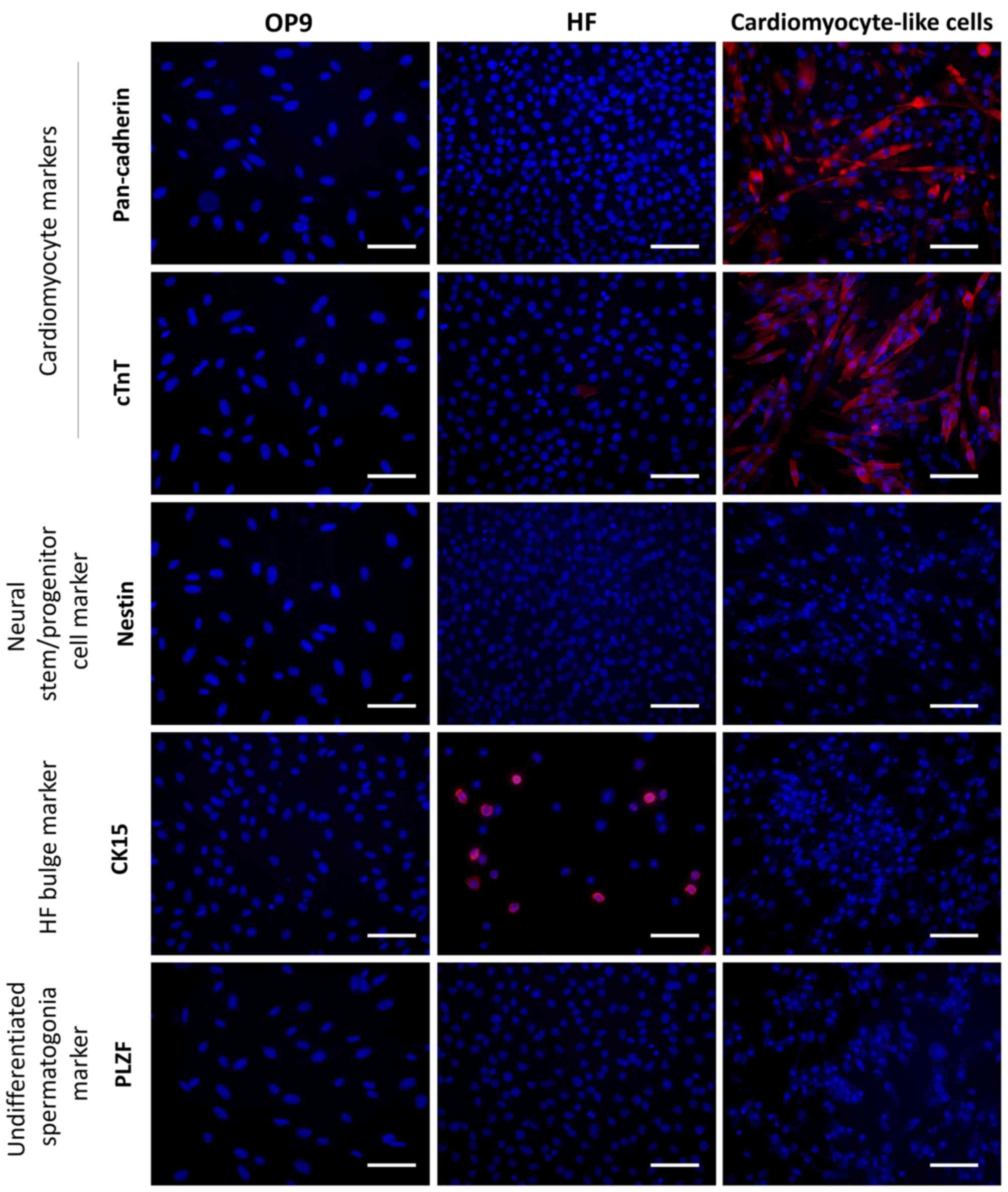
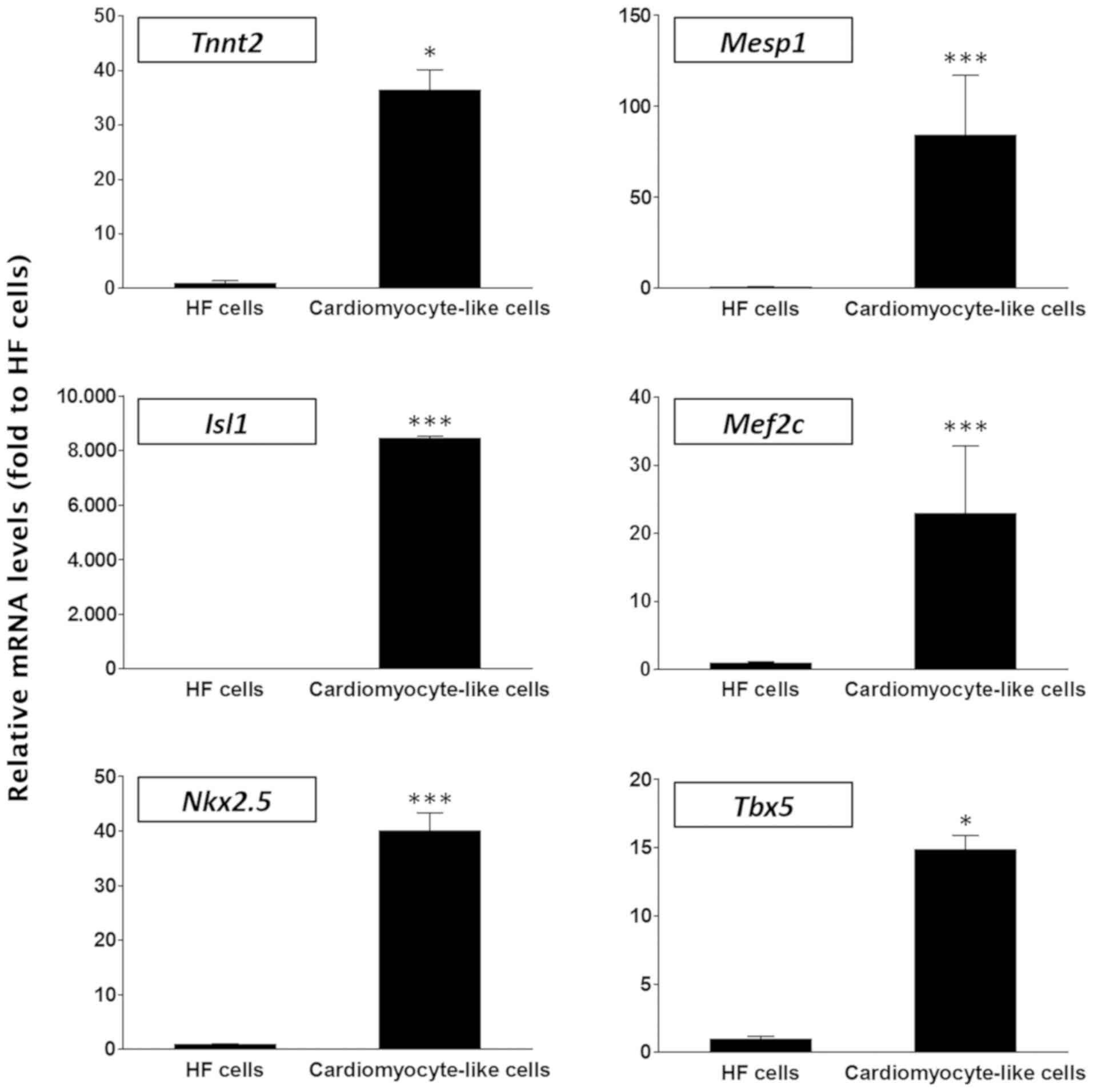
|
1
|
Mortality GBD and Causes of Death C:
Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause
mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death,
1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2015. Lancet. 388:1459–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Weir RA and McMurray JJ: Epidemiology of
heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction after acute
myocardial infarction. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 3:175–180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al
American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics–2012
update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
125:e2–220. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS and White HD: Joint
ESC/ACCF/ AHA/WHF Task Force for the redefinition of myocardial
infarction: Universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 50:2173–2195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hunter JJ and Chien KR: Signaling pathways
for cardiac hypertrophy and failure. N Engl J Med. 341:1276–1283.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beaglehole R, Bonita R, Horton R, Adams O
and McKee M: Public health in the new era: Improving health through
collective action. Lancet. 363:2084–2086. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dubois NC, Craft AM, Sharma P, Elliott DA,
Stanley EG, Elefanty AG, Gramolini A and Keller G: SIRPA is a
specific cell-surface marker for isolating cardiomyocytes derived
from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 29:1011–1018.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fijnvandraat AC, van Ginneken AC, de Boer
PA, Ruijter JM, Christoffels VM, Moorman AF and Lekanne Deprez RH:
Cardiomyocytes derived from embryonic stem cells resemble
cardiomyocytes of the embryonic heart tube. Cardiovasc Res.
58:399–409. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hidaka K, Lee JK, Kim HS, Ihm CH, Iio A,
Ogawa M, Nishikawa S, Kodama I and Morisaki T: Chamber-specific
differentiation of Nkx2.5-positive cardiac precursor cells from
murine embryonic stem cells. FASEB J. 17:740–742. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hattori F, Chen H, Yamashita H, Tohyama S,
Satoh YS, Yuasa S, Li W, Yamakawa H, Tanaka T, Onitsuka T, et al:
Nongenetic method for purifying stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
Nat Methods. 7:61–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Baba S, Heike T, Yoshimoto M, Umeda K, Doi
H, Iwasa T, Lin X, Matsuoka S, Komeda M and Nakahata T: Flk1(+)
cardiac stem/progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells
improve cardiac function in a dilated cardiomyopathy mouse model.
Cardiovasc Res. 76:119–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guan K, Wagner S, Unsöld B, Maier LS,
Kaiser D, Hemmerlein B, Nayernia K, Engel W and Hasenfuss G:
Generation of functional cardiomyocytes from adult mouse
spermatogonial stem cells. Circ Res. 100:1615–1625. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang IN, Wang X, Ge X, Anderson J, Ho M,
Ashley E, Liu J, Butte MJ, Yazawa M, Dolmetsch RE, et al: Apelin
enhances directed cardiac differentiation of mouse and human
embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 7:e383282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu WZ, Hauch KD, Xu C and Laflamme MA:
Human embryonic stem cells and cardiac repair. Transplant Rev
(Orlando). 23:53–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Klaus A, Saga Y, Taketo MM, Tzahor E and
Birchmeier W: Distinct roles of Wnt/beta-catenin and Bmp signaling
during early cardiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:18531–18536. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Taha MF and Valojerdi MR: Effect of bone
morphogenetic protein-4 on cardiac differentiation from mouse
embryonic stem cells in serum-free and low-serum media. Int J
Cardiol. 127:78–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ladd AN, Yatskievych TA and Antin PB:
Regulation of avian cardiac myogenesis by activin/TGFbeta and bone
morphogenetic proteins. Dev Biol. 204:407–419. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hoffman RM: The hair follicle as a gene
therapy target. Nat Biotechnol. 18:20–21. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oshima H, Rochat A, Kedzia C, Kobayashi K
and Barrandon Y: Morphogenesis and renewal of hair follicles from
adult multi-potent stem cells. Cell. 104:233–245. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cotsarelis G, Sun TT and Lavker RM:
Label-retaining cells reside in the bulge area of pilosebaceous
unit: Implications for follicular stem cells, hair cycle, and skin
carcinogenesis. Cell. 61:1329–1337. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morris RJ and Potten CS: Highly persistent
label-retaining cells in the hair follicles of mice and their fate
following induction of anagen. J Invest Dermatol. 112:470–475.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taylor G, Lehrer MS, Jensen PJ, Sun TT and
Lavker RM: Involvement of follicular stem cells in forming not only
the follicle but also the epidermis. Cell. 102:451–461. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tumbar T, Guasch G, Greco V, Blanpain C,
Lowry WE, Rendl M and Fuchs E: Defining the epithelial stem cell
niche in skin. Science. 303:359–363. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Toma JG, Akhavan M, Fernandes KJ,
Barnabé-Heider F, Sadikot A, Kaplan DR and Miller FD: Isolation of
multipotent adult stem cells from the dermis of mammalian skin. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:778–784. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fernandes KJ, McKenzie IA, Mill P, Smith
KM, Akhavan M, Barnabé-Heider F, Biernaskie J, Junek A, Kobayashi
NR, Toma JG, et al: A dermal niche for multipotent adult
skin-derived precursor cells. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1082–1093. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sieber-Blum M, Grim M, Hu YF and Szeder V:
Pluripotent neural crest stem cells in the adult hair follicle. Dev
Dyn. 231:258–269. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Mignone J, Yang M, Matic M, Penman
S, Enikolopov G and Hoffman RM: Nestin expression in hair follicle
sheath progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:9958–9961.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yano K, Brown LF and Detmar M: Control of
hair growth and follicle size by VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 107:409–417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mecklenburg L, Tobin DJ, Müller-Röver S,
Handjiski B, Wendt G, Peters EM, Pohl S, Moll I and Paus R: Active
hair growth (anagen) is associated with angiogenesis. J Invest
Dermatol. 114:909–916. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amoh Y, Li L, Yang M, Moossa AR, Katsuoka
K, Penman S and Hoffman RM: Nascent blood vessels in the skin arise
from nestin-expressing hair-follicle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:13291–13295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Amoh Y, Li L, Katsuoka K, Penman S and
Hoffman RM: Multipotent nestin-positive, keratin-negative
hair-follicle bulge stem cells can form neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:5530–5534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yashiro M, Mii S, Aki R, Hamada Y, Arakawa
N, Kawahara K, Hoffman RM and Amoh Y: From hair to heart:
Nestin-expressing hair-follicle-associated pluripotent (HAP) stem
cells differentiate to beating cardiac muscle cells. Cell Cycle.
14:2362–2366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
34
|
Nath M, Offers M, Hummel M and Seissler J:
Isolation and in vitro expansion of Lgr6-positive multipotent hair
follicle stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 344:435–444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kubota H, Avarbock MR and Brinster RL:
Growth factors essential for self-renewal and expansion of mouse
spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:16489–16494.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fox V, Gokhale PJ, Walsh JR, Matin M,
Jones M and Andrews PW: Cell-cell signaling through NOTCH regulates
human embryonic stem cell proliferation. Stem Cells. 26:715–723.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kattman SJ, Huber TL and Keller GM:
Multipotent flk-1+ cardiovascular progenitor cells give rise to the
cardiomyocyte, endothelial, and vascular smooth muscle lineages.
Dev Cell. 11:723–732. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jang J, Ku SY, Kim JE, Choi K, Kim YY, Kim
HS, Oh SK, Lee EJ, Cho HJ, Song YH, et al: Notch inhibition
promotes human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac mesoderm
differentiation. Stem Cells. 26:2782–2790. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Noggle SA, Weiler D and Condie BG: Notch
signaling is inactive but inducible in human embryonic stem cells.
Stem Cells. 24:1646–1653. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kattman SJ, Witty AD, Gagliardi M, Dubois
NC, Niapour M, Hotta A, Ellis J and Keller G: Stage-specific
optimization of activin/nodal and BMP signaling promotes cardiac
differentiation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell lines.
Cell Stem Cell. 8:228–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yuasa S, Itabashi Y, Koshimizu U, Tanaka
T, Sugimura K, Kinoshita M, Hattori F, Fukami S, Shimazaki T, Ogawa
S, et al: Transient inhibition of BMP signaling by Noggin induces
cardio-myocyte differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat
Biotechnol. 23:607–611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim BJ, Kim YH, Lee YA, Jung SE, Hong YH,
Lee EJ, Kim BG, Hwang S, Do JT, Pang MG, et al: Platelet-derived
growth factor receptor-alpha positive cardiac progenitor cells
derived from multipotent germline stem cells are capable of
cardiomyogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 8:29643–29656.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Org T, Duan D, Ferrari R, Montel-Hagen A,
Van Handel B, Kerényi MA, Sasidharan R, Rubbi L, Fujiwara Y,
Pellegrini M, et al: Scl binds to primed enhancers in mesoderm to
regulate hematopoietic and cardiac fate divergence. EMBO J.
34:759–777. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bai F, Ho Lim C, Jia J, Santostefano K,
Simmons C, Kasahara H, Wu W, Terada N and Jin S: Directed
differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes by
bacterial injection of defined transcription factors. Sci Rep.
5:150142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li G, Plonowska K, Kuppusamy R, Sturzu A
and Wu SM: Identification of cardiovascular lineage descendants at
single-cell resolution. Development. 142:846–857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Eng G, Lee BW, Protas L, Gagliardi M,
Brown K, Kass RS, Keller G, Robinson RB and Vunjak-Novakovic G:
Autonomous beating rate adaptation in human stem cell-derived
cardio-myocytes. Nat Commun. 7:103122016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Radaszkiewicz KA, Sýkorová D, Karas P,
Kudová J, Kohút L, Binó L, Večeřa J, Víteček J, Kubala L and
Pacherník J: Simple non-invasive analysis of embryonic stem
cell-derived cardio-myocytes beating in vitro. Rev Sci Instrum.
87:0243012016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hayashi K, Ohta H, Kurimoto K, Aramaki S
and Saitou M: Reconstitution of the mouse germ cell specification
pathway in culture by pluripotent stem cells. Cell. 146:519–532.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hayashi K, Ogushi S, Kurimoto K, Shimamoto
S, Ohta H and Saitou M: Offspring from oocytes derived from in
vitro primordial germ cell-like cells in mice. Science.
338:971–975. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Baba S, Heike T, Umeda K, Iwasa T, Kaichi
S, Hiraumi Y, Doi H, Yoshimoto M, Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Shinohara T,
et al: Generation of cardiac and endothelial cells from neonatal
mouse testis-derived multipotent germline stem cells. Stem Cells.
25:1375–1383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yao S, Chen S, Clark J, Hao E, Beattie GM,
Hayek A and Ding S: Long-term self-renewal and directed
differentiation of human embryonic stem cells in chemically defined
conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:6907–6912. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ryu BY, Kubota H, Avarbock MR and Brinster
RL: Conservation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal signaling
between mouse and rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:14302–14307.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Conlon FL, Lyons KM, Takaesu N, Barth KS,
Kispert A, Herrmann B and Robertson EJ: A primary requirement for
nodal in the formation and maintenance of the primitive streak in
the mouse. Development. 120:1919–1928. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gadue P, Huber TL, Paddison PJ and Keller
GM: Wnt and TGF-beta signaling are required for the induction of an
in vitro model of primitive streak formation using embryonic stem
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:16806–16811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu Y, Asakura M, Inoue H, Nakamura T,
Sano M, Niu Z, Chen M, Schwartz RJ and Schneider MD: Sox17 is
essential for the specification of cardiac mesoderm in embryonic
stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:3859–3864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Marvin MJ, Di Rocco G, Gardiner A, Bush SM
and Lassar AB: Inhibition of Wnt activity induces heart formation
from posterior mesoderm. Genes Dev. 15:316–327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schneider VA and Mercola M: Wnt antagonism
initiates cardio-genesis in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 15:304–315.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Schultheiss TM, Burch JB and Lassar AB: A
role for bone morphogenetic proteins in the induction of cardiac
myogenesis. Genes Dev. 11:451–462. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tzahor E and Lassar AB: Wnt signals from
the neural tube block ectopic cardiogenesis. Genes Dev. 15:255–260.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yatskievych TA, Ladd AN and Antin PB:
Induction of cardiac myogenesis in avian pregastrula epiblast: The
role of the hypoblast and activin. Development. 124:2561–2570.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Iida M, Heike T, Yoshimoto M, Baba S, Doi
H and Nakahata T: Identification of cardiac stem cells with FLK1,
CD31, and VE-cadherin expression during embryonic stem cell
differentiation. FASEB J. 19:371–378. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Murakami Y, Hirata H, Miyamoto Y,
Nagahashi A, Sawa Y, Jakt M, Asahara T and Kawamata S: Isolation of
cardiac cells from E8.5 yolk sac by ALCAM (CD166) expression. Mech
Dev. 124:830–839. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Misfeldt AM, Boyle SC, Tompkins KL, Bautch
VL, Labosky PA and Baldwin HS: Endocardial cells are a distinct
endothelial lineage derived from Flk1+ multipotent
cardiovascular progenitors. Dev Biol. 333:78–89. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|