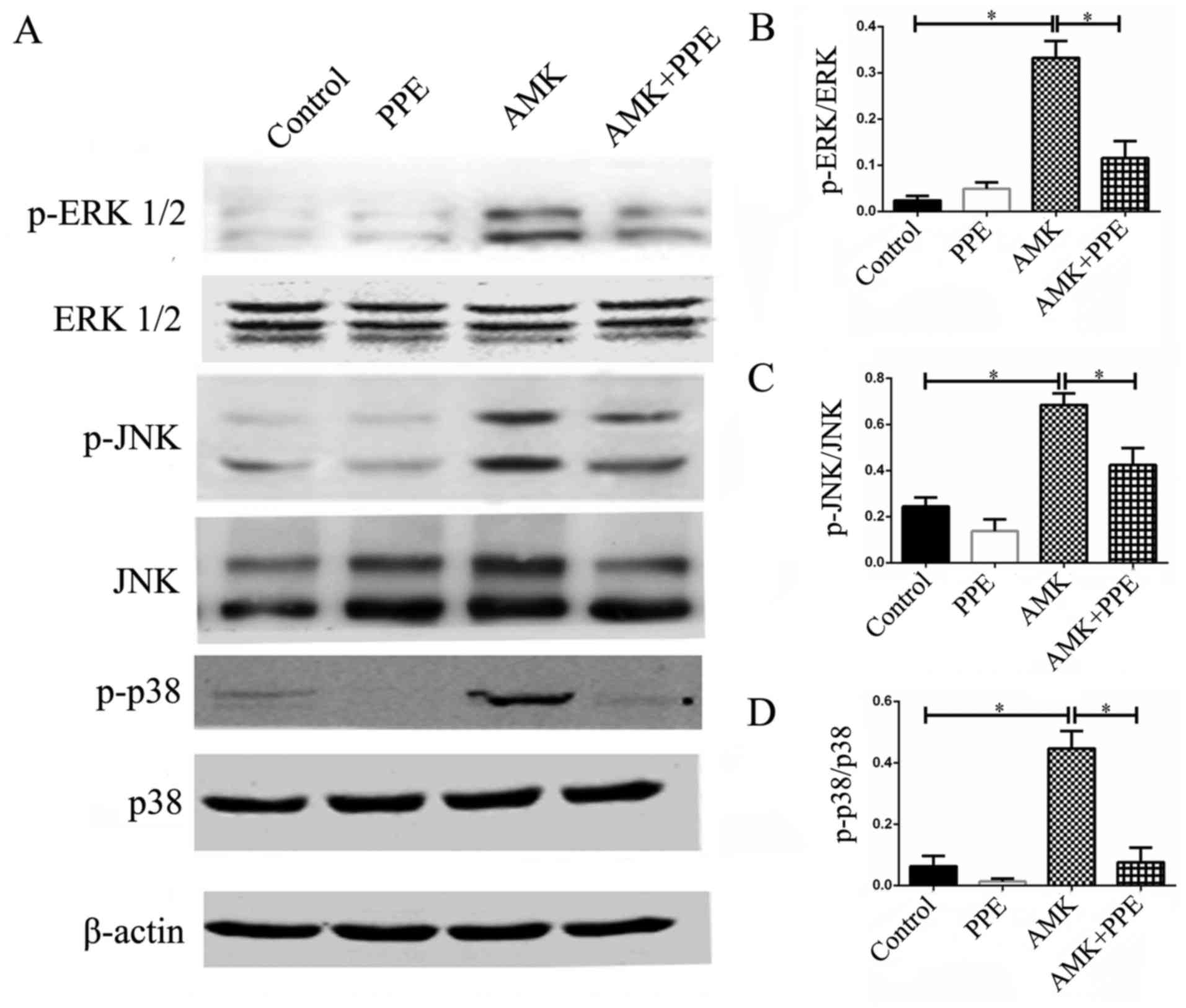
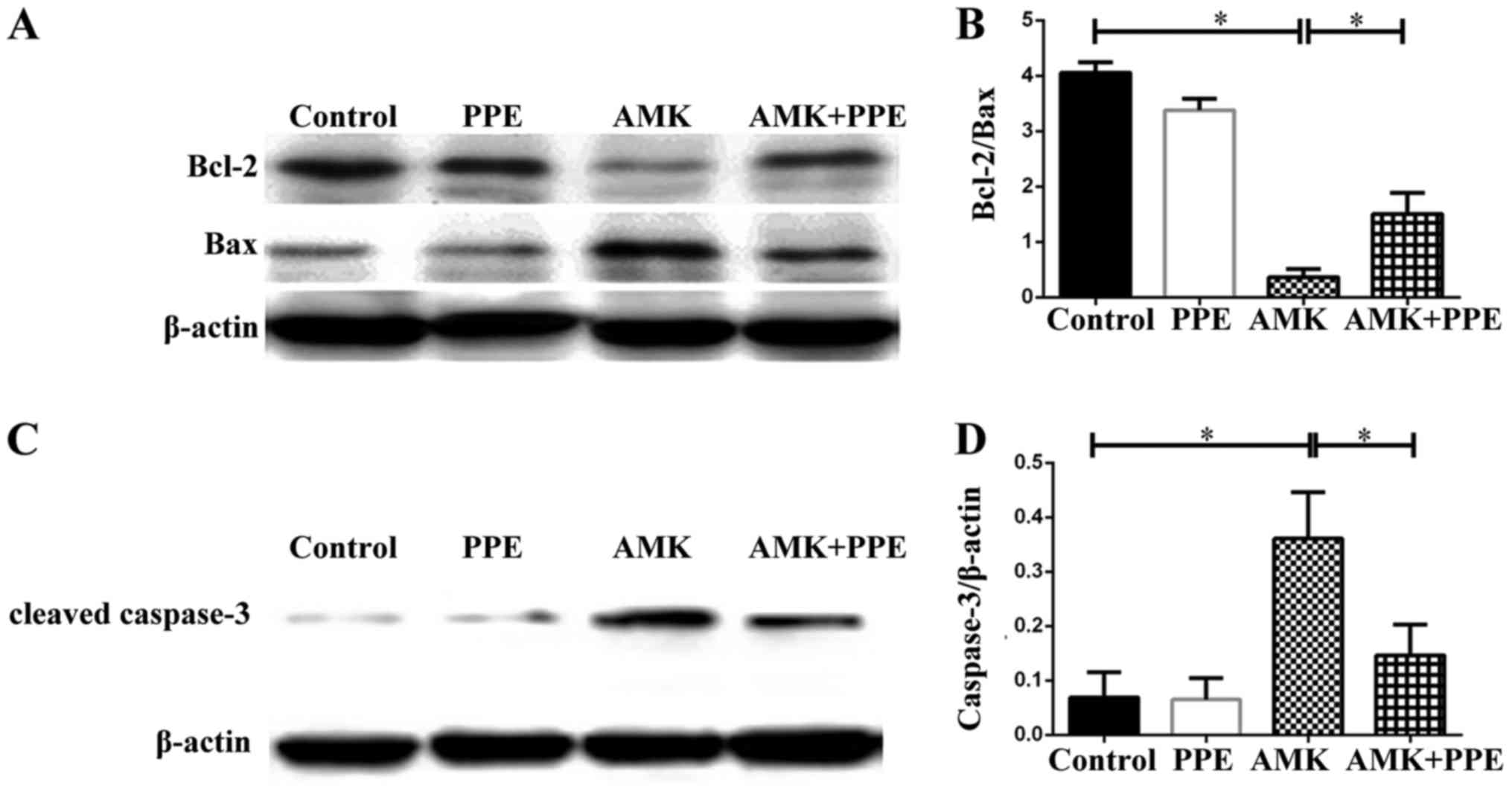
|
1
|
Michalopoulos A and Papadakis E: Inhaled
anti-infective agents: emphasis on colistin. Infection. 38:81–88.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tokgoz B, Ucar C, Kocyigit I, Somdas M,
Unal A, Vural A, Sipahioglu M, Oymak O and Utas C: Protective
effect of N-acetylcysteine from drug-induced ototoxicity in uraemic
patients with CAPD peritonitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
26:4073–4078. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aksoy F, Dogan R, Ozturan O, Eren SB,
Veyseller B, Pektas A and Hüseyinbas Ö: Protective effect of
trimetazidine on amikacin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Int J
Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 78:663–669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Forge A and Schacht J: Aminoglycoside
antibiotics. Audiol Neurootol. 5:3–22. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szczepanik W, Kaczmarek P and
Jezowska-Bojczuk M: Oxidative activity of copper(II) complexes with
aminoglycoside antibiotics as implication to the toxicity of these
drugs. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2:55–68. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Faria A and Calhau C: The bioactivity of
pomegranate: impact on health and disease. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.
51:626–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Al-Gubory KH, Blachier F, Faure P and
Garrel C: Pomegranate peel extract decreases small intestine lipid
peroxidation by enhancing activities of major antioxidant enzymes.
J Sci Food Agric. 96:3462–3468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamashita D, Jiang HY, Schacht J and
Miller JM: Delayed production of free radicals following noise
exposure. Brain Res. 1019:201–209. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang H, Sha SH and Schacht J: NF-kappaB
pathway protects cochlear hair cells from aminoglycoside-induced
ototoxicity. J Neurosci Res. 79:644–651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang H, Talaska AE, Schacht J and Sha SH:
Oxidative imbalance in the aging inner ear. Neurobiol Aging.
28:1605–1612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kahya V, Meric A, Yazici M, Yuksel M, Midi
A and Gedikli O: Antioxidant effect of pomegranate extract in
reducing acute inflammation due to myringotomy. J Laryngol Otol.
125:370–375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yazici ZM, Meric A, Midi A, Arınc YV,
Kahya V and Hafız G: Reduction of cisplatin ototoxicity in rats by
oral administration of pomegranate extract. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 269:45–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Webb AE and Brunet A: FOXO transcription
factors: key regulators of cellular quality control. Trends Biochem
Sci. 39:159–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Almeida M: Unraveling the role of FoxOs in
bone - insights from mouse models. Bone. 49:319–327. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parody JP, Ceballos MP, Quiroga AD,
Frances DE, Carnovale CE, Pisani GB, Alvarez ML and Carrillo MC:
FoxO3a modulation and promotion of apoptosis by interferon-α2b in
rat preneoplastic liver. Liver Int. 34:1566–1577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shukla S, Rizvi F, Raisuddin S and Kakkar
P: FoxO proteins' nuclear retention and BH3-only protein Bim
induction evoke mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated apoptosis in
berberine-treated HepG2 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 76:185–199.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gilels F, Paquette ST, Zhang J, Rahman I
and White PM: Mutation of Foxo3 causes adult onset auditory
neuropathy and alters cochlear synapse architecture in mice. J
Neurosci. 33:18409–18424. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murillo-Cuesta S, Contreras J, Cediel R
and Varela-Nieto I: Comparison of different aminoglycoside
antibiotic treatments to refine ototoxicity studies in adult mice.
Lab Anim. 44:124–131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang A, Hou N, Bao D, Liu S and Xu T:
Mechanism of alpha-lipoic acid in attenuating kanamycin-induced
ototoxicity. Neural Regen Res. 7:2793–2800. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shulman E, Belakhov V, Wei G, Kendall A,
Meyron-Holtz EG, Ben-Shachar D, Schacht J and Baasov T: Designer
amino-glycosides that selectively inhibit cytoplasmic rather than
mitochondrial ribosomes show decreased ototoxicity: a strategy for
the treatment of genetic diseases. J Biol Chem. 289:2318–2330.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Amora LdeA, Murashima AdeA, Rossato M,
Moreira MB, Hyppolito MÂ and Fagundes DJ: The effects of hyperbaric
oxygen therapy upon ototoxic injuries produced by amikacin in
guinea pigs. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 79:342–348. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fausti SA, Henry JA, Schaffer HI, Olson
DJ, Frey RH and McDonald WJ: High-frequency audiometric monitoring
for early detection of aminoglycoside ototoxicity. J Infect Dis.
165:1026–1032. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi CH, Chen K, Du X, Floyd RA and Kopke
RD: Effects of delayed and extended antioxidant treatment on acute
acoustic trauma. Free Radic Res. 45:1162–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khalil SR, Abd-Elhakim YM, Selim ME and
Al-Ayadhi LY: Apitoxin protects rat pups brain from propionic
acid-induced oxidative stress: the expression pattern of Bcl-2 and
caspase-3 apoptotic genes. Neurotoxicology. 49:121–131. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Storz P: Forkhead homeobox type O
transcription factors in the responses to oxidative stress.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:593–605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Vogt PK, Jiang H and Aoki M: Triple layer
control: phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination of FOXO
proteins. Cell Cycle. 4:908–913. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Yang X, Li X, Li C, Zhao L, Zhou
Y and Hou H: Butein sensitizes HeLa cells to cisplatin through the
AKT and ERK/p38 MAPK pathways by targeting FoxO3a. Int J Mol Med.
36:957–966. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Zang WJ, Wang H, Zhao M, Yu XJ, He
X, Miao Y and Zhou J: Acetylcholine promotes ROS detoxification
against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress through
FoxO3a/PGC-1α dependent superoxide dismutase. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:1614–1625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rangarajan P, Karthikeyan A, Lu J, Ling EA
and Dheen ST: Sirtuin 3 regulates Foxo3a-mediated antioxidant
pathway in microglia. Neuroscience. 311:398–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li YN, Guo Y, Xi MM, Yang P, Zhou XY, Yin
S, Hai CX, Li JG and Qin XJ: Saponins from Aralia taibaiensis
attenuate D-galactose-induced aging in rats by activating FOXO3a
and Nrf2 pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:3205132014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang J, Wu Z, Renier N, Simon DJ, Uryu K,
Park DS, Greer PA, Tournier C, Davis RJ and Tessier-Lavigne M:
Pathological axonal death through a MAPK cascade that triggers a
local energy deficit. Cell. 160:161–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dinh CT, Goncalves S, Bas E, Van De Water
TR and Zine A: Molecular regulation of auditory hair cell death and
approaches to protect sensory receptor cells and/or stimulate
repair following acoustic trauma. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:962015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dong Y, Liu D, Hu Y and Ma X: NaHS
protects cochlear hair cells from gentamicin-induced ototoxicity by
inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. PLoS One.
10:e01360512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chi NU, Tabuchi K, Nakamagoe M, Nakayama
M, Nishimura B and Hara A: Ceramide/sphingomyelin cycle involvement
in gentamicin-induced cochlear hair cell death. Arch Toxicol.
89:415–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|