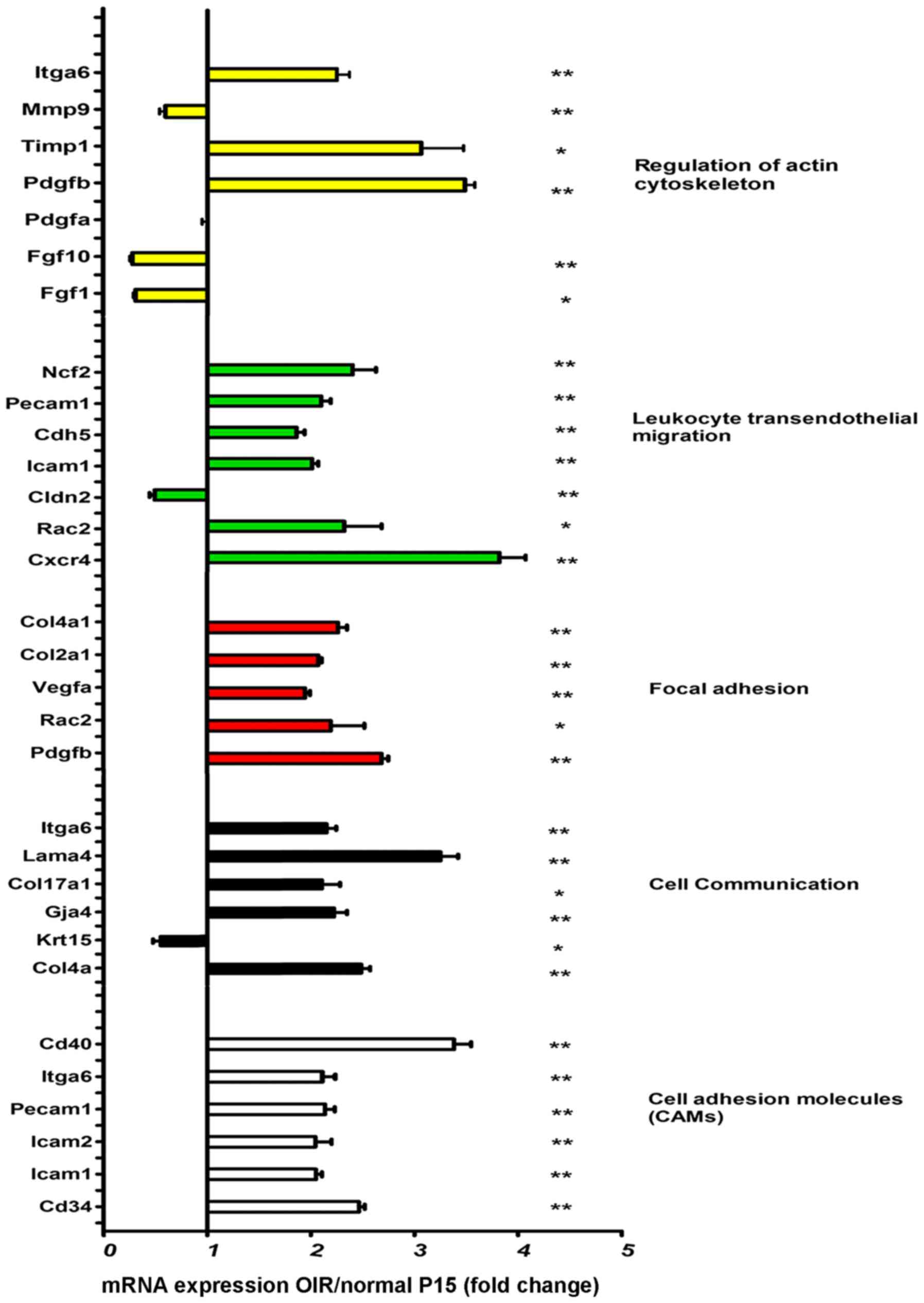
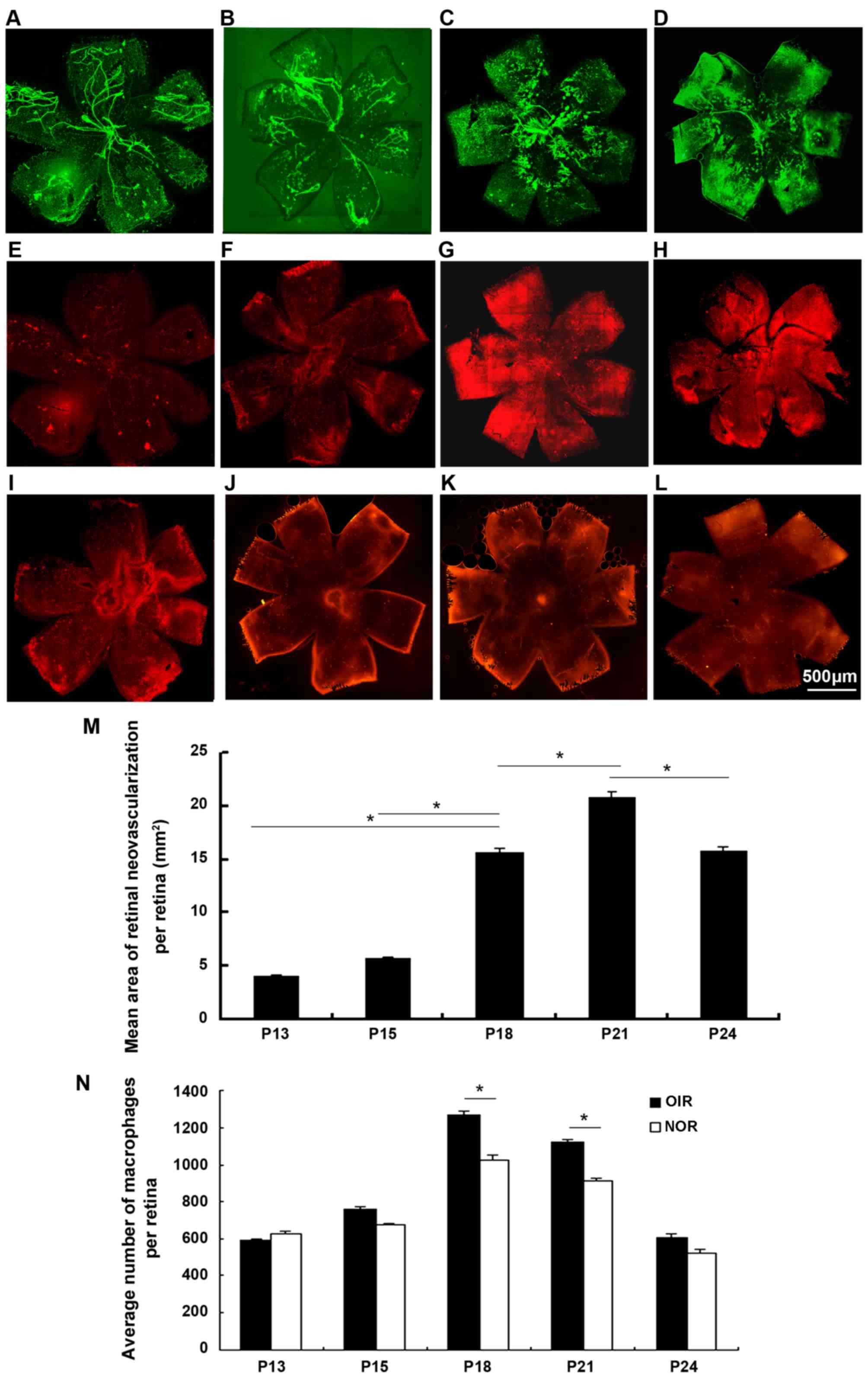
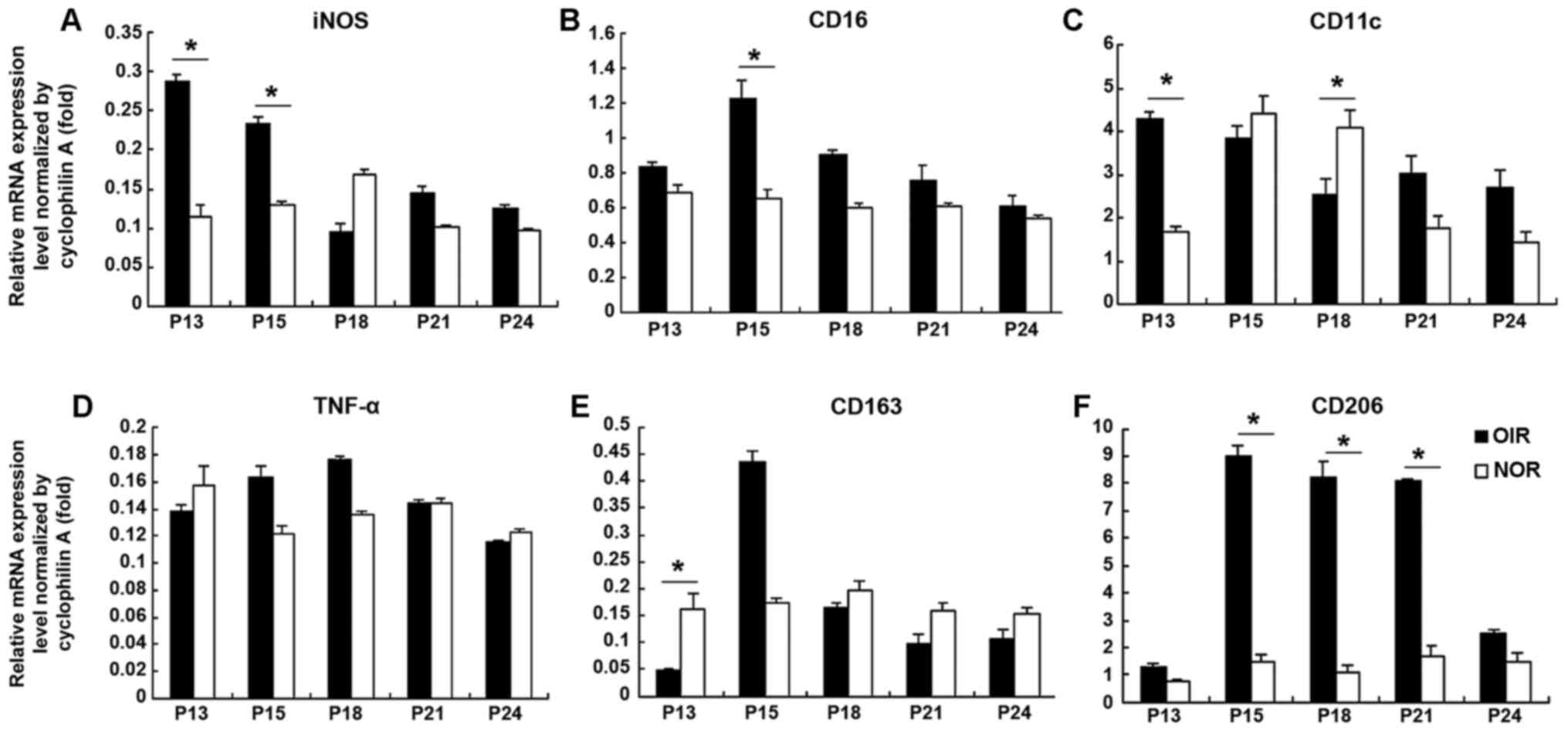
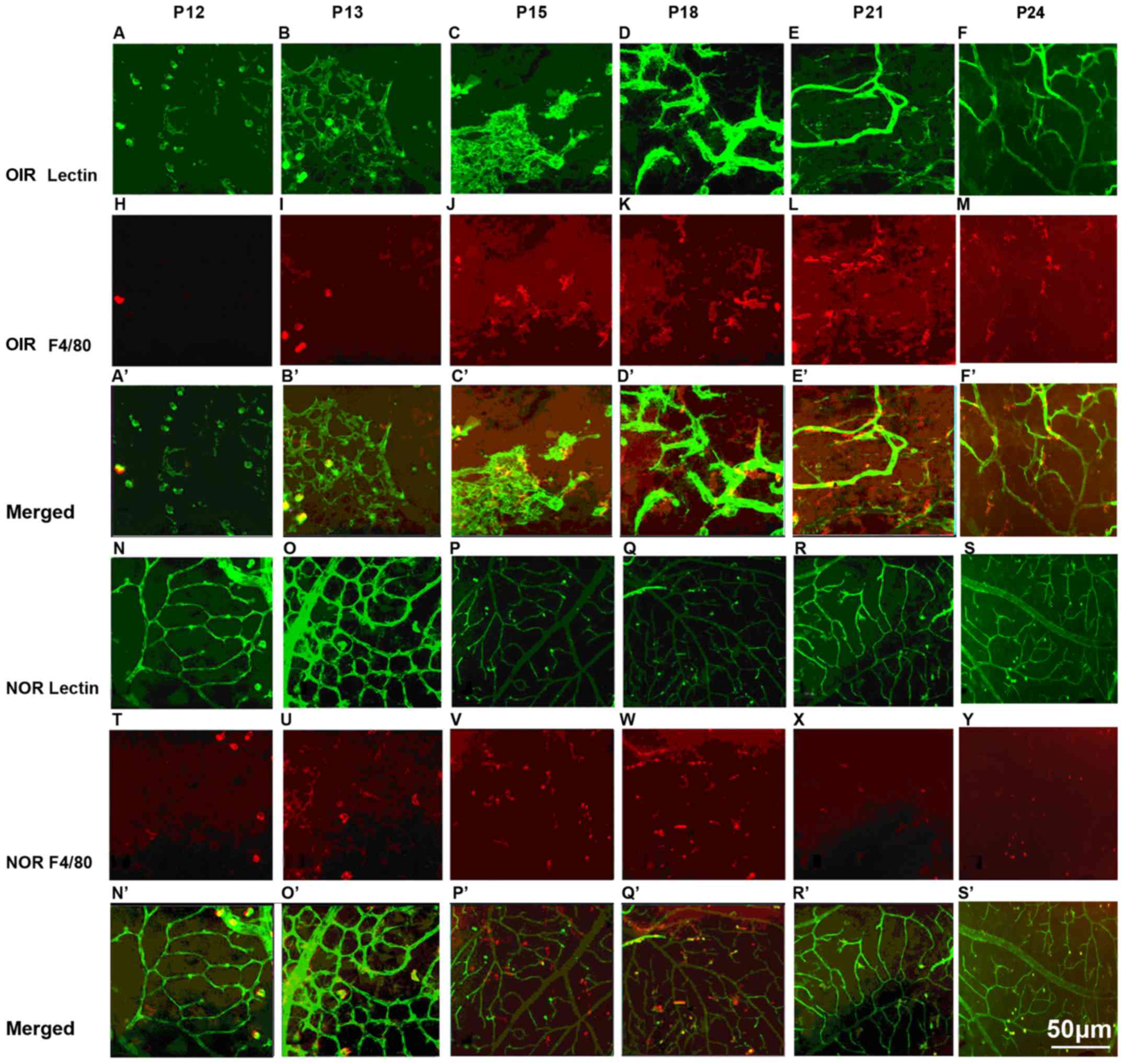
|
1
|
Hiratsuka S, Minowa O, Kuno J, Noda T and
Shibuya M: Flt-1 lacking the tyrosine kinase domain is sufficient
for normal development and angiogenesis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:9349–9354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sadiq MA, Hanout M, Sarwar S, Hassan M, Do
DV, Nguyen QD and Sepah YJ: Platelet derived growth factor
inhibitors: A potential therapeutic approach for ocular
neovascularization. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 29:287–291. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rofagha S, Bhisitkul RB, Boyer DS, Sadda
SR and Zhang K; SEVEN-UP Study Group: Seven-year outcomes in
ranibizumab-treated patients in ANCHOR, MARINA, and HORIZON: a
multicenter cohort study (SEVEN-UP). Ophthalmology. 120:2292–2299.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Comparison of Age-related Macular
Degeneration Treatments Trials (CATT) Research Group; Martin DF,
Maguire MG, Fine SL, Ying GS, Jaffe GJ, Grunwald JE, Toth C,
Redford M and Ferris FL III: Ranibizumab and bevacizumab for
treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: two-year
results. Ophthalmology. 119:1388–1398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Newman AC and Hughes CC: Macrophages and
angiogenesis: a role for Wnt signaling. Vasc Cell. 4:132012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ligresti G, Aplin AC, Zorzi P, Morishita A
and Nicosia RF: Macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha is
an early component of the molecular cascade leading to angiogenesis
in response to aortic injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
31:1151–1159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu H, Xu JB, He YL, Peng JJ, Zhang XH,
Chen CQ, Li W and Cai SR: Tumor-associated macrophages promote
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis of gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol.
106:462–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stein M, Keshav S, Harris N and Gordon S:
Interleukin 4 potently enhances murine macrophage mannose receptor
activity: a marker of alternative immunologic macrophage
activation. J Exp Med. 176:287–292. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding Y, Song N and Luo Y: Role of bone
marrow-derived cells in angiogenesis: Focus on macrophages and
pericytes. Cancer Microenviron. 5:225–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kigerl KA, Gensel JC, Ankeny DP, Alexander
JK, Donnelly DJ and Popovich PG: Identification of two distinct
macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either
neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J
Neurosci. 29:13435–13444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ashcroft GS, Jeong MJ, Ashworth JJ,
Hardman M, Jin W, Moutsopoulos N, Wild T, McCartney-Francis N, Sim
D, McGrady G, et al: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a
therapeutic target for impaired cutaneous wound healing. Wound
Repair Regen. 20:38–49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Khallou-Laschet J, Varthaman A, Fornasa G,
Compain C, Gaston AT, Clement M, Dussiot M, Levillain O,
Graff-Dubois S, Nicoletti A, et al: Macrophage plasticity in
experimental atherosclerosis. PLoS One. 5:e88522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kitajewski J: Wnts heal by restraining
angiogenesis. Blood. 121:2381–2382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Badylak SF, Valentin JE, Ravindra AK,
McCabe GP and Stewart-Akers AM: Macrophage phenotype as a
determinant of biologic scaffold remodeling. Tissue Eng Part A.
14:1835–1842. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brown BN, Valentin JE, Stewart-Akers AM,
McCabe GP and Badylak SF: Macrophage phenotype and remodeling
outcomes in response to biologic scaffolds with and without a
cellular component. Biomaterials. 30:1482–1491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fishman JM, Lowdell MW, Urbani L, Ansari
T, Burns AJ, Turmaine M, North J, Sibbons P, Seifalian AM, Wood KJ,
et al: Immunomodulatory effect of a decellularized skeletal muscle
scaffold in a discordant xenotransplantation model. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:14360–14365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Madden LR, Mortisen DJ, Sussman EM, Dupras
SK, Fugate JA, Cuy JL, Hauch KD, Laflamme MA, Murry CE and Ratner
BD: Proangiogenic scaffolds as functional templates for cardiac
tissue engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:15211–15216. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Cao Z, Bai T, Carr L, Ella-Menye
JR, Irvin C, Ratner BD and Jiang S: Zwitterionic hydrogels
implanted in mice resist the foreign-body reaction. Nat Biotechnol.
31:553–556. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bota PC, Collie AM, Puolakkainen P, Vernon
RB, Sage EH, Ratner BD and Stayton PS: Biomaterial topography
alters healing in vivo and monocyte/macrophage activation in vitro.
J Biomed Mater Res A. 95:649–657. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tolg C, Hamilton SR, Zalinska E, McCulloch
L, Amin R, Akentieva N, Winnik F, Savani R, Bagli DJ, Luyt LG, et
al: A RHAMM mimetic peptide blocks hyaluronan signaling and reduces
inflammation and fibrogenesis in excisional skin wounds. Am J
Pathol. 181:1250–1270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tous E, Weber HM, Lee MH, Koomalsingh KJ,
Shuto T, Kondo N, Gorman JH III, Lee D, Gorman RC and Burdick JA:
Tunable hydrogel-microsphere composites that modulate local
inflammation and collagen bulking. Acta Biomater. 8:3218–3227.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Apte RS, Richter J, Herndon J and Ferguson
TA: Macrophages inhibit neovascularization in a murine model of
age-related macular degeneration. PLoS Med. 3:e3102006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dace DS, Khan AA, Kelly J and Apte RS:
Interleukin-10 promotes pathological angiogenesis by regulating
macrophage response to hypoxia during development. PLoS One.
3:e33812008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Espinosa-Heidmann DG, Suner IJ, Hernandez
EP, Monroy D, Csaky KG and Cousins SW: Macrophage depletion
diminishes lesion size and severity in experimental choroidal
neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:3586–3592. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sakurai E, Anand A, Ambati BK, van Rooijen
N and Ambati J: Macrophage depletion inhibits experimental
choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
44:3578–3585. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gautier EL, Shay T, Miller J, Greter M,
Jakubzick C, Ivanov S, Helft J, Chow A, Elpek KG, Gordonov S, et
al: Immunological Genome Consortium: Gene-expression profiles and
transcriptional regulatory pathways that underlie the identity and
diversity of mouse tissue macrophages. Nat Immunol. 13:1118–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vianello E, Dozio E, Arnaboldi F, Marazzi
MG, Martinelli C, Lamont J, Tacchini L, Sigrüner A, Schmitz G and
Corsi Romanelli MM: Epicardial adipocyte hypertrophy: Association
with M1-polarization and toll-like receptor pathways in coronary
artery disease patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 26:246–253.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shu QH, Ge YS, Ma HX, Gao XQ, Pan JJ, Liu
D, Xu GL, Ma JL and Jia WD: Prognostic value of polarized
macrophages in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative resection. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1024–1035. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lumeng CN, DelProposto JB, Westcott DJ and
Saltiel AR: Phenotypic switching of adipose tissue macrophages with
obesity is generated by spatiotemporal differences in macrophage
subtypes. Diabetes. 57:3239–3246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk
SK, D'Amato R, Sullivan R and D'Amore PA: Oxygen-induced
retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 35:101–111.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen J, Xie B, Dong A, Swaim M, Hackett SF
and Campochiaro PA: In vivo immunostaining demonstrates macrophages
associate with growing and regressing vessels. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 48:4335–4341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mori K, Duh E, Gehlbach P, Ando A,
Takahashi K, Pearlman J, Mori K, Yang HS, Zack DJ, Ettyreddy D, et
al: Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits retinal and
choroidal neovascularization. J Cell Physiol. 188:253–263. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shen J, Yang X, Xie B, Chen Y, Swaim M,
Hackett SF and Campochiaro PA: MicroRNAs regulate ocular
neovascularization. Mol Ther. 16:1208–1216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fujimura S, Takahashi H, Yuda K, Ueta T,
Iriyama A, Inoue T, Kaburaki T, Tamaki Y, Matsushima K and Yanagi
Y: Angiostatic effect of CXCR3 expressed on choroidal
neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:1999–2006. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong A, Shen J, Zeng M and Campochiaro PA:
Vascular cell-adhesion molecule-1 plays a central role in the
proangiogenic effects of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:14614–14619. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xin X, Rodrigues M, Umapathi M,
Kashiwabuchi F, Ma T, Babapoor-Farrokhran S, Wang S, Hu J, Bhutto I
and Welsbie DS: Hypoxic retinal Muller cells promote vascular
permeability by HIF-1-dependent up-regulation of angiopoietin-like
4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E3425–E3434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie B, Shen J, Dong A, Swaim M, Hackett
SF, Wyder L, Worpenberg S, Barbieri S and Campochiaro PA: An Adam15
amplification loop promotes vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced ocular neovascularization. FASEB J. 22:2775–2783.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arnold L, Henry A, Poron F, Baba-Amer Y,
van Rooijen N, Plonquet A, Gherardi RK and Chazaud B: Inflammatory
monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into
antiinflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis. J Exp Med.
204:1057–1069. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Herbert SP and Stainier DY: Molecular
control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel
morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:551–564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dace DS and Apte RS: Effect of senescence
on macrophage polarization and angiogenesis. Rejuvenation Res.
11:177–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kelly J, Ali Khan A, Yin J, Ferguson TA
and Apte RS: Senescence regulates macrophage activation and
angiogenic fate at sites of tissue injury in mice. J Clin Invest.
117:3421–3426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gao X, Wang YS, Li XQ, Hou HY, Su JB, Yao
LB and Zhang J: Macrophages promote vasculogenesis of retinal
neovascularization in an oxygen-induced retinopathy model in mice.
Cell Tissue Res. 364:599–610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kelly J, Ali Khan A, Yin J, Ferguson TA
and Apte RS: Senescence regulates macrophage activation and
angiogenic fate at sites of tissue injury in mice. J Clin Invest.
117:3421–3426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sato T, Kusaka S, Hashida N, Saishin Y,
Fujikado T and Tano Y: Comprehensive gene-expression profile in
murine oxygen-induced retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 93:96–103.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Martinez FO and Gordon S: The M1 and M2
paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:132014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Spiller KL, Anfang RR, Spiller KJ, Ng J,
Nakazawa KR, Daulton JW and Vunjak-Novakovic G: The role of
macrophage phenotype in vascularization of tissue engineering
scaffolds. Biomaterials. 35:4477–4488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marchetti V, Yanes O, Aguilar E, Wang M,
Friedlander D, Moreno S, Storm K, Zhan M, Naccache S, Nemerow G, et
al: Differential macrophage polarization promotes tissue remodeling
and repair in a model of ischemic retinopathy. Sci Rep. 1:762011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Zhou Y, Yoshida S, Nakao S, Yoshimura T,
Kobayashi Y, Nakama T, Kubo Y, Miyawaki K, Yamaguchi M, Ishikawa K,
et al: M2 macrophages enhance pathological neovascularization in
the mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 56:4767–4777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fantin A, Vieira JM, Gestri G, Denti L,
Schwarz Q, Prykhozhij S, Peri F, Wilson SW and Ruhrberg C: Tissue
macrophages act as cellular chaperones for vascular anastomosis
downstream of VEGF-mediated endothelial tip cell induction. Blood.
116:829–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Caicedo A, Espinosa-Heidmann DG, Piña Y,
Hernandez EP and Cousins SW: Blood-derived macrophages infiltrate
the retina and activate Muller glial cells under experimental
choroidal neovascularization. Exp Eye Res. 81:38–47. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cao X, Shen D, Patel MM, Tuo J, Johnson
TM, Olsen TW and Chan CC: Macrophage polarization in the maculae of
age-related macular degeneration: A pilot study. Pathol Int.
61:528–535. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rae F, Woods K, Sasmono T, Campanale N,
Taylor D, Ovchinnikov DA, Grimmond SM, Hume DA, Ricardo SD and
Little MH: Characterisation and trophic functions of murine
embryonic macrophages based upon the use of a Csf1r-EGFP transgene
reporter. Dev Biol. 308:232–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Troidl C, Möllmann H, Nef H, Masseli F,
Voss S, Szardien S, Willmer M, Rolf A, Rixe J, Troidl K, et al:
Classically and alternatively activated macrophages contribute to
tissue remodelling after myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med.
13:3485–3496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yan X, Anzai A, Katsumata Y, Matsuhashi T,
Ito K, Endo J, Yamamoto T, Takeshima A, Shinmura K, Shen W, et al:
Temporal dynamics of cardiac immune cell accumulation following
acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 62:24–35. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ma J, Mehta M, Lam G, Cyr D, Ng TF, Hirose
T, Tawansy KA, Taylor AW and Lashkari K: Influence of subretinal
fluid in advanced stage retinopathy of prematurity on proangiogenic
response and cell proliferation. Mol Vis. 20:881–893.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Outtz HH, Tattersall IW, Kofler NM,
Steinbach N and Kitajewski J: Notch1 controls macrophage
recruitment and Notch signaling is activated at sites of
endothelial cell anastomosis during retinal angiogenesis in mice.
Blood. 118:3436–3439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sethi G, Sung B and Aggarwal BB: TNF: A
master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front Biosci.
13:5094–5107. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bartneck M, Heffels KH, Pan Y, Bovi M,
Zwadlo-Klarwasser G and Groll J: Inducing healing-like human
primary macrophage phenotypes by 3D hydrogel coated nanofibres.
Biomaterials. 33:4136–4146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fuentes-Duculan J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Zaba
LC, Nograles KE, Pierson KC, Mitsui H, Pensabene CA, Kzhyshkowska
J, Krueger JG and Lowes MA: A subpopulation of CD163-positive
macrophages is classically activated in psoriasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 130:2412–2422. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|