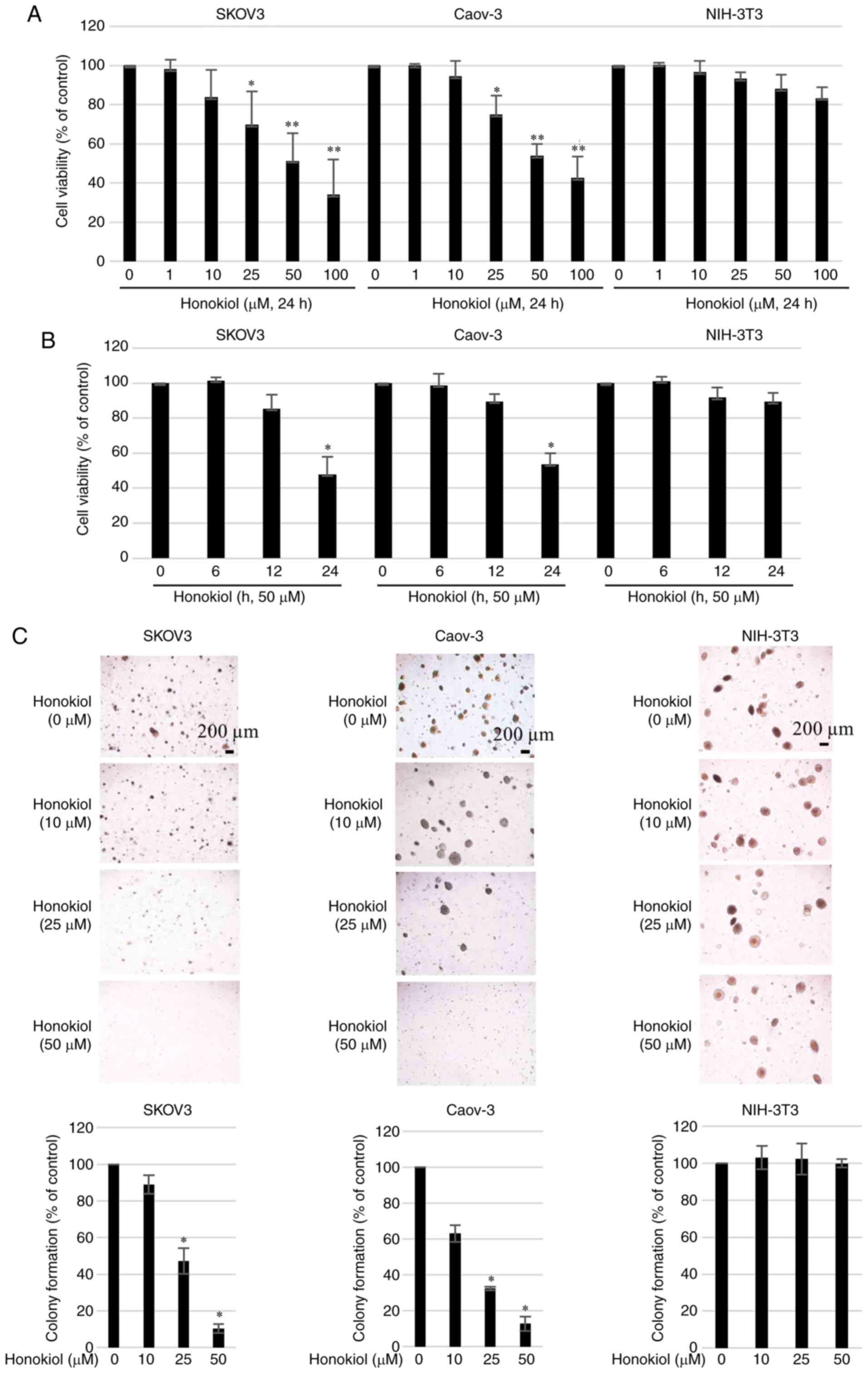
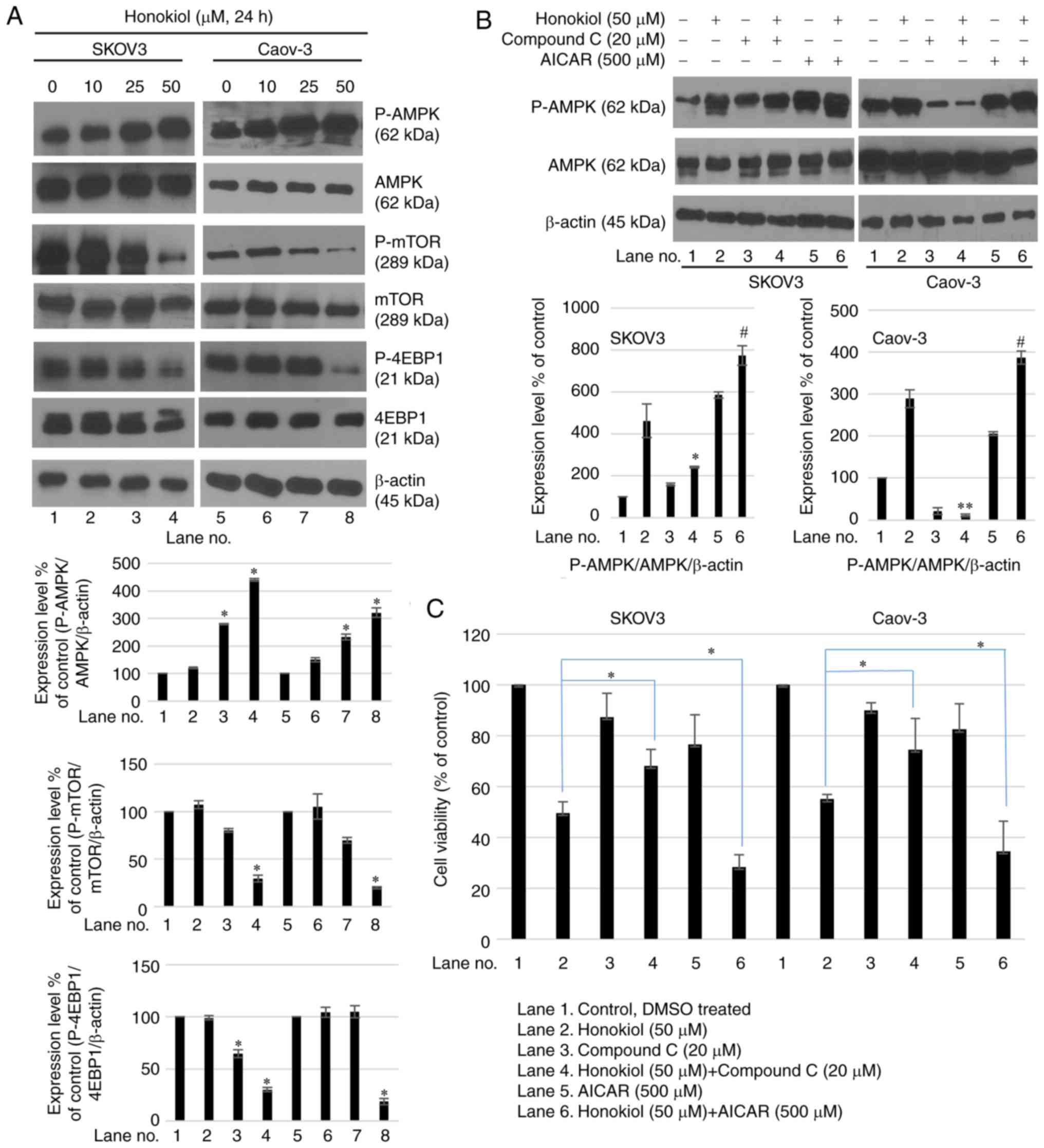
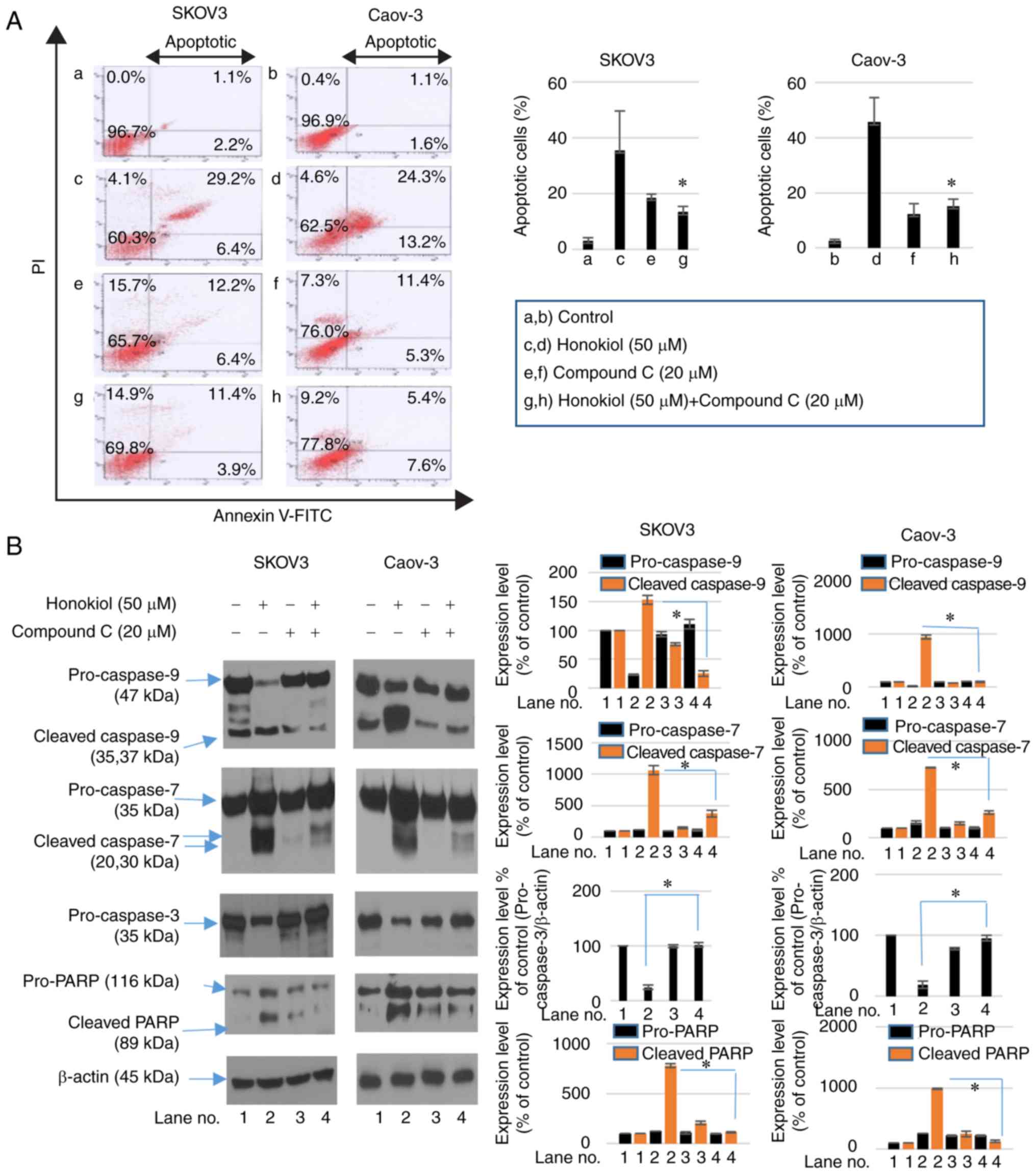
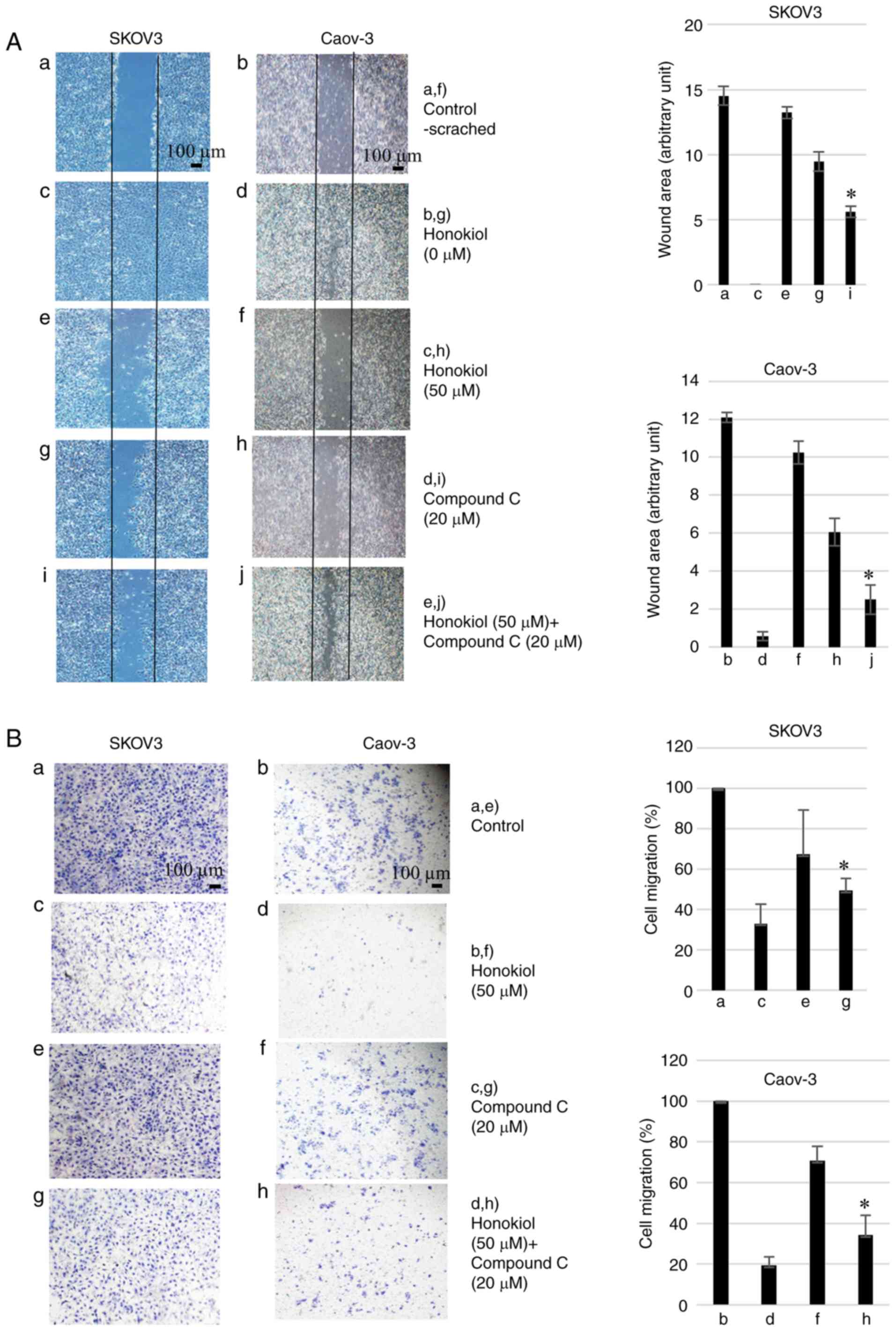
|
1
|
Hoskins WJ, McGuire WP, Brady MF, Homesley
HD, Creasman WT, Berman M, Ball H and Berek JS: The effect of
diameter of largest residual disease on survival after primary
cytoreductive surgery in patients with suboptimal residual
epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 170:974–979.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Chen L, He X, Fan L, Yang G, Chen
X, Lin X, DU L, Li Z, Ye H, et al: Enhancement of therapeutic
effectiveness by combining liposomal honokiol with cisplatin in
ovarian carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 18:652–659. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, Fowler JM,
Clarke-Pearson D, Burger RA, Mannel RS, DeGeest K, Hartenbach EM
and Baergen R; Gynecologic Oncology Group: Phase III trial of
carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel
in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: A
gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol. 21:3194–3200. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardie DG: Sensing of energy and nutrients
by AMP-activated protein kinase. Am J Clin Nutr. 93:891S–896S.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright JL and Stanford JL: Metformin use
and prostate cancer in caucasian men: Results from a
population-based case-control study. Cancer Causes Control.
20:1617–1622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Henderson D, Frieson D, Zuber J and
Solomon SS: Metformin has positive therapeutic effects in colon
cancer and lung cancer. Am J Med Sci. 354:246–251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krähenbühl S, Jick SS
and Meier CR: Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased
risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 33:1304–1308. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li D, Yeung SC, Hassan MM, Konopleva M and
Abbruzzese JL: Antidiabetic therapies affect risk of pancreatic
cancer. Gastroenterology. 137:482–488. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak
M and Sonenberg N: Metformin inhibits mammalian target of
rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang LW, Li ZS, Zou DW, Jin ZD, Gao J and
Xu GM: Metformin induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:7192–7198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He XX, Tu SM, Lee MH and Yeung SC:
Thiazolidinediones and metformin associated with improved survival
of diabetic prostate cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 22:2640–2645.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH,
Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM, Hsu L, Hung MC, Hortobagyi
GN and Gonzalez-Angulo AM: Metformin and pathologic complete
responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with
breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:3297–3302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kirpichnikov D, McFarlane SI and Sowers
JR: Metformin: An update. Ann Intern Med. 137:25–33. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zong H, Yin B, Zhou H, Cai D, Ma B and
Xiang Y: Inhibition of mTOR pathway attenuates migration and
invasion of gallbladder cancer via EMT inhibition. Mol Biol Rep.
41:4507–4512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Inoki K, Kim J and Guan KL: AMPK and mTOR
in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 52:381–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chapuis N, Tamburini J, Green AS, Willems
L, Bardet V, Park S, Lacombe C, Mayeux P and Bouscary D:
Perspectives on inhibiting mTOR as a future treatment strategy for
hematological malignancies. Leukemia. 24:1686–1699. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J, Wang S, Zhang Y, Fan HT and Lin HS:
Traditional chinese medicine and cancer: History, present
situation, and development. Thorac Cancer. 6:561–569. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seo MS, Hong SW, Yeon SH, Kim YM, Um KA,
Kim JH, Kim HJ, Chang KC and Park SW: Magnolia officinalis
attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipogenesis via AMPK
phosphorylation in hepatocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 157:140–148.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Z, Zhang X, Cui W, Zhang X, Li N, Chen
J, Wong AW and Roberts A: Evaluation of short-term and subchronic
toxicity of magnolia bark extract in rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
49:160–171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sarrica A, Kirika N, Romeo M, Salmona M
and Diomede L: Safety and toxicology of magnolol and honokiol.
Planta Med. 84:1151–1164. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fried LE and Arbiser JL: Honokiol, a
multifunctional antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:1139–1148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steinmann P, Walters DK, Arlt MJ, Banke
IJ, Ziegler U, Langsam B, Arbiser J, Muff R, Born W and Fuchs B:
Antimetastatic activity of honokiol in osteosarcoma. Cancer.
118:2117–2127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Park EJ, Min HY, Chung HJ, Hong JY, Kang
YJ, Hung TM, Youn UJ, Kim YS, Bae K, Kang SS and Lee SK:
Down-regulation of c-Src/EGFR-mediated signaling activation is
involved in the honokiol-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 277:133–140.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa C, Arbiser JL and Mori N:
Honokiol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via inhibition of
survival signals in adult T-cell leukemia. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1820:879–887. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yeh PS, Wang W, Chang YA, Lin CJ, Wang JJ
and Chen RM: Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells
through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and endoplasmic reticular
stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration.
Cancer Lett. 370:66–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dai X, Li RZ, Jiang ZB, Wei CL, Luo LX,
Yao XJ, Li GP and Leung EL: Honokiol inhibits proliferation,
invasion and induces apoptosis through targeting lyn kinase in
human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Front Pharmacol. 9:5582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen L, Zhang F, Huang R, Yan J and Shen
B: Honokiol inhibits bladder cancer cell invasion through
repressing SRC-3 expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Oncol Lett. 14:4294–4300. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagalingam A, Arbiser JL, Bonner MY,
Saxena NK and Sharma D: Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein
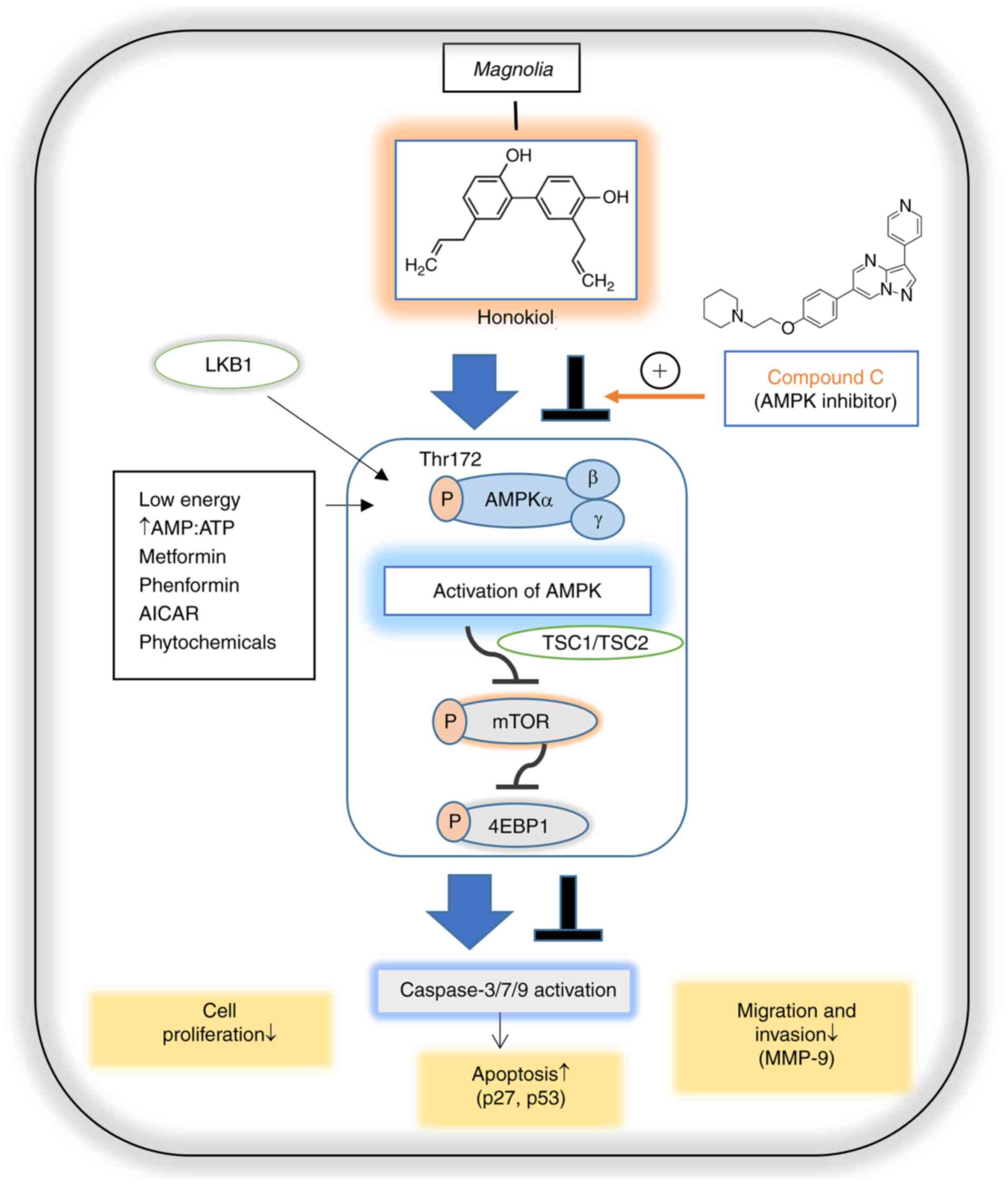
kinase in breast cancer cells via an LKB1-dependent pathway and
inhibits breast carcinogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R352012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh T and Katiyar SK: Honokiol, a
phytochemical from magnolia spp., inhibits breast cancer cell
migration by targeting nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase-2. Int J
Oncol. 38:769–776. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar A, Kumar Singh U and Chaudhary A:
Honokiol analogs: A novel class of anticancer agents targeting cell
signaling pathways and other bioactivities. Future Med Chem.
5:809–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo LX, Li Y, Liu ZQ, Fan XX, Duan FG, Li
RZ, Yao XJ, Leung EL and Liu L: Honokiol induces apoptosis, G1
arrest, and autophagy in KRAS mutant lung cancer cells. Front
Pharmacol. 8:1992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shigemura K, Arbiser JL, Sun SY, Zayzafoon
M, Johnstone PA, Fujisawa M, Gotoh A, Weksler B, Zhau HE and Chung
LW: Honokiol, a natural plant product, inhibits the bone metastatic
growth of human prostate cancer cells. Cancer. 109:1279–1289. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu H, Zang C, Emde A, Planas-Silva MD,
Rosche M, Kühnl A, Schulz CO, Elstner E, Possinger K and Eucker J:
Anti-tumor effect of honokiol alone and in combination with other
anticancer agents in breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:43–51.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng N, Xia T, Han Y, He QJ, Zhao R and
Ma JR: Synergistic antitumor effects of liposomal honokiol combined
with cisplatin in colon cancer models. Oncol Lett. 2:957–962.
2011.
|
|
35
|
Li Z, Liu Y, Zhao X, Pan X, Yin R, Huang
C, Chen L and Wei Y: Honokiol, a natural therapeutic candidate,
induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis of ovarian tumor cells.
Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 140:95–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwan HT, Chan DW, Cai PC, Mak CS, Yung MM,
Leung TH, Wong OG, Cheung AN and Ngan HY: AMPK activators suppress
cervical cancer cell growth through inhibition of DVL3 mediated
Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity. PLoS One. 8:e535972013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gurumurthy S, Hezel AF, Sahin E, Berger
JH, Bosenberg MW and Bardeesy N: LKB1 deficiency sensitizes mice to
carcinogen-induced tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 68:55–63. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhou Y and You H: Molecular
mechanism of LKB1 in the invasion and metastasis of colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 41:1035–1044. 2019.
|
|
39
|
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C,
Lopez-Bonet E and Menendez JA: AMPK: Evidence for an energy-sensing
cytokinetic tumor suppressor. Cell Cycle. 8:3679–3683. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hardie DG: The AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway-new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci.
117:5479–5487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duan P, Hu C, Quan C, Yu T, Huang W, Chen
W, Tang S, Shi Y, Martin FL and Yang K: 4-Nonylphenol induces
autophagy and attenuates mTOR-p70S6K/4EBP1 signaling by modulating
AMPK activation in sertoli cells. Toxicol Lett. 267:21–31. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Al-Moujahed A, Nicolaou F, Brodowska K,
Papakostas TD, Marmalidou A, Ksander BR, Miller JW, Gragoudas E and
Vavvas DG: Uveal melanoma cell growth is inhibited by
aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) partially through
activation of AMP-dependent kinase. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
55:4175–4185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yung MM, Chan DW, Liu VW, Yao KM and Ngan
HY: Activation of AMPK inhibits cervical cancer cell growth through
AKT/FOXO3a/FOXM1 signaling cascade. BMC Cancer. 13:3272013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Whang YM, Kim MJ, Cho MJ, Yoon H, Choi YW,
Kim TH and Chang IH: Rapamycin enhances growth inhibition on
urothelial carcinoma cells through LKB1 deficiency-mediated
mitochondrial dysregulation. J Cell Physiol. 1–14. 2018.
|
|
46
|
Zhang JW, Zhao F and Sun Q: Metformin
synergizes with rapamycin to inhibit the growth of pancreatic
cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett. 15:1811–1816.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Chatterjee A, Kogan D,
Patel D and Foster DA:
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-4-ribofura noside (AICAR)
enhances the efficacy of rapamycin in human cancer cells. Cell
Cycle. 14:3331–3339. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Arora S, Singh S, Piazza GA, Contreras CM,
Panyam J and Singh AP: Honokiol: A novel natural agent for cancer
prevention and therapy. Curr Mol Med. 12:1244–1252. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kaushik G, Kwatra D, Subramaniam D, Jensen
RA, Anant S and Mammen JM: Honokiol affects melanoma cell growth by
targeting the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Am J
Surg. 208:995–1002. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Queiroz EA, Puukila S, Eichler R, Sampaio
SC, Forsyth HL, Lees SJ, Barbosa AM, Dekker RF, Fortes ZB and
Khaper N: Metformin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest
mediated by oxidative stress, AMPK and FOXO3a in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 9. pp. e982072014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ,
DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, Viollet B and Thompson CB: Systemic
treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs
p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67:6745–6752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shin JA, Kwon KH and Cho SD:
AMPK-activated protein kinase activation by Impatiens balsamina L.
is related to apoptosis in HSC-2 human oral cancer cells.
Pharmacogn Mag. 11:136–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ferla R, Haspinger E and Surmacz E:
Metformin inhibits leptin-induced growth and migration of
glioblastoma cells. Oncol Lett. 4:1077–1081. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cheng S, Castillo V, Eliaz I and Sliva D:
Honokiol suppresses metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by targeting
KISS1/KISS1R signaling. Int J Oncol. 46:2293–2298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|