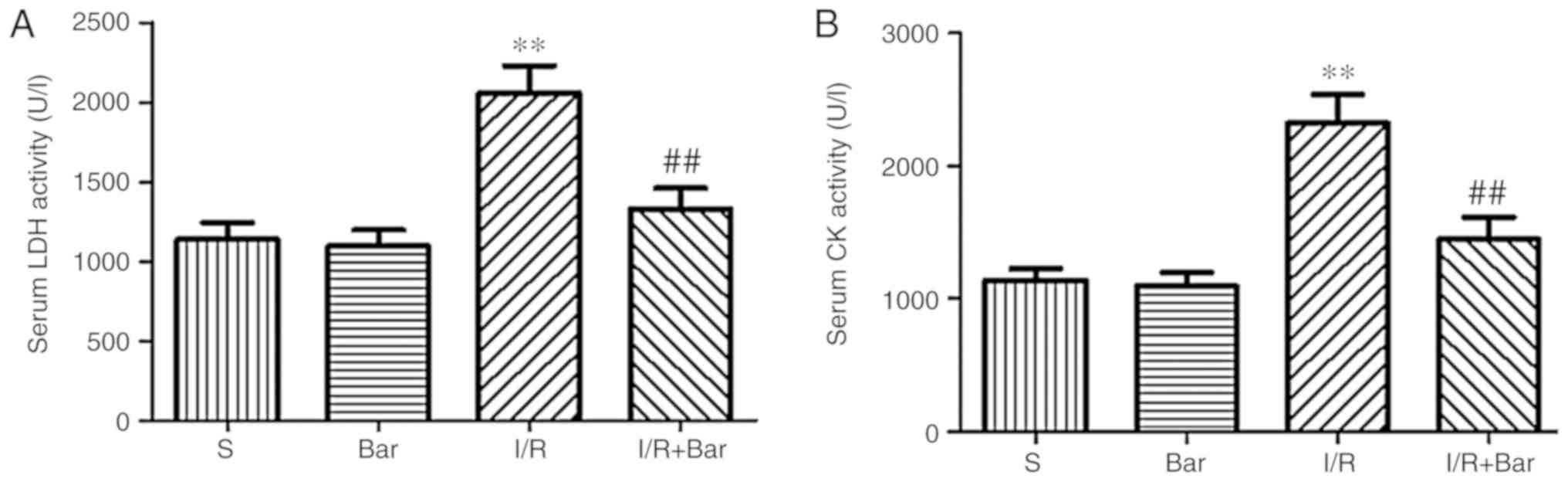
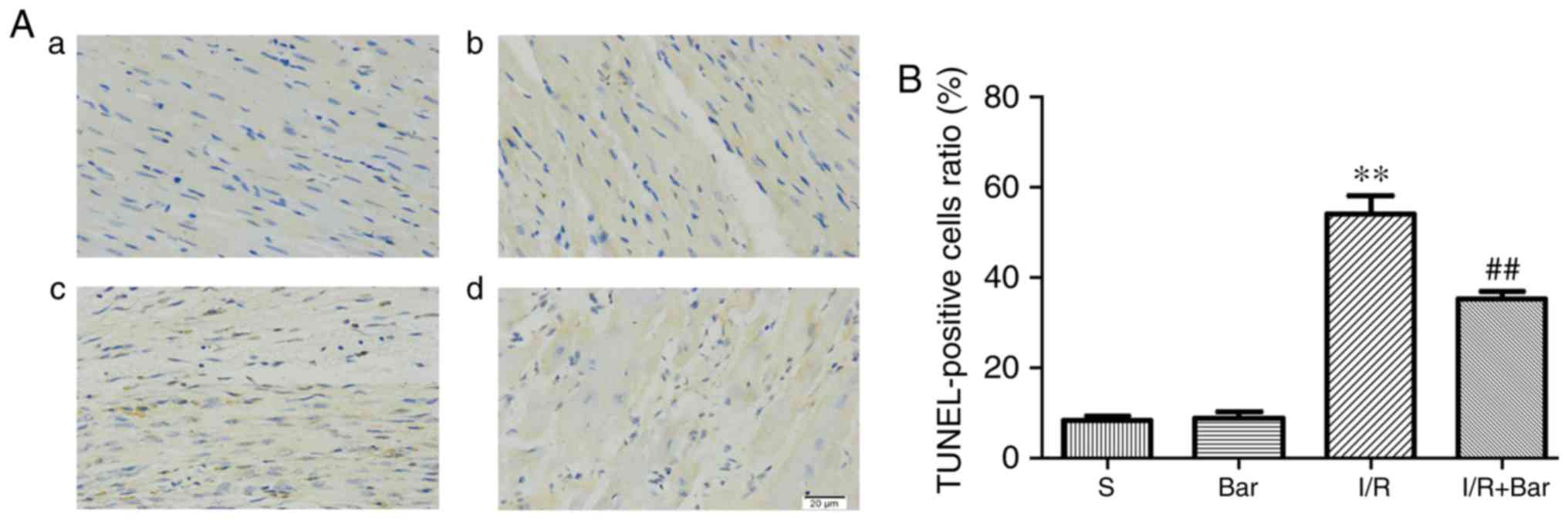
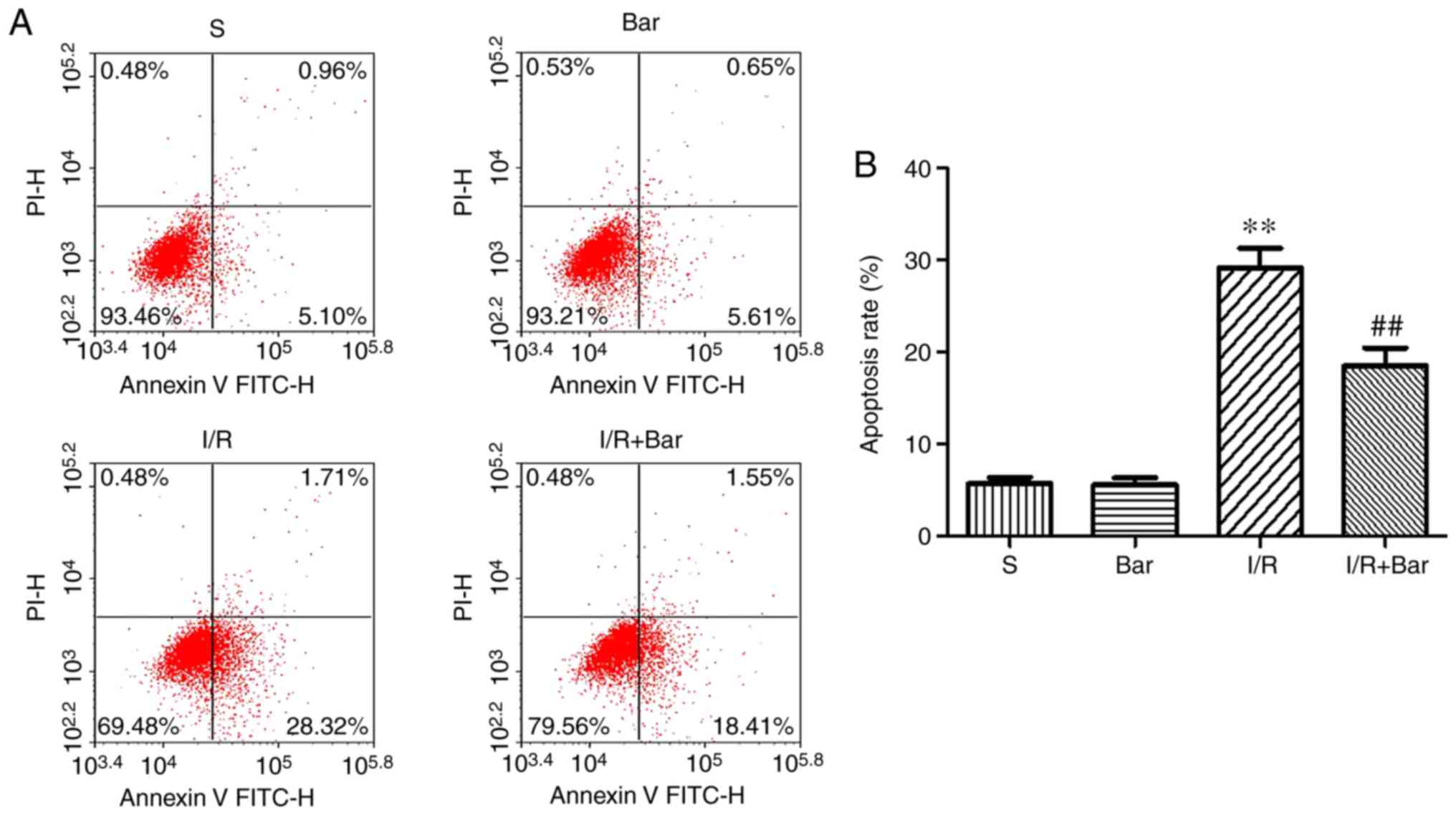
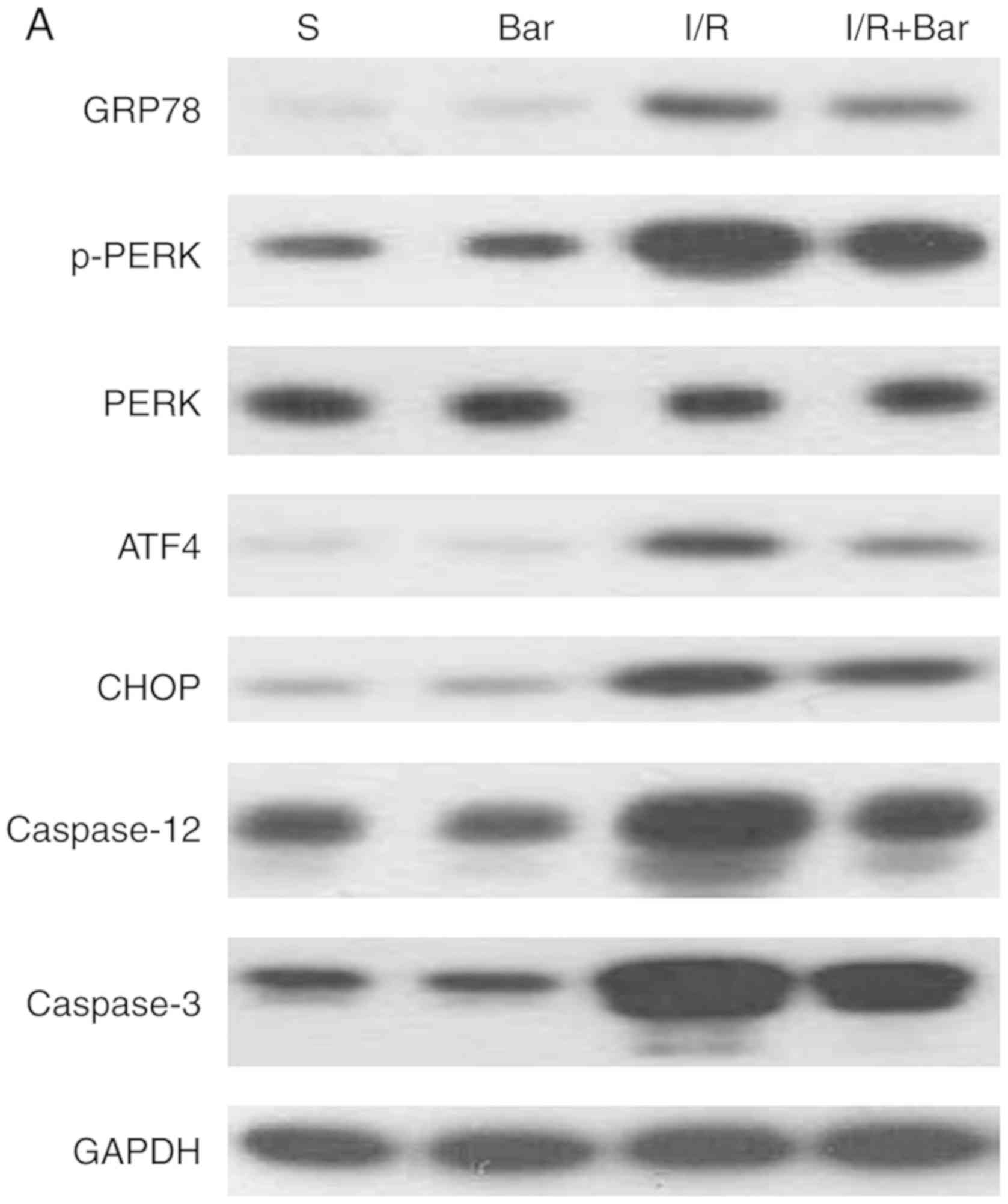
|
1
|
Puaschitz NG, Assmus J, Strand E, Karlsson
T, Vinknes KJ, Lysne V, Drevon CA, Tell GS, Dierkes J and Nygård O:
Adherence to the Healthy Nordic Food Index and the incidence of
acute myocardial infarction and mortality among patients with
stable angina pectoris. J Hum Nutr Diet. 32:86–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Prondzinsky R, Lemm H, Geppert A, Buerke
M, Russ M and Werdan K: Infarct-related cardiogenic shock:
Prognosis and treatment. Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed. 113:267–276.
2018.In German. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou H, Ma Q, Zhu P, Ren J, Reiter RJ and
Chen Y: Protective role of melatonin in cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury: From pathogenesis to targeted therapy.
J Pineal Res. Epub. Feb 8–2018.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Muntean DM, Sturza A, Dănilă MD, Borza C,
Duicu OM and Mornoș C: The role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species in cardiovascular injury and protective strategies. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2016:82549422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ye G, Fu Q, Jiang L and Li Z: Vascular
smooth muscle cells activate PI3K/Akt pathway to attenuate
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy by
secreting bFGF. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1779–1785. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Ding K, Zhang H, Zhao Q,
Liu Z and Xu Y: Involvement of JNK1/2-NF-κBp65 in the regulation of
HMGB2 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in human
AC16 cardiomyocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:1063–1071. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia P, Liu Y and Cheng Z: Signaling
pathways in cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Biomed Res Int.
2016:95832682016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Haunstetter A and Izumo S: Apoptosis:
Basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease.
Circul Res. 82:1111–1129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Baines CP and Molkentin JD: STRESS
signaling pathways that modulate cardiac myocyte apoptosis. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 38:47–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bernecker OY, Huq F, Heist EK, Podesser BK
and Hajjar RJ: Apoptosis in heart failure and the senescent heart.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 3:183–190. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mattson MP and Kroemer G: Mitochondria in
cell death: Novel targets for neuroprotection and cardioprotection.
Trends Mol Med. 9:196–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rao RV, Ellerby HM and Bredesen DE:
Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program.
Cell Death Differ. 11:372–380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Minamino T and Kitakaze M: ER stress in
cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:1105–1110. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Tang Y, Li Y, Xie L, Zhuang W,
Liu J and Gong J: Unfolded protein response plays a critical role
in heart damage after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats. PLoS
One. 12:e01790422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 7:113–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singab AN, El-Hefnawy HM, Esmat A, Gad HA
and Nazeam JA: A systemic review on Aloe arborescens
pharmacological profile: Biological activities and pilot clinical
trials. Phytother Res. 29:1858–1867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Anuszewska EL: Mechanisms of therapeutic
action of aloe. Wiad Lek. 68:168–172. 2015.In Polish.
|
|
20
|
Akaberi M, Sobhani Z, Javadi B, Sahebkar A
and Emami SA: Therapeutic effects of Aloe spp. in traditional and
modern medicine: A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:759–772. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patel DK, Patel K and Tahilyani V:
Barbaloin: A concise report of its pharmacological and analytical
aspects. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2:835–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cao ZZ, Tian YJ, Hao J, Zhang PH, Liu ZP,
Jiang WZ, Zeng ML, Zhang PP and Ma JH: Barbaloin inhibits
ventricular arrhythmias in rabbits by modulating voltage-gated ion
channels. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:357–370. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Zhang P, Liu X, Huang G, Bai C, Zhang Z
and Li H: Barbaloin pretreatment attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of AMPK. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 490:1215–1220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chimenti S, Carlo E, Masson S, Bai A and
Latini R: Myocardial infarction: Animal models. Methods Mol Med.
98:217–226. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li F, Zheng X, Fan X, Zhai K, Tan Y, Kou J
and Yu B: YiQiFuMai powder injection attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial apoptosis through AMPK
activation. Rejuvenation Res. 19:495–508. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qi X, Vallentin A, Churchill E and
Mochly-Rosen D: DeltaPKC participates in the endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced response in cultured cardiac myocytes and ischemic
heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 43:420–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo J, Mihic A, Wu J, Zhang Y, Singh K,
Dhingra S, Weisel RD and Li RK: Canopy 2 attenuates the transition
from compensatory hypertrophy to dilated heart failure in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 36:2530–2540. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hatta K, Guo J, Ludke A, Dhingra S, Singh
K, Huang ML, Weisel RD and Li RK: Expression of CNPY2 in mouse
tissues: Quantification and localization. PLoS One. 9:e1113702014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ding S, Fan Z, Lin C, Dai Q, Zhou J, Huang
H, Xu Y and Zhong C: Therapeutic effects of ischemic-preconditioned
exosomes in cardiovascular diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 998:271–281.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yasuda S and Shimokawa H: Acute myocardial
infarction: The enduring challenge for cardiac protection and
survival. Circ J. 73:2000–2008. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kalra S, Bhatt H and Kirtane AJ: Stenting
in primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J.
14:14–22. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Piper HM, Kasseckert SA, Schlüter KD and
Abdallah Y: Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury. Dtsch
Med Wochenschr. 133:586–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ and Kitsis RN: The
mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ
Res. 95:957–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu T, Ding W, Tariq MA, Wang Y, Wan Q, Li
M and Wang J: Molecular mechanism and therapy application of
necrosis during myocardial injury. J Cell Mol Med. 22:2547–2557.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Khosravi-Far R and Esposti MD: Death
receptor signals to mitochondria. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:1051–1057.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iurlaro R and Muñoz-Pinedo C: Cell death
induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 283:2640–2652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ferri KF and Kroemer G: Organelle-
specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol.
3:E255–E263. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yuksel Y, Guven M, Kaymaz B, Sehitoglu MH,
Aras AB, Akman T, Tosun M and Cosar M: Effects of aloe vera on
spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury of rats. J Invest Surg.
29:389–398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guven M, Gölge UH, Aslan E, Sehitoglu MH,
Aras AB, Akman T and Cosar M: The effect of aloe vera on
ischemia-reperfusion injury of sciatic nerve in rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 79:201–207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu ZQ, Deng YJ and Lu JX: Effect of aloe
polysaccharide on caspase-3 expression following cerebral ischemia
and reper-fusion injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 6:371–374. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sahin H, Yener AU, Karaboga I, Sehitoglu
MH, Dogu T, Altinisik HB, Altinisik U and Simsek T: Protective
effect of gel form of gastric gavage applicated aloe vera on
ischemia reperfusion injury in renal and lung tissue. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 63:34–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hong F, Liu B, Wu BX, Morreall J, Roth B,
Davies C, Sun S, Diehl JA and Li Z: CNPY2 is a key initiator of the
PERK-CHOP pathway of the unfolded protein response. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 24:834–839. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Urra H and Hetz C: Fine-tuning PERK
signaling to control cell fate under stress. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
24:789–790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|