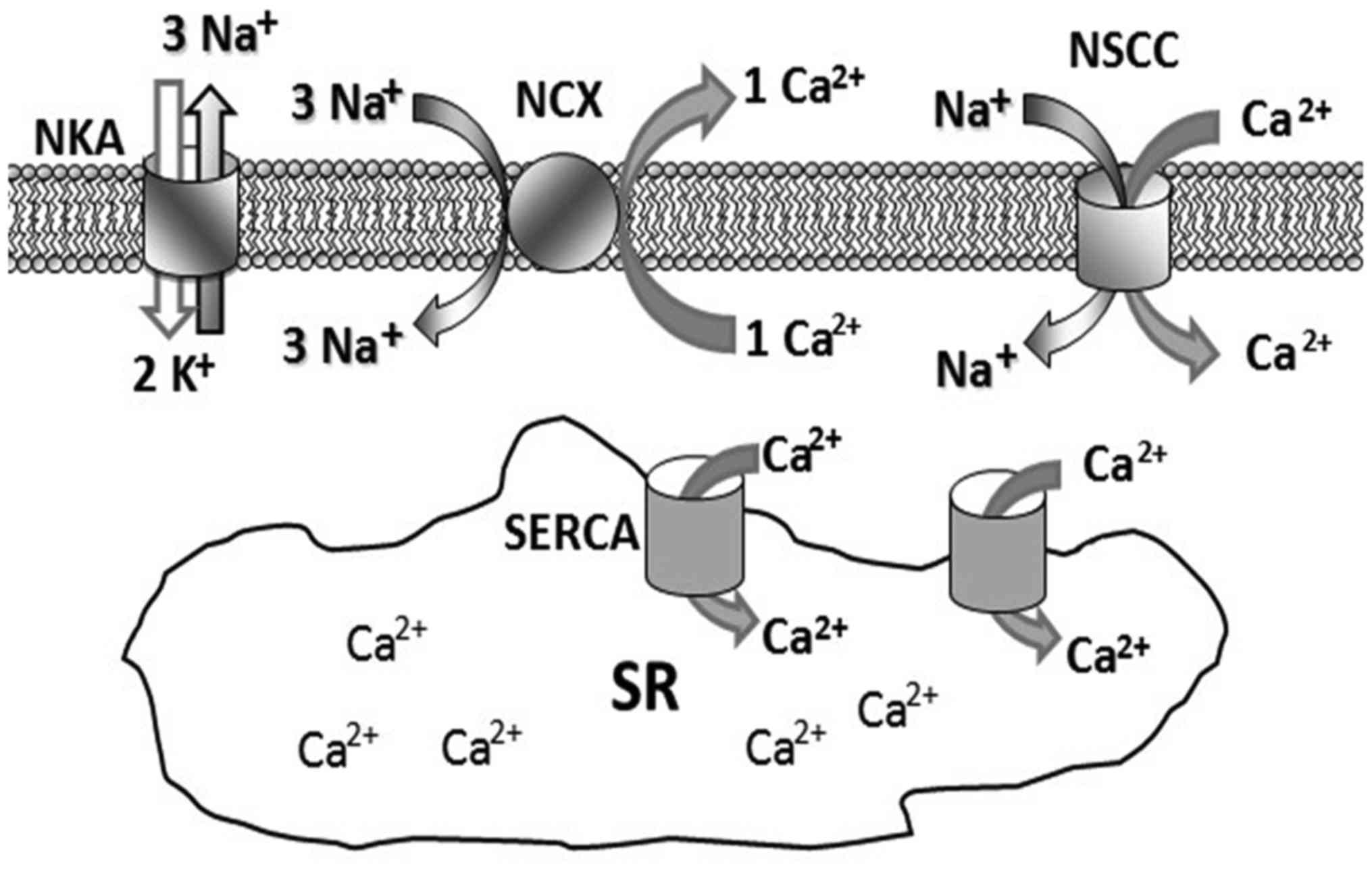
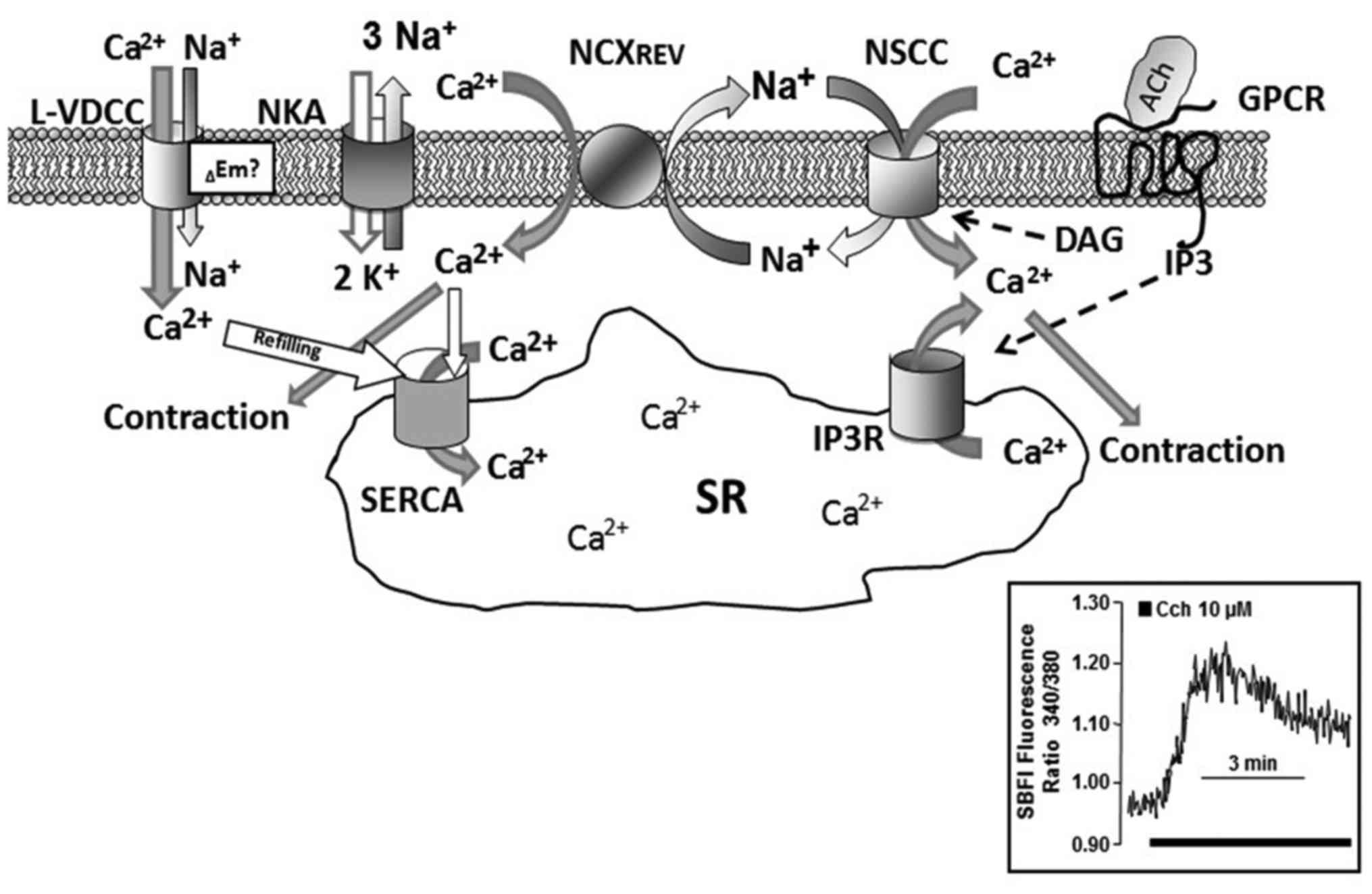
|
1
|
Woloski JR, Heston S and Escobedo Calderon
SP: Respiratory Allergic Disorders. Prim Care. 43:401–415. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bostantzoglou C, Delimpoura V, Samitas K,
Zervas E, Kanniess F and Gaga M: Clinical asthma phenotypes in the
real world: Opportunities and challenges. Breathe Sheff.
11:186–193. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lommatzsch M and Stoll P: Novel strategies
for the treatment of asthma. Allergo J Int. 25:11–17. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koopmans T, Anaparti V, Castro-Piedras I,
Yarova P, Irechukwu N, Nelson C, Perez-Zoghbi J, Tan X, Ward JP and
Wright DB: Ca2+ handling and sensitivity in airway
smooth muscle: Emerging concepts for mechanistic understanding and
therapeutic targeting. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 29:108–120. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carbajal V, Vargas MH, Flores-Soto E,
Martínez-Cordero E, Bazán-Perkins B and Montaño LM: LTD4 induces
hyperrespon-siveness to histamine in bovine airway smooth muscle:
Role of SR-ATPase Ca2+ pump and tyrosine kinase. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L84–L92. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu C, Tazzeo T and Janssen LJ:
Isoprostane-induced airway hyperresponsiveness is dependent on
internal Ca2+ handling and Rho/ROCK signaling. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 291:L1177–L1184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morin C and Rousseau E: Enhanced
Ca2+ sensitivity in hyper-responsive cultured bronchi is
mediated by TNFalpha and NF-kappaB. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
84:1029–1041. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sweeney D, Hollins F, Gomez E, Saunders R,
Challiss RA and Brightling CE: [Ca2+]i
oscillations in ASM: Relationship with persistent airflow
obstruction in asthma. Respirology. 19:763–766. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fleischmann BK, Washabau RJ and Kotlikoff
MI: Control of resting membrane potential by delayed rectifier
potassium currents in ferret airway smooth muscle cells. J Physiol.
469:625–638. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blaustein MP: Sodium ions, calcium ions,
blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: A reassessment and a
hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 232:C165–C173. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B and Nicotera P:
Regulation of cell death: The calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:552–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eder P, Poteser M, Romanin C and Groschner
K: Na(+) entry and modulation of Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange as a key
mechanism of TRPC signaling. Pflugers Arch. 451:99–104. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blaustein MP and Lederer WJ:
Sodium/calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol
Rev. 79:763–854. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Blaustein MP and Wier WG: Local sodium,
global reach: Filling the gap between salt and hypertension. Circ
Res. 101:959–961. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Poburko D, Fameli N, Kuo KH and van
Breemen C: Ca2+ signaling in smooth muscle: TRPC6, NCX
and LNats in nanodomains. Channels (Austin). 2:10–12. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dai JM, Kuo KH, Leo JM, Paré PD, van
Breemen C and Lee CH: Acetylcholine-induced asynchronous calcium
waves in intact human bronchial muscle bundle. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 36:600–608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Flores-Soto E, Reyes-García J, Sommer B
and Montaño LM: Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) refilling is
determined by L-type Ca(2+) and store operated Ca(2+) channels in
guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 721:21–28. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Perusquía M, Flores-Soto E, Sommer B,
Campuzano-González E, Martínez-Villa I, Martínez-Banderas AI and
Montaño LM: Testosterone-induced relaxation involves L-type and
store-operated Ca2+ channels blockade, and
PGE2 in guinea pig airway smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch.
467:767–777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sommer B, Flores-Soto E, Reyes-García J,
Díaz-Hernández V, Carbajal V and Montaño LM: Na(+) permeates
through L-type Ca(2+) channel in bovine airway smooth muscle. Eur J
Pharmacol. 782:77–88. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lingrel JB: The physiological significance
of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,
K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:395–412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Agrawal A, Agrawal KP, Ram A, Sondhi A,
Chhabra SK, Gangal SV and Mehta D: Basis of rise in intracellular
sodium in airway hyperresponsiveness and asthma. Lung. 183:375–387.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chhabra SK, Khanduja A and Jain D:
Increased intracellular calcium and decreased activities of
leucocyte Na+, K+-ATPase and
Ca2+-ATPase in asthma. Clin Sci (Lond). 97:595–601.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gentile DA and Skoner DP: The relationship
between airway hyperreactivity (AHR) and sodium, potassium
adenosine triphosphatase (Na+, K+ ATPase)
enzyme inhibition. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 99:367–373. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skoner DP, Gentile D and Evans RW: A
circulating inhibitor of the platelet Na+, K+
adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) enzyme in allergy. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 87:476–482. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tribe RM, Barton JR, Poston L and Burney
PG: Dietary sodium intake, airway responsiveness, and cellular
sodium transport. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 149:1426–1433. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Deusen MA, Gentile DA and Skoner DP:
Inhibition of the sodium, potassium adenosine triphosphatase enzyme
in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of subjects with allergic
rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 78:259–264. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hamlyn JM, Blaustein MP, Bova S, DuCharme
DW, Harris DW, Mandel F, Mathews WR and Ludens JH: Identification
and characterization of a ouabain-like compound from human plasma.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:6259–6263. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ferrandi M, Manunta P, Balzan S, Hamlyn
JM, Bianchi G and Ferrari P: Ouabain-like factor quantification in
mammalian tissues and plasma: Comparison of two independent assays.
Hypertension. 30:886–896. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Laredo J, Hamilton BP and Hamlyn JM:
Ouabain is secreted by bovine adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology.
135:794–797. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schoner W: Ouabain, a new steroid hormone
of adrenal gland and hypothalamus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.
108:449–454. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Komiyama Y, Nishimura N, Munakata M, Mori
T, Okuda K, Nishino N, Hirose S, Kosaka C, Masuda M and Takahashi
H: Identification of endogenous ouabain in culture supernatant of
PC12 cells. J Hypertens. 19:229–236. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
el-Masri MA, Clark BJ, Qazzaz HM and
Valdes R Jr: Human adrenal cells in culture produce both
ouabain-like and dihydroouabain-like factors. Clin Chem.
48:1720–1730. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Murrell JR, Randall JD, Rosoff J, Zhao JL,
Jensen RV, Gullans SR and Haupert GT Jr: Endogenous ouabain:
Upregulation of steroidogenic genes in hypertensive hypothalamus
but not adrenal. Circulation. 112:1301–1308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Laredo J, Shah JR, Lu ZR, Hamilton BP and
Hamlyn JM: Angiotensin II stimulates secretion of endogenous
ouabain from bovine adrenocortical cells via angiotensin type 2
receptors. Hypertension. 29:401–407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shah JR, Laredo J, Hamilton BP and Hamlyn
JM: Effects of angiotensin II on sodium potassium pumps, endogenous
ouabain, and aldosterone in bovine zona glomerulosa cells.
Hypertension. 33:373–377. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saklani P and Skanes A: Novel
anti-arrhythmic medications in the treatment of atrial
fibrillation. Curr Cardiol Rev. 8:302–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cortijo J, Sarria B, Mata M, Naline E,
Advenier C and Morcillo EJ: Effects of ouabain on human bronchial
muscle in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 368:393–403.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Blaustein MP and Hamlyn JM: Signaling
mechanisms that link salt retention to hypertension: Endogenous
ouabain, the Na(+) pump, the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger and TRPC
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:1219–1229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Katz A, Lifshitz Y, Bab-Dinitz E,
Kapri-Pardes E, Goldshleger R, Tal DM and Karlish SJ: Selectivity
of digitalis glycosides for isoforms of human Na, K-ATPase. J Biol
Chem. 285:19582–19592. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Floyd R and Wray S: Calcium transporters
and signalling in smooth muscles. Cell Calcium. 42:467–476. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
DiPolo R and Beaugé L: Sodium/calcium
exchanger: Influence of metabolic regulation on ion carrier
interactions. Physiol Rev. 86:155–203. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kofuji P, Lederer WJ and Schulze DH:
Mutually exclusive and cassette exons underlie alternatively
spliced isoforms of the Na/Ca exchanger. J Biol Chem.
269:5145–5149. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Quednau BD, Nicoll DA and Philipson KD:
Tissue specificity and alternative splicing of the
Na+/Ca2+ exchanger isoforms NCX1, NCX2, and
NCX3 in rat. Am J Physiol. 272:C1250–C1261. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mejía-Elizondo R, Espinosa-Tanguma R and
Saavedra-Alanis VM: Molecular identification of the NCX isoform
expressed in tracheal smooth muscle of guinea pig. Ann NY Acad Sci.
976:73–76. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Philipson KD, Nicoll DA, Ottolia M,
Quednau BD, Reuter H, John S and Qiu Z: The
Na+/Ca2+ exchange molecule: An overview. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 976:1–10. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pitt A and Knox AJ: Molecular
characterization of the human airway smooth muscle
Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 15:726–730. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Janssen LJ, Walters DK and Wattie J:
Regulation of [Ca2+] in canine airway smooth muscle by
Ca(2+)-ATPase and Na+/Cai2+ exchange
mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 273:L322–L330. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Flores-Soto E, Carbajal V, Reyes-García J,
García-Hernández LM, Figueroa A, Checa M, Barajas-López C and
Montaño LM: In airways ATP refills sarcoplasmic reticulum via P2X
smooth muscle receptors and induces contraction through P2Y
epithelial receptors. Pflugers Arch. 461:261–275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu B, Peel SE, Fox J and Hall IP: Reverse
mode Na+/Ca2+ exchange mediated by STIM1
contributes to Ca2+ influx in airway smooth muscle
following agonist stimulation. Respir Res. 11:1682010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Putney JW and Tomita T: Phospholipase C
signaling and calcium influx. Adv Biol Regul. 52:152–164. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Pedersen SF, Owsianik G and Nilius B: TRP
channels: An overview. Cell Calcium. 38:233–252. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Trebak M, Lemonnier L, Smyth JT, Vazquez G
and Putney JW Jr: Phospholipase C-coupled receptors and activation
of TRPC channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 179:593–614. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Trebak M, Vazquez G, Bird GS and Putney JW
Jr: The TRPC3/6/7 subfamily of cation channels. Cell Calcium.
33:451–461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vazquez G, Wedel BJ, Aziz O, Trebak M and
Putney JW Jr: The mammalian TRPC cation channels. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1742:21–36. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ong HL and Ambudkar IS: The dynamic
complexity of the TRPC1 channelosome. Channels (Austin). 5:424–431.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yuan JP, Lee KP, Hong JH and Muallem S:
The closing and opening of TRPC channels by Homer1 and STIM1. Acta
Physiol (Oxf). 204:238–247. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cheng KT, Liu X, Ong HL, Swaim W and
Ambudkar IS: Local Ca2+ entry via Orai1
regulates plasma membrane recruitment of TRPC1 and controls
cytosolic Ca2+ signals required for specific
cell functions. PLoS Biol. 9:e10010252011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Soboloff J, Madesh M and Gill DL: Sensing
cellular stress through STIM proteins. Nat Chem Biol. 7:488–492.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu X, Jiang M, Peyton M, Boulay G, Hurst
R, Stefani E and Birnbaumer L: Trp, a novel mammalian gene family
essential for agonist-activated capacitative Ca2+ entry.
Cell. 85:661–671. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kiselyov K, Xu X, Mozhayeva G, Kuo T,
Pessah I, Mignery G, Zhu X, Birnbaumer L and Muallem S: Functional
interaction between InsP3 receptors and store-operated Htrp3
channels. Nature. 396:478–482. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
McKay RR, Szymeczek-Seay CL, Lievremont
JP, Bird GS, Zitt C, Jüngling E, Lückhoff A and Putney JW Jr:
Cloning and expression of the human transient receptor potential 4
(TRP4) gene: Localization and functional expression of human TRP4
and TRP3. Biochem J. 351:735–746. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kiselyov K, Mignery GA, Zhu MX and Muallem
S: The N-terminal domain of the IP3 receptor gates store-operated
hTrp3 channels. Mol Cell. 4:423–429. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xiao JH, Zheng YM, Liao B and Wang YX:
Functional role of canonical transient receptor potential 1 and
canonical transient receptor potential 3 in normal and asthmatic
airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:17–25.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Putney JW: The physiological function of
store-operated calcium entry. Neurochem Res. 36:1157–1165. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bradley E, Webb TI, Hollywood MA, Sergeant
GP, McHale NG and Thornbury KD: The cardiac sodium current Na(v)1.5
is functionally expressed in rabbit bronchial smooth muscle cells.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 305:C427–C435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Snetkov VA, Hirst SJ and Ward JP: Ion
channels in freshly isolated and cultured human bronchial smooth
muscle cells. Exp Physiol. 81:791–804. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Jo T, Nagata T, Iida H, Imuta H, Iwasawa
K, Ma J, Hara K, Omata M, Nagai R, Takizawa H, et al: Voltage-gated
sodium channel expressed in cultured human smooth muscle cells:
Involvement of SCN9A. FEBS Lett. 567:339–343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Nakajima T, Jo T, Meguro K, Oonuma H, Ma
J, Kubota N, Imuta H, Takano H, Iida H, Nagase T, et al: Effect of
dexamethasone on voltage-gated Na+ channel in cultured
human bronchial smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 82:1210–1215. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Knox AJ, Ajao P, Britton JR and
Tattersfield AE: Effect of sodium-transport inhibitors on airway
smooth muscle contractility in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond). 79:315–323.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Knudsen T, Bertelsen H and Johansen T:
Ouabain enhancement of compound 48/80 induced histamine secretion
from rat peritoneal mast cells: Dependence on extracellular sodium.
Pharmacol Toxicol. 70:412–418. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
de Vasconcelos DI, Leite JA, Carneiro LT,
Piuvezam MR, de Lima MR, de Morais LC, Rumjanek VM and
Rodrigues-Mascarenhas S: Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive
activity of ouabain in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2011:9129252011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Choi JP, Kim YS, Kim OY, Kim YM, Jeon SG,
Roh TY, Park JS, Gho YS and Kim YK: TNF-alpha is a key mediator in
the development of Th2 cell response to inhaled allergens induced
by a viral PAMP double-stranded RNA. Allergy. 67:1138–1148. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hallstrand TS: New insights into
pathogenesis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Curr Opin
Allergy Clin Immunol. 12:42–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Anderson SD: Indirect challenge tests:
Airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma: its measurement and clinical
significance. Chest. 138(Suppl): 25S–30S. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hallstrand TS, Moody MW, Wurfel MM,
Schwartz LB, Henderson WR Jr and Aitken ML: Inflammatory basis of
exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
172:679–686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hallstrand TS, Lai Y, Ni Z, Oslund RC,
Henderson WR Jr, Gelb MH and Wenzel SE: Relationship between levels
of secreted phospholipase A2 groups IIA and X in the
airways and asthma severity. Clin Exp Allergy. 41:801–810. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Schmitt L, Wiebel M, Frese F, Dehnert C,
Zugck C, Bärtsch P and Mairbäurl H: Exercise reduces airway sodium
ion reabsorption in cystic fibrosis but not in exercise asthma. Eur
Respir J. 37:342–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Aneiros E, Philipp S, Lis A, Freichel M
and Cavalié A: Modulation of Ca2+ signaling by
Na+/Ca2+ exchangers in mast cells. J Immunol.
174:119–130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Praetorius HA, Friis UG, Praetorius J and
Johansen T: Evidence for a Na+/Ca2+ exchange
mechanism in rat peritoneal mast cells. Pflugers Arch. 437:86–93.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Rundell KW and Jenkinson DM:
Exercise-induced bronchospasm in the elite athlete. Sports Med.
32:583–600. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gotshall RW, Mickleborough TD and Cordain
L: Dietary salt restriction improves pulmonary function in
exercise-induced asthma. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 32:1815–1819. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
McKeever TM, Lewis SA, Smit HA, Burney P,
Cassano PA and Britton J: A multivariate analysis of serum nutrient
levels and lung function. Respir Res. 9:67–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mickleborough TD, Lindley MR and Ray S:
Dietary salt, airway inflammation, and diffusion capacity in
exercise-induced asthma. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 37:904–914.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Pogson Z and McKeever T: Dietary sodium
manipulation and asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0004362011.
|
|
85
|
Ardern KD and Ardern KD: Dietary salt
reduction or exclusion for allergic asthma. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. 2:CD0004362004.
|